要想全面快速学习Spring的内容,最好的方法肯定是先去Spring官网去查阅文档,在Spring官网中找到了适合新手了解的官网Guides,一共68篇,打算全部过一遍,能尽量全面的了解Spring框架的每个特性和功能。

接着上篇看过的guide41,接着往下看。
guide41、Messaging with JMS
JMS即Java消息服务(Java Message Service)应用程序接口,是一个Java平台中关于面向消息中间件(MOM)的API,用于在两个应用程序之间,或分布式系统中发送消息,进行异步通信。Java消息服务是一个与具体平台无关的API,绝大多数MOM提供商都对JMS提供支持。
创建一个简单的bean
public class Email {
private String to;
private String body;
...
以及定义一个消息接收器
@Component
public class Receiver {
@JmsListener(destination = "mailbox", containerFactory = "myFactory")
public void receiveMessage(Email email) {
System.out.println("Received <" + email + ">");
}
}
JmsListener注释定义了此方法应该侦听的目标的名称,以及用于创建基础消息侦听器容器的JmsListenerContainerFactory的引用。严格来说,最后一个属性不是必须的,除非你需要自定义容器的构建方式,因为Spring Boot会在必要时注册一个默认工厂。
接下来进行消息发送:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableJms
public class Application {
@Bean
public JmsListenerContainerFactory<?> myFactory(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory,
DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactoryConfigurer configurer) {
DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory factory = new DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory();
// This provides all boot's default to this factory, including the message converter
configurer.configure(factory, connectionFactory);
// You could still override some of Boot's default if necessary.
return factory;
}
@Bean // Serialize message content to json using TextMessage
public MessageConverter jacksonJmsMessageConverter() {
MappingJackson2MessageConverter converter = new MappingJackson2MessageConverter();
converter.setTargetType(MessageType.TEXT);
converter.setTypeIdPropertyName("_type");
return converter;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Launch the application
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
JmsTemplate jmsTemplate = context.getBean(JmsTemplate.class);
// Send a message with a POJO - the template reuse the message converter
System.out.println("Sending an email message.");
jmsTemplate.convertAndSend("mailbox", new Email("info@example.com", "Hello"));
}
}
为了清晰起见,我们还定义了一个myFactory bean,它在接收器的JmsListener注释中被引用。
默认的MessageConverter只能转换基本类型(例如String、Map、Serializable),我们的电子邮件是不可序列化的。我们想使用Jackson并将内容序列化为文本格式的JSON(即作为TextMessage)。
用JmsTemplate来发送消息,它是Spring提供的一个工具类,和JdbcTemplate类似,可以简化发送消息的代码。
@EnableJMS: Spring根据AppConfig的注解@EnableJms自动扫描带有@JmsListener的Bean方法,并为其创建一个MessageListener把它包装起来。
guide42、Securing a Web Application
讲了spring security的简单使用.
主要是下述代码:
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeHttpRequests((requests) -> requests
.requestMatchers("/", "/home").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.formLogin((form) -> form
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
)
.logout((logout) -> logout.permitAll());
return http.build();
}
@Bean
public UserDetailsService userDetailsService() {
UserDetails user = User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder()
.username("user")
.password("password")
.roles("USER")
.build();
return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(user);
}}
WebSecurityConfig类添加了@EnableWebSecurity注解,以启用Spring Security的web安全支持,并提供Spring MVC集成。
SecurityFilterChain bean定义哪些URL路径应该被保护,哪些不应该。具体来说,/和/home路径被配置为不需要任何身份验证。所有其他路径都必须经过身份验证。当用户成功登录后,他们会被重定向到之前请求的需要身份验证的页面。有一个自定义/登录页面(由loginPage()指定),每个人都可以查看它。
UserDetailsService bean使用单个用户建立了一个内存中的用户存储。该用户被赋予user用户名、password密码和user角色。
guide43、Accessing Data in Pivotal GemFire
基于Apache Geode数据管理系统构建应用程序的过程
Apache Geode 是一个数据管理平台,可在广泛分布的云架构中提供对数据密集型应用程序的实时、一致的访问。Geode 跨多个进程汇集内存、CPU、网络资源和可选的本地磁盘,以管理应用程序对象和行为。它使用动态复制和数据分区技术来实现高可用性、改进的性能、可伸缩性和容错性。除了作为分布式数据容器之外,Geode 还是一个内存数据管理系统,可提供可靠的异步事件通知和有保证的消息传递。
Apache Geode是一个键值对存储系统,region实现了java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap接口。不过你也可以把一个region当作java.util。它比简单的Java Map复杂得多,因为数据是在区域内分发、复制和管理的。
在本例中,通过使用少量注释,将Person对象存储在Apache Geode
@Region(value = "People")
public class Person implements Serializable {
@Id
@Getter
private final String name;
@Getter
private final int age;
@PersistenceConstructor
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
注意,这个类带有@Region(“People”)注解。当Apache Geode存储这个类的实例时,在People区域中会创建一个新条目。这个类还用@Id标记name字段。这表示用于识别和跟踪Apache Geode中的人员数据的标识符。本质上,带@Id注解的字段(如name)是键,Person实例是键值对条目中的值。在Apache Geode中没有自动生成密钥,因此必须在将实体持久化到Apache Geode之前设置ID(名称)。
@PersistenceConstructor注解:声明构造函数,作用是把从数据库取出的数据实例化为对象。
Spring Data for Apache Geode专注于使用Spring在Apache Geode中存储和访问数据。它还继承了Spring Data Commons项目的强大功能,比如派生查询的能力。
public interface PersonRepository extends CrudRepository<Person, String> {
@Trace
Person findByName(String name);
@Trace
Iterable<Person> findByAgeGreaterThan(int age);
@Trace
Iterable<Person> findByAgeLessThan(int age);
@Trace
Iterable<Person> findByAgeGreaterThanAndAgeLessThan(int greaterThanAge, int lessThanAge);
}
PersonRepository扩展了Spring Data Commons的CrudRepository接口,并为存储库使用的值和ID(键)指定了泛型类型参数的类型(分别是Person和String)。这个接口提供了许多操作,包括基本的CRUD(创建、读取、更新、删除)和简单的查询数据访问操作(例如findById(…))。
@SpringBootApplication
@ClientCacheApplication(name = "AccessingDataGemFireApplication")
@EnableEntityDefinedRegions(
basePackageClasses = Person.class,
clientRegionShortcut = ClientRegionShortcut.LOCAL
)
@EnableGemfireRepositories
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@Bean
ApplicationRunner run(PersonRepository personRepository) {
return args -> {
Person alice = new Person("Adult Alice", 40);
Person bob = new Person("Baby Bob", 1);
Person carol = new Person("Teen Carol", 13);
System.out.println("Before accessing data in Apache Geode...");
asList(alice, bob, carol).forEach(person -> System.out.println("\t" + person));
System.out.println("Saving Alice, Bob and Carol to Pivotal GemFire...");
personRepository.save(alice);
personRepository.save(bob);
personRepository.save(carol);
System.out.println("Lookup each person by name...");
asList(alice.getName(), bob.getName(), carol.getName())
.forEach(name -> System.out.println("\t" + personRepository.findByName(name)));
System.out.println("Query adults (over 18):");
stream(personRepository.findByAgeGreaterThan(18).spliterator(), false)
.forEach(person -> System.out.println("\t" + person));
System.out.println("Query babies (less than 5):");
stream(personRepository.findByAgeLessThan(5).spliterator(), false)
.forEach(person -> System.out.println("\t" + person));
System.out.println("Query teens (between 12 and 20):");
stream(personRepository.findByAgeGreaterThanAndAgeLessThan(12, 20).spliterator(), false)
.forEach(person -> System.out.println("\t" + person));
};
}
}
需要一个包含一个或多个region的Apache Geode缓存来存储所有数据。要做到这一点,你可以使用Spring的一个数据,为Apache Geode提供方便的基于配置的注解:@ClientCacheApplication。
guide44、Caching Data with Pivotal GemFire
构建一个服务,调用其他地方接口并将结果缓存到appache geode.
新建实体类:
@Data
@JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true)
@SuppressWarnings("unused")public class Quote {
private Long id;
private String quote;
... ...
@Data
@JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true)
public class QuoteResponse {
@JsonProperty("value")
private Quote quote;
@JsonProperty("type")
private String status;
...
@SuppressWarnings(“unused”)是一个Java注解,用于抑制未使用变量、方法或参数等代码元素的编译器警告。
@JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown=true) 是一个 Jackson 序列化/反序列化注解,用于指示 Jackson 在反序列化 JSON 时忽略未知的属性。
当 Java 对象与 JSON 之间相互转换时,如果 JSON 字符串中包含 Java 对象中没有的属性,Jackson 在默认情况下会抛出异常。使用 @JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown=true) 注解可以告诉 Jackson 忽略 JSON 字符串中未知的属性,以避免抛出异常。
@JsonProperty(“value”) 是一个 Jackson 序列化/反序列化注解,用于指示 Jackson 在序列化/反序列化时使用指定的属性名。 Java 对象与 JSON 之间相互转换时,Jackson 默认使用 Java 对象属性的名称作为 JSON 字段的名称。
在创建一个查询quote的服务类
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
@Service
public class QuoteService {
protected static final String ID_BASED_QUOTE_SERVICE_URL = "https://quoters.apps.pcfone.io/api/{id}";
protected static final String RANDOM_QUOTE_SERVICE_URL = "https://quoters.apps.pcfone.io/api/random";
private volatile boolean cacheMiss = false;
private final RestTemplate quoteServiceTemplate = new RestTemplate();
-- 确定之前的服务方法调用是否导致缓存未命中。 * Determines whether the previous service method invocation resulted in a cache miss.
public boolean isCacheMiss() {
boolean cacheMiss = this.cacheMiss;
this.cacheMiss = false;
return cacheMiss;
}
protected void setCacheMiss() {
this.cacheMiss = true;
}
-- 使用给定的标识符请求一个quote。 * Requests a quote with the given identifier.
@Cacheable("Quotes")
public Quote requestQuote(Long id) {
setCacheMiss();
return requestQuote(ID_BASED_QUOTE_SERVICE_URL, Collections.singletonMap("id", id));
}
-- 请求一个随机quote * Requests a random quote.
@CachePut(cacheNames = "Quotes", key = "#result.id")
public Quote requestRandomQuote() {
setCacheMiss();
return requestQuote(RANDOM_QUOTE_SERVICE_URL);
}
protected Quote requestQuote(String URL) {
return requestQuote(URL, Collections.emptyMap());
}
protected Quote requestQuote(String URL, Map<String, Object> urlVariables) {
return Optional.ofNullable(this.quoteServiceTemplate.getForObject(URL, QuoteResponse.class, urlVariables))
.map(QuoteResponse::getQuote)
.orElse(null);
}
}
@Cacheable(“”) 是 Spring 框架提供的注解之一,用于将方法的返回值缓存到缓存中,以便在后续调用时可以直接从缓存中获取结果,从而提高应用程序的性能。
@CachePut(cacheNames = “Quotes”, key = “#result.id”) 是 Spring 框架提供的注解之一,用于将方法的返回值更新缓存中的数据,以便在后续调用时可以直接从缓存中获取最新结果,从而提高应用程序的性能。
与 @Cacheable 注解不同,@CachePut 注解不会检查缓存中是否已经存在相同键值的数据,而是直接将方法的返回值更新到缓存中。其中,cacheNames 参数指定了缓存的名称,key 参数指定了缓存的键,可以使用 SpEL 表达式生成缓存键。
QuoteService使用Spring的RestTemplate来查询Quote服务的API。Quote服务返回一个JSON对象,但Spring使用Jackson将数据绑定到QuoteResponse,最终绑定到Quote对象。
主类:
@SpringBootApplication
@ClientCacheApplication(name = "CachingGemFireApplication")
@EnableCachingDefinedRegions(clientRegionShortcut = ClientRegionShortcut.LOCAL)
@EnableGemfireCaching
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@Bean
ApplicationRunner runner(QuoteService quoteService) {
return args -> {
Quote quote = requestQuote(quoteService, 12L);
requestQuote(quoteService, quote.getId());
requestQuote(quoteService, 10L);
};
}
private Quote requestQuote(QuoteService quoteService, Long id) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Quote quote = Optional.ofNullable(id)
.map(quoteService::requestQuote)
.orElseGet(quoteService::requestRandomQuote);
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.printf("\"%1$s\"%nCache Miss [%2$s] - Elapsed Time [%3$s ms]%n", quote,
quoteService.isCacheMiss(), (elapsedTime - startTime));
return quote;
}
}
@ClientCacheApplication(name = “CachingGemFireApplication”) 是 Pivotal GemFire 提供的 Spring Boot 集成注解之一,用于在 Spring Boot 应用程序中启用 GemFire 客户端缓存并指定缓存的名称。
@EnableCachingDefinedRegions(clientRegionShortcut = ClientRegionShortcut.LOCAL) 是 Pivotal GemFire 提供的 Spring Boot 集成注解之一,用于在 Spring Boot 应用程序中启用 GemFire 缓存,并定义客户端缓存区域及其行为。
@EnableGemfireCaching 是 Pivotal GemFire 提供的 Spring Boot 集成注解之一,用于在 Spring Boot 应用程序中启用 GemFire 缓存支持。
结果:
Cache Miss [true] - Elapsed Time [776 ms]
Cache Miss [false] - Elapsed Time [0 ms]
Cache Miss [true] - Elapsed Time [96 ms]
guide45、Accessing Data with JPA
使用 Spring Data JPA 在关系数据库中存储和检索数据
Spring Data JPA 是 Spring Framework 提供的一个模块,用于简化与 JPA(Java Persistence
API)的集成。JPA 是 Java EE 规范中的 ORM(对象关系映射)框架,用于将 Java 对象映射到关系数据库。
Spring Data JPA 提供了一组简单且易于使用的 API,用于在 Spring 应用程序中使用
JPA。它提供了自动化存储库(Repository)创建,基于方法名称的查询和 Criteria API 的支持,以及与 Spring 的集成。
构建实体类:
@Entity
public class Customer {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
...
Spring Data JPA 专注于使用 JPA 将数据存储在关系数据库中。它最引人注目的特性是能够在运行时从存储库接口自动创建存储库实现。
创建一个与实体一起工作的存储库接口:
public interface CustomerRepository extends CrudRepository<Customer, Long> {
List<Customer> findByLastName(String lastName);
Customer findById(long id);
}
CrudRepository 是 Spring Data JPA 提供的基本存储库接口,它提供了一组简单的 CRUD(创建、读取、更新、删除)操作方法。通过继承 CrudRepository 接口,可以轻松地定义自己的存储库接口,而无需编写任何实现代码。
最后新建主类:
@SpringBootApplication
public class AccessingDataJpaApplication {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AccessingDataJpaApplication.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AccessingDataJpaApplication.class);
}
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner demo(CustomerRepository repository) {
return (args) -> {
// save a few customers
repository.save(new Customer("Jack", "Bauer"));
repository.save(new Customer("Chloe", "O'Brian"));
repository.save(new Customer("Kim", "Bauer"));
repository.save(new Customer("David", "Palmer"));
repository.save(new Customer("Michelle", "Dessler"));
// fetch all customers
log.info("Customers found with findAll():");
log.info("-------------------------------");
for (Customer customer : repository.findAll()) {
log.info(customer.toString());
}
log.info("");
// fetch an individual customer by ID
Customer customer = repository.findById(1L);
log.info("Customer found with findById(1L):");
log.info("--------------------------------");
log.info(customer.toString());
log.info("");
// fetch customers by last name
log.info("Customer found with findByLastName('Bauer'):");
log.info("--------------------------------------------");
repository.findByLastName("Bauer").forEach(bauer -> {
log.info(bauer.toString());
});
// for (Customer bauer : repository.findByLastName("Bauer")) {
// log.info(bauer.toString());
// }
log.info("");
};
}
}
运行结果:
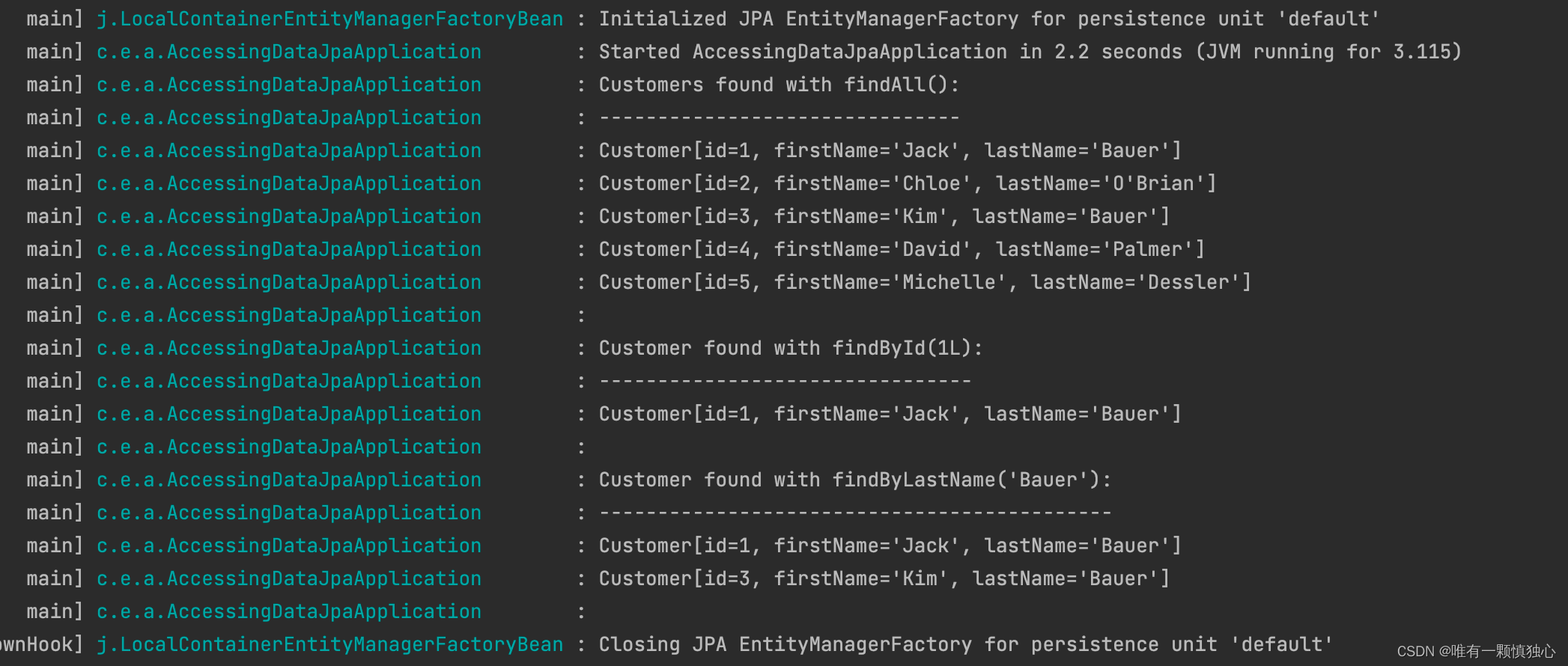
可以尝试下mapper层代码与spring data的结合,感觉可以少些点CURD代码。