目录
- 散列表
- hash 函数
- 种类:
- 布隆过滤器
- 场景:
- 构成
- 原理
- 应用分析
- 选择 hash 函数
- 问题:只用2GB内存在20亿个整数中找到出现次数最多的数
- 完整代码:
- 分布式一致性 hash
- hash迁移
- hash 偏移
- 虚拟节点
散列表
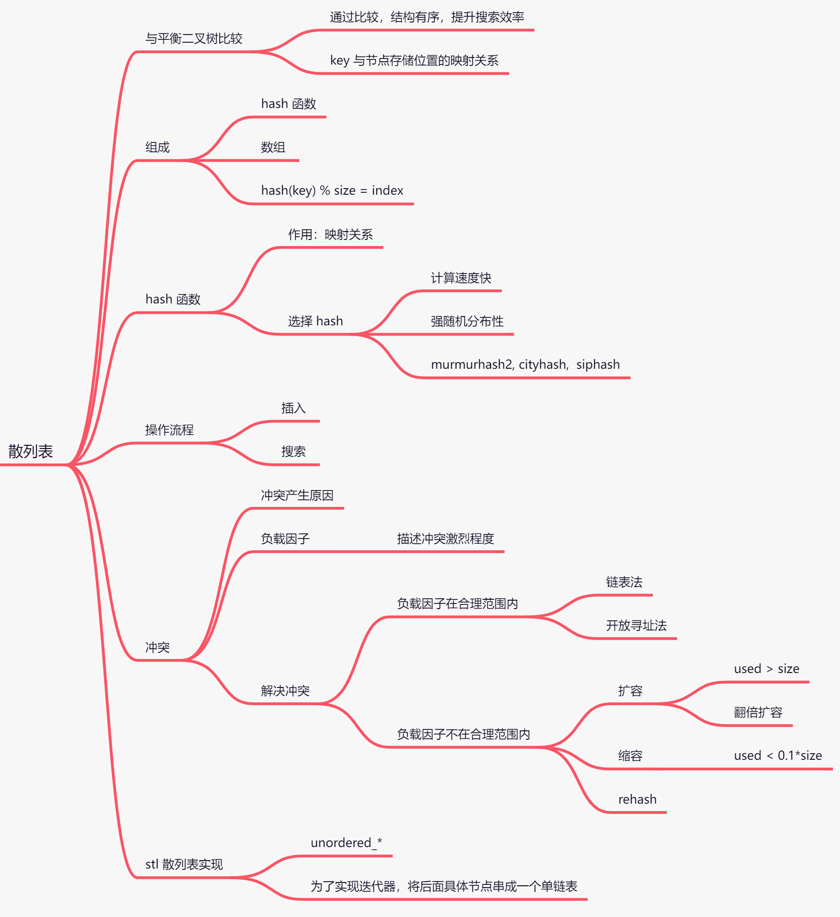
hash 函数
计算速度快
强随机分布(等概率、均匀地分布在整个地址空间)
种类:
murmurhash1,速度最快,质量一般
murmurhash2,速度可以,质量可以(通常使用)
murmurhash3,速度最慢,质量最好
siphash( redis6.0 当中使用,rust 等大多数语言选用的 hash 算法来实现 hashmap)siphash 主要解决字符串接近的强随机分布性 ;(10001,10002)
cityhash 都具备强随机分布性;测试地址如下:
https://github.com/aappleby/smhasher
布隆过滤器
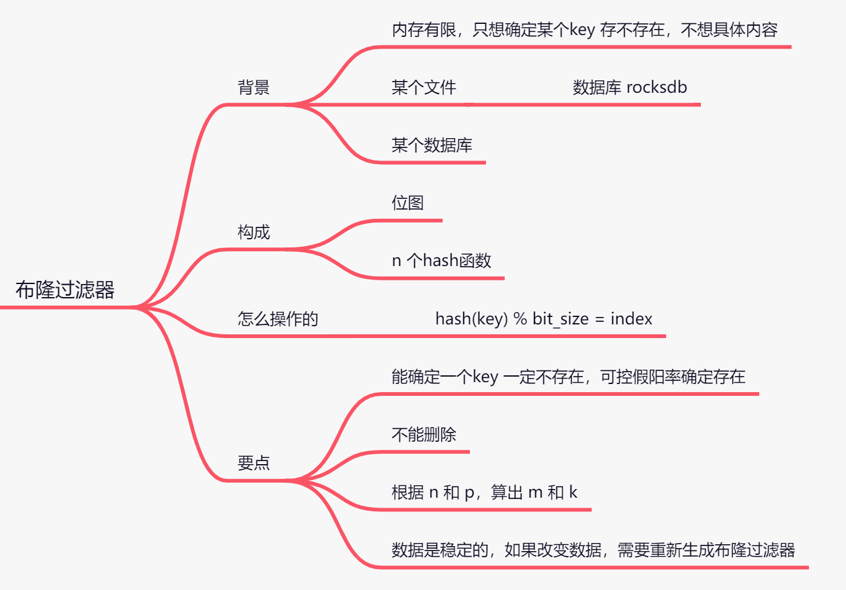
是高效地插入和查询,能确定某个字符串一定不存在或者可能存在;不能删除!
场景:
内存有限,只想确定某个key存不存在,不想知道具体内容。
某个文件是否存在---------->数据库rockdb,某个数据库是否存在。
构成

原理
当一个元素加入位图时,通过 k 个 hash 函数将这个元素映射到位图的 k 个点,并把它们置为 1;当检索时,再通过 k 个 hash函数运算检测位图的 k 个点是否都为 1;如果有不为 1 的点,那么认为该 key 不存在;如果全部为 1,则可能存在;
为什么不支持删除操作?
在位图中每个槽位只有两种状态(0 或者 1),一个槽位被设置为 1 状态,但不确定它被设置了多少次;也就是不知道
被多少个 key 哈希映射而来以及是被具体哪个 hash 函数映射而来;
不存在 只要一个索引位为0;如果都为1,是否一定存在?
不一定,可控的(假阳率);
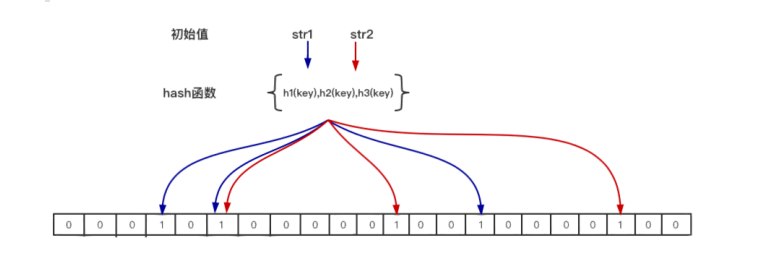
应用分析
n – 预期布隆过滤器中元素的个数,如上图 只有str1和str2 两
个元素 那么 n=2
p – 假阳率,在0-1之间 0.000000
m – 位图所占空间
k – hash函数的个数
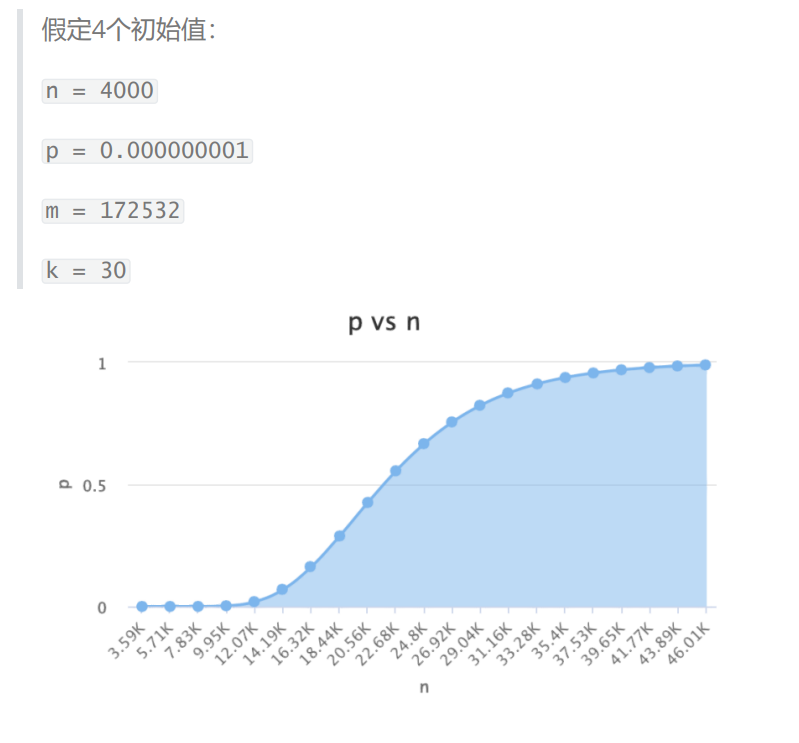
确定 n 和 p
在实际使用布隆过滤器时,首先需要确定 n 和 p,通过上面的运算得出 m 和 k;通常可以在下面这个网站上选出合适的值;
https://hur.st/bloomfilter
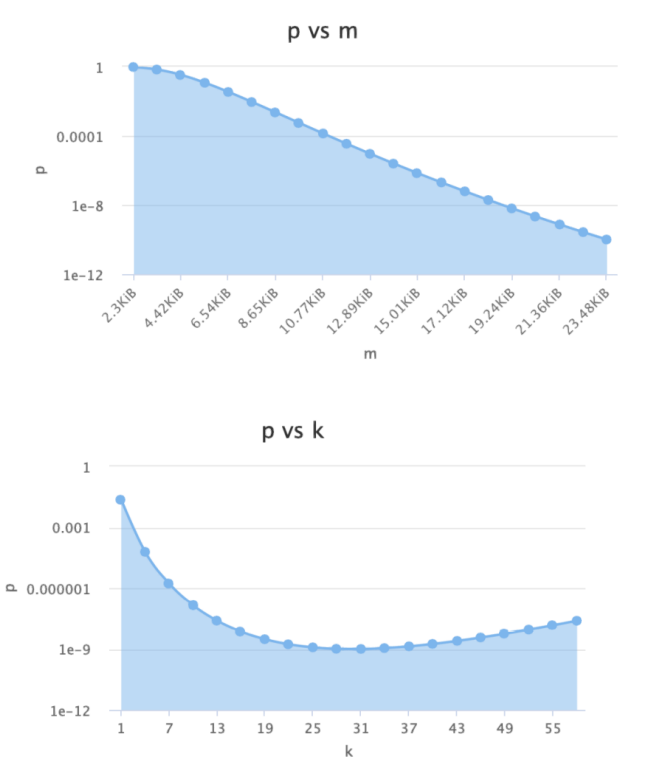
31左右假阳率最低。
选择 hash 函数
选择一个 hash 函数,通过给 hash 传递不同的种子偏移值,采用线性探寻的方式构造多个 hash 函数;
#define MIX_UINT64(v) ((uint32_t)((v>>32)^(v)))
uint64_t hash1 = MurmurHash2_x64(key, len, Seed);//seed就是salt值
uint64_t hash2 = MurmurHash2_x64(key, len,
MIX_UINT64(hash1));
for (i = 0; i < k; i++) // k 是hash函数的个数
{
Pos[i] = (hash1 + i*hash2) % m; // m 是位图的
⼤⼩
}
问题:只用2GB内存在20亿个整数中找到出现次数最多的数
假设一个数重复出现了20亿次,因为整数的范围是-231~231-1 大约21亿,所以4个字节可以统计
1、用到HashMap数据结构,因为是整数类型,key为4B value为4B,和为8B
1.6GB大概能存储2亿数据(1.6G/8=2亿)
因为整数共42亿个(-21亿到21亿),按照2亿的间隔划分成21个小文件,再对这21个小文件进行统计
2、如果这20 亿个数数值比较集中的话,例如都处于 1~20000000 之间,那么你都会把他们全部映射到同一个文件中,存不了这么多,怎么解决?
那我可以先把每个数先做哈希函数映射,根据哈希函数得到的哈希值,再把他们存放到对应的文件中,如果哈希函数设计到好的话,那么这些数就会分布的比较平均。
3、如果是40亿呢?
扩大文件数目到42个文件,但是可能该数字出现次数超过了int类型的范围,怎么办?可以将value初始化为-21亿,这样如果value是21亿 则表明出现了42亿次。
4、80亿?
可以一边遍历一遍判断啊,如果我在统计的过程中,发现某个 key 出现的次数超过了 40 亿次,那么,就不可能再有另外一个 key 出现的次数比它多了,那我直接把这个 key 返回就搞定了。
5、类似“大”问题:
大文件 hash 拆成小文件
单台机器 hash 分流到多台机器
完整代码:
bloom_filter.hpp
/*
*********************************************************************
* *
* Open Bloom Filter *
* *
* Author: Arash Partow - 2000 *
* URL: http://www.partow.net *
* URL: http://www.partow.net/programming/hashfunctions/index.html *
* *
* Copyright notice: *
* Free use of the Open Bloom Filter Library is permitted under the *
* guidelines and in accordance with the MIT License. *
* http://www.opensource.org/licenses/MIT *
* *
*********************************************************************
*/
#ifndef INCLUDE_BLOOM_FILTER_HPP
#define INCLUDE_BLOOM_FILTER_HPP
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstddef>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iterator>
#include <limits>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
static const std::size_t bits_per_char = 0x08; // 8 bits in 1 char(unsigned)
static const unsigned char bit_mask[bits_per_char] = {
0x01, //00000001
0x02, //00000010
0x04, //00000100
0x08, //00001000
0x10, //00010000
0x20, //00100000
0x40, //01000000
0x80 //10000000
};
class bloom_parameters
{
public:
bloom_parameters()
: minimum_size(1),
maximum_size(std::numeric_limits<unsigned long long int>::max()),
minimum_number_of_hashes(1),
maximum_number_of_hashes(std::numeric_limits<unsigned int>::max()),
projected_element_count(10000),
false_positive_probability(1.0 / projected_element_count),
random_seed(0xA5A5A5A55A5A5A5AULL)
{}
virtual ~bloom_parameters()
{}
inline bool operator!()
{
return (minimum_size > maximum_size) ||
(minimum_number_of_hashes > maximum_number_of_hashes) ||
(minimum_number_of_hashes < 1) ||
(0 == maximum_number_of_hashes) ||
(0 == projected_element_count) ||
(false_positive_probability < 0.0) ||
(std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity() == std::abs(false_positive_probability)) ||
(0 == random_seed) ||
(0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFULL == random_seed);
}
// Allowable min/max size of the bloom filter in bits
unsigned long long int minimum_size;
unsigned long long int maximum_size;
// Allowable min/max number of hash functions
unsigned int minimum_number_of_hashes;
unsigned int maximum_number_of_hashes;
// The approximate number of elements to be inserted
// into the bloom filter, should be within one order
// of magnitude. The default is 10000.
unsigned long long int projected_element_count;
// The approximate false positive probability expected
// from the bloom filter. The default is assumed to be
// the reciprocal of the projected_element_count.
double false_positive_probability;
unsigned long long int random_seed;
struct optimal_parameters_t
{
optimal_parameters_t()
: number_of_hashes(0),
table_size(0)
{}
unsigned int number_of_hashes;
unsigned long long int table_size;
};
optimal_parameters_t optimal_parameters;
virtual bool compute_optimal_parameters()
{
/*
Note:
The following will attempt to find the number of hash functions
and minimum amount of storage bits required to construct a bloom
filter consistent with the user defined false positive probability
and estimated element insertion count.
*/
if (!(*this))
return false;
double min_m = std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity();
double min_k = 0.0;
double k = 1.0;
while (k < 1000.0)
{
const double numerator = (- k * projected_element_count);
const double denominator = std::log(1.0 - std::pow(false_positive_probability, 1.0 / k));
const double curr_m = numerator / denominator;
if (curr_m < min_m)
{
min_m = curr_m;
min_k = k;
}
k += 1.0;
}
optimal_parameters_t& optp = optimal_parameters;
optp.number_of_hashes = static_cast<unsigned int>(min_k);
optp.table_size = static_cast<unsigned long long int>(min_m);
optp.table_size += (((optp.table_size % bits_per_char) != 0) ? (bits_per_char - (optp.table_size % bits_per_char)) : 0);
if (optp.number_of_hashes < minimum_number_of_hashes)
optp.number_of_hashes = minimum_number_of_hashes;
else if (optp.number_of_hashes > maximum_number_of_hashes)
optp.number_of_hashes = maximum_number_of_hashes;
if (optp.table_size < minimum_size)
optp.table_size = minimum_size;
else if (optp.table_size > maximum_size)
optp.table_size = maximum_size;
return true;
}
};
class bloom_filter
{
protected:
typedef unsigned int bloom_type;
typedef unsigned char cell_type;
typedef std::vector<unsigned char> table_type;
public:
bloom_filter()
: salt_count_(0),
table_size_(0),
projected_element_count_(0),
inserted_element_count_ (0),
random_seed_(0),
desired_false_positive_probability_(0.0)
{}
bloom_filter(const bloom_parameters& p)
: projected_element_count_(p.projected_element_count),
inserted_element_count_(0),
random_seed_((p.random_seed * 0xA5A5A5A5) + 1),
desired_false_positive_probability_(p.false_positive_probability)
{
salt_count_ = p.optimal_parameters.number_of_hashes;
table_size_ = p.optimal_parameters.table_size;
generate_unique_salt();
bit_table_.resize(table_size_ / bits_per_char, static_cast<unsigned char>(0x00));
}
bloom_filter(const bloom_filter& filter)
{
this->operator=(filter);
}
inline bool operator == (const bloom_filter& f) const
{
if (this != &f)
{
return
(salt_count_ == f.salt_count_ ) &&
(table_size_ == f.table_size_ ) &&
(bit_table_.size() == f.bit_table_.size() ) &&
(projected_element_count_ == f.projected_element_count_ ) &&
(inserted_element_count_ == f.inserted_element_count_ ) &&
(random_seed_ == f.random_seed_ ) &&
(desired_false_positive_probability_ == f.desired_false_positive_probability_) &&
(salt_ == f.salt_ ) &&
(bit_table_ == f.bit_table_ ) ;
}
else
return true;
}
inline bool operator != (const bloom_filter& f) const
{
return !operator==(f);
}
inline bloom_filter& operator = (const bloom_filter& f)
{
if (this != &f)
{
salt_count_ = f.salt_count_;
table_size_ = f.table_size_;
bit_table_ = f.bit_table_;
salt_ = f.salt_;
projected_element_count_ = f.projected_element_count_;
inserted_element_count_ = f.inserted_element_count_;
random_seed_ = f.random_seed_;
desired_false_positive_probability_ = f.desired_false_positive_probability_;
}
return *this;
}
virtual ~bloom_filter()
{}
inline bool operator!() const
{
return (0 == table_size_);
}
inline void clear()
{
std::fill(bit_table_.begin(), bit_table_.end(), static_cast<unsigned char>(0x00));
inserted_element_count_ = 0;
}
inline void insert(const unsigned char* key_begin, const std::size_t& length)
{
std::size_t bit_index = 0;
std::size_t bit = 0;
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < salt_.size(); ++i)
{
compute_indices(hash_ap(key_begin, length, salt_[i]), bit_index, bit);
bit_table_[bit_index / bits_per_char] |= bit_mask[bit];//相应位置1
}
++inserted_element_count_;
}
template <typename T>
inline void insert(const T& t)
{
// Note: T must be a C++ POD type.
insert(reinterpret_cast<const unsigned char*>(&t),sizeof(T));
}
inline void insert(const std::string& key)
{
insert(reinterpret_cast<const unsigned char*>(key.data()),key.size());
}
inline void insert(const char* data, const std::size_t& length)
{
insert(reinterpret_cast<const unsigned char*>(data),length);
}
template <typename InputIterator>
inline void insert(const InputIterator begin, const InputIterator end)
{
InputIterator itr = begin;
while (end != itr)
{
insert(*(itr++));
}
}
inline virtual bool contains(const unsigned char* key_begin, const std::size_t length) const
{
std::size_t bit_index = 0;
std::size_t bit = 0;
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < salt_.size(); ++i)
{
compute_indices(hash_ap(key_begin, length, salt_[i]), bit_index, bit);
if ((bit_table_[bit_index / bits_per_char] & bit_mask[bit]) != bit_mask[bit])
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
template <typename T>
inline bool contains(const T& t) const
{
return contains(reinterpret_cast<const unsigned char*>(&t),static_cast<std::size_t>(sizeof(T)));
}
inline bool contains(const std::string& key) const
{
return contains(reinterpret_cast<const unsigned char*>(key.c_str()),key.size());
}
inline bool contains(const char* data, const std::size_t& length) const
{
return contains(reinterpret_cast<const unsigned char*>(data),length);
}
template <typename InputIterator>
inline InputIterator contains_all(const InputIterator begin, const InputIterator end) const
{
InputIterator itr = begin;
while (end != itr)
{
if (!contains(*itr))
{
return itr;
}
++itr;
}
return end;
}
template <typename InputIterator>
inline InputIterator contains_none(const InputIterator begin, const InputIterator end) const
{
InputIterator itr = begin;
while (end != itr)
{
if (contains(*itr))
{
return itr;
}
++itr;
}
return end;
}
inline virtual unsigned long long int size() const
{
return table_size_;
}
inline unsigned long long int element_count() const
{
return inserted_element_count_;
}
inline double effective_fpp() const
{
/*
Note:
The effective false positive probability is calculated using the
designated table size and hash function count in conjunction with
the current number of inserted elements - not the user defined
predicated/expected number of inserted elements.
*/
return std::pow(1.0 - std::exp(-1.0 * salt_.size() * inserted_element_count_ / size()), 1.0 * salt_.size());
}
inline bloom_filter& operator &= (const bloom_filter& f)
{
/* intersection */
if (
(salt_count_ == f.salt_count_ ) &&
(table_size_ == f.table_size_ ) &&
(random_seed_ == f.random_seed_)
)
{
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < bit_table_.size(); ++i)
{
bit_table_[i] &= f.bit_table_[i];
}
}
return *this;
}
inline bloom_filter& operator |= (const bloom_filter& f)
{
/* union */
if (
(salt_count_ == f.salt_count_ ) &&
(table_size_ == f.table_size_ ) &&
(random_seed_ == f.random_seed_)
)
{
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < bit_table_.size(); ++i)
{
bit_table_[i] |= f.bit_table_[i];
}
}
return *this;
}
inline bloom_filter& operator ^= (const bloom_filter& f)
{
/* difference */
if (
(salt_count_ == f.salt_count_ ) &&
(table_size_ == f.table_size_ ) &&
(random_seed_ == f.random_seed_)
)
{
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < bit_table_.size(); ++i)
{
bit_table_[i] ^= f.bit_table_[i];
}
}
return *this;
}
inline const cell_type* table() const
{
return bit_table_.data();
}
inline std::size_t hash_count()
{
return salt_.size();
}
protected:
inline virtual void compute_indices(const bloom_type& hash, std::size_t& bit_index, std::size_t& bit) const
{
bit_index = hash % table_size_;
bit = bit_index % bits_per_char;
}
void generate_unique_salt()
{
/*
Note:
A distinct hash function need not be implementation-wise
distinct. In the current implementation "seeding" a common
hash function with different values seems to be adequate.
*/
const unsigned int predef_salt_count = 128;
static const bloom_type predef_salt[predef_salt_count] =
{
0xAAAAAAAA, 0x55555555, 0x33333333, 0xCCCCCCCC,
0x66666666, 0x99999999, 0xB5B5B5B5, 0x4B4B4B4B,
0xAA55AA55, 0x55335533, 0x33CC33CC, 0xCC66CC66,
0x66996699, 0x99B599B5, 0xB54BB54B, 0x4BAA4BAA,
0xAA33AA33, 0x55CC55CC, 0x33663366, 0xCC99CC99,
0x66B566B5, 0x994B994B, 0xB5AAB5AA, 0xAAAAAA33,
0x555555CC, 0x33333366, 0xCCCCCC99, 0x666666B5,
0x9999994B, 0xB5B5B5AA, 0xFFFFFFFF, 0xFFFF0000,
0xB823D5EB, 0xC1191CDF, 0xF623AEB3, 0xDB58499F,
0xC8D42E70, 0xB173F616, 0xA91A5967, 0xDA427D63,
0xB1E8A2EA, 0xF6C0D155, 0x4909FEA3, 0xA68CC6A7,
0xC395E782, 0xA26057EB, 0x0CD5DA28, 0x467C5492,
0xF15E6982, 0x61C6FAD3, 0x9615E352, 0x6E9E355A,
0x689B563E, 0x0C9831A8, 0x6753C18B, 0xA622689B,
0x8CA63C47, 0x42CC2884, 0x8E89919B, 0x6EDBD7D3,
0x15B6796C, 0x1D6FDFE4, 0x63FF9092, 0xE7401432,
0xEFFE9412, 0xAEAEDF79, 0x9F245A31, 0x83C136FC,
0xC3DA4A8C, 0xA5112C8C, 0x5271F491, 0x9A948DAB,
0xCEE59A8D, 0xB5F525AB, 0x59D13217, 0x24E7C331,
0x697C2103, 0x84B0A460, 0x86156DA9, 0xAEF2AC68,
0x23243DA5, 0x3F649643, 0x5FA495A8, 0x67710DF8,
0x9A6C499E, 0xDCFB0227, 0x46A43433, 0x1832B07A,
0xC46AFF3C, 0xB9C8FFF0, 0xC9500467, 0x34431BDF,
0xB652432B, 0xE367F12B, 0x427F4C1B, 0x224C006E,
0x2E7E5A89, 0x96F99AA5, 0x0BEB452A, 0x2FD87C39,
0x74B2E1FB, 0x222EFD24, 0xF357F60C, 0x440FCB1E,
0x8BBE030F, 0x6704DC29, 0x1144D12F, 0x948B1355,
0x6D8FD7E9, 0x1C11A014, 0xADD1592F, 0xFB3C712E,
0xFC77642F, 0xF9C4CE8C, 0x31312FB9, 0x08B0DD79,
0x318FA6E7, 0xC040D23D, 0xC0589AA7, 0x0CA5C075,
0xF874B172, 0x0CF914D5, 0x784D3280, 0x4E8CFEBC,
0xC569F575, 0xCDB2A091, 0x2CC016B4, 0x5C5F4421
};
if (salt_count_ <= predef_salt_count)
{
std::copy(predef_salt,
predef_salt + salt_count_,
std::back_inserter(salt_));
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < salt_.size(); ++i)
{
/*
Note:
This is done to integrate the user defined random seed,
so as to allow for the generation of unique bloom filter
instances.
*/
salt_[i] = salt_[i] * salt_[(i + 3) % salt_.size()] + static_cast<bloom_type>(random_seed_);
}
}
else
{
std::copy(predef_salt, predef_salt + predef_salt_count, std::back_inserter(salt_));
srand(static_cast<unsigned int>(random_seed_));
while (salt_.size() < salt_count_)
{
bloom_type current_salt = static_cast<bloom_type>(rand()) * static_cast<bloom_type>(rand());
if (0 == current_salt)
continue;
if (salt_.end() == std::find(salt_.begin(), salt_.end(), current_salt))
{
salt_.push_back(current_salt);
}
}
}
}
inline bloom_type hash_ap(const unsigned char* begin, std::size_t remaining_length, bloom_type hash) const
{
const unsigned char* itr = begin;
unsigned int loop = 0;
while (remaining_length >= 8)
{
const unsigned int& i1 = *(reinterpret_cast<const unsigned int*>(itr)); itr += sizeof(unsigned int);
const unsigned int& i2 = *(reinterpret_cast<const unsigned int*>(itr)); itr += sizeof(unsigned int);
hash ^= (hash << 7) ^ i1 * (hash >> 3) ^
(~((hash << 11) + (i2 ^ (hash >> 5))));
remaining_length -= 8;
}
if (remaining_length)
{
if (remaining_length >= 4)
{
const unsigned int& i = *(reinterpret_cast<const unsigned int*>(itr));
if (loop & 0x01)
hash ^= (hash << 7) ^ i * (hash >> 3);
else
hash ^= (~((hash << 11) + (i ^ (hash >> 5))));
++loop;
remaining_length -= 4;
itr += sizeof(unsigned int);
}
if (remaining_length >= 2)
{
const unsigned short& i = *(reinterpret_cast<const unsigned short*>(itr));
if (loop & 0x01)
hash ^= (hash << 7) ^ i * (hash >> 3);
else
hash ^= (~((hash << 11) + (i ^ (hash >> 5))));
++loop;
remaining_length -= 2;
itr += sizeof(unsigned short);
}
if (remaining_length)
{
hash += ((*itr) ^ (hash * 0xA5A5A5A5)) + loop;
}
}
return hash;
}
std::vector<bloom_type> salt_;
std::vector<unsigned char> bit_table_;
unsigned int salt_count_;
unsigned long long int table_size_;
unsigned long long int projected_element_count_;
unsigned long long int inserted_element_count_;
unsigned long long int random_seed_;
double desired_false_positive_probability_;
};
inline bloom_filter operator & (const bloom_filter& a, const bloom_filter& b)
{
bloom_filter result = a;
result &= b;
return result;
}
inline bloom_filter operator | (const bloom_filter& a, const bloom_filter& b)
{
bloom_filter result = a;
result |= b;
return result;
}
inline bloom_filter operator ^ (const bloom_filter& a, const bloom_filter& b)
{
bloom_filter result = a;
result ^= b;
return result;
}
class compressible_bloom_filter : public bloom_filter
{
public:
compressible_bloom_filter(const bloom_parameters& p)
: bloom_filter(p)
{
size_list.push_back(table_size_);
}
inline unsigned long long int size() const
{
return size_list.back();
}
inline bool compress(const double& percentage)
{
if (
(percentage < 0.0) ||
(percentage >= 100.0)
)
{
return false;
}
unsigned long long int original_table_size = size_list.back();
unsigned long long int new_table_size = static_cast<unsigned long long int>((size_list.back() * (1.0 - (percentage / 100.0))));
new_table_size -= new_table_size % bits_per_char;
if (
(bits_per_char > new_table_size) ||
(new_table_size >= original_table_size)
)
{
return false;
}
desired_false_positive_probability_ = effective_fpp();
const unsigned long long int new_tbl_raw_size = new_table_size / bits_per_char;
table_type tmp(new_tbl_raw_size);
std::copy(bit_table_.begin(), bit_table_.begin() + new_tbl_raw_size, tmp.begin());
typedef table_type::iterator itr_t;
itr_t itr = bit_table_.begin() + (new_table_size / bits_per_char);
itr_t end = bit_table_.begin() + (original_table_size / bits_per_char);
itr_t itr_tmp = tmp.begin();
while (end != itr)
{
*(itr_tmp++) |= (*itr++);
}
std::swap(bit_table_, tmp);
size_list.push_back(new_table_size);
return true;
}
private:
inline void compute_indices(const bloom_type& hash, std::size_t& bit_index, std::size_t& bit) const
{
bit_index = hash;
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < size_list.size(); ++i)
{
bit_index %= size_list[i];
}
bit = bit_index % bits_per_char;
}
std::vector<unsigned long long int> size_list;
};
#endif
/*
Note 1:
If it can be guaranteed that bits_per_char will be of the form 2^n then
the following optimization can be used:
bit_table_[bit_index >> n] |= bit_mask[bit_index & (bits_per_char - 1)];
Note 2:
For performance reasons where possible when allocating memory it should
be aligned (aligned_alloc) according to the architecture being used.
*/
演示代码main.c:
/*
*********************************************************************
* *
* Open Bloom Filter *
* *
* Description: Basic Bloom Filter Usage *
* Author: Arash Partow - 2000 *
* URL: http://www.partow.net *
* URL: http://www.partow.net/programming/hashfunctions/index.html *
* *
* Copyright notice: *
* Free use of the Open Bloom Filter Library is permitted under the *
* guidelines and in accordance with the MIT License. *
* http://www.opensource.org/licenses/MIT *
* *
*********************************************************************
*/
/*
Description: This example demonstrates basic usage of the Bloom filter.
Initially some values are inserted then they are subsequently
queried, noting any false positives or errors.
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "bloom_filter.hpp"
int main()
{
bloom_parameters parameters;
// How many elements roughly do we expect to insert?
parameters.projected_element_count = 1000;
// Maximum tolerable false positive probability? (0,1)
parameters.false_positive_probability = 0.0001; // 1 in 10000
// Simple randomizer (optional)
parameters.random_seed = 0xA5A5A5A5;
if (!parameters)
{
std::cout << "Error - Invalid set of bloom filter parameters!" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
parameters.compute_optimal_parameters();
//Instantiate Bloom Filter
bloom_filter filter(parameters);
std::string str_list[] = { "AbC", "iJk", "XYZ" };
// Insert into Bloom Filter
{
// Insert some strings
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < (sizeof(str_list) / sizeof(std::string)); ++i)
{
filter.insert(str_list[i]);
}
// Insert some numbers
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
filter.insert(i);
}
}
// Query Bloom Filter
{
// Query the existence of strings
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < (sizeof(str_list) / sizeof(std::string)); ++i)
{
if (filter.contains(str_list[i]))
{
std::cout << "BF contains: " << str_list[i] << std::endl;
}
}
// Query the existence of numbers
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
if (filter.contains(i))
{
std::cout << "BF contains: " << i << std::endl;
}
}
std::string invalid_str_list[] = { "AbCX", "iJkX", "XYZX" };
// Query the existence of invalid strings
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < (sizeof(invalid_str_list) / sizeof(std::string)); ++i)
{
if (filter.contains(invalid_str_list[i]))
{
std::cout << "BF falsely contains: " << invalid_str_list[i] << std::endl;
}
}
// Query the existence of invalid numbers
for (int i = -1; i > -100; --i)
{
if (filter.contains(i))
{
std::cout << "BF falsely contains: " << i << std::endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
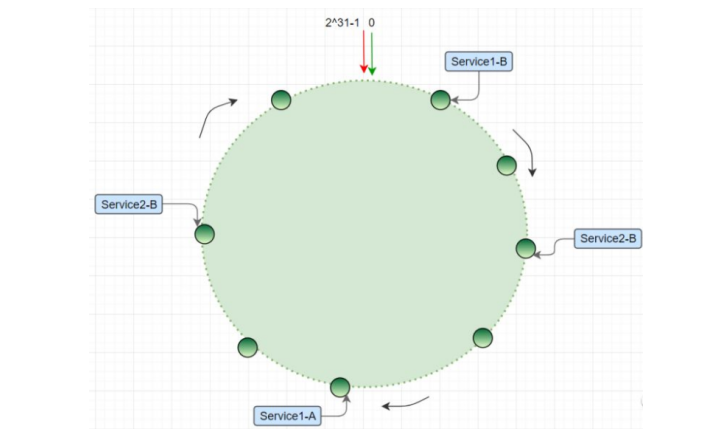
分布式一致性 hash
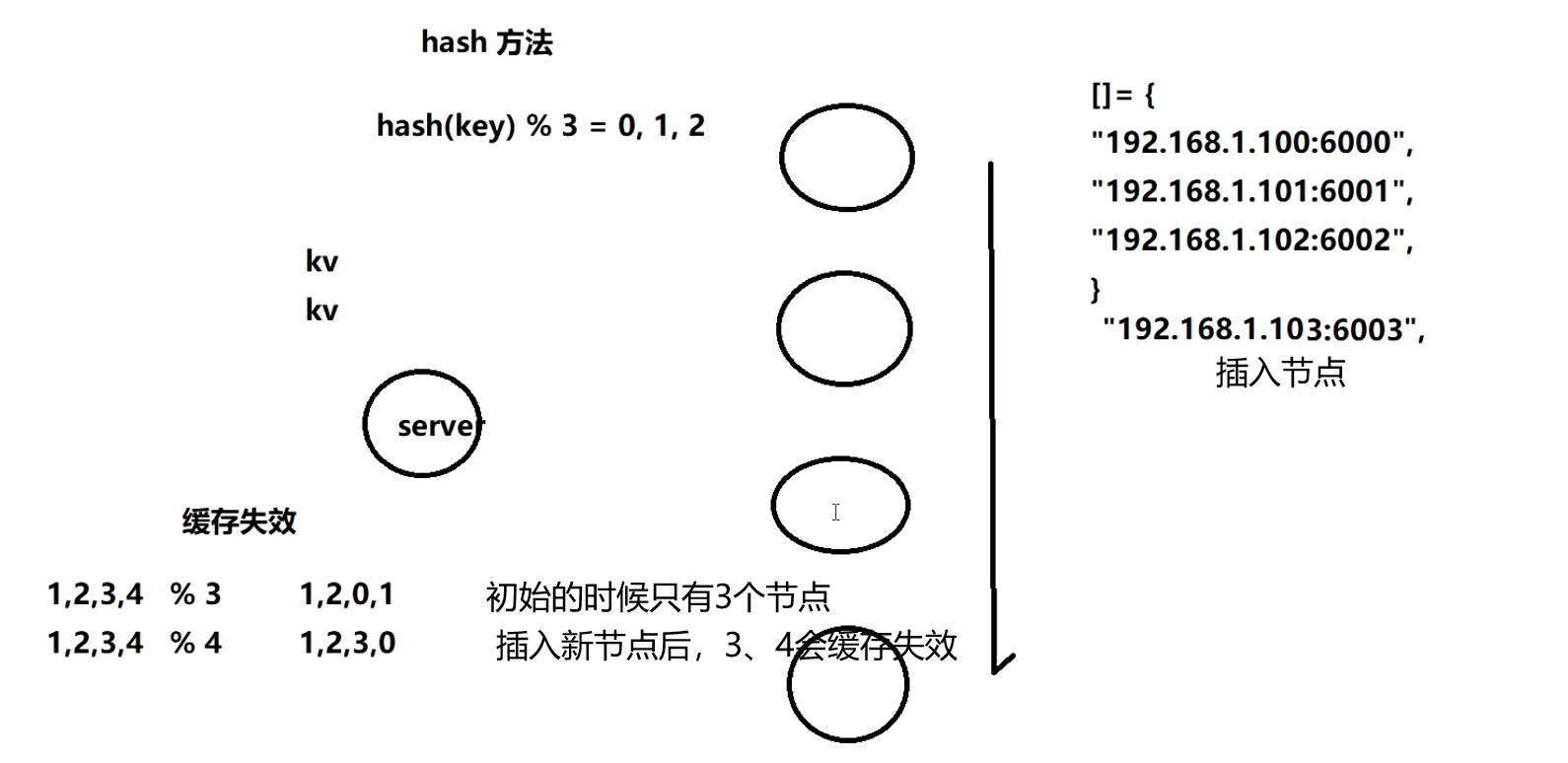
hash迁移
固定的算法hash(key)%2^32=index
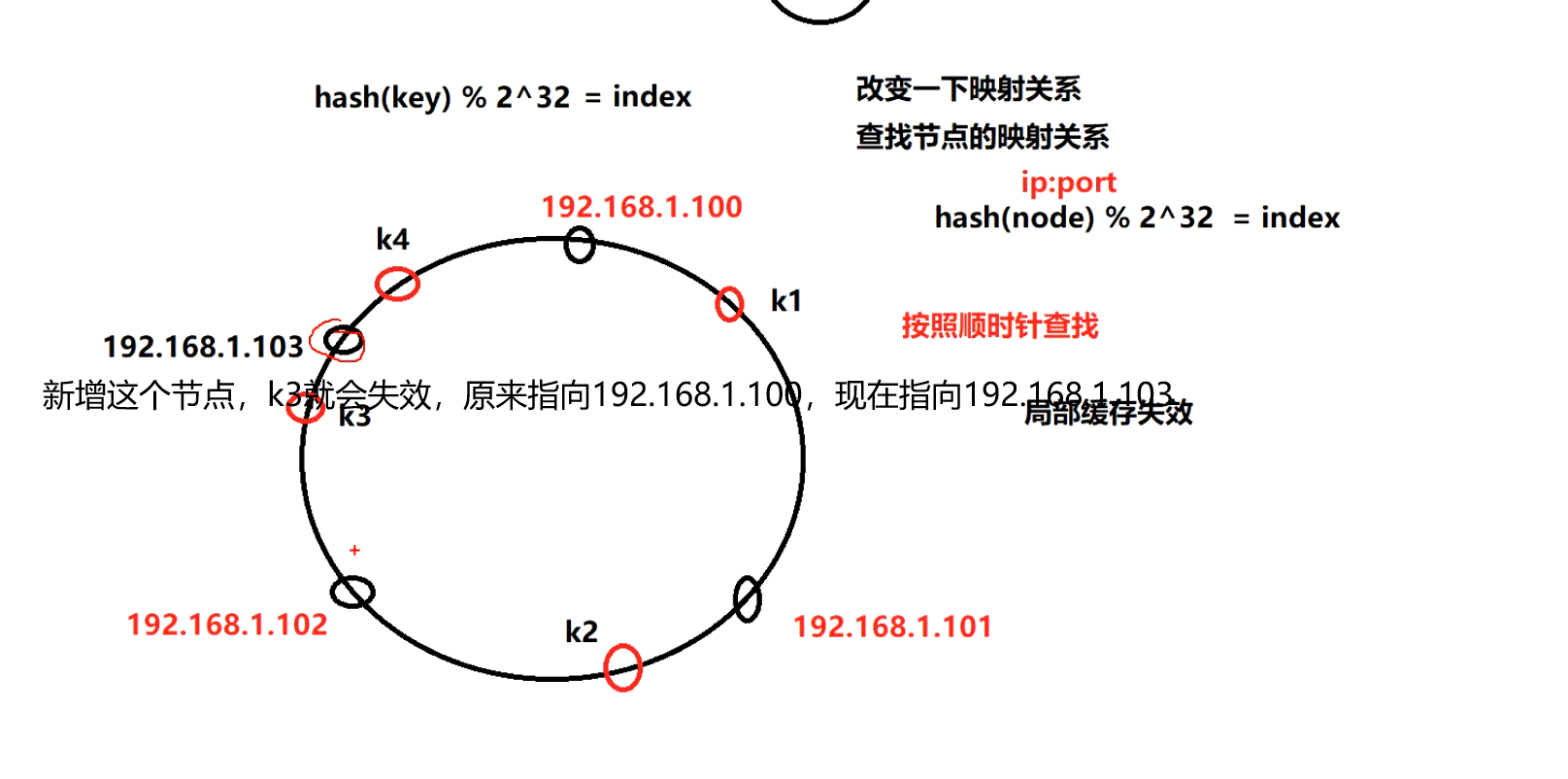
相比于图1,只有小范围(192.168.1.102~192.168.1.103的节点)的k3失效,将小范围的数据挪到192.168.1.103,这叫hash迁移。
hash 偏移
hash 算法得到的结果是随机的,不能保证服务器节点均匀分布在哈希环上;分布不均匀造成请求访问不均匀,服务器承受的压力不均匀;
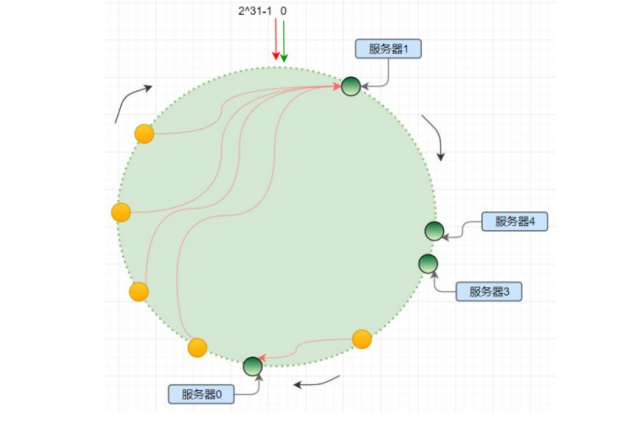
有的节点上数据很少,有的节点服务器过多。
解决:增加虚拟节点;
虚拟节点
为了解决哈希偏移的问题,增加了虚拟节点的概念;理论上,哈希环上节点数越多,数据分布越均衡;
为每个服务节点计算多个哈希节点(虚拟节点);通常做法是,hash(“IP:PORT:seqno”) %32;
有一个大的map结构,映射真实节点和虚拟节点。