⛄一、简介
该课题为基于MATLAB差影法的人体姿态识别。需要准备对应的模板图片作为背景图,然后测试图和背景图进行作差,结合形态学知识,提取出人体轮廓,接上最外接矩形,得出矩形长宽,计算长宽比例,从而判断人体姿态。优点是通俗易懂,缺点是局限性大,因为对背景图片要求比较高。另外可改造成不需要模板图片的纯形态学或者利用帧差法识别的基于视频的人体行为检测。

⛄二、部分源代码
% [X, R, t] = function recon3DPose(xy,im,varargin)
%
% Inputs: xy - [2 x 14] matrix of 2D joint locations
% im - Input image
%
%
%
% Outputs: X - [3 x 14] matrix of 3D joint locations.
% R - [3 x 3] Relative Camera Rotation.
% t - [3 x 1] Relative Camera translation.
%
% Wrapper for reconstruction of the 3D Pose of a human figure given the
% locations of the 2D anatomical landmarks.
% Copyright © 2012 Varun Ramakrishna.
%
% This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
% it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
% the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
% (at your option) any later version.
%
% This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
% but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
% MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
% GNU General Public License for more details.
%
% You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
% along with this program. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/.
function [X, R, t] = recon3DPose(im,xy,varargin)
% [X, R, t] = recon3DPose(xy,im,varargin)
% Parse parameters.
[pose.skel, pose.BOMP, pose.mu, pose.lambda1,…
pose.lamda2, pose.K, pose.numIter,…
pose.numIters2, pose.tol1, pose.tol2, pose.ks,…
pose.optType, pose.viz, pose.annoids,pose.numPoints] = process_options(varargin,…
‘skel’,‘’,…
‘BOMP’,‘’,…
‘mu’ ,‘’,…
‘lambda2’,0.01,…
‘lambda1’,0.01,…
‘K’, setK(size(im,2),size(im,1),2),…
‘numIter’, 20,…
‘numIters2’,30,…
‘tol1’, 500, …
‘tol2’, 1, …
‘ks’, 15, …
‘optType’, 1, …
‘viz’, 0,…
‘annoids’,1:15,…
‘numPoints’,15);
pose.im = im;
pose.xy = [xy; ones(1,size(xy,2))];
% Load default basis and skeleton
if(isempty(pose.BOMP)||isempty(pose.mu)||isempty(pose.skel))
basis = load(‘mocapReducedModel.mat’);
pose.BOMP = basis.B;
pose.mu = basis.mu;
pose.skel = basis.skel;
pose.numPoints = length(pose.skel.tree);
pose.annoids = [1:length(pose.skel.tree)];
end
% Reconstruct camera and pose.
[camera, pose] = cameraAndPose(pose);
% Assign outputs
X = pose.XnewR;
R = camera.R;
t = camera.t;
% Show aligned output
if(pose.viz)
load frontCam;
Xnew1 = alignToCamera(pose.XnewR,camera.R,camera.t,R,t);
figure(9);clf;
visualizeGaussianModel(Xnew1,pose.skel);
drawCam(R,t);
end
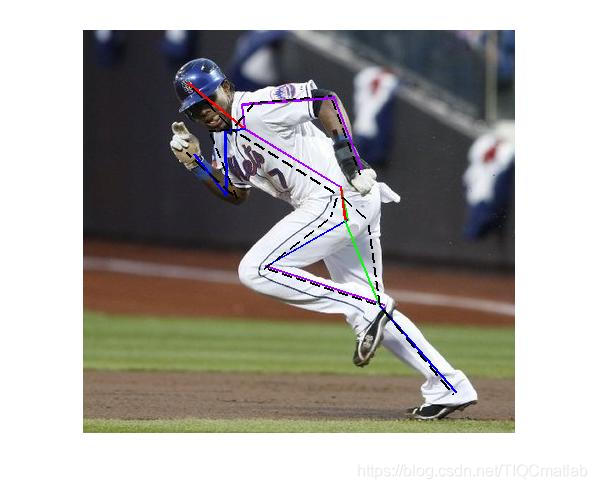
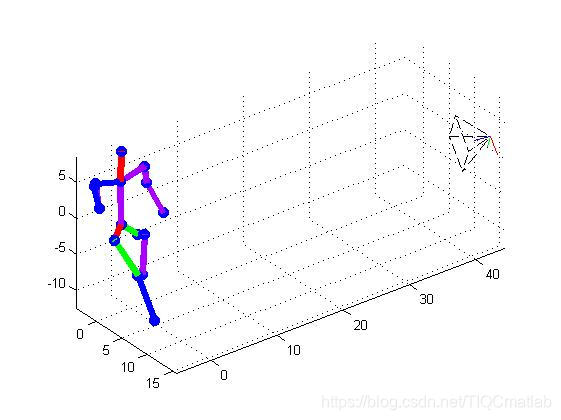
## ⛄三、运行结果

## ⛄四、matlab版本及参考文献
**1 matlab版本**
2014a
**2 参考文献**
[1] 蔡利梅.MATLAB图像处理——理论、算法与实例分析[M].清华大学出版社,2020.
[2]杨丹,赵海滨,龙哲.MATLAB图像处理实例详解[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[3]周品.MATLAB图像处理与图形用户界面设计[M].清华大学出版社,2013.
[4]刘成龙.精通MATLAB图像处理[M].清华大学出版社,2015.
**3 备注**
简介此部分摘自互联网,仅供参考,若侵权,联系删除



![[附源码]计算机毕业设计毕业生就业管理系统Springboot程序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6984e5400e57446b83e8a554a38b3e02.png)