🍉文章主页:阿博历练记
📖文章专栏:数据结构与算法
🚍代码仓库:阿博编程日记
🍥欢迎关注:欢迎友友们点赞收藏+关注哦🌹

文章目录
- 🌾前言
- 🎬队列
- 🔍1.队列的结构框架
- 🔍2.队列的初始化
- 👑为什么初始化不使用二级指针
- 🔍3.队列的释放
- 🔍4.队列的插入数据
- 🔍5.队列的删除数据
- 🔍6.队列取队头数据
- 🔍7.队列取队尾数据
- 🔍8.返回队列数据的个数
- 🔍9.判断队列是否为空
- 🚀Queue.h代码
- 🛸Queue.c代码
- 🛳Test.c代码
- 🧋代码效果展示
- 1.🖋题目描述
- 💡逻辑分析
- 🎥代码实现
- 2.🖋题目描述
- 💡逻辑分析
- 🎥代码实现
🌾前言
友友们,上期阿博给大家介绍了栈的实现,今天阿博给大家介绍一种新的数据结构:队列.
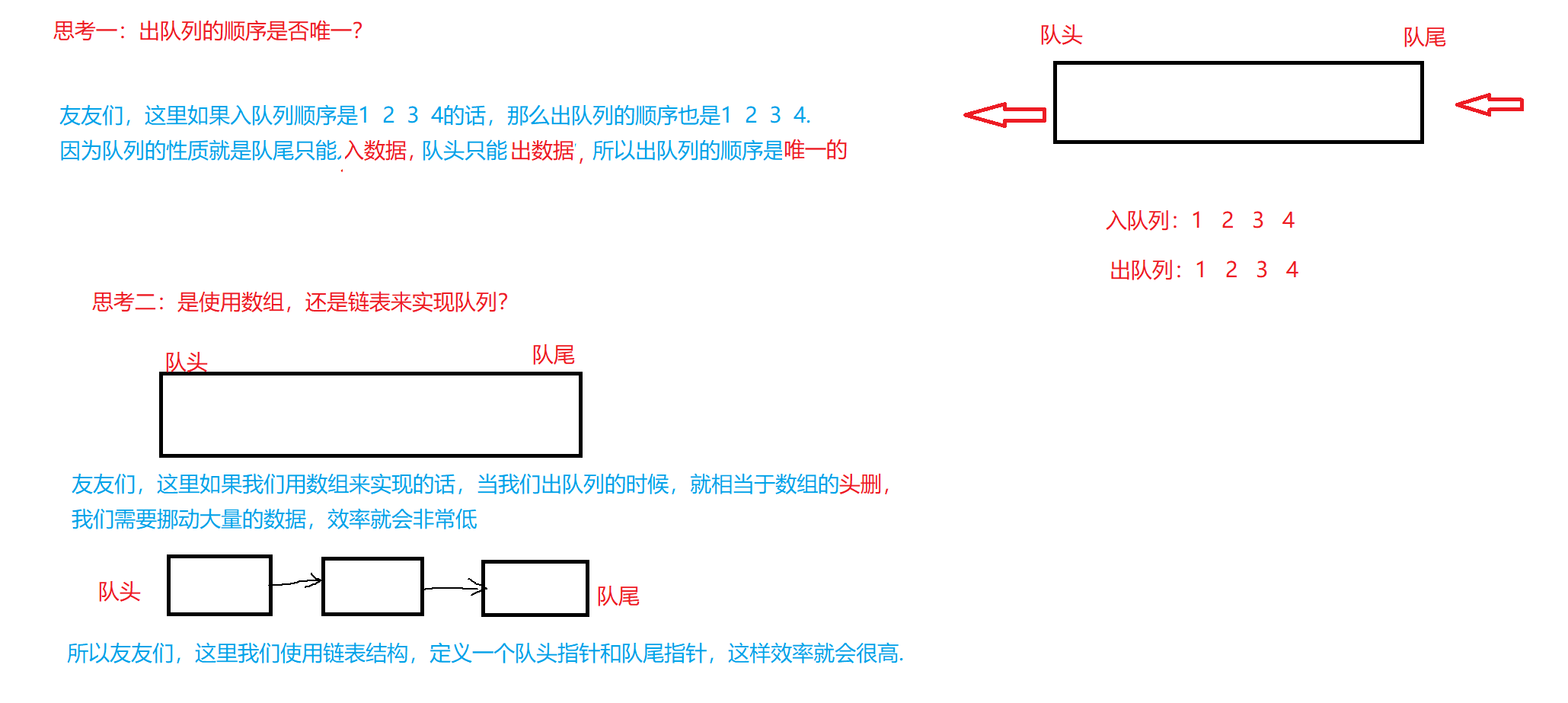
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out)的性质。
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾。
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头。
队列也可以使用数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低.
🎬队列
🔍1.队列的结构框架
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
⛳⛳友友们注意,这两个结构体不能合并到一起,因为它们所代表的意义不一样,第一个结构体是每一个结点的结构,第二个结构体代表的是这个队列的结构,它表示的是队列整体.
🔍2.队列的初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
👑为什么初始化不使用二级指针
⛳⛳这里有可能友友们会有疑问,我们初始化不是要改变phead指针和ptail指针,它们两个都是结构体指针,我们要改变它们,为什么不用二级指针呢?这里友友们注意了,phead指针和ptail指针又在一个新的结构体Queue里面放着,它们就属于这个结构体里面的成员,我们要改变它,只需要传这个新结构体的地址就可以访问并改变它们了.
这里阿博给友友们总结几种不用二级指针的方法:
⭐1.我们在函数外部定义一个同类型的指针,通过返回值的方式接收,这本质上是一个值拷贝(赋值)
⭐2.带哨兵位的头结点,它的本质是改变结构体里面的next指针,next指针属于结构体的成员,所以我们只需要传结构体的指针就可以访问到它了.
⭐3.把结构体指针重新放在一个结构体里面,这样它就属于这个结构体的成员了,我们只需要传这个结构体的地址就可以改变结构体指针了.
🔍3.队列的释放
1.保存下一结点的地址迭代释放
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
2.保存当前结点的地址迭代释放
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* del = cur;
cur = cur->next;
free(del);
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
🚩🚩友友们,这里要注意两个点:⭐1.如果保存当前结点的地址的话,我们就需要先让cur=cur->next往后迭代,然后在释放保留的那个地址,如果先释放的话,那么cur=cur->next这一步就会报错,此时cur已经被释放了,我们还在使用,它就是一个
野指针.⭐2.如果保留下一结点地址的话,我们就需要先释放当前结点,在让cur=next往后进行迭代,如果我们先往后迭代的话,此时cur=next已经指向下一结点了,我们在把它释放,这样就会导致上一个结点没有释放和下次再使用cur就是野指针.🌈🌈
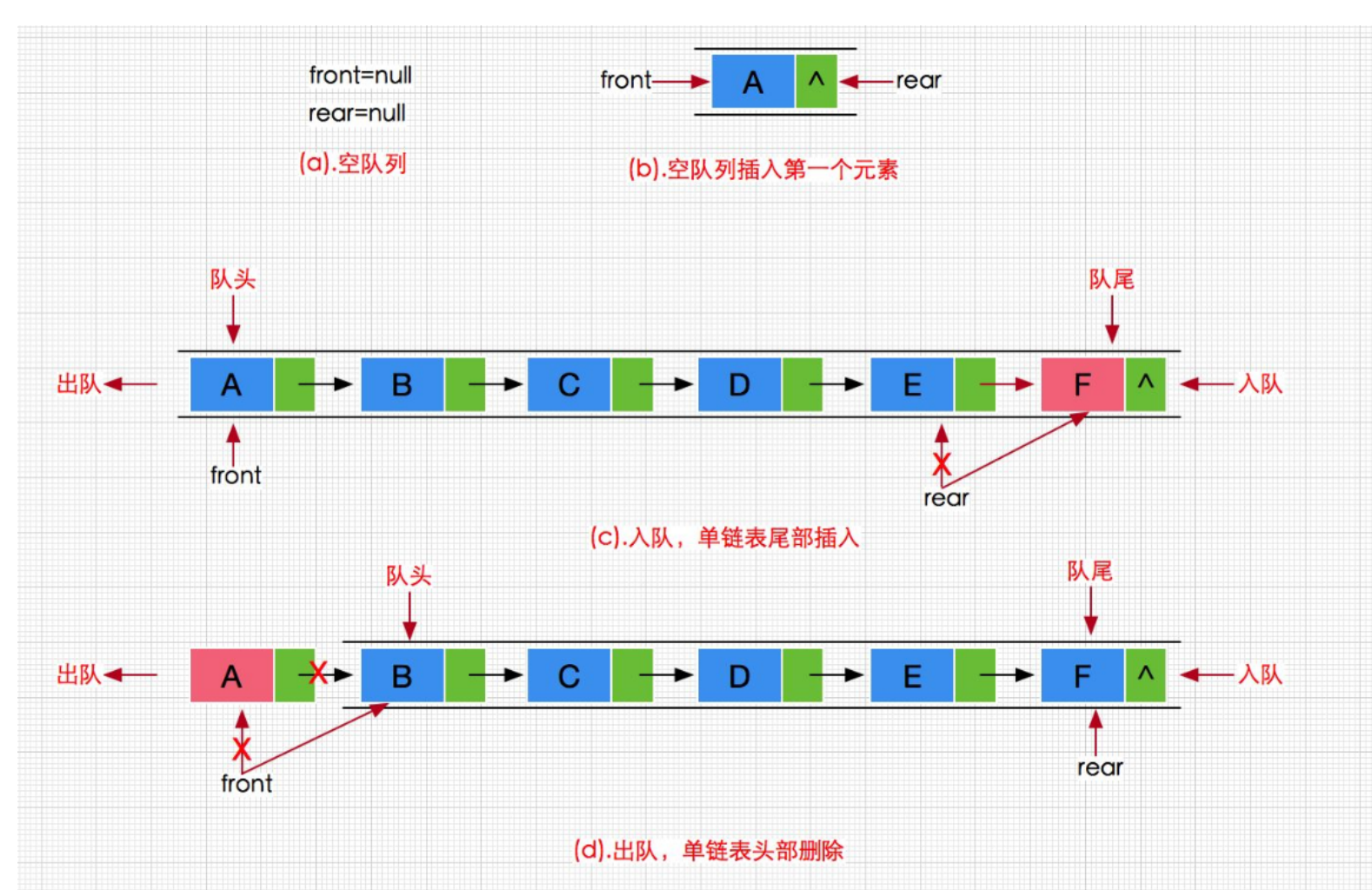
🔍4.队列的插入数据
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->phead == NULL)
{
assert(pq->ptail == NULL);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
⛳⛳友友们注意,就算这里是首次插入数据,我们也不需要
二级指针,因为phead和ptail指针都在结构体里面放着,所以我们传这个结构体的指针就可以改变它们.
🔍5.队列的删除数据
❌错误案例
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
pq->size--;
}

✔代码纠正
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
//1个结点
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead =pq->ptail= NULL; //不能对同一动态开辟出来的空间进行多次free释放,这里我们释放完pq->phead之后,pq->ptail也已经被释放了,所以我们主要的目的就是把pq->phead和pq->ptail都置空
}
//多个结点
else
{
QNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
⛳⛳友友们注意,pq->phead和pq->ptail指向相同的结点,free(pq->phead)之后就已经把这块内存空间释放了,此时我们就不能再free(pq->ptail)了,因为动态开辟出来的空间不能进行多次free释放.
🔍6.队列取队头数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->phead->data;
}
这里我们需要断言队列不能为空,如果为空,pq->phead就是空指针,这时pq->phead->data就是对空指针的解引用,程序就会报错.
🔍7.队列取队尾数据
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->ptail->data;
}
🔍8.返回队列数据的个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
🔍9.判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->phead == NULL
&& pq->ptail == NULL;
}
🚀Queue.h代码
#pragma once
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue*pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
🛸Queue.c代码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
/*QNode* del = cur;
cur = cur->next;
free(del);*/
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->phead == NULL)
{
assert(pq->ptail == NULL);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
//1个结点
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail=NULL; //不能对同一动态开辟出来的空间进行多次free释放,这里我们释放完pq->phead之后,pq->ptail也已经被释放了,所以我们主要的目的就是把pq->phead和pq->ptail都置空
}
//多个结点
else
{
QNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->phead->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->ptail->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->phead == NULL
&& pq->ptail == NULL;
}
🛳Test.c代码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Queue.h"
#include<stdio.h>
TestQueue()
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
QueuePush(&q, 3);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
TestQueue();
return 0;
}
🧋代码效果展示

1.🖋题目描述

💡逻辑分析
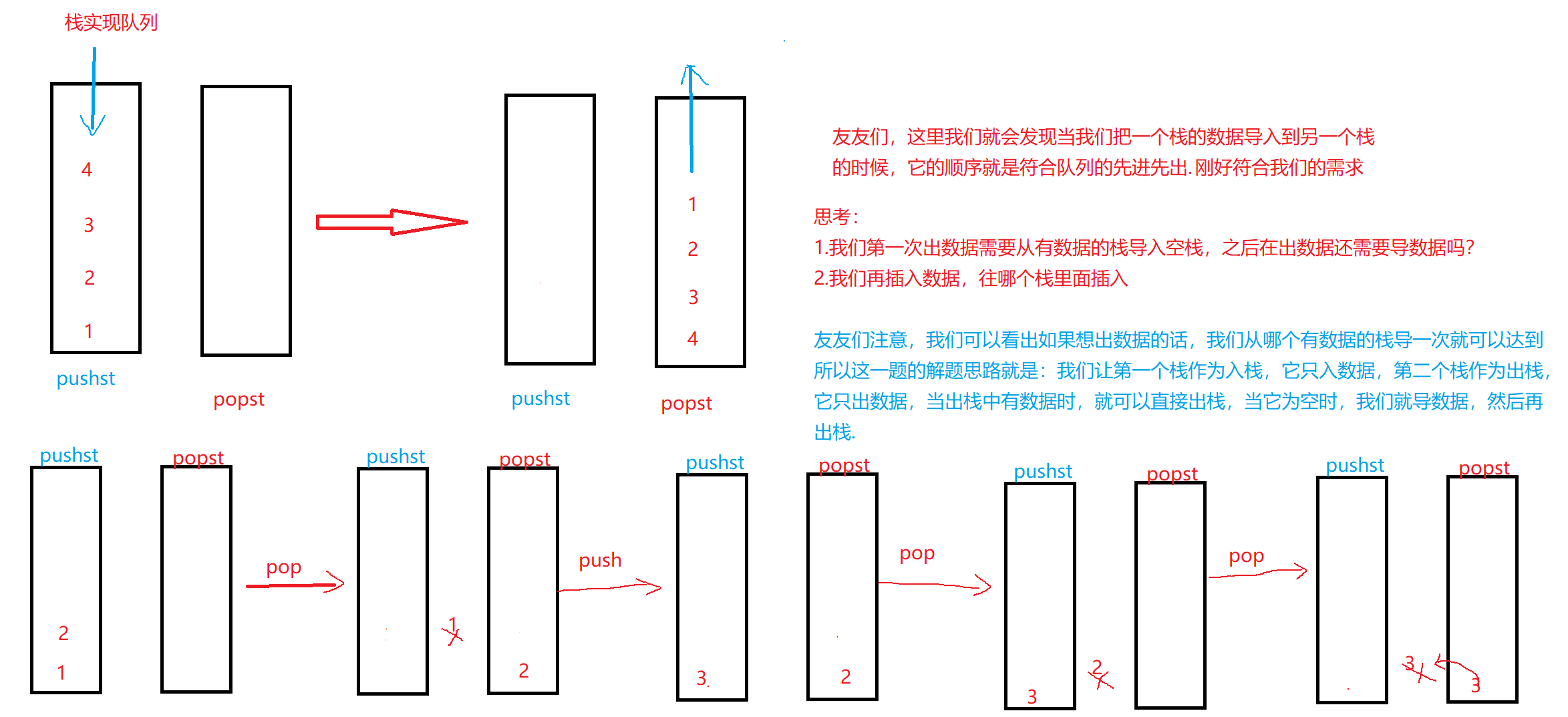
友友们,通过这里也可以看出我们的入栈顺序是1,2,3,我们的出栈顺序也是1,2,3.
🎥代码实现
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; //top指向栈顶的位置
int capacity;
}ST;
void STInit(ST* pst);
void STDestroy(ST* pst);
void STPush(ST* pst,STDataType x);
STDataType STTop(ST* pst);
void STPop(ST* pst);
bool STEmpty(ST* pst);
int STSize(ST* pst);
void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = 0; //如果我们初始化为0,top就指向栈顶元素的下一个位置,初始化为-1,top就是指向栈顶元素.
pst->capacity = 0;
}
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = pst->top = 0;
}
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int newcapacity= pst->capacity==0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2 ;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a,newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!STEmpty(pst));
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!STEmpty(pst));
pst->top--;
}
int STSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}
typedef struct {
ST pushst;
ST popst;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue*obj=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
if(obj==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
STInit(&obj->pushst);
STInit(&obj->popst);
return obj;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
STPush(&obj->pushst,x);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
int front=myQueuePeek(obj);
STPop(&obj->popst);
return front;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
if(STEmpty(&obj->popst))
{
while(!STEmpty(&obj->pushst))
{
STPush(&obj->popst,STTop(&obj->pushst));
STPop(&obj->pushst);
}
}
return STTop(&obj->popst);
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return (STEmpty(&obj->pushst))
&&(STEmpty(&obj->popst));
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
STDestroy(&obj->popst);
STDestroy(&obj->pushst);
free(obj);
}
2.🖋题目描述

💡逻辑分析
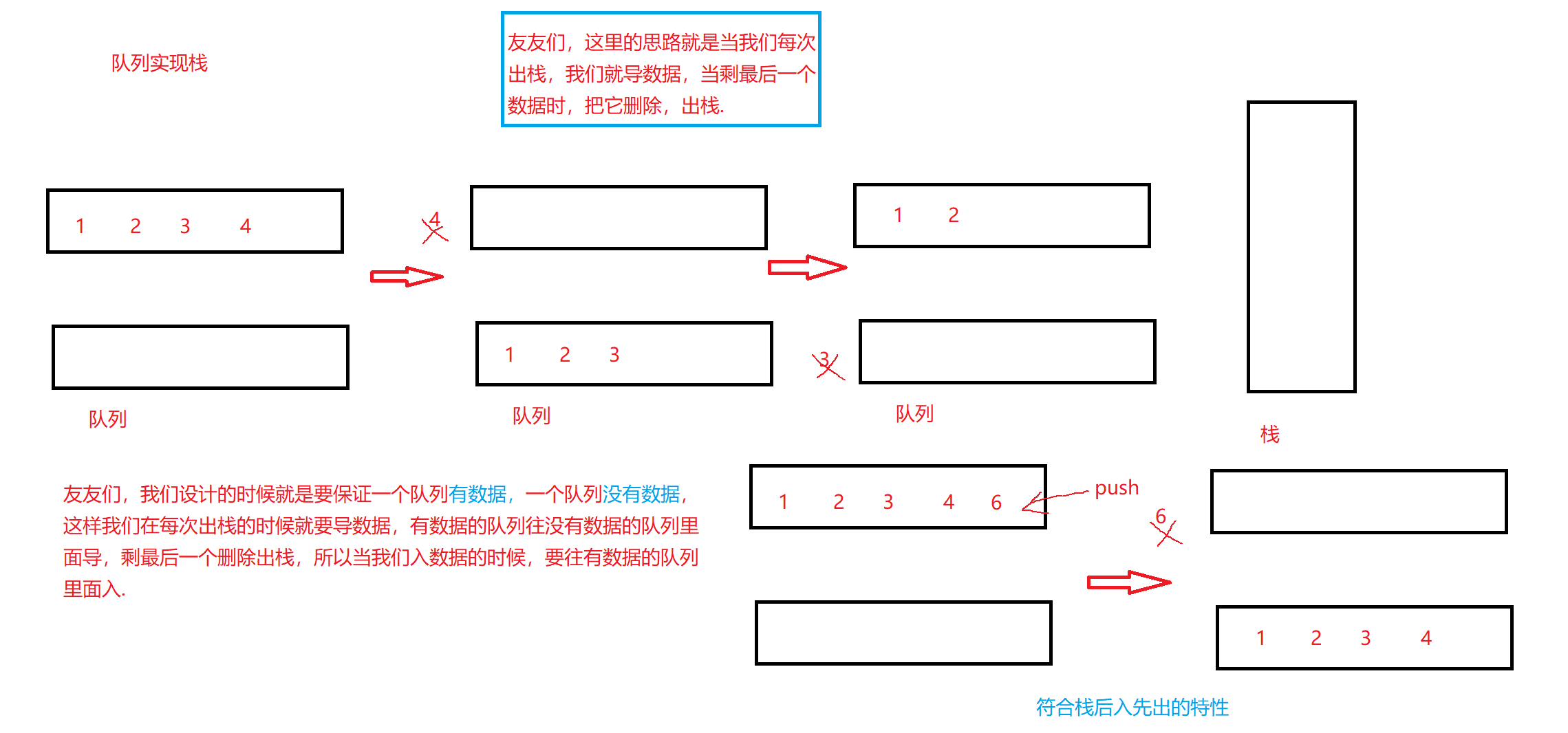
🎥代码实现
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue*pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
/*QNode* del = cur;
cur = cur->next;
free(del);*/
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->phead == NULL)
{
assert(pq->ptail == NULL);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
//1个结点
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead =pq->ptail= NULL; //不能对同一动态开辟出来的空间进行多次free释放,这里我们释放完pq->phead之后,pq->ptail也已经被释放了,所以我们主要的目的就是把pq->phead和pq->ptail都置空
}
//多个结点
else
{
QNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->phead->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->ptail->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->phead == NULL
&& pq->ptail == NULL;
}
typedef struct {
Queue p;
Queue q;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack*obj=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
if(obj==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
QueueInit(&obj->p);
QueueInit(&obj->q);
return obj;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q,x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->p,x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
Queue* NoFull=&obj->p;
Queue* Full=&obj->q;
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->p))
{
Full=&obj->p;
NoFull=&obj->q;
}
while(QueueSize(NoFull)>1)
{
QueuePush(Full,QueueFront(NoFull));
QueuePop(NoFull);
}
int top=QueueBack(NoFull);
QueuePop(NoFull);
return top;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->p))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->p);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q);
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->p)
&&QueueEmpty(&obj->q);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestroy(&obj->p);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q);
free(obj);
}