目录
ArraryList
引用基本类型
案例1:定义一个集合添加学生姓名年龄
案例2:查看是否存在这个id
案例3:手机
案例4:学生管理系统(不完整)
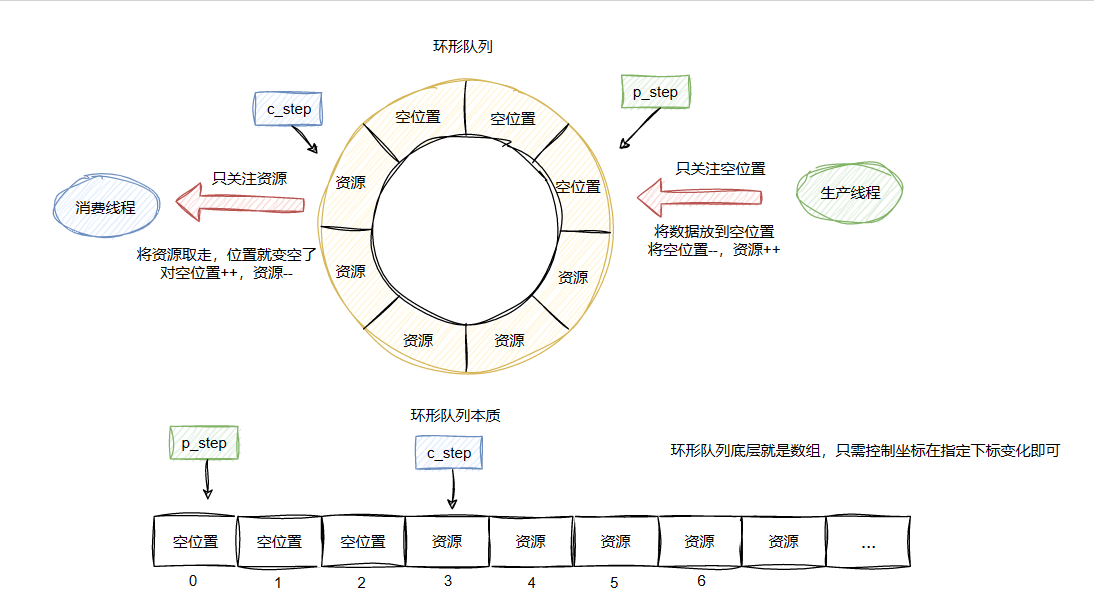
- 集合长度可变:自动扩容
- 集合和数据
长度 存储数据类型 数组 长度固定 基本数据类型
引用数据类型集合 长度可变 引用数据类型
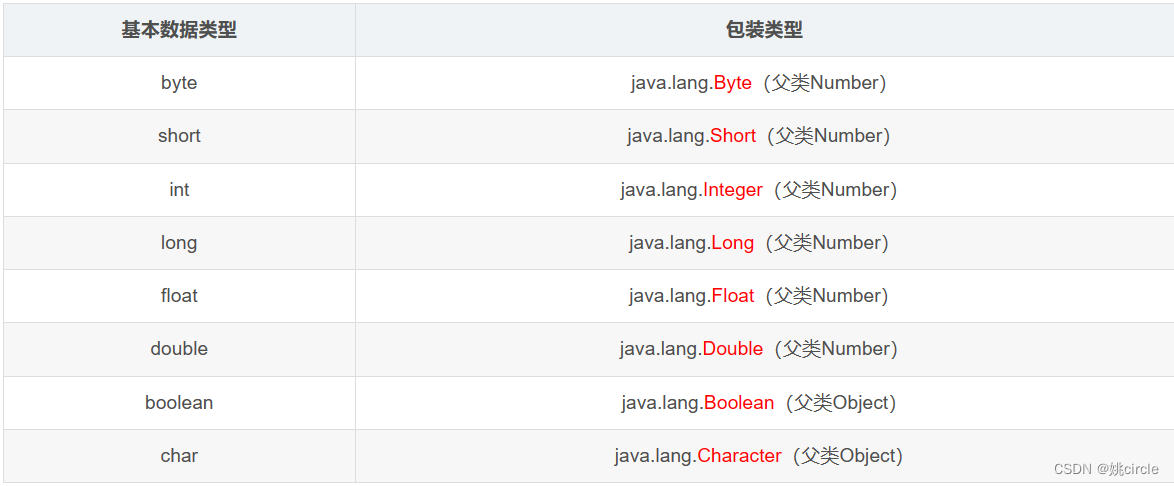
基本数据类型需变成包装类
ArraryList
- 打印的是数据内容,不是地址值
- 常用方法
- 1.添加 add
- 2.获取元素 get
- 3.删除 remove
- 4.修改 set
- 5.查看长度 size

-
引用基本类型
- 需要用到包装类:ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
- 包装类
-
案例1:定义一个集合添加学生姓名年龄
- Student类
package com.day1.day2; public class Student { private String name; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } } - 测试类
package com.day1.day2; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>(); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("请输入学生人数:"); int num = sc.nextInt(); for (int i = 0; i < num;i++){ Student sd = new Student(); System.out.print("请输入学生名字:"); String name = sc.next(); System.out.print("请输入学生年龄:"); int age = sc.nextInt(); sd.setName(name); sd.setAge(age); list.add(sd); } for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){ Student stu = list.get(i); System.out.println(stu.getName() + " " + stu.getAge()); } } }
- Student类
-
案例2:查看是否存在这个id
- 需求:
- main方法中定义一个集合,存入三个用户对象用户属性为:id,username,password,
- 要求:定义一个方法,根据id查找对应的用户信息
如果存在,返回true
如果不存在,返回false
- User类
package com.day1.day2; public class User { private String id; private String username; private String password; public User(){} public User(String id, String username, String password) { this.id = id; this.username = username; this.password = password; } public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } } - 测试类
package com.day1.day2; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Test2 { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<User> list = new ArrayList<>(); User user1 = new User("001", "谢怜", "333"); User user2 = new User("002", "花城", "666"); User user3 = new User("003", "风师", "555555"); list.add(user1); list.add(user2); list.add(user3); boolean contaions = contaions(list, "002"); System.out.println(contaions); } public static boolean contaions(ArrayList<User> list, String id){ for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){ User u = list.get(i); String uid = u.getId(); if (uid.equals(id)){ return true; } } return false; } }
- 需求:
-
案例3:手机
- 需求:
- 定义avabean类:PhonePhone属性:品牌,价格main方法中定义一个集合,存入三个手机对象。分别为:小米 2650 华为 5999 oppo 3569
- 定义一个方法,将价格低于3000的手机信息返回
- Phone类
package com.day1.day2; import javax.crypto.spec.PSource; public class Phone { private String brand; private double price; public Phone(){} public Phone(String brand, double price) { this.brand = brand; this.price = price; } public String getBrand() { return brand; } public void setBrand(String brand) { this.brand = brand; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } } - 测试类
package com.day1.day2; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Test3 { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Phone> list = new ArrayList<>(); Phone p1 = new Phone("小米", 2650); Phone p2 = new Phone("华为", 5999); Phone p3 = new Phone("oppo", 3569); list.add(p1); list.add(p2); list.add(p3); getPhoneInfo(list); } public static void getPhoneInfo(ArrayList<Phone> list){ for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){ Phone phone = list.get(i); double price = phone.getPrice(); if (price < 3000){ System.out.println(phone.getBrand() + phone.getPrice()) ; } } } }
- 需求:
-
案例4:学生管理系统(不完整)
- Student类
package com.StudentGuanli; public class Student { private String id; private String name; private int age; private String address; public Student(){} public Student(String id, String name, int age, String address) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; this.address = address; } public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(String address) { this.address = address; } } - User类
package com.StudentGuanli; public class User { private String username; private String password; private String personID; private String phoneNumber; public User(){ } public User(String username, String password, String personID, String phoneNumber) { this.username = username; this.password = password; this.personID = personID; this.phoneNumber = phoneNumber; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public String getPersonID() { return personID; } public void setPersonID(String personID) { this.personID = personID; } public String getPhoneNumber() { return phoneNumber; } public void setPhoneNumber(String phoneNumber) { this.phoneNumber = phoneNumber; } } - 查询学生类
package com.StudentGuanli; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; public class StudentSystem { public static void startStudentSystem() { ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>(); Student student1 = new Student("01", "谢怜", 600, "仙乐"); list.add(student1); loop: while (true) { System.out.println("=======================欢迎来到学生管理系统=========================="); System.out.println("1:添加学生"); System.out.println("2:删除学生"); System.out.println("3:修改学生"); System.out.println("4:查询学生"); System.out.println("5:退出"); System.out.println("请输入您的选择"); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String choose = sc.next(); switch (choose) { case "1": addStudent(list); break; case "2": { delectStudent(list); } break; case "3": updataStudent(list); break; case "4": selectStudent(list); break; case "5": { System.out.println("退出"); break loop; } } } } public static void addStudent(ArrayList<Student> list) { System.out.println("====================添加学生====================="); Student stu = new Student(); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String id; while (true) { System.out.print("添加学生id:"); id = sc.next(); boolean ifequals = ifequals(list, id); if (ifequals) { System.out.println("id存在 重新录入"); } else { stu.setId(id); break; } } System.out.print("添加学生名字:"); String name = sc.next(); stu.setName(name); System.out.print("添加学生年龄:"); int age = sc.nextInt(); stu.setAge(age); System.out.print("添加学生地址:"); String address = sc.next(); stu.setAddress(address); list.add(stu); System.out.println("===学生信息添加成功==="); } public static void delectStudent(ArrayList<Student> list) { System.out.println("====================删除学生===================="); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("请输入学生学号:"); String id = sc.next(); boolean ifequals = ifequals(list, id); if (ifequals) { //查找uid的id索引 int idid = idid(list, id); list.remove(idid); System.out.printf("========学号为%s的学生信息删除成功=======", id); System.out.println(); } else { System.out.println("id不存在"); } } public static void updataStudent(ArrayList<Student> list) { System.out.println("==========修改学生==============="); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("请输入学生学号:"); String id = sc.next(); // boolean ifequals = ifequals(list, id); // if (ifequals==false){ // System.out.println("输入的学号不存在"); // return; // } int idid = idid(list, id); System.out.println(idid); if (idid == -1) { System.out.println("输入的学号不存在"); return; } Student student = list.get(idid); //需要修改的学生 System.out.printf("修改%s学生的姓名:", id + "\t"); String newname = sc.next(); student.setName(newname); System.out.printf("修改%s学生的年龄:", id + "\t"); int newage = sc.nextInt(); student.setAge(newage); System.out.printf("修改%s学生的地址:", id + "\t"); String newaddress = sc.next(); student.setAddress(newaddress); System.out.printf("====%s学生信息修改成功====", id); } public static void selectStudent(ArrayList<Student> list) { System.out.println("====================查询学生===================="); if (list.size() == 0) { System.out.println("========没有学生数据========="); return; } System.out.println("id\t姓名\t年龄\t地址"); for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { Student stu = list.get(i); System.out.println(stu.getId() + "\t" + stu.getName() + "\t" + stu.getAge() + "\t\t" + stu.getAddress()); } } public static void forlist(ArrayList<Student> list) { for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { Student stu = list.get(i); System.out.println(stu.getId() + stu.getName() + stu.getAge() + stu.getAddress()); } } public static boolean ifequals(ArrayList<Student> list, String id) { for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { Student stu = list.get(i); String id1 = stu.getId(); if (id.equals(id1)) { return true; } } return false; } //返回id的索引(findIdIndex) public static int idid(ArrayList<Student> list, String id) { for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { Student student = list.get(i); String id1 = student.getId(); System.out.println(id1); if (id1.equals(id)) { return i; } } return -1; } } - 用户登录类
package com.StudentGuanli; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); User user = new User(); ArrayList<User> list = new ArrayList<>(); loop: while (true) { System.out.println("===========欢迎来到学生管理系统登录界面==========="); System.out.println("1:登录"); System.out.println("2:注册"); System.out.println("3:忘记密码"); System.out.println("4:谢谢使用"); System.out.println("5:查看用户"); System.out.print("请选择操作:"); int choose = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("================================================="); switch (choose) { case 1: login(list); break; case 2: register(list); break; case 3: forgetPassword(list); break; case 4: System.out.println("4"); break loop; case 5: lookUsername(list); break; default: System.out.println("没有这个选项"); } } } private static void login(ArrayList<User> list) { System.out.println("============登录============"); User user = new User(); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("请输入用户用户名:"); String username = sc.next(); System.out.print("输入密码:"); String password = sc.next(); //查看是否有这个用户名 boolean userByUsername = findUserByUsername(list, username); if (userByUsername){ //查看密码是否匹配 boolean b = checkPassword(list, username, password); if (b){ System.out.println("==============登录成功=============="); StudentSystem studentSystem = new StudentSystem(); studentSystem.startStudentSystem(); return; }else { System.out.println("==============密码错误 登录失败=============="); } }else { System.out.println("用户名不存在"); } } private static void register(ArrayList<User> list) { System.out.println("============注册============"); User user = new User(); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); while (true) { System.out.print("请输入用户名:"); String username = sc.next(); boolean b = checkUsername(username); if (b) { user.setUsername(username); break; } else { System.out.println("用户名格式不规范,重新输入"); } } while (true){ System.out.print("请输入密码:"); String password = sc.next(); System.out.print("请重复输入密码:"); String newpassword = sc.next(); boolean b = checkTwoPassword(password, newpassword); if (b){ user.setPassword(password); break; }else { System.out.println("==========两次密码不一致=========="); } } System.out.print("请输入身份证号码:"); String personID = sc.next(); user.setPersonID(personID); System.out.print("请输入手机号码:"); String phoneNumber = sc.next(); user.setPhoneNumber(phoneNumber); list.add(user); } private static void forgetPassword(ArrayList<User> list) { System.out.println("============忘记密码============"); System.out.println("输入要查询的用户名"); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String username = sc.next(); String s = userIdIndex(list, username); System.out.printf("%s的密码是",username + s); } //查询用户名 private static void lookUsername(ArrayList<User> list) { for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { User user = list.get(i); System.out.println(user.getUsername()); } } //查询名称是否规范 private static boolean checkUsername(String username) { //用户名长度在3-15 int num = username.length(); String name = ""; int count = 0; if (num >= 3 && num <= 15) { //只能是字母+数字 //纯字母可以 for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { char c = username.charAt(i); if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z' || c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z' || c >= '0' && c <= '9') { name = name + c; } else { return false; } } for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { char c = name.charAt(i); if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z' || c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z') { count++; } } if (count == 0) { return false; } ; return true; } return false; } //是否存在这个用户名 private static boolean findUserByUsername(ArrayList<User> list, String username) { for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { User user1 = list.get(i); String username1 = user1.getUsername(); if (username.equals(username1)){ return true; } } return false; } //返回用户名的index public static String userIdIndex(ArrayList<User> list,String username){ String a = "用户名不存在"; for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { User user = list.get(i); String username1 = user.getUsername(); if (username.equals(username1)){ String password = user.getPassword(); return password; } } return a; } //查看密码是否匹配 private static boolean checkPassword(ArrayList<User> list, String username, String password) { for (int i = 0; i < list.size() ; i++) { boolean eq = list.get(i).getUsername().equals(username); if (eq){ String password1 = list.get(i).getPassword(); if (password.equals(password1)){ return true; } } } return false; } //两次密码是否一致 private static boolean checkTwoPassword(String password, String newpassword) { if (password.equals(newpassword)){ return true; } return false; } }
- Student类