v0.1版本的oSLAM实现了基于orb特征点的简单视觉里程计,通过连续两帧的rgbd数据实现相机相对位姿的估计。
这部分理论上相对简单一点,咱们就直接上实现。
- VisualOdometer类
VisualOdometer.hpp
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
#include "Frame.hpp"
namespace oSLAM
{
class VisualOdometer
{
private:
std::vector<Frame> frames;
int max_key_points_num;
double cx, cy, fx, fy;
double depth_scale;
std::vector<cv::DMatch> matches;
void feature_extract(const cv::Mat& rgb, Frame& frame);
void calc_depth(const cv::Mat& depth, Frame& frame);
void feature_match(const Frame& ref, const Frame& cur, std::vector<cv::DMatch>& matches);
void calc_pose_relative(const Frame& ref, Frame& cur, const std::vector<cv::DMatch>& matches);
void pose_estimation_3d2d(const std::vector<cv::Point3d> &pts1, const std::vector<cv::Point2d> &pts2, cv::Mat &R, cv::Mat &t);
void pose_estimation_3d3d(const std::vector<cv::Point3d> &pts1, const std::vector<cv::Point3d> &pts2, cv::Mat &R, cv::Mat &t);
public:
void add(double timestamp, const cv::Mat &rgb, const cv::Mat& depth);
void set_pose(int frame_idx, const cv::Mat& R, const cv::Mat& T);
void get_pose(int frame_idx, cv::Mat& R, cv::Mat& T);
void get_3d_points(int frame_idx, std::vector<cv::Point3d> &key_points_3d);
VisualOdometer(int max_key_points_num, double cx, double cy, double fx, double fy, double depth_scale);
~VisualOdometer();
};
}
VisualOdometer.cpp
#include "VisualOdometer.hpp"
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <Eigen/SVD>
using namespace oSLAM;
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
VisualOdometer::VisualOdometer(int max_key_points_num, double cx, double cy, double fx, double fy, double depth_scale)
{
VisualOdometer::max_key_points_num = max_key_points_num;
VisualOdometer::cx = cx;
VisualOdometer::cy = cy;
VisualOdometer::fx = fx;
VisualOdometer::fy = fy;
VisualOdometer::depth_scale = depth_scale;
}
VisualOdometer::~VisualOdometer()
{
}
void VisualOdometer::feature_extract(const cv::Mat &rgb, Frame &frame)
{
Ptr<ORB> orb_detector = ORB::create(max_key_points_num);
orb_detector->detect(rgb, frame.key_points);
orb_detector->compute(rgb, frame.key_points, frame.descriptors);
}
void VisualOdometer::calc_depth(const cv::Mat &depth, Frame &frame)
{
for (int i=0;i<frame.key_points.size();i++)
{
double x = frame.key_points[i].pt.x;
double y = frame.key_points[i].pt.y;
double dis = depth.at<uint16_t>(int(y),int(x)) / depth_scale;
frame.key_points_3d.push_back(Point3d((x-cx)/fx*dis, (y-cy)/fy*dis, dis));
}
}
void VisualOdometer::pose_estimation_3d2d(const std::vector<cv::Point3d> &pts1, const std::vector<cv::Point2d> &pts2, cv::Mat &R, cv::Mat &t)
{
// 利用PnP求解位姿初值
Mat K = (Mat_<double>(3,3) << fx, 0, cx,
0, fy, cy,
0, 0, 1);
Mat rvec, tvec;
solvePnPRansac(pts1, pts2, K, Mat::zeros(1, 5, CV_64FC1), rvec, tvec);
Rodrigues(rvec, R);
t = (Mat_<double>(3,1) << tvec.at<double>(0), tvec.at<double>(1), tvec.at<double>(2));
// 优化位姿和3D点坐标
// ToDo
}
void VisualOdometer::pose_estimation_3d3d(const std::vector<cv::Point3d> &pts1, const std::vector<cv::Point3d> &pts2, cv::Mat &R, cv::Mat &t)
{
Point3d p1(0, 0, 0), p2(0, 0, 0); // center of mass
int N = pts1.size();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
p1 += pts1[i];
p2 += pts2[i];
}
p1 = Point3d(Vec3d(p1) / N);
p2 = Point3d(Vec3d(p2) / N);
vector<Point3d> q1(N), q2(N); // remove the center
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
q1[i] = pts1[i] - p1;
q2[i] = pts2[i] - p2;
}
// compute q1*q2^T
Eigen::Matrix3d W = Eigen::Matrix3d::Zero();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
W += Eigen::Vector3d(q1[i].x, q1[i].y, q1[i].z) * Eigen::Vector3d(q2[i].x, q2[i].y, q2[i].z).transpose();
}
// SVD on W
Eigen::JacobiSVD<Eigen::Matrix3d> svd(W, Eigen::ComputeFullU | Eigen::ComputeFullV);
Eigen::Matrix3d U = svd.matrixU();
Eigen::Matrix3d V = svd.matrixV();
Eigen::Matrix3d R_ = U * (V.transpose());
if (R_.determinant() < 0)
{
R_ = -R_;
}
Eigen::Vector3d t_ = Eigen::Vector3d(p1.x, p1.y, p1.z) - R_ * Eigen::Vector3d(p2.x, p2.y, p2.z);
// convert to cv::Mat
R = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << R_(0, 0), R_(0, 1), R_(0, 2),
R_(1, 0), R_(1, 1), R_(1, 2),
R_(2, 0), R_(2, 1), R_(2, 2));
t = (Mat_<double>(3, 1) << t_(0, 0), t_(1, 0), t_(2, 0));
}
void VisualOdometer::calc_pose_relative(const Frame& ref, Frame& cur, const std::vector<cv::DMatch>& matches)
{
vector<Point3d> ref_key_points_3d, cur_key_points_3d;
vector<Point2d> ref_key_points_2d, cur_key_points_2d;
// 筛选3D点
for(auto match : matches)
{
Point3d ref_key_point_3d = ref.key_points_3d[match.queryIdx];
Point3d cur_key_point_3d = cur.key_points_3d[match.trainIdx];
if (ref_key_point_3d.z == 0 || cur_key_point_3d.z == 0)
{
continue;
}
ref_key_points_3d.push_back(ref_key_point_3d);
cur_key_points_3d.push_back(cur_key_point_3d);
ref_key_points_2d.push_back(ref.key_points[match.queryIdx].pt);
cur_key_points_2d.push_back(cur.key_points[match.trainIdx].pt);
}
// 3D点计算位姿
Mat R, T;
//pose_estimation_3d3d(cur_key_points_3d, ref_key_points_3d, R, T);
pose_estimation_3d2d(ref_key_points_3d, cur_key_points_2d, R, T);
cur.R = R * ref.R;
cur.T = R * ref.T + T;
}
void VisualOdometer::feature_match(const Frame& ref, const Frame& cur, std::vector<cv::DMatch>& matches)
{
vector<DMatch> initial_matches;
BFMatcher matcher(NORM_HAMMING);
matcher.match(ref.descriptors, cur.descriptors, initial_matches);
double min_dis = initial_matches[0].distance;
for(auto match : initial_matches)
{
if (match.distance < min_dis)
min_dis = match.distance;
}
matches.clear();
for(auto match : initial_matches)
{
if (match.distance <= MAX(min_dis * 2, 30))
matches.push_back(match);
}
}
void VisualOdometer::add(double timestamp, const Mat &rgb, const Mat &depth)
{
Frame frame;
frame.time_stamp = timestamp;
frame.rgb = rgb.clone();
frame.depth = depth.clone();
// 提取rgb图像的orb特征点
VisualOdometer::feature_extract(rgb, frame);
// 提取关键点的深度信息
VisualOdometer::calc_depth(depth, frame);
// 如果不是第一帧
if (VisualOdometer::frames.size() == 0)
{
frame.R = Mat::eye(3,3,CV_64FC1);
frame.T = Mat::zeros(3,1,CV_64FC1);
}
else
{
// 当前帧与上一帧特征点匹配
VisualOdometer::feature_match(
VisualOdometer::frames[VisualOdometer::frames.size()-1],
frame,
VisualOdometer::matches);
// 计算相对位姿关系
VisualOdometer::calc_pose_relative(
VisualOdometer::frames[VisualOdometer::frames.size()-1],
frame,
VisualOdometer::matches);
}
// 将当前帧加入队列
VisualOdometer::frames.push_back(frame);
}
void VisualOdometer::get_pose(int frame_idx, Mat &R, Mat &T)
{
if (VisualOdometer::frames.size() <= abs(frame_idx))
{
R = Mat();
T = Mat();
return;
}
else
{
if (frame_idx >= 0)
{
R = VisualOdometer::frames[frame_idx].R.clone();
T = VisualOdometer::frames[frame_idx].T.clone();
}
else
{
R = VisualOdometer::frames[VisualOdometer::frames.size() + frame_idx].R.clone();
T = VisualOdometer::frames[VisualOdometer::frames.size() + frame_idx].T.clone();
}
}
}
void VisualOdometer::set_pose(int frame_idx, const cv::Mat& R, const cv::Mat& T)
{
if (VisualOdometer::frames.size() <= abs(frame_idx))
{
return;
}
else
{
if (frame_idx >= 0)
{
VisualOdometer::frames[frame_idx].R = R.clone();
VisualOdometer::frames[frame_idx].T = T.clone();
}
else
{
VisualOdometer::frames[VisualOdometer::frames.size() + frame_idx].R = R.clone();
VisualOdometer::frames[VisualOdometer::frames.size() + frame_idx].T = T.clone();
}
}
}
void VisualOdometer::get_3d_points(int frame_idx, std::vector<cv::Point3d> &key_points_3d)
{
if (VisualOdometer::frames.size() <= abs(frame_idx))
{
key_points_3d.clear();
return;
}
else
{
if (frame_idx >= 0)
{
key_points_3d = VisualOdometer::frames[frame_idx].key_points_3d;
}
else
{
key_points_3d = VisualOdometer::frames[VisualOdometer::frames.size() + frame_idx].key_points_3d;
}
}
}
- Frame类
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
namespace oSLAM
{
class Frame
{
public:
std::vector<cv::KeyPoint> key_points;
cv::Mat descriptors;
std::vector<cv::Point3d> key_points_3d;
cv::Mat R;
cv::Mat T;
cv::Mat rgb;
cv::Mat depth;
double time_stamp;
};
}
最终在rgbd_dataset_freiburg2_desk数据集上测试类一下效果,感觉有点拉,跑着跑着就飘了(红色的是真值,绿色的是计算结果),等实现了完整的vo在回来分析一下。
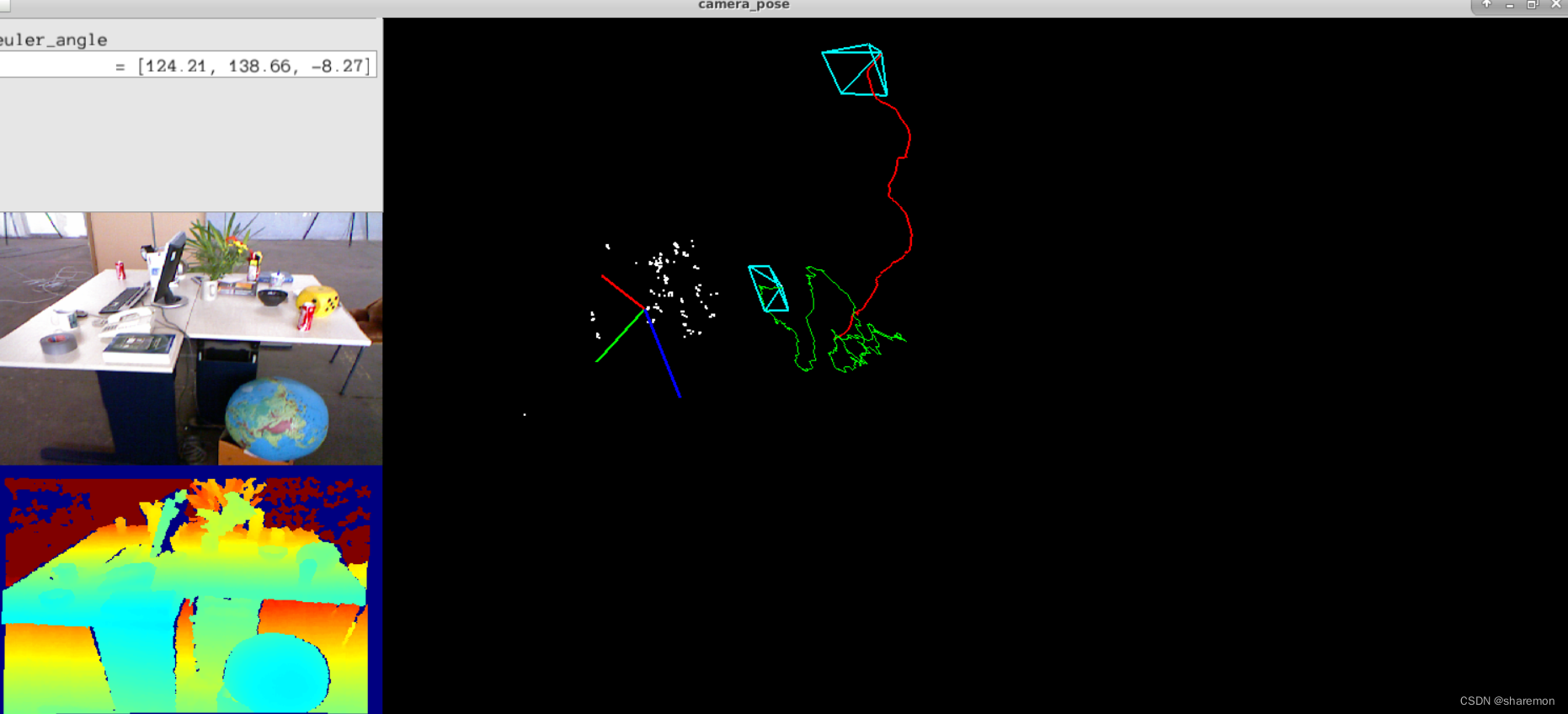
结果展示使用了Pangolin和yuntianli91的pangolin_tutorial