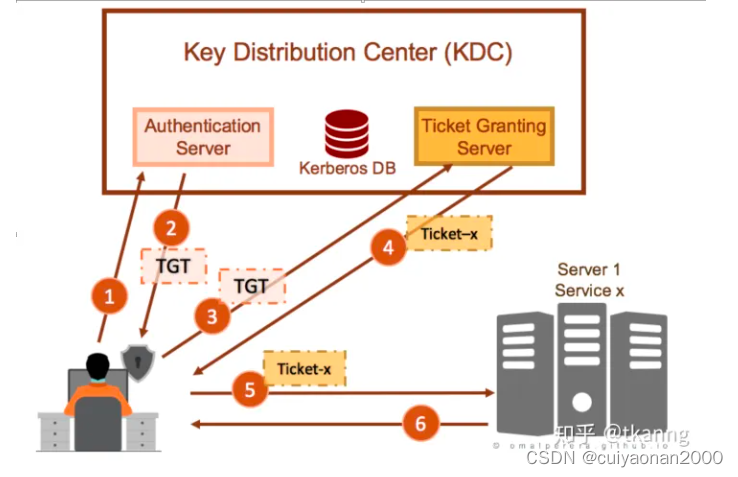
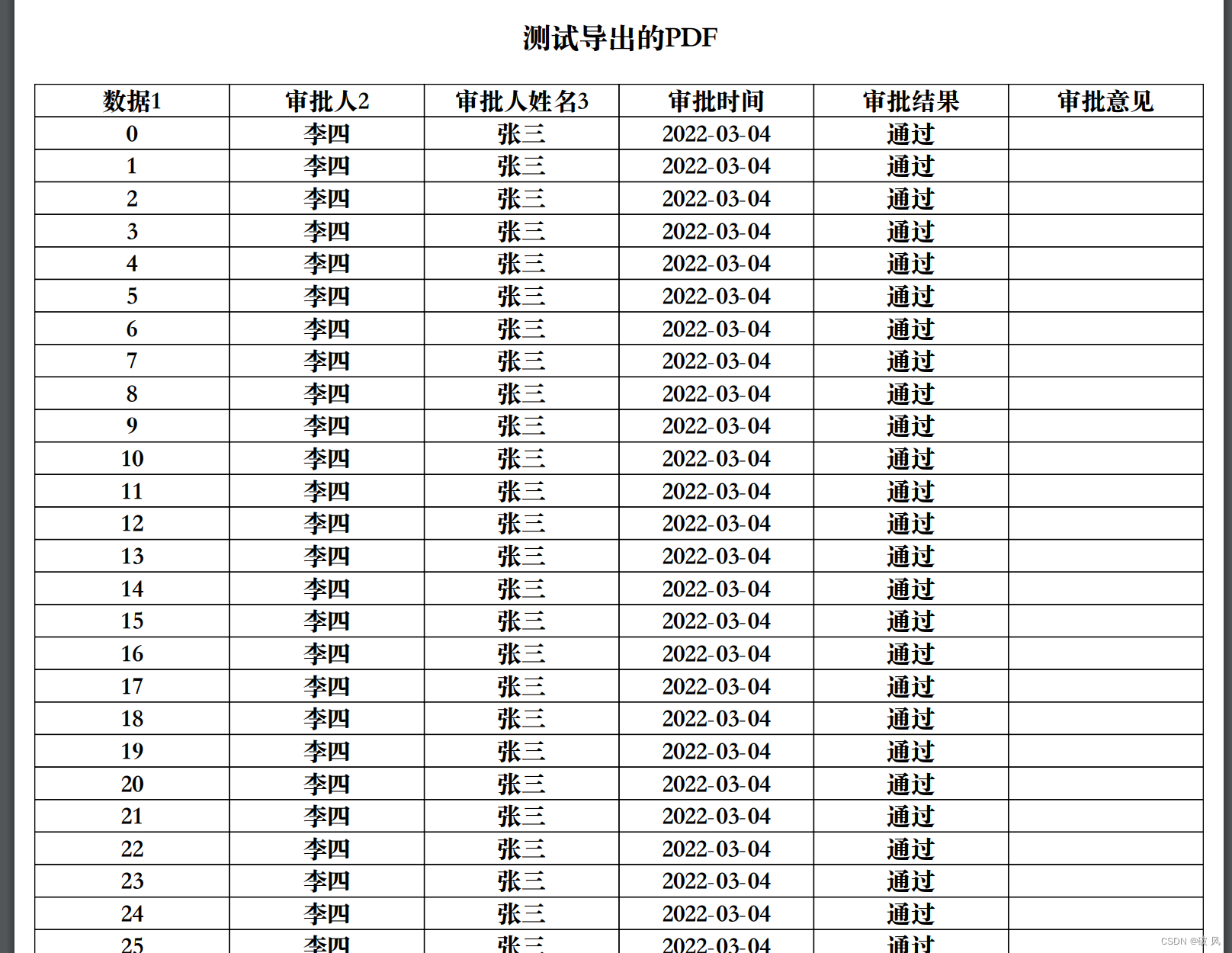
既然有带头 那么就有不带头 为什么我要将带头 而不讲不带头?
在之前我讲单链表时就说过 如果不带头会出现讨论的情况 为什么会出现讨论的情况
假设链表有一个节点 进行尾插 就只是将新的节点连接到链表的尾节点之后
那么如果链表没有节点 就没有尾节点 自然也就不能尾插 也就是说这个新节点要作为链表的头节点 这个操作自然就和上面的尾插不同了 所以要进行讨论
那么接下来就开始 带头双向循环链表的讲解
既然是链表就离不开结构体 就先定义一个结构体出来
这是双向循环链表的图形
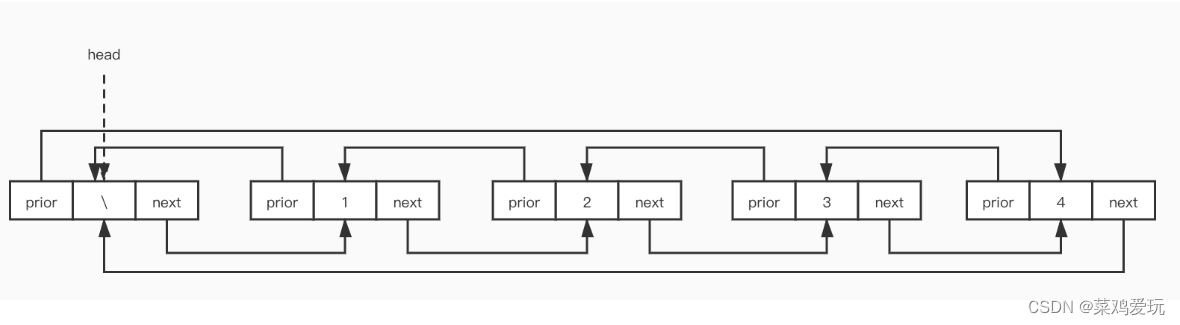
如上图所示 该结构体中有两个指针 一个指向下一个节点 另一个指向前一个节点 循环也就是尾节点的next 指向头节点 将prior改为prev 头结点的prev指向尾节点
如此就形成了一个环形结构
typedef struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
struct ListNode* prev;
}ListNode;
接下来就对节点进行初始化
void ListInti(ListNode* frist)
{
frist->val = 0;
frist->next = frist;
frist->prev = frist;
}写一个开辟节点的函数
ListNode* BuyNode(int x)
{
ListNode* tmp = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("节点开辟失败.");
return;
}
tmp->val = x;
return tmp;
}因为下面尾插和头插 都要用到开辟节点 所以都要用 那不如写一个函数进行赋用
void ListPushBack(ListNode* frist, int x)
{
ListNode* node = BuyNode(x);
ListNode* tmp = frist->prev;
tmp->next = node;
node->prev = tmp;
node->next = frist;
frist->prev = node;
}
void ListPushFront(ListNode* frist, int x)
{
ListNode* node = BuyNode(x);
ListNode* tmp = frist->next;
node->prev = frist;
tmp->prev = node;
frist->next = node;
node->next = tmp;
}计算链表的大小
static int ListSize(ListNode* frist)
{
ListNode* cur = frist->next;
int sz = 1;
while (frist != cur)
{
sz++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return sz;
}下面就是任意位置插入的函数
void ListNodeInsert(ListNode* frist, int pos, int x)
{
assert(frist);
if (pos > ListSize(frist))
{
printf("插入位置,超过链表长度.\n");
return;
}
ListNode* node = BuyNode(x);
ListNode* cur = frist, * str = cur->next;
while (pos > 1)
{
pos--;
cur = cur->next;
str = str->next;
}
node->next = str;
node->prev = cur;
cur->next = node;
str->prev = node;
}既然可以任意位置插入 那么头插和尾插 都可以赋用这个函数
void ListPushBack(ListNode* frist, int x)
{
//ListNode* node = BuyNode(x);
//ListNode* tmp = frist->prev;
//tmp->next = node;
//node->prev = tmp;
//node->next = frist;
//frist->prev = node;
ListNodeInsert(frist, ListSize(frist), x);
}
void ListPushFront(ListNode* frist, int x)
{
//ListNode* node = BuyNode(x);
//ListNode* tmp = frist->next;
//node->prev = frist;
//tmp->prev = node;
//frist->next = node;
//node->next = tmp;
ListNodeInsert(frist, 1, x);
}节点的增添已经写完了 接下来就是删除的操作
因为节点在堆上开辟 所以要写一个释放节点的函数
void ListNodeDestroy(ListNode* tmp)
{
free(tmp);
tmp->next = NULL;
tmp->prev = NULL;
}
如果链表是空的 那么就没有必要删除
static bool Empty(ListNode* frist)
{
return frist->next == frist;
}
那么开始就写删除节点的函数 尾删和头删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* frist)
{
assert(frist);
assert(!Empty(frist));
ListNode* tmp = frist->prev, * tail = tmp->prev;
tail->next = frist;
frist->prev = tail;
ListNodeDestroy(tmp);
}
void ListPopFront(ListNode* frist)
{
assert(frist);
assert(!Empty(frist));
ListNode* tmp = frist->next, * tail = tmp->next;
frist->next = tail;
tail->prev = frist;
ListNodeDestroy(tmp);
}既然上面插入有任意位置 那么就有任意位置的删除操作
void ListNodeErase(ListNode* frist,int pos)
{
assert(frist);
ListNode* cur = frist->next, * str = cur->next;
while (pos > 1)
{
pos--;
cur = cur->next;
str = str->next;
}
str->prev = cur->prev;
cur->prev->next = str;
ListNodeDestroy(cur);
}双向链表的增添 删除 已经完成
链表的打印
static void Print(ListNode* frist)
{
assert(frist);
ListNode* cur = frist->next;
while (frist != cur)
{
printf("%d->", cur->val);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}上面就是双向带头循环链表
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* frist,int x)
{
assert(frist);
assert(!Empty(frist));
ListNode* cur = frist->next;
int pos = 0;
while (frist != cur)
{
pos++;
if (cur->val == x)
{
printf("存在该数据 在第%d个位置\n",pos);
}
cur = cur->next;
}
}完整的双向循环链表链表结构
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
struct ListNode* prev;
}ListNode;
void ListInti(ListNode* frist)
{
frist->val = 0;
frist->next = frist;
frist->prev = frist;
}
ListNode* BuyNode(int x)
{
ListNode* tmp = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("节点开辟失败.");
return;
}
tmp->val = x;
return tmp;
}
static void Print(ListNode* frist)
{
assert(frist);
ListNode* cur = frist->next;
while (frist != cur)
{
printf("%d->", cur->val);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
static bool Empty(ListNode* frist)
{
return frist->next == frist;
}
void ListNodeDestroy(ListNode* tmp)
{
free(tmp);
tmp->next = NULL;
tmp->prev = NULL;
}
void ListPopBack(ListNode* frist)
{
assert(frist);
assert(!Empty(frist));
ListNode* tmp = frist->prev, * tail = tmp->prev;
tail->next = frist;
frist->prev = tail;
ListNodeDestroy(tmp);
}
void ListPopFront(ListNode* frist)
{
assert(frist);
assert(!Empty(frist));
ListNode* tmp = frist->next, * tail = tmp->next;
frist->next = tail;
tail->prev = frist;
ListNodeDestroy(tmp);
}
void ListDestroy(ListNode* frist)
{
assert(frist);
assert(!Empty(frist));
ListNode* tmp = frist->next, * cur = tmp->next;
while (frist != tmp)
{
ListNodeDestroy(tmp);
tmp = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
static int ListSize(ListNode* frist)
{
ListNode* cur = frist->next;
int sz = 1;
while (frist != cur)
{
sz++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return sz;
}
void ListNodeInsert(ListNode* frist, int pos, int x)
{
assert(frist);
if (pos > ListSize(frist))
{
printf("插入位置,超过链表长度.\n");
return;
}
ListNode* node = BuyNode(x);
ListNode* cur = frist, * str = cur->next;
while (pos > 1)
{
pos--;
cur = cur->next;
str = str->next;
}
node->next = str;
node->prev = cur;
cur->next = node;
str->prev = node;
}
void ListNodeErase(ListNode* frist,int pos)
{
assert(frist);
ListNode* cur = frist->next, * str = cur->next;
while (pos > 1)
{
pos--;
cur = cur->next;
str = str->next;
}
str->prev = cur->prev;
cur->prev->next = str;
ListNodeDestroy(cur);
}
//void ListPushBack(ListNode* frist, int x)
//{
// ListNode* node = BuyNode(x);
// ListNode* tmp = frist->prev;
//
// tmp->next = node;
// node->prev = tmp;
//
// node->next = frist;
// frist->prev = node;
//}
//
//void ListPushFront(ListNode* frist, int x)
//{
// ListNode* node = BuyNode(x);
// ListNode* tmp = frist->next;
//
// node->prev = frist;
// tmp->prev = node;
// frist->next = node;
// node->next = tmp;
//}
void ListPushBack(ListNode* frist, int x)
{
//ListNode* node = BuyNode(x);
//ListNode* tmp = frist->prev;
//tmp->next = node;
//node->prev = tmp;
//node->next = frist;
//frist->prev = node;
ListNodeInsert(frist, ListSize(frist), x);
}
void ListPushFront(ListNode* frist, int x)
{
//ListNode* node = BuyNode(x);
//ListNode* tmp = frist->next;
//node->prev = frist;
//tmp->prev = node;
//frist->next = node;
//node->next = tmp;
ListNodeInsert(frist, 1, x);
}
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* frist,int x)
{
assert(frist);
assert(!Empty(frist));
ListNode* cur = frist->next;
int pos = 0;
while (frist != cur)
{
pos++;
if (cur->val == x)
{
printf("存在该数据 在第%d个位置\n",pos);
}
cur = cur->next;
}
}
void test()
{
ListNode frist;
ListInti(&frist);
ListPushBack(&frist, 1);
ListPushBack(&frist, 2);
ListPushBack(&frist, 3);
ListPushBack(&frist, 4);
ListPushFront(&frist, 9);
ListPushFront(&frist, 8);
ListPushFront(&frist, 7);
ListPushFront(&frist, 6);
ListPopBack(&frist);
ListPopBack(&frist);
ListPopFront(&frist);
ListPopFront(&frist);
ListNodeInsert(&frist, 1, 10);
ListNodeInsert(&frist, 4, 11);
ListNodeInsert(&frist, 5, 12);
ListNodeInsert(&frist, 8, 13);
ListNodeErase(&frist, 2);
ListNodeErase(&frist, 7);
ListFind(&frist, 0);
ListFind(&frist, 2);
Print(&frist);
ListDestroy(&frist);
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}上续双向循环链表已完成链表~