本文基于transformers中BLOOM模型代码来解析BLOOM的原理及实现。
相关博客
【自然语言处理】【大模型】BLOOM模型结构源码解析(单机版)
【自然语言处理】【大模型】极低资源微调大模型方法LoRA以及BLOOM-LORA实现代码
【深度学习】【分布式训练】Collective通信操作及Pytorch示例
【自然语言处理】【大模型】Chinchilla:训练计算利用率最优的大语言模型
【自然语言处理】【大模型】大语言模型BLOOM推理工具测试
【自然语言处理】【大模型】GLM-130B:一个开源双语预训练语言模型
【自然语言处理】【大模型】用于大型Transformer的8-bit矩阵乘法介绍
【自然语言处理】【大模型】BLOOM:一个176B参数且可开放获取的多语言模型
【自然语言处理】【ChatGPT系列】FLAN:微调语言模型是Zero-Shot学习器
【自然语言处理】【ChatGPT系列】ChatGPT的智能来自哪里?
【自然语言处理】【ChatGPT系列】大模型的涌现能力
一、掩码(Mask)
1.1 原理
BLOOM使用的是Transformer中的Decoder,其使用到的Mask有两个:(1) 构建batch时的padding需要被mask;(2) Decoder中,当前token只能见到其左侧的token,因此需要对注意力进行mask。称前一种为Padding Mask,后一种为Causal Mask。
Causal Mask。给定一个长度为 n n n的序列,其注意力分数矩阵为 A ∈ R n × n A\in\mathbb{R}^{n\times n} A∈Rn×n。 A i , j A_{i,j} Ai,j表示query q i \textbf{q}_i qi和key k j \textbf{k}_j kj的注意力分数。但是,生成任务是从左到右的,其在生成过程中没有办法看到其右侧的tokens。为了在训练时也保证"仅左侧tokne可见",可以通过Causal Mask来实现。具体来说,就是mask掉注意力矩阵 A A A的上三角。下图就是 n = 5 n=5 n=5情况下的Causal Mask。
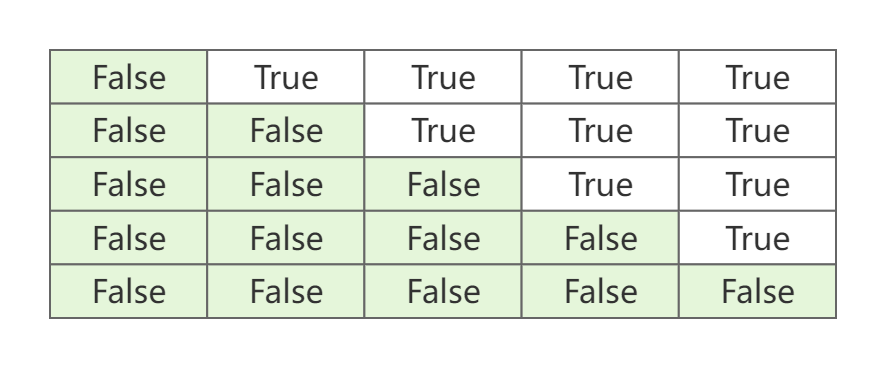
Padding Mask。模型训练时,由于输入样本的长度不等,因此需要padding到相等长度。但是,在模型前后向传播时需要忽略掉padding的部分,因此需要Padding Mask。Padding Mask也是针对注意力分数矩阵 A A A的,因此其形状下也要与 A A A相同。下图是长度为3,但被padding至5的Padding Mask例子。
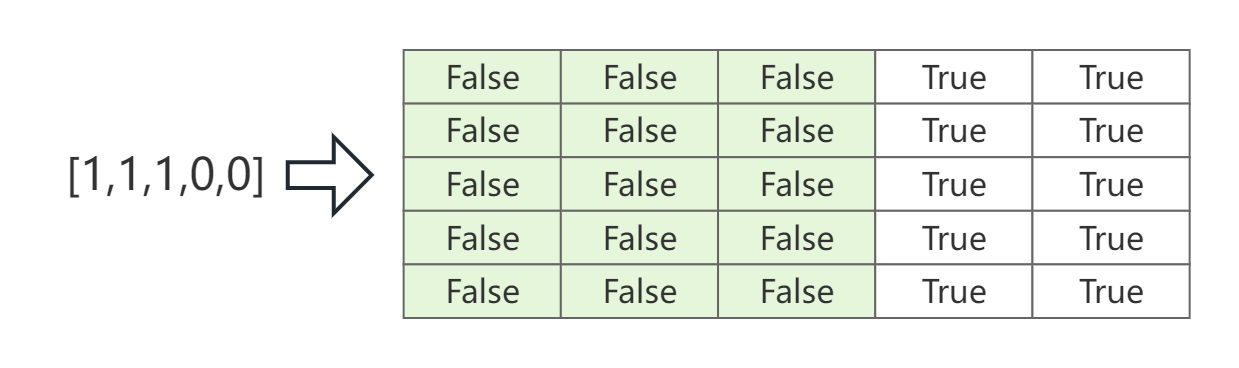
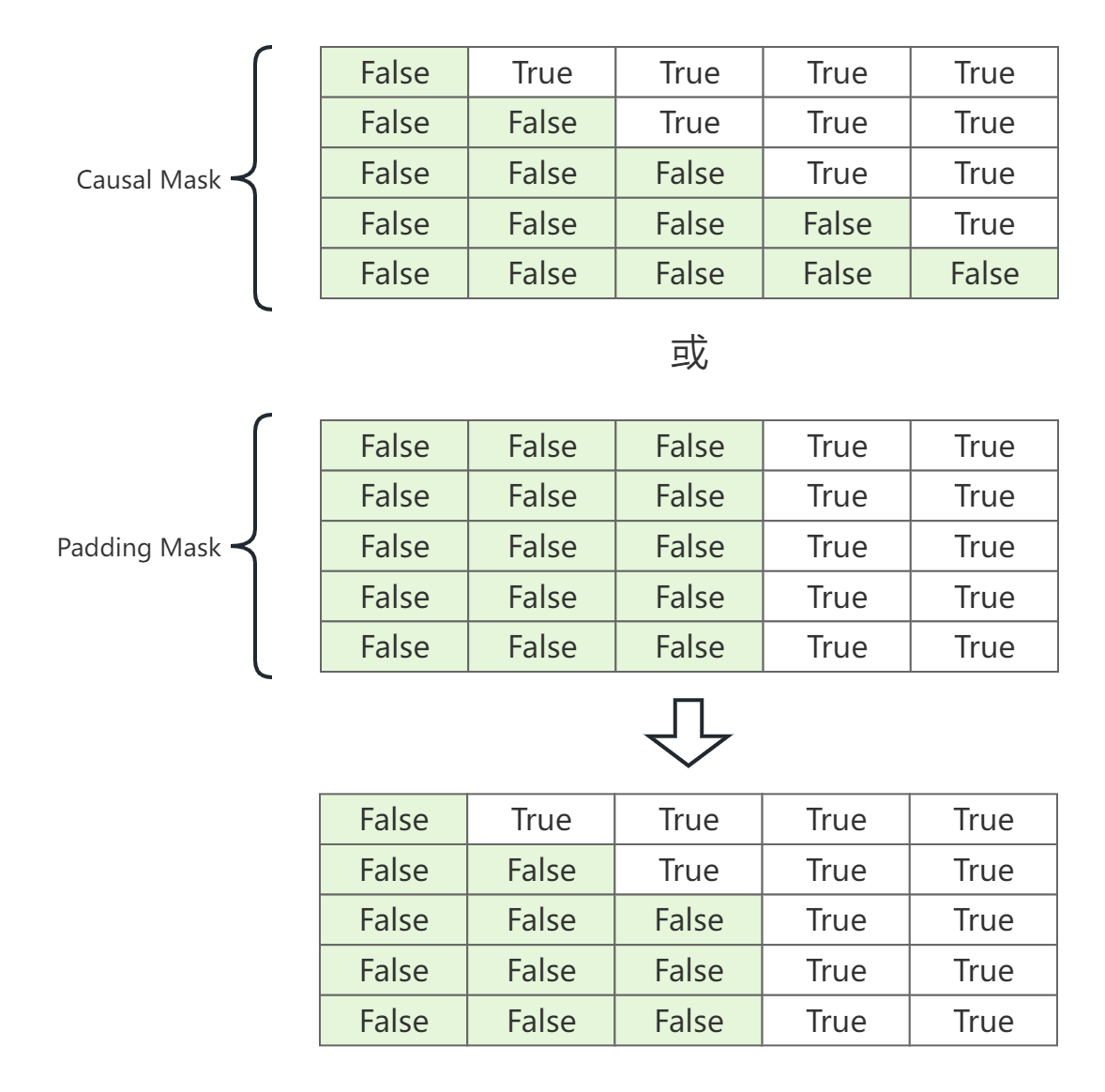
注意力分数矩阵的完整Mask就是"Causal Mask或Padding Mask",过程如下图。
1.2 代码
Causal Mask
def _make_causal_mask(
input_ids_shape: torch.Size, device: torch.device, past_key_values_length: int
) -> torch.BoolTensor:
"""
input_ids_shape:(batch_size, seq_length)
"""
batch_size, target_length = input_ids_shape
mask = torch.empty((target_length, target_length + past_key_values_length), dtype=torch.bool, device=device)
# ONNX doesn't support `torch.Tensor.triu` properly, thus we use this workaround
seq_ids = torch.arange(target_length, device=device)
mask[:, past_key_values_length:] = seq_ids[:, None] < seq_ids[None, :]
if past_key_values_length > 0:
mask[:, :past_key_values_length] = False
expanded_mask = mask[None, None, :, :].expand(batch_size, 1, target_length, target_length + past_key_values_length)
return expanded_mask
Padding Mask
def _expand_mask(mask: torch.Tensor, tgt_length: int) -> torch.BoolTensor:
"""
mask: (batch_size, seq_length)
"""
batch_size, src_length = mask.shape
tgt_length = tgt_length if tgt_length is not None else src_length
expanded_mask = ~(mask[:, None, None, :].to(torch.bool))
return expanded_mask.expand(batch_size, 1, tgt_length, src_length)
二、激活函数
bloom的激活函数采用
GELU
\text{GELU}
GELU,
GELU
\text{GELU}
GELU在实现时可以近似为
GELU
(
x
)
≈
0.5
x
(
1
+
tanh
(
2
π
(
x
+
0.044715
x
3
)
)
)
\text{GELU}(x)\approx 0.5x(1+\tanh(\sqrt{\frac{2}{\pi}}(x+0.044715x^3)))
GELU(x)≈0.5x(1+tanh(π2(x+0.044715x3)))
def bloom_gelu_forward(x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
GELLU前向
"""
return x * 0.5 * (1.0 + torch.tanh(0.79788456 * x * (1 + 0.044715 * x * x)))
def bloom_gelu_back(g: torch.Tensor, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
GELU后向
"""
x = x[0] # x is a tuple of 1 element, needs to unpack it first
tanh_out = torch.tanh(0.79788456 * x * (1 + 0.044715 * x * x))
# sqrt(2/pi) * 3 * 0.044715 -> 0.1070322243
ff = 0.5 * x * ((1 - tanh_out * tanh_out) * (0.79788456 + 0.1070322243 * x * x)) + 0.5 * (1 + tanh_out)
return ff * g
class GeLUFunction(torch.autograd.Function):
"""
完整的GeLU激活函数
"""
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
ctx.save_for_backward(input)
return bloom_gelu_forward(input)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
input = ctx.saved_tensors
tmp = bloom_gelu_back(grad_output, input)
return tmp
class BloomGelu(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
if self.training:
return GeLUFunction.apply(x)
else:
# 非训练时,只执行前向传播
return bloom_gelu_forward(x)
三、MLP层
MLP ( X , R ) = dropout ( GELU ( X W 1 ) W 2 ) + R ; X 是输入、 R 是残差 \text{MLP}(X, R) = \text{dropout}(\text{GELU}(XW_1)W_2)+R; \quad X是输入、R是残差 MLP(X,R)=dropout(GELU(XW1)W2)+R;X是输入、R是残差
class BloomMLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: BloomConfig):
super().__init__()
hidden_size = config.hidden_size
# 预训练时的张量并行度
self.pretraining_tp = config.pretraining_tp
self.slow_but_exact = config.slow_but_exact
# h至4h的全链接层
self.dense_h_to_4h = nn.Linear(hidden_size, 4 * hidden_size)
self.gelu_impl = BloomGelu()
# 4h到h的全链接层
self.dense_4h_to_h = nn.Linear(4 * hidden_size, hidden_size)
# dorpout
self.hidden_dropout = config.hidden_dropout
def forward(self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor, residual: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
hidden_states: (batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size)
residual与hidden_states形状相同
"""
# 全链接层+GLUE
hidden_states = self.gelu_impl(self.dense_h_to_4h(hidden_states))
# 将hidden_states从4h在映射会h
# intermediate_output的形状同hidden_states
if self.pretraining_tp > 1 and self.slow_but_exact:
# 判断预训练时是否使用了张量并行,且要采用慢且精确的前向传播
intermediate_output = torch.zeros_like(residual)
slices = self.dense_4h_to_h.weight.shape[-1] / self.pretraining_tp
for i in range(self.pretraining_tp):
intermediate_output = intermediate_output + F.linear(
hidden_states[:, :, int(i * slices) : int((i + 1) * slices)],
self.dense_4h_to_h.weight[:, int(i * slices) : int((i + 1) * slices)],
)
else:
intermediate_output = self.dense_4h_to_h(hidden_states)
# 对intermediate_output执行dropout后,加上残差residual
output = dropout_add(intermediate_output, residual, self.hidden_dropout, self.training)
return output
四、ALiBi:注入位置信息
1. 原理
BLOOM使用ALiBi来向模型注入位置信息。给定一个长度为
L
L
L的输入序列, 那么每个注意力头的第
i
i
i个query
q
i
∈
R
1
×
d
(
1
≤
i
≤
L
)
\textbf{q}_i\in\mathbb{R}^{1\times d}(1\leq i\leq L)
qi∈R1×d(1≤i≤L)针对前
i
i
i个key
K
∈
R
i
×
d
\textbf{K}\in\mathbb{R}^{i\times d}
K∈Ri×d的注意力分数为
softmax
(
q
i
K
⊤
)
\text{softmax}(\textbf{q}_i\textbf{K}^\top)
softmax(qiK⊤)
在使用ALiBi时,不需要向网络添加位置嵌入。仅需要在query-key点积中添加静态偏差即可。
softmax
(
q
i
K
⊤
+
m
⋅
[
−
(
i
−
1
)
,
…
,
−
2
,
−
1
,
0
]
)
\text{softmax}(\textbf{q}_i\textbf{K}^\top+m\cdot[-(i-1),\dots,-2,-1,0])
softmax(qiK⊤+m⋅[−(i−1),…,−2,−1,0])
其中
m
m
m是与注意力头相关的斜率(slope),也就是超参;
[
−
(
i
−
1
)
,
…
,
−
2
,
−
1
,
0
]
[-(i-1),\dots,-2,-1,0]
[−(i−1),…,−2,−1,0]其实就是
q
i
\textbf{q}_i
qi与各个key的相对距离。
对于8个注意力头, m m m是等比序列: 1 2 1 , 1 2 2 , … , 1 2 8 \frac{1}{2^1},\frac{1}{2^2},\dots,\frac{1}{2^8} 211,221,…,281。对于16个注意力头的模型, m m m则是等比序列: 1 2 0.5 , 1 2 1 , 1 2 1.5 , … , 1 8 \frac{1}{2^{0.5}},\frac{1}{2^1},\frac{1}{2^{1.5}},\dots,\frac{1}{8} 20.51,211,21.51,…,81。
2. 实现
def build_alibi_tensor(attention_mask: torch.Tensor, num_heads: int, dtype: torch.dtype) -> torch.Tensor:
batch_size, seq_length = attention_mask.shape
# closet_power_of_2是与num_head接近的2的次方
# 例如:num_heads为5/6/7时,closest_power_of_2为4
closest_power_of_2 = 2 ** math.floor(math.log2(num_heads))
# 计算斜率
base = torch.tensor(
2 ** (-(2 ** -(math.log2(closest_power_of_2) - 3))), device=attention_mask.device, dtype=torch.float32
)
powers = torch.arange(1, 1 + closest_power_of_2, device=attention_mask.device, dtype=torch.int32)
slopes = torch.pow(base, powers)
# 注意力头数量不是2的次方
if closest_power_of_2 != num_heads:
extra_base = torch.tensor(
2 ** (-(2 ** -(math.log2(2 * closest_power_of_2) - 3))), device=attention_mask.device, dtype=torch.float32
)
num_remaining_heads = min(closest_power_of_2, num_heads - closest_power_of_2)
extra_powers = torch.arange(1, 1 + 2 * num_remaining_heads, 2, device=attention_mask.device, dtype=torch.int32)
slopes = torch.cat([slopes, torch.pow(extra_base, extra_powers)], dim=0)
# 相对距离
arange_tensor = ((attention_mask.cumsum(dim=-1) - 1) * attention_mask)[:, None, :]
# alibi会与query和key的乘积相加
# alibi的形状为[batch_size, num_heads, query_length, key_length]
alibi = slopes[..., None] * arange_tensor
return alibi.reshape(batch_size * num_heads, 1, seq_length).to(dtype)
实现时,为了避免斜率计算中的除法操作,按如下的方式计算斜率:
base
=
2
−
(
2
−
(
log
2
n
−
3
)
)
=
1
2
8
/
n
=
1
2
8
n
power
=
[
1
,
…
,
n
]
\begin{align} &\text{base} = 2^{-(2^{-(\log_2 n-3)})}=\frac{1}{2^{8/n}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt[n]{2^8}} \\ &\text{power} = [1,\dots, n] \\ \end{align}
base=2−(2−(log2n−3))=28/n1=n281power=[1,…,n]
函数的返回值就是 m ⋅ [ − ( i − 1 ) , … , − 2 , − 1 , 0 ] m\cdot[-(i-1),\dots,-2,-1,0] m⋅[−(i−1),…,−2,−1,0]。
五、多头注意力层
1. 原理
BLOOM多头注意力就是在标准多头注意力上添加ALiBi。
单头注意力:
Q
=
W
q
X
K
=
W
k
X
V
=
W
v
X
Attention
(
Q
,
K
,
V
,
A
)
=
softmax
(
Q
K
T
d
k
+
A
)
V
\begin{align} Q &= W_q X \\ K &= W_k X \\ V &= W_v X \\ \text{Attention}(Q,K,V,A) &= \text{softmax}(\frac{QK^T}{\sqrt{d_k}}+A)V \end{align}
QKVAttention(Q,K,V,A)=WqX=WkX=WvX=softmax(dkQKT+A)V
其中,
X
X
X是输入,
W
q
,
W
k
,
W
v
W_q,W_k,W_v
Wq,Wk,Wv分别是query、key、value的投影矩阵,
A
A
A是ALiBi偏差矩阵。
多头注意力:
多头注意力就是将多个单头注意力的结果拼接起来。
head
i
=
Attention
(
Q
i
,
K
i
,
V
i
,
A
i
)
MultiHead
(
Q
,
K
,
V
,
A
)
=
Concat
(
head
1
,
…
,
head
h
)
W
o
\begin{align} \text{head}_i&=\text{Attention}(Q_i,K_i,V_i,A_i) \\ \text{MultiHead}(Q,K,V,A)&=\text{Concat}(\text{head}_1,\dots,\text{head}_h)W_o \end{align}
headiMultiHead(Q,K,V,A)=Attention(Qi,Ki,Vi,Ai)=Concat(head1,…,headh)Wo
2. 实现
class BloomAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: BloomConfig):
super().__init__()
# 预训练时,张量并行相关的参数(这里不需要关注)
self.pretraining_tp = config.pretraining_tp
self.slow_but_exact = config.slow_but_exact
self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size
self.num_heads = config.n_head
self.head_dim = self.hidden_size // self.num_heads
self.split_size = self.hidden_size
self.hidden_dropout = config.hidden_dropout
if self.head_dim * self.num_heads != self.hidden_size:
raise ValueError(
f"`hidden_size` must be divisible by num_heads (got `hidden_size`: {self.hidden_size} and `num_heads`:"
f" {self.num_heads})."
)
# Layer-wise attention scaling
self.inv_norm_factor = 1.0 / math.sqrt(self.head_dim)
self.beta = 1.0
# query、key、value的投影层
self.query_key_value = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, 3 * self.hidden_size, bias=True)
# 输出投影层
self.dense = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.hidden_size)
self.attention_dropout = nn.Dropout(config.attention_dropout)
def _split_heads(self, fused_qkv: torch.Tensor) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
"""
fused_qkv: [batch_size, seq_length, 3*hidden_size]
"""
batch_size, seq_length, three_times_hidden_size = fused_qkv.shape
# 1. 将Q、K、V拆分出来;2. 拆分出多个头
fused_qkv = fused_qkv.view(batch_size, seq_length, self.num_heads, 3, self.head_dim)
return fused_qkv[..., 0, :], fused_qkv[..., 1, :], fused_qkv[..., 2, :]
def _merge_heads(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
# 目标:batch_size * num_heads, seq_length, head_dim -> batch_size, seq_length, num_heads * head_dim
batch_size_and_num_heads, seq_length, _ = x.shape
batch_size = batch_size_and_num_heads // self.num_heads
# 将batch_size拆分出来:batch_size * num_heads, seq_length, head_dim -> batch_size, num_heads, seq_length, head_dim
x = x.view(batch_size, self.num_heads, seq_length, self.head_dim)
# batch_size, num_heads, seq_length, head_dim -> batch_size, seq_length, num_heads, head_dim
x = x.permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
# batch_size, seq_length, num_heads, head_dim -> batch_size, seq_length, num_heads * head_dim
return x.reshape(batch_size, seq_length, self.num_heads * self.head_dim)
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
residual: torch.Tensor,
alibi: torch.Tensor,
attention_mask: torch.Tensor,
layer_past: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None,
head_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
use_cache: bool = False,
output_attentions: bool = False,
):
# [batch_size, seq_length, 3 x hidden_size]
# 一次性得到投影的Q、K、V,减少执行矩阵乘法的次数
fused_qkv = self.query_key_value(hidden_states)
# 多头拆分
# 3 x [batch_size, seq_length, num_heads, head_dim]
(query_layer, key_layer, value_layer) = self._split_heads(fused_qkv)
batch_size, q_length, _, _ = query_layer.shape
query_layer = query_layer.transpose(1, 2).reshape(batch_size * self.num_heads, q_length, self.head_dim)
key_layer = key_layer.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).reshape(batch_size * self.num_heads, self.head_dim, q_length)
value_layer = value_layer.transpose(1, 2).reshape(batch_size * self.num_heads, q_length, self.head_dim)
# 处理传入的key和value(忽略)
if layer_past is not None:
past_key, past_value = layer_past
key_layer = torch.cat((past_key, key_layer), dim=2)
value_layer = torch.cat((past_value, value_layer), dim=1)
_, _, kv_length = key_layer.shape
# 忽略
if use_cache is True:
present = (key_layer, value_layer)
else:
present = None
# [batch_size * num_heads, q_length, kv_length]
# inv_norm_factor*(query_layer*key_layer) + beta*alibi
matmul_result = alibi.baddbmm(
batch1=query_layer,
batch2=key_layer,
beta=self.beta,
alpha=self.inv_norm_factor,
)
# [batch_size, num_heads, q_length, kv_length]
attention_scores = matmul_result.view(batch_size, self.num_heads, q_length, kv_length)
# 若输入类型是float16,则将注意力分数转换为float32
# 注意力分数的精度会显著影响模型的效果
input_dtype = attention_scores.dtype
if input_dtype == torch.float16:
attention_scores = attention_scores.to(torch.float)
# mask
attn_weights = torch.masked_fill(attention_scores, attention_mask, torch.finfo(attention_scores.dtype).min)
# softmax
attention_probs = F.softmax(attn_weights, dim=-1, dtype=torch.float32).to(input_dtype)
# [batch_size, num_heads, q_length, kv_length]
# dropout
attention_probs = self.attention_dropout(attention_probs)
# 若传入注意力头的mask
if head_mask is not None:
attention_probs = attention_probs * head_mask
# attention_probs_reshaped:[batch_size x num_heads, q_length, kv_length]
attention_probs_reshaped = attention_probs.view(batch_size * self.num_heads, q_length, kv_length)
# context_layer: [batch_size * num_heads, q_length, head_dim]
# 乘以value
context_layer = torch.bmm(attention_probs_reshaped, value_layer)
# context_layer: batch_size, seq_length, num_heads * head_dim
# 合并多头
context_layer = self._merge_heads(context_layer)
# 输出投影
if self.pretraining_tp > 1 and self.slow_but_exact:
slices = self.hidden_size / self.pretraining_tp
output_tensor = torch.zeros_like(context_layer)
for i in range(self.pretraining_tp):
output_tensor = output_tensor + F.linear(
context_layer[:, :, int(i * slices) : int((i + 1) * slices)],
self.dense.weight[:, int(i * slices) : int((i + 1) * slices)],
)
else:
output_tensor = self.dense(context_layer)
# dropout+残差
output_tensor = dropout_add(output_tensor, residual, self.hidden_dropout, self.training)
outputs = (output_tensor, present)
if output_attentions:
outputs += (attention_probs,)
return outputs
六、BloomBlock
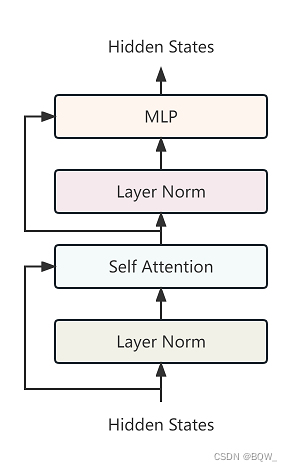
class BloomBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: BloomConfig):
super().__init__()
hidden_size = config.hidden_size
self.input_layernorm = LayerNorm(hidden_size, eps=config.layer_norm_epsilon)
self.num_heads = config.n_head
self.self_attention = BloomAttention(config)
self.post_attention_layernorm = LayerNorm(hidden_size, eps=config.layer_norm_epsilon)
self.mlp = BloomMLP(config)
self.apply_residual_connection_post_layernorm = config.apply_residual_connection_post_layernorm
self.hidden_dropout = config.hidden_dropout
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
alibi: torch.Tensor,
attention_mask: torch.Tensor,
layer_past: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None,
head_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
use_cache: bool = False,
output_attentions: bool = False,
):
# hidden_states: [batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size]
# 先对hidden_states进行Layer Norm
layernorm_output = self.input_layernorm(hidden_states)
# 残差
if self.apply_residual_connection_post_layernorm:
residual = layernorm_output
else:
residual = hidden_states
# Self attention.
attn_outputs = self.self_attention(
layernorm_output,
residual,
layer_past=layer_past,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
alibi=alibi,
head_mask=head_mask,
use_cache=use_cache,
output_attentions=output_attentions,
)
attention_output = attn_outputs[0]
outputs = attn_outputs[1:]
layernorm_output = self.post_attention_layernorm(attention_output)
# Get residual
if self.apply_residual_connection_post_layernorm:
residual = layernorm_output
else:
residual = attention_output
# MLP.
output = self.mlp(layernorm_output, residual)
if use_cache:
outputs = (output,) + outputs
else:
outputs = (output,) + outputs[1:]
return outputs # hidden_states, present, attentions
七、BloomModel
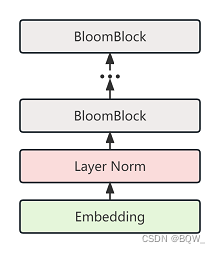
class BloomModel(BloomPreTrainedModel):
def __init__(self, config: BloomConfig):
super().__init__(config)
self.embed_dim = config.hidden_size
self.num_heads = config.n_head
# Embedding + LN Embedding
self.word_embeddings = nn.Embedding(config.vocab_size, self.embed_dim)
self.word_embeddings_layernorm = LayerNorm(self.embed_dim, eps=config.layer_norm_epsilon)
# BloomBlocks
self.h = nn.ModuleList([BloomBlock(config) for _ in range(config.num_hidden_layers)])
# 最终Layer Norm
self.ln_f = LayerNorm(self.embed_dim, eps=config.layer_norm_epsilon)
self.gradient_checkpointing = False
self.post_init()
def build_alibi_tensor(self, attention_mask: torch.Tensor, num_heads: int, dtype: torch.dtype) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
封装build_alibi_tensor函数
"""
return build_alibi_tensor(attention_mask, num_heads, dtype)
def get_input_embeddings(self):
return self.word_embeddings
def _prepare_attn_mask(
self, attention_mask: torch.Tensor, input_shape: Tuple[int, int], past_key_values_length: int
) -> torch.BoolTensor:
# 构建注意力分数的mask句子,见文章第一节的掩码(Mask)部分
combined_attention_mask = None
device = attention_mask.device
_, src_length = input_shape
if src_length > 1:
# 构建causal mask
combined_attention_mask = _make_causal_mask(
input_shape, device=device, past_key_values_length=past_key_values_length
)
# [batch_size, seq_length] -> [batch_size, 1, tgt_length, src_length]
# 构建padding mask
expanded_attn_mask = _expand_mask(attention_mask, tgt_length=src_length)
# 两种mask合并
combined_attention_mask = (
expanded_attn_mask if combined_attention_mask is None else expanded_attn_mask | combined_attention_mask
)
return combined_attention_mask
def set_input_embeddings(self, new_embeddings: torch.Tensor):
self.word_embeddings = new_embeddings
@add_start_docstrings_to_model_forward(BLOOM_INPUTS_DOCSTRING)
@add_code_sample_docstrings(
checkpoint=_CHECKPOINT_FOR_DOC,
output_type=BaseModelOutputWithPastAndCrossAttentions,
config_class=_CONFIG_FOR_DOC,
)
def forward(
self,
input_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
past_key_values: Optional[Tuple[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor], ...]] = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
head_mask: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
inputs_embeds: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
use_cache: Optional[bool] = None,
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = None,
output_hidden_states: Optional[bool] = None,
return_dict: Optional[bool] = None,
**deprecated_arguments,
) -> Union[Tuple[torch.Tensor, ...], BaseModelOutputWithPastAndCrossAttentions]:
### (开始)一些输入输出和参数设置,可以忽略
if deprecated_arguments.pop("position_ids", False) is not False:
# `position_ids` could have been `torch.Tensor` or `None` so defaulting pop to `False` allows to detect if users were passing explicitly `None`
warnings.warn(
"`position_ids` have no functionality in BLOOM and will be removed in v5.0.0. You can safely ignore"
" passing `position_ids`.",
FutureWarning,
)
if len(deprecated_arguments) > 0:
raise ValueError(f"Got unexpected arguments: {deprecated_arguments}")
output_attentions = output_attentions if output_attentions is not None else self.config.output_attentions
output_hidden_states = (
output_hidden_states if output_hidden_states is not None else self.config.output_hidden_states
)
use_cache = use_cache if use_cache is not None else self.config.use_cache
return_dict = return_dict if return_dict is not None else self.config.use_return_dict
if input_ids is not None and inputs_embeds is not None:
raise ValueError("You cannot specify both input_ids and inputs_embeds at the same time")
elif input_ids is not None:
batch_size, seq_length = input_ids.shape
elif inputs_embeds is not None:
batch_size, seq_length, _ = inputs_embeds.shape
else:
raise ValueError("You have to specify either input_ids or inputs_embeds")
if past_key_values is None:
past_key_values = tuple([None] * len(self.h))
### (结束)一些输入输出和参数设置,可以忽略
# 准备head mask,1.0表示保留注意力头
head_mask = self.get_head_mask(head_mask, self.config.n_layer)
if inputs_embeds is None:
inputs_embeds = self.word_embeddings(input_ids)
# 在embedding后添加了layernorm
hidden_states = self.word_embeddings_layernorm(inputs_embeds)
presents = () if use_cache else None
all_self_attentions = () if output_attentions else None
all_hidden_states = () if output_hidden_states else None
### (开始) gradient checkpointing和past_key_values处理,忽略
if self.gradient_checkpointing and self.training:
if use_cache:
logger.warning_once(
"`use_cache=True` is incompatible with gradient checkpointing. Setting `use_cache=False`..."
)
use_cache = False
# Compute alibi tensor: check build_alibi_tensor documentation
seq_length_with_past = seq_length
past_key_values_length = 0
if past_key_values[0] is not None:
past_key_values_length = past_key_values[0][0].shape[2]
seq_length_with_past = seq_length_with_past + past_key_values_length
### (结束) gradient checkpointing和past_key_values处理,忽略
# 构建注意力分数掩码
if attention_mask is None:
attention_mask = torch.ones((batch_size, seq_length_with_past), device=hidden_states.device)
else:
attention_mask = attention_mask.to(hidden_states.device)
alibi = self.build_alibi_tensor(attention_mask, self.num_heads, dtype=hidden_states.dtype)
causal_mask = self._prepare_attn_mask(
attention_mask,
input_shape=(batch_size, seq_length),
past_key_values_length=past_key_values_length,
)
# BloomBlock前向传播
for i, (block, layer_past) in enumerate(zip(self.h, past_key_values)):
if output_hidden_states:
all_hidden_states = all_hidden_states + (hidden_states,)
if self.gradient_checkpointing and self.training:
def create_custom_forward(module):
def custom_forward(*inputs):
# None for past_key_value
return module(*inputs, use_cache=use_cache, output_attentions=output_attentions)
return custom_forward
outputs = torch.utils.checkpoint.checkpoint(
create_custom_forward(block),
hidden_states,
alibi,
causal_mask,
layer_past,
head_mask[i],
)
else:
outputs = block(
hidden_states,
layer_past=layer_past,
attention_mask=causal_mask,
head_mask=head_mask[i],
use_cache=use_cache,
output_attentions=output_attentions,
alibi=alibi,
)
hidden_states = outputs[0]
if use_cache is True:
presents = presents + (outputs[1],)
if output_attentions:
all_self_attentions = all_self_attentions + (outputs[2 if use_cache else 1],)
# Add last hidden state
hidden_states = self.ln_f(hidden_states)
if output_hidden_states:
all_hidden_states = all_hidden_states + (hidden_states,)
if not return_dict:
return tuple(v for v in [hidden_states, presents, all_hidden_states, all_self_attentions] if v is not None)
return BaseModelOutputWithPastAndCrossAttentions(
last_hidden_state=hidden_states,
past_key_values=presents,
hidden_states=all_hidden_states,
attentions=all_self_attentions,
)