前言
我们知道App进程是由SystemServer启动的Android启动流程
那App对应的Application以及第一个Activity又是如何创建的呢?
源码分析(API 30为例)
我们从ActivityThread.main函数入手;
public static void main(String[] args) {
...
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false, startSeq);
...
}
首先会创建一个ActivityThread对象并调用attach方法;
// ActivityThread.attach方法
private void attach(boolean system, long startSeq) {
sCurrentActivityThread = this;
mSystemThread = system;
if (!system) {
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManager.getService();
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread, startSeq);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} else {
...
}
...
}
由于传入的system参数为false,我们只看if (!system) 里的代码执行逻辑:
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManager.getService();
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread, startSeq);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
我们知道IActivityManager是AMS的代理,因此attachApplication方法具体实现在ActivityManagerService中;
// ActivityManagerService.attachApplication
public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread, long startSeq) {
if (thread == null) {
throw new SecurityException("Invalid application interface");
}
synchronized (this) {
int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid, callingUid, startSeq);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
attachApplication会调用attachApplicationLocked方法;
// ActivityManagerService.attachApplicationLocked
private boolean attachApplicationLocked(@NonNull IApplicationThread thread,
int pid, int callingUid, long startSeq) {
...
//1.获取ActiveInstrumentation对象
final ActiveInstrumentation instr = app.getActiveInstrumentation();
if (instr != null) {
//通过PMS获取ApplicationInfo信息
notifyPackageUse(instr.mClass.getPackageName(),
PackageManager.NOTIFY_PACKAGE_USE_INSTRUMENTATION);
}
ApplicationInfo appInfo = instr != null ? instr.mTargetInfo : app.info;
if (app.isolatedEntryPoint != null) {
...//这里没有isolatedEntryPoint赋值的地方,因此不会走
} else if (instr2 != null) {
//2.此处thread即为ApplicationThread对象,因此会回调ApplicationThread.bindApplication方法
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providerList,
instr2.mClass,
profilerInfo, instr2.mArguments,
instr2.mWatcher,
instr2.mUiAutomationConnection, testMode,
mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.isPersistent(),
new Configuration(app.getWindowProcessController().getConfiguration()),
app.compat, getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked(),
buildSerial, autofillOptions, contentCaptureOptions,
app.mDisabledCompatChanges);
} else {
...
}
...
if (normalMode) {
try {
// 3.这里会做Activity启动
didSomething = mAtmInternal.attachApplication(app.getWindowProcessController());
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown launching activities in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
...
}
可以看到attachApplicationLocked方法主要做了以下几件事:
- 与
PMS通信,获取ApplicationInfo对象信息,即PMS解析APP包时缓存的应用信息;【详细流程可以参考浅谈Android PMS解析APP信息流程】 - 回调ApplicationThread.bindApplication方法,实际上就是启动Application;
- 执行
mAtmInternal.attachApplication方法,实际上就是启动Activity;
我们首先看下thread.bindApplication方法:
public final void bindApplication(String processName, ApplicationInfo appInfo,
ProviderInfoList providerList, ComponentName instrumentationName,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle instrumentationArgs,
IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher,
IUiAutomationConnection instrumentationUiConnection, int debugMode,
boolean enableBinderTracking, boolean trackAllocation,
boolean isRestrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent, Configuration config,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map services, Bundle coreSettings,
String buildSerial, AutofillOptions autofillOptions,
ContentCaptureOptions contentCaptureOptions, long[] disabledCompatChanges) {
...
AppBindData data = new AppBindData();
data.processName = processName;
data.appInfo = appInfo;
data.providers = providerList.getList();
data.instrumentationName = instrumentationName;
data.instrumentationArgs = instrumentationArgs;
data.instrumentationWatcher = instrumentationWatcher;
data.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection = instrumentationUiConnection;
data.debugMode = debugMode;
data.enableBinderTracking = enableBinderTracking;
data.trackAllocation = trackAllocation;
data.restrictedBackupMode = isRestrictedBackupMode;
data.persistent = persistent;
data.config = config;
data.compatInfo = compatInfo;
data.initProfilerInfo = profilerInfo;
data.buildSerial = buildSerial;
data.autofillOptions = autofillOptions;
data.contentCaptureOptions = contentCaptureOptions;
data.disabledCompatChanges = disabledCompatChanges;
sendMessage(H.BIND_APPLICATION, data);
}
就是构造AppBindData对象,把拿到的app数据保存起来,然后调用HandlerH发送BIND_APPLICATION消息;
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case BIND_APPLICATION:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "bindApplication");
AppBindData data = (AppBindData)msg.obj;
handleBindApplication(data);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
...
}
紧接着会调用handleBindApplication方法;
private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) {
...
app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
...
}
handleBindApplication会调用data.info.makeApplication方法
//LoadedApk.makeApplication
public Application makeApplication(boolean forceDefaultAppClass,
Instrumentation instrumentation) {
...
//1.mInstrumentation.newApplication
mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.newApplication(
cl, appClass, appContext);
appContext.setOuterContext(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
mActivityThread.mAllApplications.add(app);
mApplication = app;
if (instrumentation != null) {
try {
//2. instrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate
instrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
}
return app;
}
在LoadedApk.makeApplication方法中,我们主要关注以下两个方法:
-
mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.newApplication( cl, appClass, appContext);首先会通过反射创建出Application对象,然后调用attachBaseContext方法,因此attachBaseContext方法是Application中调用的最早的方法; -
instrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app)中会调用Application.onCreate方法;
至此,Application就完成创建以及onCreate方法的调用;
Application创建时序图
Activity启动
当Application创建并启动完毕,我们再回到ActivityManagerService.attachApplicationLocked方法中,
重点关注下
mAtmInternal.attachApplication(app.getWindowProcessController());
会调用ActivityTaskManagerInternal.attachApplication方法,如下:
//ActivityTaskManagerInternal.attachApplication
public abstract boolean attachApplication(WindowProcessController wpc);
很明显是抽象方法,对应的实现类为ActivityTaskManagerService
//ActivityTaskManagerService.attachApplication
public boolean attachApplication(WindowProcessController wpc) throws RemoteException {
synchronized (mGlobalLockWithoutBoost) {
...
}
try {
return mRootWindowContainer.attachApplication(wpc);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER);
}
}
}
会调用mRootWindowContainer.attachApplication方法;
//RootWindowContainer.attachApplication
boolean attachApplication(WindowProcessController app) throws RemoteException {
final String processName = app.mName;
boolean didSomething = false;
for (int displayNdx = getChildCount() - 1; displayNdx >= 0; --displayNdx) {
...
RootWindowContainer::startActivityForAttachedApplicationIfNeeded, this,
PooledLambda.__(ActivityRecord.class), app, stack.topRunningActivity());
stack.forAllActivities(c);
c.recycle();
...
return didSomething;
}
接着调用startActivityForAttachedApplicationIfNeeded方法
private boolean startActivityForAttachedApplicationIfNeeded(ActivityRecord r,
WindowProcessController app, ActivityRecord top) {
...
try {
if (mStackSupervisor.realStartActivityLocked(r, app, top == r
...
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception in new application when starting activity "
+ top.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
mTmpRemoteException = e;
return true;
}
return false;
}
mStackSupervisor.realStartActivityLocked这句代码是不是很熟悉,我们对照之前分析Activity的启动时序图:
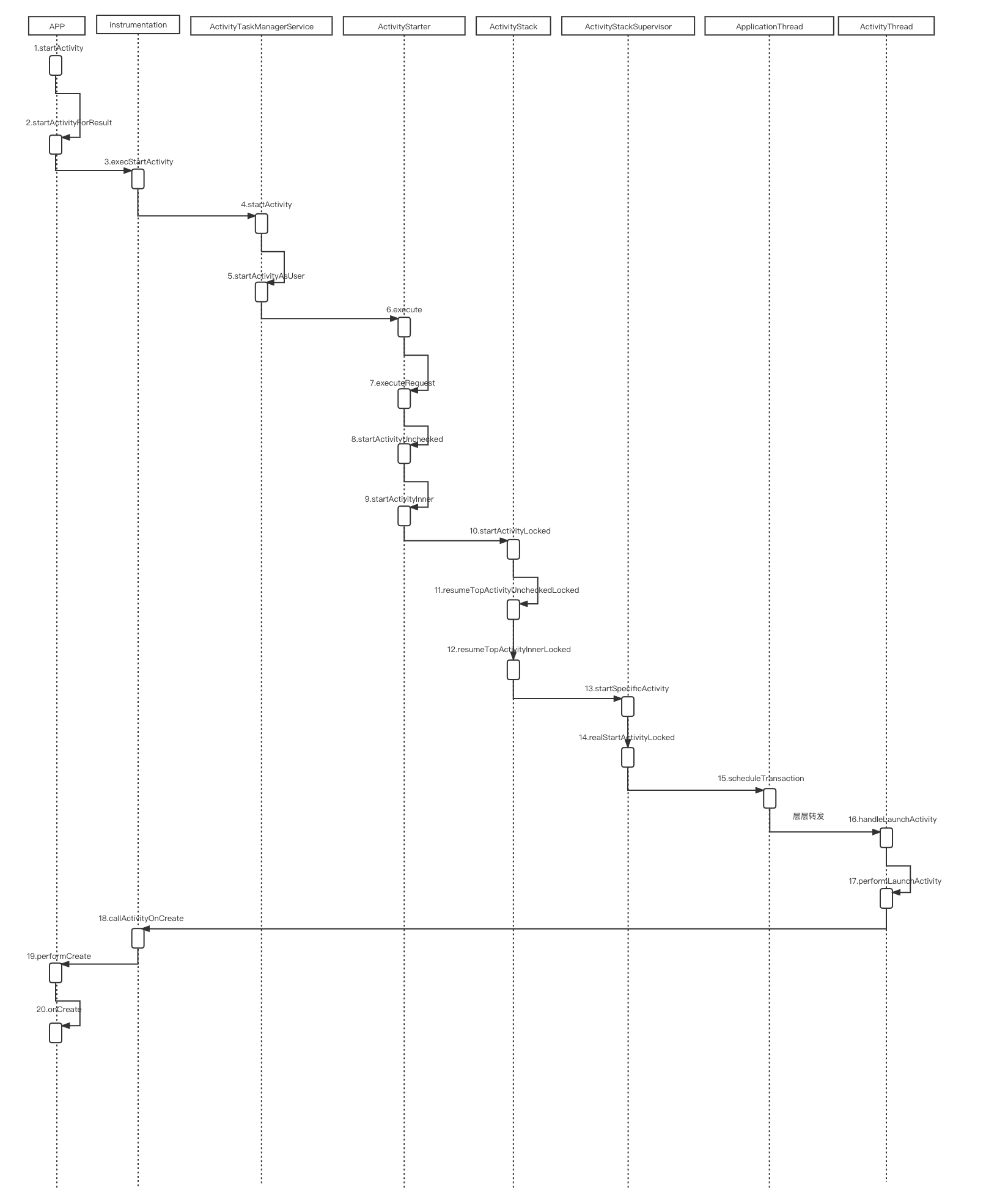
这里就对应时序图中的第14步骤,后续层层调用,最终还是交由ActivityThread调用handleLaunchActivity、performLaunchActivity完成Activity的启动!
结语
如果以上文章对您有一点点帮助,希望您不要吝啬的点个赞加个关注,您每一次小小的举动都是我坚持写作的不懈动力!ღ( ´・ᴗ・` )