不同libc版本的fastbin_dup.c源码有点小区别:主要是有tcache的,需要先填充
以下为有tcache的源码示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
int main()
{
setbuf(stdout, NULL);
printf("This file demonstrates a simple double-free attack with fastbins.\n");
printf("Fill up tcache first.\n");
void *ptrs[8];
for (int i=0; i<8; i++) {
ptrs[i] = malloc(8);
}
for (int i=0; i<7; i++) {
free(ptrs[i]);
}
printf("Allocating 3 buffers.\n");
int *a = calloc(1, 8);
int *b = calloc(1, 8);
int *c = calloc(1, 8);
printf("1st calloc(1, 8): %p\n", a);
printf("2nd calloc(1, 8): %p\n", b);
printf("3rd calloc(1, 8): %p\n", c);
printf("Freeing the first one...\n");
free(a);
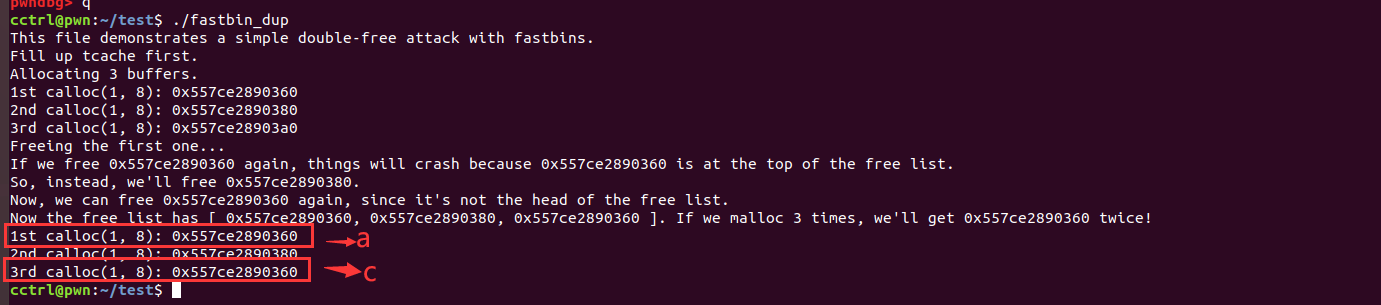
printf("If we free %p again, things will crash because %p is at the top of the free list.\n", a, a);
// free(a);
printf("So, instead, we'll free %p.\n", b);
free(b);
printf("Now, we can free %p again, since it's not the head of the free list.\n", a);
free(a);
printf("Now the free list has [ %p, %p, %p ]. If we malloc 3 times, we'll get %p twice!\n", a, b, a, a);
a = calloc(1, 8);
b = calloc(1, 8);
c = calloc(1, 8);
printf("1st calloc(1, 8): %p\n", a);
printf("2nd calloc(1, 8): %p\n", b);
printf("3rd calloc(1, 8): %p\n", c);
assert(a == c);
}
编译:
gcc -g fastbin_dup.c -o fastbin_dup
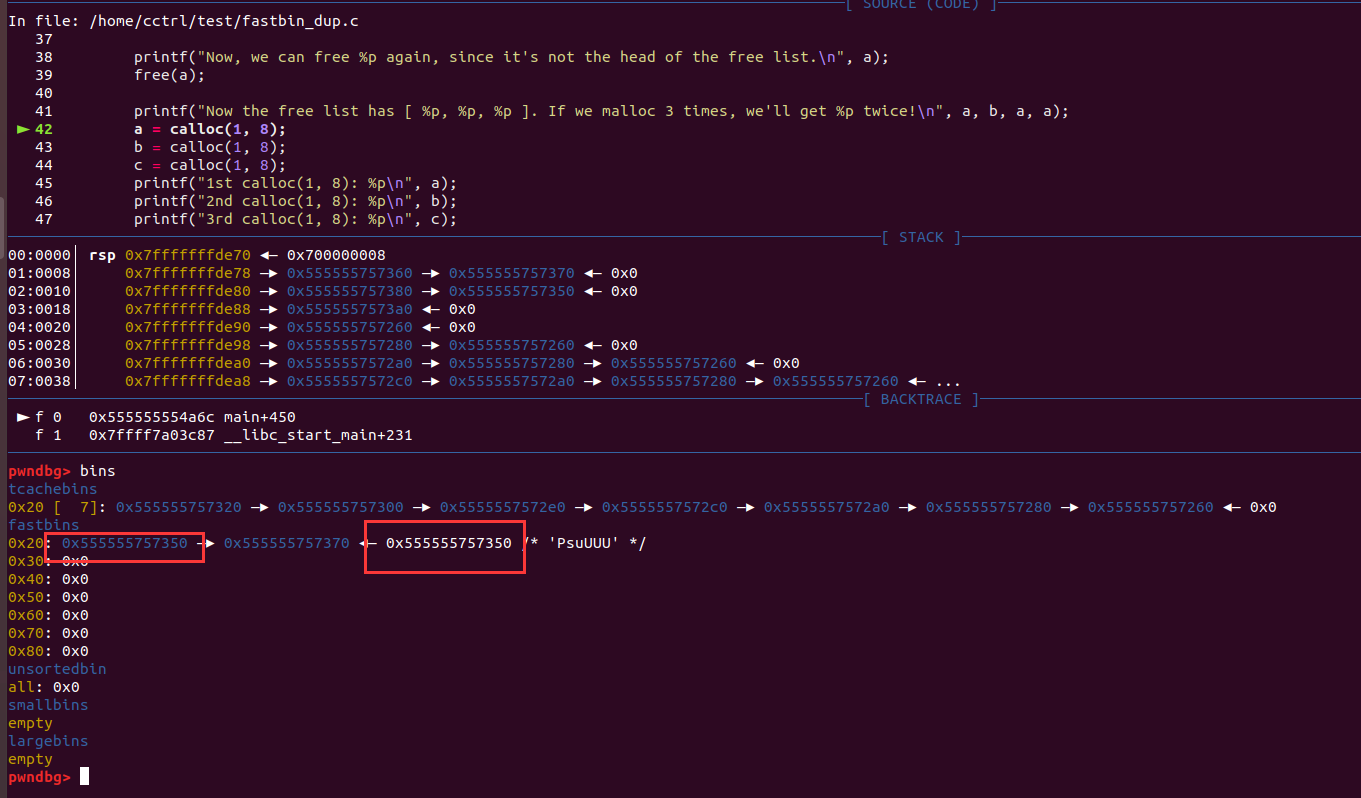
tcache[count]特点:
count= 7
优先分配-用malloc(8)的大小即可free后占用
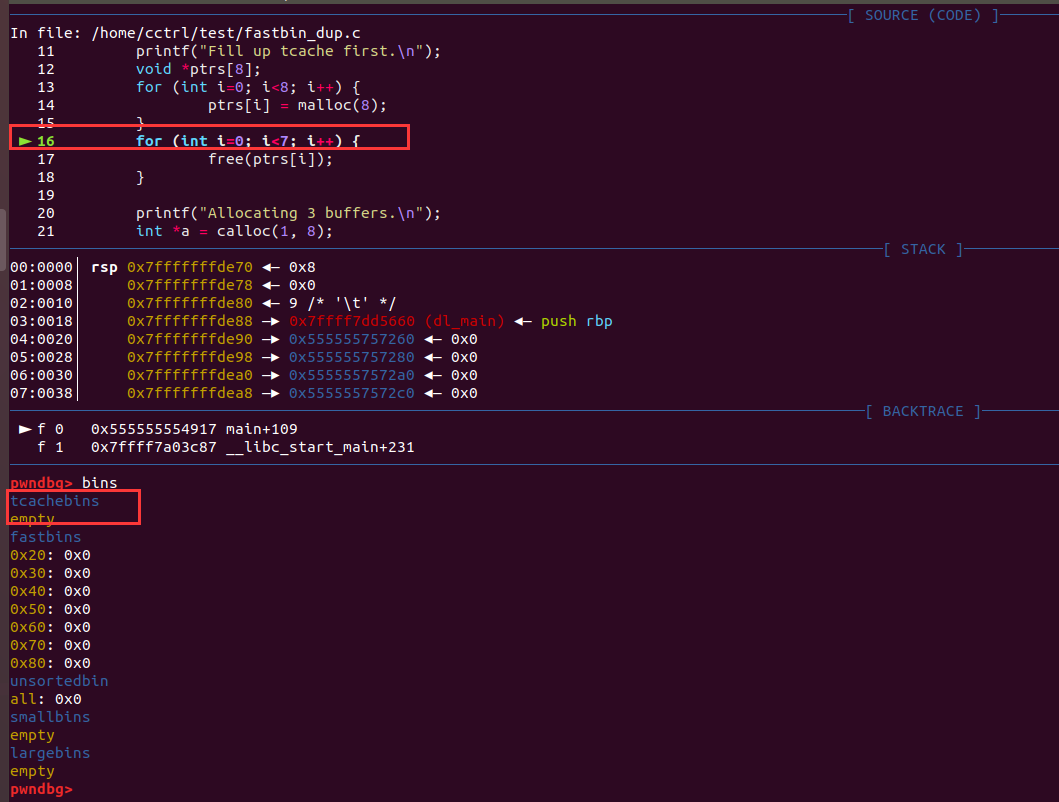 7个tcache
7个tcache
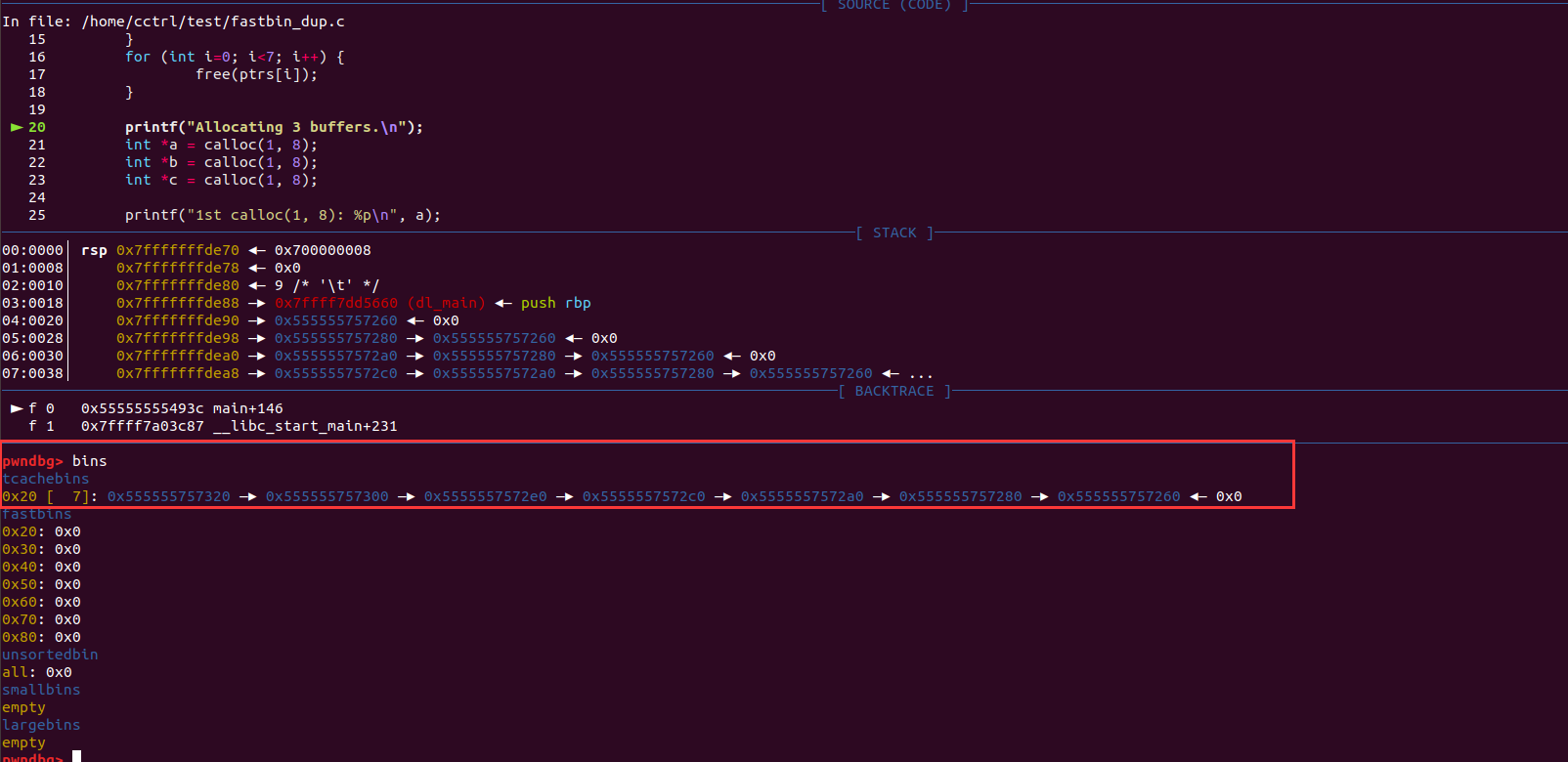 fastbin_dup注意事项:
fastbin_dup注意事项:
头结点不能同时free两次。

释放b把头结点变成b,即可再次free(a):
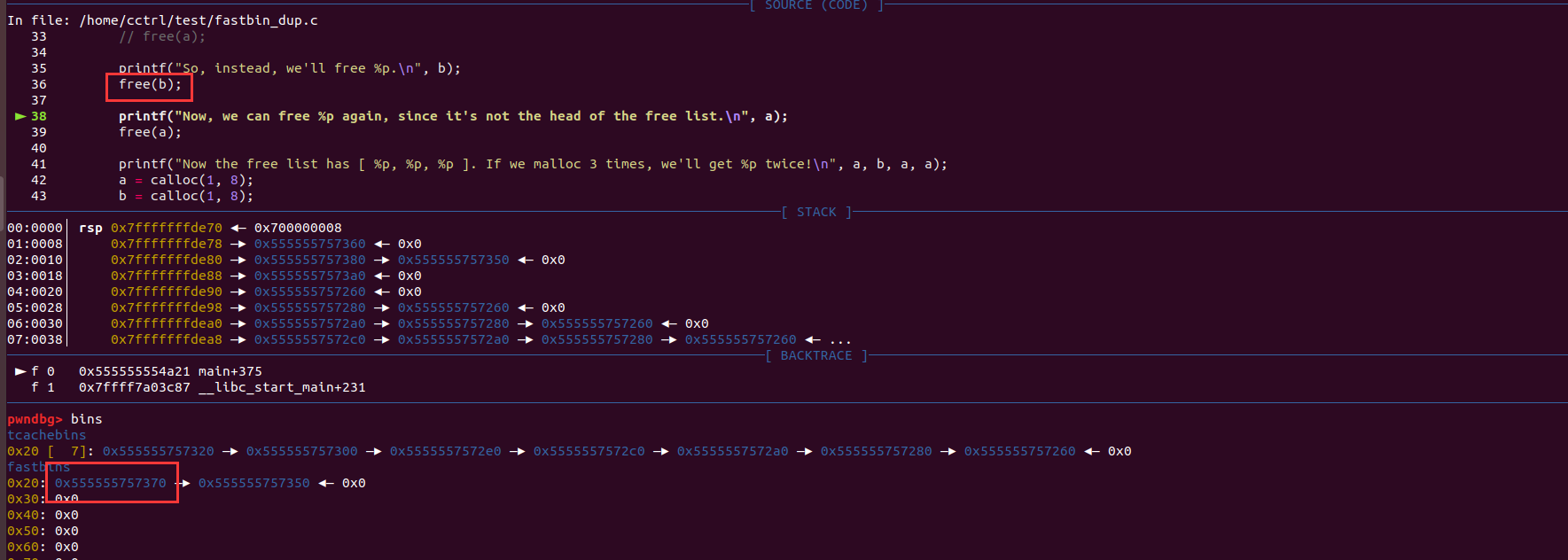 达成利用:
达成利用:
 执行结果:
执行结果:
fastbin_dup总结:
有tcache先malloc(8)*7,在free掉7个占满tcache;
double free的chunk不能是头结点,需要利用一个中间替换头结点;