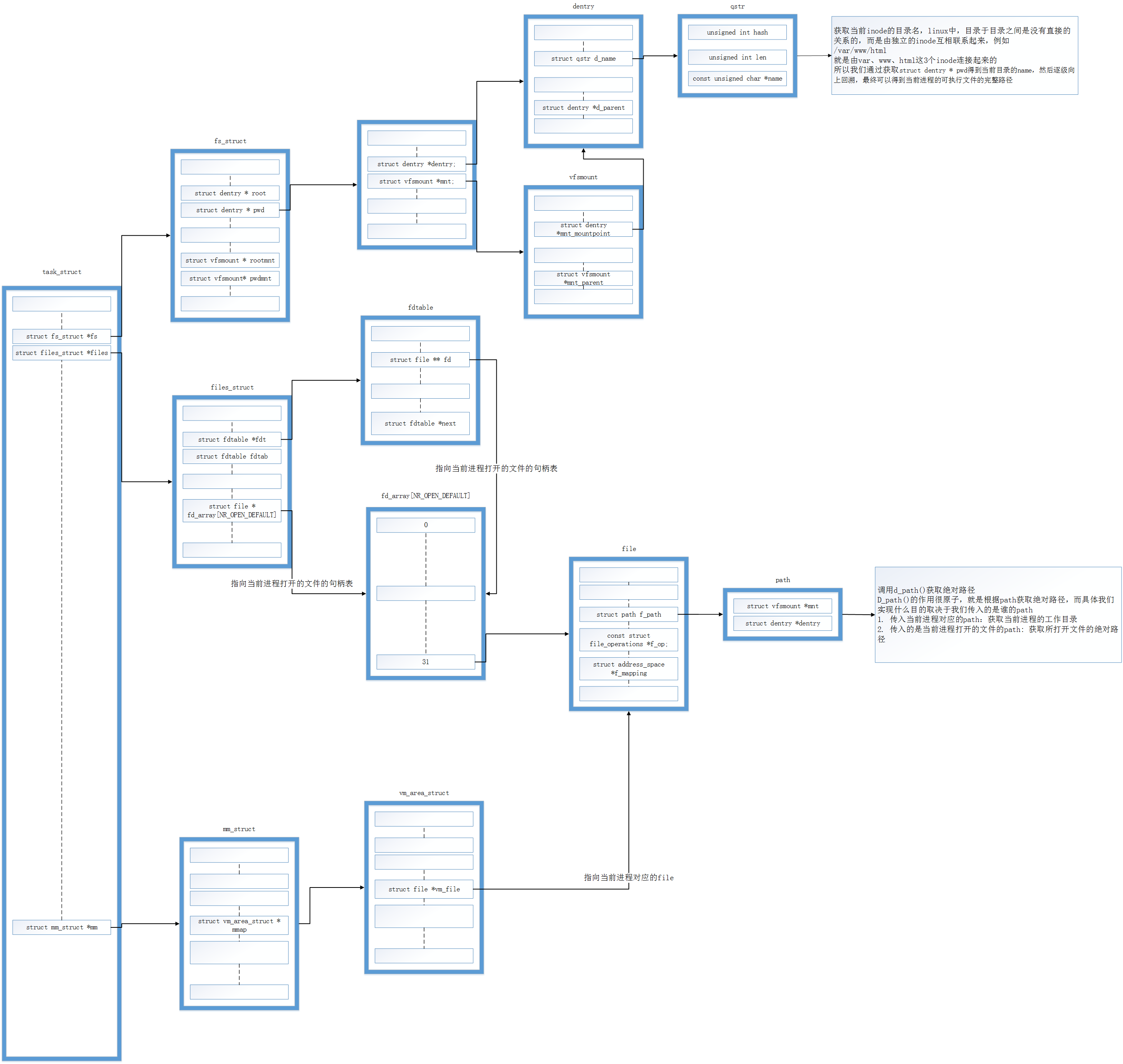
React 的路由跳转需要引用第三方的 React Router
npm i react-router-dom@5.2.0React Router 分为 BrowserRouter 和 HashRouter
如果我们的应用有服务器响应 web 的请求,建议使用
<BrowserRouter>组件; 如果使用静态文件服务器,建议使用<HashRouter>组件
在 React router 中通常使用的组件有三种(这里使用的是Router5):
- 路由组件(作为根组件): BrowserRouter(history模式) 和 HashRouter(hash模式)
- 路径匹配组件: Route 和 Switch
- 导航组件: Link 和 NavLink
BrowserRouter 和 HashRouter 的使用
- BrowserRouter 和 HashRouter 包裹的路由组件会自动传入match、history、location。
- BrowserRouter 的路径:localhost:3000/demo/a
- HashRouter 的路径:localhost:3000/#/demo/a
- BrowserRouter 刷新没有任何影响,因为 state 保存在 history 对象中。
- HashRouter 刷新后会导致路由state参数的丢失!!!
- BrowserRouter 可以传递任意参数,HashRouter 需要手动拼接 URL
//BrowserRouter
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<BrowserRouter>
<Header />
<Route path='/' exact component={Home}></Route>
<Route path='/login' exact component={Login}></Route>
<Route path='/detail/:id' exact component={Detail}></Route>
</BrowserRouter>
)
}
}
//HashRouter
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<HashRouter>
<Header />
<Route path='/' exact component={Home}></Route>
<Route path='/login' exact component={Login}></Route>
<Route path='/detail/:id' exact component={Detail}></Route>
</HashRouter>
)
}
}
Route: 用来控制路径对应显示的组件
- path:指定路由跳转路径
- exact:精确匹配路由
- component:路由对应的组件
- render:通过写render函数返回具体的dom
- location: 将 与当前历史记录位置以外的位置相匹配,则此功能在路由过渡动效中非常有用
- sensitive:是否区分路由大小写
- strict: 是否配置路由后面的 '/'
<Route path='/about' exact render={() => <About /> }></Route>
Switch:只是匹配到第一个路由后,就不再继续匹配
<Switch>
<Route path='/home' component={Home}></Route>
<Route path='/login' component={Login}></Route>
<Route path='/detail' exact component={detail}></Route>
<Route path='/detail/:id' component={detailId}></Route>
<Redirect to="/home" from='/' /> //重定向
</Switch>
【注意】:如果路由 Route 外部包裹 Switch 时,路由匹配到对应的组件后,就不会继续渲染其他组件了。但是如果外部不包裹 Switch 时,所有路由组件会先渲染一遍,然后选择到匹配的路由进行显示。
Link 和 NavLink:它们都可以用来指定路由跳转,NavLink 的可选参数更多。
Link跳转
- pathname: 表示要链接到的路径的字符串。
- search: 表示查询参数的字符串形式。
- hash: 放入网址的 hash,例如 #a-hash。
- state: 状态持续到 location。通常用于隐式传参(埋点),可以用来统计页面来源
通过字符串执行跳转路由:
<Link to='/login'>
<span>登录</span>
</Link>
通过对象指定跳转路由:
<Link to={{
pathname: '/login',
search: '?name=cedric',
hash: '#someHash',
state: { fromWechat: true }
}}>
<span>登录</span>
</Link>
NavLink跳转:
可以看做 一个特殊版本的 Link,当它与当前 URL 匹配时,为其渲染元素添加样式属性。
- exact: 如果为 true,则仅在位置完全匹配时才应用 active 的类/样式。
- strict: 当为 true,要考虑位置是否匹配当前的URL时,pathname 尾部的斜线要考虑在内。
- location 接收一个location对象,当url满足这个对象的条件才会跳转
- isActive: 接收一个回调函数,只有当 active 状态变化时才能触发,如果返回false则跳转失败
<NavLink
to="/login"
activeStyle={{
fontWeight: 'bold',
color: 'red'
}}
>
<span>登录</span>
</NavLink>
或
const oddEvent = (match, location) => {
if (!match) {
return false
}
const eventID = parseInt(match.params.eventID)
return !isNaN(eventID) && eventID % 2 === 1
}
<NavLink
to="/login"
isActive={oddEvent}
>login</NavLink>
withRouter
withRouter 是一个高阶组件,可以将一个非路由组件包裹返回一个新的路由组件,使这个非路由组件也能访问到当前路由的 match、location、history 对象,同时还拥有非路由组件的特点。
import { Typography } from "antd";
// 高阶组件 把两个组件的优点合二为一 类似于手机和手机壳关系
import { withRouter } from "react-router-dom/cjs/react-router-dom";
const Proimg11 = (props) => {
return (
<div onClick={() => props.history.push(`detail/${props.id}`)}>
{
props.size == 'large' ? (
<img src={props.imageSrc} height={285} width={490} alt="" />
) : (
<img src={props.imageSrc} height={120} width={240} alt="" />
)
}
<div>
<Typography.Text type="secondary">
{props.title.slice(0, 25)}
</Typography.Text>
<Typography.Text type="danger" strong>
¥{props.price}起
</Typography.Text>
</div>
</div>
)
}
// 为什么 必须包裹withRouter才能生效
export const Proimg = withRouter(Proimg11)
// withRouter + Proimg11 两者优点合二为一 变成 Proimg 组件
// 将 withRouter 的逻辑和 Proimg11 的UI组合路由的三种传参:params、search、state
params:
路由链接(携带参数):<Link to='/demo/test/tom/18'}>详情</Link>
注册路由(声明接收):<Route path="/demo/test/:name/:age" component={Test}/>
接收参数:this.props.match.params
search:
路由链接(携带参数):<Link to='/demo/test?name=tom&age=18'}>详情</Link>
注册路由(无需声明,正常注册即可):<Route path="/demo/test" component={Test}/>
接收参数:this.props.location.search
// 接收search参数
import qs from 'querystring'
const {search} = this.props.location
const {id, title} = qs.parse(search.slice(1))
//备注:获取到的search是urlencoded编码字符串,需要借助querystring解析
let obj = {name: 'tom', age: 18}
console.log(qs.stringify((obj)));// name=tom&age=18 key=value&key=value (urlencoded)
let str = 'cartName=奔驰&price=199'
console.log(qs.parse(str));// {cartName: "奔驰", price: "199"}
state:
路由链接(携带参数):
<Link to={{pathname:'/demo/test',state:{name:'tom',age:18}}}>详情</Link>
注册路由(无需声明,正常注册即可):
<Route path="/demo/test" component={Test}/>
接收参数:this.props.location.state
//备注:刷新也可以保留住参数(hash路由刷新参数会丢失)

![[golang gin框架] 29.Gin 商城项目-用户登录,注册操作](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/8a833de536380bbfa7a8347e9a8dcb10.png)