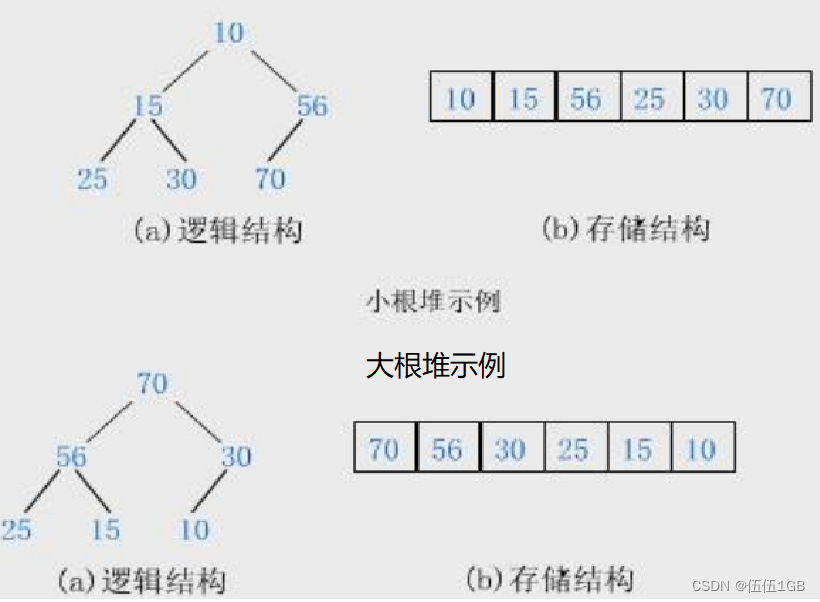
文件系统相关的数据结构
4.1 file结构体
-
文件结构体代表一个打开的文件,系统中的每个打开的文件在内核空间都有一个关联的struct file。它由内核在打开文件时创建,并传递给在文件上进行操作的任何函数。在文件的所有实例都关闭后,内核释放这个数据结构。
struct file { /* * fu_list becomes invalid after file_free is called and queued via * fu_rcuhead for RCU freeing */ union { struct list_head fu_list; //所有打开的文件形成一个链表 struct rcu_head fu_rcuhead; } f_u; struct path f_path; #define f_dentry f_path.dentry #define f_vfsmnt f_path.mnt const struct file_operations *f_op; //指向文件操作表的指针 spinlock_t f_lock; // f_ep_links, f_flags, no IRQ atomic_long_t f_count; //记录对文件对象的引用计数,也即当前有多少个进程在使用该文件 unsigned int f_flags; //打开文件时用户指定的标志,对应open的flags参数。 fmode_t f_mode; //对文件的读写模式,对应open的mode参数,unsigned int类型 loff_t f_pos; //当前的文件指针位置,即文件的读写位置,long long类型 struct fown_struct f_owner; //通过信号进行I/O时通知的数据 const struct cred *f_cred; struct file_ra_state f_ra; u64 f_version; //记录文件的版本号,每次使用后都自动递增 #ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY void *f_security; #endif void *private_data; #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL struct list_head f_ep_links; //文件的事件轮询等待者链表的头 struct list_head f_tfile_llink; #endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL */ struct address_space *f_mapping; //指向文件地址空间的指针 #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_WRITECOUNT unsigned long f_mnt_write_state; #endif }; -
成员解析:
-
fu_rcuhead:RCU(Read-Copy Update)是Linux 2.6内核中新的锁机制
/* *定义在linux/include/linux/rcupdate.h中 */ struct rcu_head { struct rcu_head *next; void (*func)(struct rcu_head *head); }; -
fu_path
/* 定义在linux/include/linux/namei.h中 */ struct path { struct vfsmount *mnt; //指出该文件的已安装的文件系统,即指向VFS安装点的指针 struct dentry *dentry;//与文件相关的目录项对象,指向相关目录项的指针 }; -
file_operations:当打开一个文件时,内核就创建一个与该文件相关联的struct file结构,其中的*f_op就指向的是具体对该文件进行操作的函数。例如用户调用系统调用read来读取该文件的内容时,那么系统调用read最终会陷入内核调用sys_read函数,而sys_read最终会调用于该文件关联的struct file结构中的f_op->read函数对文件内容进行读取。
//定义在linux/include/linux/fs.h中,其中包含着与文件关联的操作,例如 struct file_operations { struct module *owner; loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int); ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); ssize_t (*aio_read) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t); ssize_t (*aio_write) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t); int (*readdir) (struct file *, void *, filldir_t); unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *); int (*ioctl) (struct inode *, struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *); int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *); int (*flush) (struct file *, fl_owner_t id); int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *); int (*fsync) (struct file *, struct dentry *, int datasync); int (*aio_fsync) (struct kiocb *, int datasync); int (*fasync) (int, struct file *, int); int (*lock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *); ssize_t (*sendpage) (struct file *, struct page *, int, size_t, loff_t *, int); unsigned long (*get_unmapped_area)(struct file *, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long); int (*check_flags)(int); int (*flock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *); ssize_t (*splice_write)(struct pipe_inode_info *, struct file *, loff_t *, size_t, unsigned int); ssize_t (*splice_read)(struct file *, loff_t *, struct pipe_inode_info *, size_t, unsigned int); int (*setlease)(struct file *, long, struct file_lock **); }; -
f_owner:
struct fown_struct在linux/include/linux/fs.h被定义。struct fown_struct { rwlock_t lock; /* protects pid, uid, euid fields */ struct pid *pid; /* pid or -pgrp where SIGIO should be sent */ enum pid_type pid_type; /* Kind of process group SIGIO should be sent to */ uid_t uid, euid; /* uid/euid of process setting the owner */ int signum; /* posix.1b rt signal to be delivered on IO */ }; -
f_ra:该结构标识了文件预读状态,文件预读算法使用的主要数据结构,当打开一个文件时,f_ra中出了prev_page(默认为-1)和ra_pages(对该文件允许的最大预读量)这两个字段外,其他的所有东西都置为0
//位/linux/include/linux/fs.h中 struct file_ra_state { pgoff_t start; /* where readahead started */ unsigned long size; /* # of readahead pages */ unsigned long async_size; /* do asynchronous readahead when there are only # of pages ahead */ unsigned long ra_pages; /* Maximum readahead window */ unsigned long mmap_hit; /* Cache hit stat for mmap accesses */ unsigned long mmap_miss; /* Cache miss stat for mmap accesses */ unsigned long prev_index; /* Cache last read() position */ unsigned int prev_offset; /* Offset where last read() ended in a page */ }; -
f_security:如果在编译内核时配置了安全措施,那么struct file结构中就会有
void *f_security数据项,用来描述安全措施或者是记录与安全有关的信息。 -
f_private_data:系统在调用驱动程序的open方法前将这个指针置为NULL。驱动程序可以将这个字段用于任意目的,也可以忽略这个字段。驱动程序可以用这个字段指向已分配的数据,但是一定要在内核释放file结构前的release方法中清除它。
-
-
每个文件对象总是包含在下列的一个双向循环链表之中:
- "未使用"文件对象的链表——该链表既可以用做文件对象的内存高速缓存,又可以当作超级用户的备用存储器,也就是说,即使系统的动态内存用完,也允许超级用户打开文件。由于这些对象是未使用的,它们的f_count域是NULL,该链表首元素的地址存放在变量
free_list中,内核必须确认该链表总是至少包含NR_RESERVED_FILES个对象,通常该值设为10 - "正在使用"文件对的象链表——该链表中的每个元素至少由一个进程使用,因此,各个元素的
f_count域不会为NULL,该链表中第一个元素的地址存放在变量anon_list中。如果VFS需要分配一个新的文件对象,就调用函数get_empty_filp()。该函数检测"未使用"文件对象链表的元素个数是否多于NR_RESERVED_FILES,如果是,可以为新打开的文件使用其中的一个元素;如果没有,则退回到正常的内存分配,也就是说这是一种高速缓存机制。
- "未使用"文件对象的链表——该链表既可以用做文件对象的内存高速缓存,又可以当作超级用户的备用存储器,也就是说,即使系统的动态内存用完,也允许超级用户打开文件。由于这些对象是未使用的,它们的f_count域是NULL,该链表首元素的地址存放在变量
-
拓展链接:
- http://linux.chinaunix.net/techdoc/system/2008/07/24/1020195.shtml
- http://blog.csdn.net/fantasyhujian/article/details/9166117
4.2 inode结构体
-
在linux内核中,用file结构表示打开的文件描述符,而用inode结构表示具体的文件。
struct inode { struct hlist_node i_hash; //哈希表 struct list_head i_list; //索引节点链表 struct list_head i_sb_list; struct list_head i_dentry; //目录项链表 unsigned long i_ino; //节点号 atomic_t i_count; //引用记数 unsigned int i_nlink; //硬链接数 uid_t i_uid; //使用者id gid_t i_gid; //使用者所在组id dev_t i_rdev; //实设备标识符 u64 i_version; //版本号 loff_t i_size; //以字节为单位的文件大小 #ifdef __NEED_I_SIZE_ORDERED seqcount_t i_size_seqcount; #endif struct timespec i_atime; //最后访问时间 struct timespec i_mtime; //最后修改(modify)时间 struct timespec i_ctime; //最后改变(change)时间 blkcnt_t i_blocks; //文件的块数 unsigned int i_blkbits; //以位为单位的块大小 unsigned short i_bytes;//使用的字节数 umode_t i_mode; //访问权限控制 spinlock_t i_lock; //自旋锁 struct mutex i_mutex; struct rw_semaphore i_alloc_sem; //索引节点信号量 const struct inode_operations *i_op; //索引节点操作 const struct file_operations *i_fop; //默认的索引节点操作 struct super_block *i_sb; //相关的超级块 struct file_lock *i_flock; //文件锁链表 struct address_space *i_mapping; //相关的地址映射 struct address_space i_data; #ifdef CONFIG_QUOTA struct dquot *i_dquot[MAXQUOTAS]; //节点的磁盘限额 #endif struct list_head i_devices; //块设备链表 union { struct pipe_inode_info *i_pipe; //管道信息 struct block_device *i_bdev; //块设备驱动 struct cdev *i_cdev; }; __u32 i_generation; //索引节点版本号 #ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY __u32 i_fsnotify_mask; //目录通知掩码 struct hlist_head i_fsnotify_mark_entries; /* fsnotify mark entries */ #endif #ifdef CONFIG_INOTIFY struct list_head inotify_watches; /* watches on this inode */ struct mutex inotify_mutex; /* protects the watches list */ #endif unsigned long i_state; //状态标志 unsigned long dirtied_when; //首次修改时间 unsigned int i_flags; //文件系统标志 atomic_t i_writecount; //写者记数 #ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY void *i_security; //安全模块 #endif #ifdef CONFIG_FS_POSIX_ACL struct posix_acl *i_acl; struct posix_acl *i_default_acl; #endif void *i_private; /* fs or device private pointer */ }; -
成员解析:
-
i_op:索引节点操作表
// 索引节点的操作inode_operations定义在linux/fs.h struct inode_operations { /* 1. VFS通过系统调用create()和open()来调用该函数, 从而为dentry对象创建一个新的索引节点。在创建时使用mode制定初始模式 */ int (*create) (struct inode *, struct dentry *,int); /* 2. 该函数在特定目录中寻找索引节点,该索引节点要对应于dentry中给出的文件名 */ struct dentry * (*lookup) (struct inode *, struct dentry *); /* 3. 该函数被系统调用link()调用,用来创建硬连接。硬链接名称由dentry参数指定, 连接对象是dir目录中ld_dentry目录想所代表的文件 */ int (*link) (struct dentry *, struct inode *, struct dentry *); /* 4. 该函数被系统调用unlink()调用,从目录dir中删除由目录项dentry制动的索引节点对象 */ int (*unlink) (struct inode *, struct dentry *); /* 5. 该函数被系统调用symlik()调用,创建符号连接,该符号连接名称由symname指定, 连接对象是dir目录中的dentry目录项 */ int (*symlink) (struct inode *, struct dentry *, const char *); /* 6. 该函数被mkdir()调用,创建一个新路径。创建时使用mode制定的初始模式 */ int (*mkdir) (struct inode *, struct dentry *, int); /* 7. 该函数被系统调用rmdir()调用,删除dir目录中的dentry目录项代表的文件 */ int (*rmdir) (struct inode *, struct dentry *); /* 8. 该函数被系统调用mknod()调用,创建特殊文件(设备文件、命名管道或套接字)。 要创建的文件放在dir目录中,其目录项问dentry,关联的设备为rdev,初始权限由mode指定 */ int (*mknod) (struct inode *, struct dentry *, int, dev_t); /* 9. VFS调用该函数来移动文件。文件源路径在old_dir目录中,源文件由old_dentry目录项所指定, 目标路径在new_dir目录中,目标文件由new_dentry指定 */ int (*rename) (struct inode *, struct dentry *, struct inode *, struct dentry *); /* 10. 该函数被系统调用readlink()调用,拷贝数据到特定的缓冲buffer中。 拷贝的数据来自dentry指定的符号链接,最大拷贝大小可达到buflen字节 */ int (*readlink) (struct dentry *, char *, int); /* 11. 该函数由VFS调用,从一个符号连接查找他指向的索引节点,由dentry指向的连接被解析 */ int (*follow_link) (struct dentry *, struct nameidata *); /* 12. 在follow_link()调用之后,该函数由vfs调用进行清楚工作 */ int (*put_link) (struct dentry *, struct nameidata *); /* 13. 该函数由VFS调用,修改文件的大小,在调用之前,索引节点的i_size项必须被设置成预期的大小 */ void (*truncate) (struct inode *); /* 该函数用来检查inode所代表的文件是否允许特定的访问模式,如果允许特定的访问模式,返回0, 否则返回负值的错误码。多数文件系统都将此区域设置为null,使用VFS提供的通用方法进行检查, 这种检查操作仅仅比较索引及诶但对象中的访问模式位是否和mask一致,比较复杂的系统, 比如 支持访问控制链(ACL)的文件系统,需要使用特殊的permission()方法 */ int (*permission) (struct inode *, int); /* 该函数被notify_change调用,在修改索引节点之后,通知发生了改变事件 */ int (*setattr) (struct dentry *, struct iattr *); /* 在通知索引节点需要从磁盘中更新时,VFS会调用该函数 */ int (*getattr) (struct vfsmount *, struct dentry *, struct kstat *); /* 该函数由VFS调用,向dentry指定的文件设置扩展属性,属性名为name,值为value */ int (*setxattr) (struct dentry *, const char *, const void *, size_t, int); /* 该函数被VFS调用,向value中拷贝给定文件的扩展属性name对应的数值 */ ssize_t (*getxattr) (struct dentry *, const char *, void *, size_t); /* 该函数将特定文件所有属性别表拷贝到一个缓冲列表中 */ ssize_t (*listxattr) (struct dentry *, char *, size_t); /* 该函数从给定文件中删除指定的属性 */ int (*removexattr) (struct dentry *, const char *); }; -
i_data:设备地址映射。
- address_space结构与文件的对应:一个具体的文件在打开后,内核会在内存中为之建立一个struct inode结构,其中的i_mapping域指向一个address_space结构。这样,一个文件就对应一个address_space结构,一个 address_space与一个偏移量能够确定一个page cache 或swap cache中的一个页面。因此,当要寻址某个数据时,很容易根据给定的文件及数据在文件内的偏移量而找到相应的页面。
-
4.3 stat结构体
-
struct stat在我们进行文件、目录属性读写、磁盘IO状态监控的时候常常会用到的数据结构。
struct stat { dev_t st_dev; // ID of device containing file -文件所在设备的ID ino_t st_ino; // inode number -inode节点号 mode_t st_mode; // protection -保护模式? nlink_t st_nlink; // number of hard links -链向此文件的连接数(硬连接) uid_t st_uid; // user ID of owner -user id gid_t st_gid; // group ID of owner - group id dev_t st_rdev; // device ID (if special file) -设备号,针对设备文件 off_t st_size; // total size, in bytes -文件大小,字节为单位 blksize_t st_blksize; // blocksize for filesystem I/O -系统块的大小 blkcnt_t st_blocks; // number of blocks allocated -文件所占块数 time_t st_atime; // time of last access - 最近存取时间 time_t st_mtime; // time of last modification - 最近修改时间 time_t st_ctime; // time of last status change - 最近创建时间 }; -
拓展链接
- http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_7943319e01018m4h.html
- http://www.cnblogs.com/QJohnson/archive/2011/06/24/2089414.html
- http://blog.csdn.net/tianmohust/article/details/6609470
4.4 fs_struct结构体
-
系统上的每个进程都有自己的打开文件列表、根文件系统、当前工作目录、挂载点等。file_struct、fs_struct和namespace 这三个数据结构将VFS层与系统上的进程联系起来。
-
第二个与进程相关的结构是fs_struct,它包含与进程相关的文件系统信息,并由进程描述符的fs字段指向。该结构体定义在 <linux/fs_struct.h>。
-
struct fs_struct { atomic_t count; //共享这个表的进程个数 rwlock_t lock; //用于表中字段的读/写自旋锁 int umask; //当打开文件设置文件权限时所使用的位掩码 struct dentry * root; //根目录的目录项 struct dentry * pwd; //当前工作目录的目录项 struct dentry * altroot;//模拟根目录的目录项(在80x86结构上始终为NULL) struct vfsmount * rootmnt; //根目录所安装的文件系统对象 struct vfsmount* pwdmnt; //当前工作目录所安装的文件系统对象 struct vfsmount* altrootmnt; //模拟根目录所安装的文件系统对象(在80x86结构上始终为NULL) };
4.5 files_struct结构体
-
files_struct定义在<linux/file.h>中。该表的地址由处理器描述符中的files entry指向。所有关于打开文件和文件描述符的进程级信息都包含在其中。
-
表示进程当前打开的文件,表的地址存放于进程描述符task_struct的files字段,每个进程用一个files_struct结构来记录文件描述符的使用情况,这个files_struct结构称为用户打开文件表,它是进程的私有数据。
struct files_struct { atomic_t count; //共享该表的进程数 struct fdtable *fdt; //指向fdtable结构的指针 struct fdtable fdtab; //指向fdtable结构 spinlock_t file_lock ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp; int next_fd; //已分配的文件描述符加1 struct embedded_fd_set close_on_exec_init; //指向执行exec()时需要关闭的文件描述符 struct embedded_fd_set open_fds_init; //文件描述符的初值集合 struct file * fd_array[NR_OPEN_DEFAULT]; //文件对象指针的初始化数组 };
4.6 fdtable结构体
struct fdtable
{
unsigned int max_fds;
int max_fdset;
/*
current fd array
指向文件对象的指针数组,通常,fd字段指向files_struct结构的fd_array字段,该字段包括32个文件对象指针。如果进程打开的文件数目多于32,内核就分配一个新的、更大的文件指针数组,并将其地址存放在fd字段中,内核同时也更新max_fds字段的值
对于在fd数组中所有元素的每个文件来说,数组的索引就是文件描述符(file descriptor)。通常,数组的第一个元素(索引为0)是进程的标准输入文件,数组的第二个元素(索引为1)是进程的标准输出文件,数组的第三个元素(索引为2)是进程的标准错误文件
*/
struct file ** fd;
fd_set *close_on_exec;
fd_set *open_fds;
struct rcu_head rcu;
struct files_struct *free_files;
struct fdtable *next;
};
#define NR_OPEN_DEFAULT BITS_PER_LONG
#define BITS_PER_LONG 32 /* asm-i386 */
- 用一张图表示task_struct、fs_struct、files_struct、fdtable、file的关系:
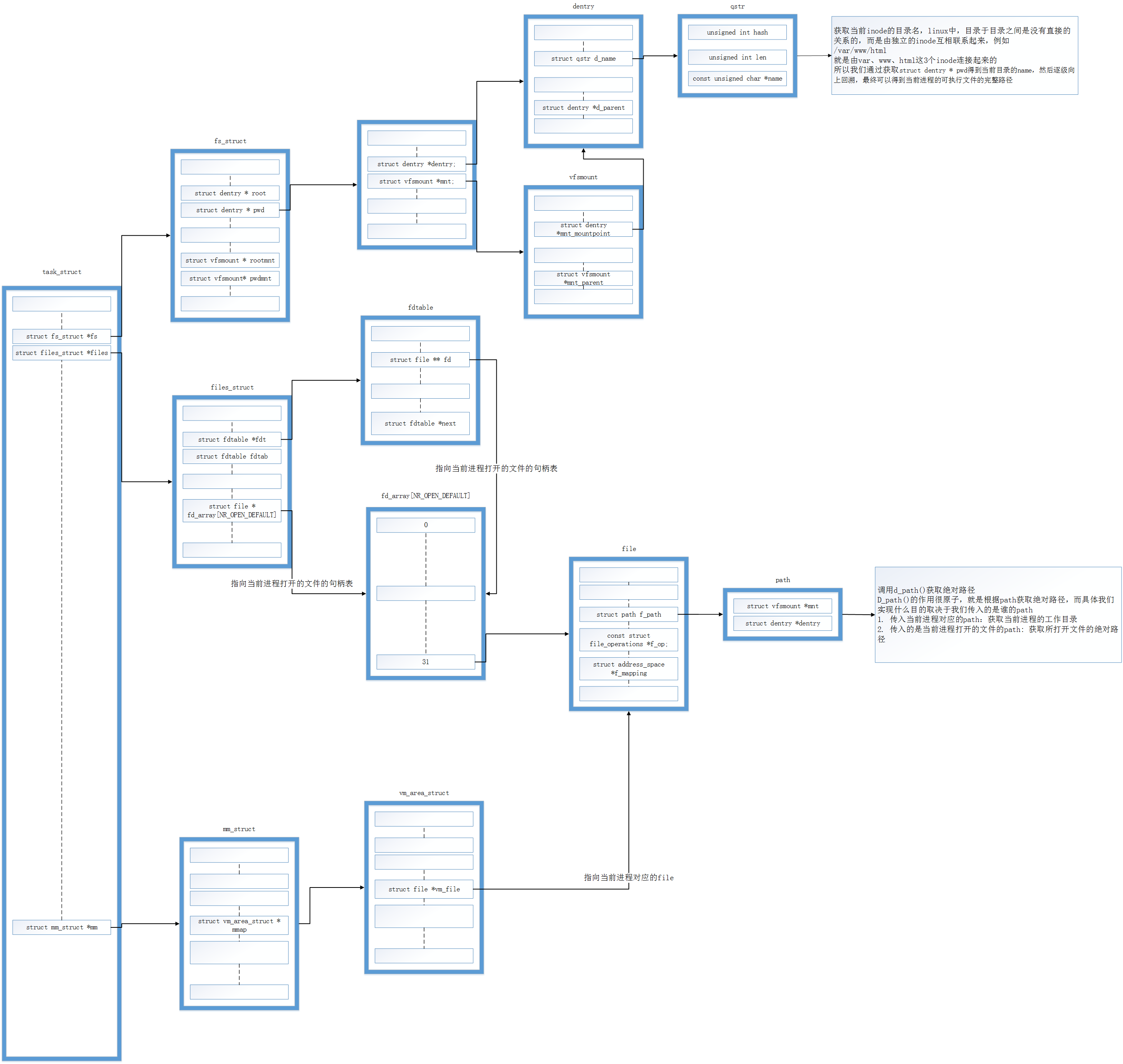
- 拓展链接
- http://oss.org.cn/kernel-book/ch08/8.2.4.htm
- http://www.makelinux.net/books/lkd2/ch12lev1sec10
4.7 dentry结构体
struct dentry
{
//目录项引用计数器
atomic_t d_count;
unsigned int d_flags;
//per dentry lock
spinlock_t d_lock;
int d_mounted; //如果当前dentry对象表示一个装载点,那么d_mounted设置为1,否则为0
struct inode *d_inode; //文件名所属的inode,如果为NULL,则表示不存在的文件名
/*
The next three fields are touched by __d_lookup. Place them here so they all fit in a cache line.
*/
struct hlist_node d_hash; //用于查找的散列表
struct dentry *d_parent; //指向当前的dentry实例的父dentry实例,对于根目录(没有父目录),
//d_parent指向其自身的dentry实例.当前的dentry实例即位于
//父目录的d_subdirs链表中
/*
d_iname指定了文件的名称,qstr是一个内核字符串的包装器,它存储了实际的char*字符串以及字符串长度和散列值,这使得更容易处理查找工作. 要注意的是,这里并不存储绝对路径,而是只有路径的最后一个分量,例如对/usr/bin/emacs只存储emacs,因为在linux中,路径信息隐含在了dentry层次链表结构中了
*/
struct qstr d_name;
struct list_head d_lru; //LRU list
/*
* d_child and d_rcu can share memory
*/
union
{
/* child of parent list */
struct list_head d_child;
struct rcu_head d_rcu; //用于将dentry连接到inode的i_dentry链表中
} d_u;
struct list_head d_subdirs; //子目录/文件的目录项链表
/*
d_alias用作链表元素,以连接表示相同文件的各个dentry对象,在利用硬链接用两个不同名称表示同一文件时,会发生这种情况,对应于文件的inode的i_dentry成员用作该链表的表头,各个dentry对象通过d_alias连接到该链表中
*/
struct list_head d_alias;
unsigned long d_time; //used by d_revalidate
const struct dentry_operations *d_op;
struct super_block *d_sb; //dentry树的根,超级块
void *d_fsdata; //特定文件系统的数据
/*
短文件名small names存储在这里
如果文件名由少量字符组成,则只保存在d_iname中,而不是dname中,用于加速访问
*/
unsigned char d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN_MIN];
};
-
成员分析:
-
d_flags:目录项标志,由 d_lock进行读写保护。
#define DCACHE_AUTOFS_PENDING 0x0001 // autofs: "under construction" #define DCACHE_NFSFS_RENAMED 0x0002 // 这个dentry已经被“重命名”了,必须在最后一次dput()之后删除。 #define DCACHE_DISCONNECTED 0x0004 //指定了一个dentry当前没有连接到超级块的dentry树 #define DCACHE_REFERENCED 0x0008 //Recently used, don't discard. #define DCACHE_UNHASHED 0x0010 //该dentry实例没有包含在任何inode的散列表中 #define DCACHE_INOTIFY_PARENT_WATCHED 0x0020 // Parent inode is watched by inotify #define DCACHE_COOKIE 0x0040 // For use by dcookie subsystem #define DCACHE_FSNOTIFY_PARENT_WATCHED 0x0080 // Parent inode is watched by some fsnotify listener -
d_op: 指向一个结构,其中包含了各种函数指针,提供对dentry对象的各种操作,这些操作必须由底层文件系统实现
struct dentry_operations { //在把目录项对象转换为一个文件路径名之前,判定该目录项对象是否依然有效 int (*d_revalidate)(struct dentry *, struct nameidata *); //生成一个散列值,用于目录项散列表 int (*d_hash) (struct dentry *, struct qstr *); //比较两个文件名 int (*d_compare) (struct dentry *, struct qstr *, struct qstr *); //当对目录项对象的最后一个引用被删除,调用该方法 int (*d_delete)(struct dentry *); //当要释放一个目录项对象时,调用该方法 void (*d_release)(struct dentry *); //当一个目录对象变为负状态时,调用该方法 void (*d_iput)(struct dentry *, struct inode *); char *(*d_dname)(struct dentry *, char *, int); };
-
-
拓展链接:
- http://blog.csdn.net/fudan_abc/article/details/1775313
4.8 vfsmount结构体
struct vfsmount
{
struct list_head mnt_hash;
//装载点所在的父文件系统的vfsmount结构
struct vfsmount *mnt_parent;
//装载点在父文件系统中的dentry,即装载点自身对应的dentry
struct dentry *mnt_mountpoint;
//当前文件系统的相对根目录的dentry
struct dentry *mnt_root;
/*
指向超级块的指针 pointer to superblock
mnt_sb指针建立了与相关的超级块之间的关联(对每个装载的文件系统而言,都有且只有一个超级块实例)
*/
struct super_block *mnt_sb;
//子文件系统链表
struct list_head mnt_mounts;
//链表元素,用于父文件系统中的mnt_mounts链表
struct list_head mnt_child;
int mnt_flags;
/* 4 bytes hole on 64bits arches */
const char *mnt_devname; //设备名称,例如/dev/dsk/hda1
struct list_head mnt_list;
//链表元素,用于特定于文件系统的到期链表中
struct list_head mnt_expire;
//链表元素,用于共享装载的循环链表
struct list_head mnt_share;
//从属装载的链表
struct list_head mnt_slave_list;
//链表元素,用于从属装载的链表项
struct list_head mnt_slave;
//指向主装载,从属装载位于master->mnt_slave_list链表上
struct vfsmount *mnt_master;
//所属的命名空间
struct mnt_namespace *mnt_ns;
int mnt_id; /* mount identifier */
int mnt_group_id; /* peer group identifier */
/*
mnt_count实现了一个使用计数器,每当一个vfsmount实例不再需要时,都必须用mntput将计数器减1.mntget与mntput相对
我们在结构体vfsmount的末尾放置了mnt_count和mnt_expiry_mark,以使这些经常修改的字段位于单独的缓存行中(这样在SMP计算机上读取mnt_flags就不会产生乒乓效应)。
*/
atomic_t mnt_count;
int mnt_expiry_mark; //如果标记为到期,则其值为true
int mnt_pinned;
int mnt_ghosts;
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
int *mnt_writers;
#else
int mnt_writers;
#endif
};
-
成员解析
-
mm_flags:
#define MNT_NOSUID 0x01 (禁止setuid执行) #define MNT_NODEV 0x02 (装载的文件系统是虚拟的,没有物理后端设备) #define MNT_NOEXEC 0x04 #define MNT_NOATIME 0x08 #define MNT_NODIRATIME 0x10 #define MNT_RELATIME 0x20 #define MNT_READONLY 0x40 // does the user want this to be r/o? #define MNT_STRICTATIME 0x80 #define MNT_SHRINKABLE 0x100 (专用于NFS、AFS 用来标记子装载,设置了该标记的装载允许自动移除) #define MNT_WRITE_HOLD 0x200 #define MNT_SHARED 0x1000 //共享装载 #define MNT_UNBINDABLE 0x2000 //不可绑定装载 #define MNT_PNODE_MASK 0x3000 //传播标志掩码
-
-
拓展链接
- http://www.cnblogs.com/Wandererzj/archive/2012/04/12/2444888.html
4.9 nameidata结构体
-
路径查找是VFS的一个很重要的操作:给定一个文件名,获取该文件名的inode。路径查找是VFS中相当繁琐的一部分,主要是因为:
- 符号链接——一个文件可能通过符号链接引用另一个文件,查找代码必须考虑到这种可能性,能够识别出链接,并在相应的处理后跳出循环
- 文件系统装载点——必须检测装载点,而后据此重定向查找操作
- 在通向目标文件名的路径上,必须检查所有目录的访问权限,进程必须有适当的权限,否则操作将终止,并给出错误信息
.以及..·以及/等特殊路径引入了复杂性
-
路径查找过程涉及到很多函数调用,在这些调用过程中,nameidata起到了很重要的作用:
- 向查找函数传递参数
- 保存查找结果
-
inode是类Unix系统的文件系统的基本索引方法,每个文件都对应一个inode,再通过inode找到文件中的实际数据,因此根据文件路径名找到具体的inode节点就是一个很重要的处理步骤。系统会缓存用过的每个文件或目录对应的dentry结构, 从该结构可以指向相应的inode, 每次打开文件, 都会最终对应到文件的inode,中间查找过程称为namei。结构体定义如下
struct nameidata { /* 用于确定文件路径 struct path { struct vfsmount *mnt; struct dentry *dentry; }; */ struct path path; //需要查找的名称,这是一个快速字符串,除了路径字符串本身外,还包含字符串的长度和一个散列值 struct qstr last; struct path root; unsigned int flags; int last_type; //当前路径深度 unsigned depth; //由于在符号链接处理时,nd的名字一直发生变化,这里用来保存符号链接处理中的路径名 char *saved_names[MAX_NESTED_LINKS + 1]; /* Intent data */ union { struct open_intent open; } intent; }; -
拓展链接
- http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man7/path_resolution.7.html
- http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4a2f24830100l2h4.html
- http://blog.csdn.net/kickxxx/article/details/9529961
- http://blog.csdn.net/air_snake/article/details/2690554
- http://losemyheaven.blog.163.com/blog/static/17071980920124593256317/
4.10 super_block结构体
/*
* /source/include/linux/fs.h
*/
struct super_block
{
/*
指向超级块链表的指针,用于将系统中所有的超级块聚集到一个链表中,该链表的表头是全局变量super_blocks
*/
struct list_head s_list;
dev_t s_dev; //设备标识符
//以字节为单位的块大小
unsigned long s_blocksize;
//以位为单位的块大小
unsigned char s_blocksize_bits;
//修改脏标志,如果以任何方式改变了超级块,需要向磁盘回写,都会将s_dirt设置为1,否则为0
unsigned char s_dirt;
//文件大小上限 Max file size
loff_t s_maxbytes;
//文件系统类型
struct file_system_type *s_type;
const struct super_operations *s_op;
//磁盘限额方法
const struct dquot_operations *dq_op;
//磁盘限额方法
const struct quotactl_ops *s_qcop;
//导出方法
const struct export_operations *s_export_op;
//挂载标志
unsigned long s_flags;
//文件系统魔数
unsigned long s_magic;
//目录挂载点
struct dentry *s_root;
//卸载信号量
struct rw_semaphore s_umount;
//超级块信号量
struct mutex s_lock;
//引用计数
int s_count;
//尚未同步标志
int s_need_sync;
//活动引用计数
atomic_t s_active;
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *s_security; //安全模块
#endif
struct xattr_handler **s_xattr;
//all inodes
struct list_head s_inodes;
//匿名目录项
struct hlist_head s_anon;
//被分配文件链表,列出了该超级块表示的文件系统上所有打开的文件。内核在卸载文件系统时将参考该列表,如果其中仍然包含为写入而打开的文件,则文件系统仍然处于使用中,卸载操作失败,并将返回适当的错误信息
struct list_head s_files;
/* s_dentry_lru and s_nr_dentry_unused are protected by dcache_lock */
struct list_head s_dentry_lru;
//unused dentry lru of dentry on lru
int s_nr_dentry_unused;
//指向了底层文件系统的数据所在的相关块设备
struct block_device *s_bdev;
struct backing_dev_info *s_bdi;
struct mtd_info *s_mtd;
//该类型文件系统
struct list_head s_instances;
//限额相关选项 Diskquota specific options
struct quota_info s_dquot;
int s_frozen;
wait_queue_head_t s_wait_unfrozen;
//文本名字 Informational name
char s_id[32];
//Filesystem private info
void *s_fs_info;
fmode_t s_mode;
/*
* The next field is for VFS *only*. No filesystems have any business
* even looking at it. You had been warned.
*/
struct mutex s_vfs_rename_mutex; /* Kludge */
/* Granularity of c/m/atime in ns. Cannot be worse than a second 指定了文件系统支持的各种时间戳的最大可能的粒度 */
u32 s_time_gran;
/*
* Filesystem subtype. If non-empty the filesystem type field
* in /proc/mounts will be "type.subtype"
*/
char *s_subtype;
/*
* Saved mount options for lazy filesystems using
* generic_show_options()
*/
char *s_options;
};
-
成员解析
-
s_op:
struct super_operations { //给定的超级块下创建和初始化一个新的索引节点对象; struct inode *(*alloc_inode)(struct super_block *sb); //用于释放给定的索引节点; void (*destroy_inode)(struct inode *); //VFS在索引节点脏(被修改)时会调用此函数,日志文件系统(如ext3,ext4)执行该函数进行日志更新; void (*dirty_inode) (struct inode *); //用于将给定的索引节点写入磁盘,wait参数指明写操作是否需要同步; int (*write_inode) (struct inode *, struct writeback_control *wbc); //在最后一个指向索引节点的引用被释放后,VFS会调用该函数,VFS只需要简单地删除这个索引节点后,普通Uinx文件系统就不会定义这个函数了; void (*drop_inode) (struct inode *); //用于从磁盘上删除给定的索引节点; void (*delete_inode) (struct inode *); //在卸载文件系统时由VFS调用,用来释放超级块,调用者必须一直持有s_lock锁; void (*put_super) (struct super_block *); //用给定的超级块更新磁盘上的超级块。VFS通过该函数对内存中的超级块和磁盘中的超级块进行同步。调用者必须一直持有s_lock锁; void (*write_super) (struct super_block *); //使文件系统的数据元与磁盘上的文件系统同步。wait参数指定操作是否同步; int (*sync_fs)(struct super_block *sb, int wait); int (*freeze_fs) (struct super_block *); int (*unfreeze_fs) (struct super_block *); //VFS通过调用该函数获取文件系统状态。指定文件系统县官的统计信息将放置在statfs中; int (*statfs) (struct dentry *, struct kstatfs *); //当指定新的安装选项重新安装文件系统时,VFS会调用该函数。调用者必须一直持有s_lock锁; int (*remount_fs) (struct super_block *, int *, char *); //VFS调用该函数释放索引节点,并清空包含相关数据的所有页面; void (*clear_inode) (struct inode *); //VFS调用该函数中断安装操作。该函数被网络文件系统使用,如NFS; void (*umount_begin) (struct super_block *); int (*show_options)(struct seq_file *, struct vfsmount *); int (*show_stats)(struct seq_file *, struct vfsmount *); #ifdef CONFIG_QUOTA ssize_t (*quota_read)(struct super_block *, int, char *, size_t, loff_t); ssize_t (*quota_write)(struct super_block *, int, const char *, size_t, loff_t); #endif int (*bdev_try_to_free_page)(struct super_block*, struct page*, gfp_t); }; -
s_root:将超级块与全局根目录的dentry项关联起来,只有通常可见的文件系统的超级块,才指向/(根)目录的dentry实例。具有特殊功能、不出现在通常的目录层次结构中的文件系统(例如管道或套接字文件系统),指向专门的项,不能通过普通的文件命令访问。处理文件系统对象的代码经常需要检查文件系统是否已经装载,而s_root可用于该目的,如果它为NULL,则该文件系统是一个伪文件系统,只在内核内部可见。否则,该文件系统在用户空间中是可见的
-
-
拓展链接
- http://linux.chinaunix.net/techdoc/system/2008/09/06/1030468.shtml
- http://lxr.free-electrons.com/source/include/linux/fs.h
4.11 file_system_type结构体
struct file_system_type
{
//文件系统的类型名,以字符串的形式出现,保存了文件系统的名称(例如reiserfs、ext3)
const char *name;
int fs_flags;
int (*get_sb) (struct file_system_type *, int, const char *, void *, struct vfsmount *);
//kill_sb在不再需要某个文件系统类型时执行清理工作
void (*kill_sb) (struct super_block *);
struct module *owner;
//把所有的file_system_type结构链接成单项链表的链接指针,变量file_systems指向这个链表。这个链表是一个临界资源,受file_systems_lock自旋读写锁的保护
struct file_system_type * next;
struct list_head fs_supers;
struct lock_class_key s_lock_key;
struct lock_class_key s_umount_key;
struct lock_class_key i_lock_key;
struct lock_class_key i_mutex_key;
struct lock_class_key i_mutex_dir_key;
struct lock_class_key i_alloc_sem_key;
};
-
成员解析
-
fs_flags:使用的标志,指明具体文件系统的一些特性,有关标志定义于fs.h中
#define FS_REQUIRES_DEV 1 #define FS_BINARY_MOUNTDATA 2 #define FS_HAS_SUBTYPE 4 #define FS_REVAL_DOT 16384 // Check the paths ".", ".." for staleness #define FS_RENAME_DOES_D_MOVE 32768 // FS will handle d_move() during rename() internally. -
get_sb:用于从底层存储介质读取超级块的函数,地址保存在get_sb中,这个函数对装载过程很重要,逻辑上,该函数依赖具体的文件系统,不能实现为抽象,而且该函数也不能保存在super_operations结构中,因为超级块对象和指向该结构的指针都是在调用get_sb之后创建的。
-
owner:
- 如果file_system_type所代表的文件系统是通过可安装模块(LKM)实现的,则该指针指向代表着具体模块的module结构
- 如果文件系统是静态地链接到内核,则这个域为NULL
- 实际上,我们只需要把这个域置为THIS_MODLUE(宏),它就能自动地完成上述工作
-
fs_supers
- 对于每个已经装载的文件系统,在内存中都创建了一个超级块结构,该结构保存了文件系统它本身和装载点的有关信息。由于可以装载几个同一类型的文件系统(例如home、root分区,它们的文件系统类型通常相同),同一文件系统类型可能对应了多个超级块结构,这些超级块聚集在一个链表中。fs_supers是对应的表头
- 这个域是Linux2.4.10以后的内核版本中新增加的,这是一个双向链表。链表中的元素是超级块结构,每个文件系统都有一个超级块,但有些文件系统可能被安装在不同的设备上,而且每个具体的设备都有一个超级块,这些超级块就形成一个双向链表
-
-
拓展链接:http://oss.org.cn/kernel-book/ch08/8.4.1.htm