1 websocket 轻量客户端
因以前发过这个代码,但是一直没有整理,这次整理了一下,持续修改,主要是要使用在arm的linux上,发送接收的数据压缩成图片发送出去。
要达到轻量websocket 使用,必须要达到几个方面才能足够简单,
1、不用加入其他的库
2、只需要使用头文件包含就可以
3、跨平台
如果正常应用,可以使用websocketpp等库,问题就是比较麻烦,要使用boost或者asio库,当然asio也是足够简单,头文件包含,编译通过要设置参数,问题不大,不过不够简单
2 应用场景
1 windows 使用
2 linux使用
3 linux arm 板子上使用
在arm上编译的时候,就不用编译那么多的库文件了
3 原理
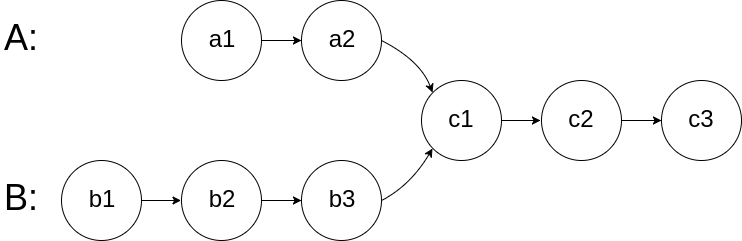
使用select模型 和原始操作系统的socket来直接编写代码,select模型比较简单,非长时间阻塞模式,以下是webscoket协议字节示意图
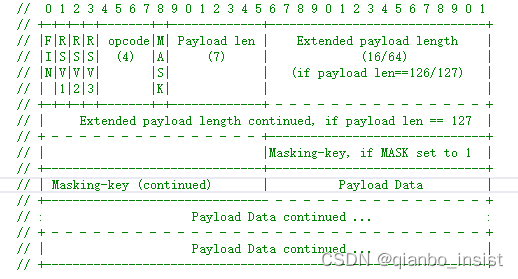
本文函数根据上图实现了websocket协议。定义的主要数据结构如下所示,websocket协议里面包含两种数据,一种是二进制,一种是文本,是可以指定的
struct wsheader_type {
unsigned header_size;
bool fin;
bool mask;
enum opcode_type {
CONTINUATION = 0x0,
TEXT_FRAME = 0x1,
BINARY_FRAME = 0x2,
CLOSE = 8,
PING = 9,
PONG = 0xa,
} opcode;
int N0;
uint64_t N;
uint8_t masking_key[4];
};
websocket链接
websocket链接使用的是http协议,所不同的是必须做upgrade
static const char* desthttp = "GET /%s HTTP/1.1\r\n"
"Host: %s:%d\r\n"
"Upgrade: websocket\r\n"
"Connection: Upgrade\r\n"
"Origin: %s\r\n"
"Sec-WebSocket-Key: x3JJHMbDL1EzLkh9GBhXDw==\r\n"
"Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13\r\n\r\n";
上面把http协议升级为websocket协议的内容写出,把客户端的内容填充过去发送到服务端就行,从下面代码可以看出我们需要哪些内容
char line[256];
int status;
int i;
sprintf(line, desthttp, path, host, port, origin.c_str());
::send(sockfd, line, (int)strlen(line), 0);
发送和接收
使用select来做异步的模式,发送的时候指定参数
很简单,就如下所示
fd_set wfds;
timeval tv = { timeout / 1000, (timeout % 1000) * 1000 };
FD_ZERO(&wfds);
if (txbuf.size()) { FD_SET(sockfd, &wfds); }
select((int)(sockfd + 1), NULL, &wfds, 0, timeout > 0 ? &tv : 0);
当然,如果要将socket置为非阻塞,开始的时候还是要设置的
#ifdef _WIN32
u_long on = 1;
ioctlsocket(sockfd, FIONBIO, &on);
#else
fcntl(sockfd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
#endif
下面是发送的函数,参数为毫秒
//参数是毫秒
void pollSend(int timeout)
{
if (v_state == CLOSED) {
if (timeout > 0) {
timeval tv = { timeout / 1000, (timeout % 1000) * 1000 };
select(0, NULL, NULL, NULL, &tv);
}
return;
}
if (timeout != 0) {
fd_set wfds;
timeval tv = { timeout / 1000, (timeout % 1000) * 1000 };
FD_ZERO(&wfds);
if (txbuf.size()) { FD_SET(sockfd, &wfds); }
select((int)(sockfd + 1), NULL, &wfds, 0, timeout > 0 ? &tv : 0);
}
while (txbuf.size()) {
int ret = ::send(sockfd, (char*)&txbuf[0], (int)txbuf.size(), 0);
if (ret < 0 && (socketerrno == SOCKET_EWOULDBLOCK || socketerrno == SOCKET_EAGAIN_EINPROGRESS)) {
break;
}
else if (ret <= 0) {
closesocket(sockfd);
v_state = CLOSED;
fputs(ret < 0 ? "Connection error!\n" : "Connection closed!\n", stderr);
break;
}
else {
txbuf.erase(txbuf.begin(), txbuf.begin() + ret);
}
}
if (!txbuf.size() && v_state == CLOSING) {
closesocket(sockfd);
v_state = CLOSED;
}
}
下面是接收函数
void pollRecv(int timeout)
{
if (v_state == CLOSED) {
if (timeout > 0) {
timeval tv = { timeout / 1000, (timeout % 1000) * 1000 };
select(0, NULL, NULL, NULL, &tv);
}
return;
}
if (timeout != 0) {
fd_set rfds;
//fd_set wfds;
timeval tv = { timeout / 1000, (timeout % 1000) * 1000 };
FD_ZERO(&rfds);
FD_SET(sockfd, &rfds);
select((int)(sockfd + 1), &rfds, NULL, 0, timeout > 0 ? &tv : 0);
if (!FD_ISSET(sockfd, &rfds))
{
printf("out of here ,no data\n");
return;
}
}
while (true) {
// FD_ISSET(0, &rfds) will be true
int N = (int)rxbuf.size();
ssize_t ret;
//钱波 64K 一个IP包长
rxbuf.resize(N + 64000);
ret = recv(sockfd, (char*)&rxbuf[0] + N, 64000, 0);
if (ret < 0 && (socketerrno == SOCKET_EWOULDBLOCK || socketerrno == SOCKET_EAGAIN_EINPROGRESS)) {
rxbuf.resize(N);
break;
}
else if (ret <= 0) {
rxbuf.resize(N);
closesocket(sockfd);
v_state = CLOSED;
fputs(ret < 0 ? "Connection error!\n" : "Connection closed!\n", stderr);
break;
}
else {//接收到的数据
rxbuf.resize(N + ret);
}
}
}
可以看出,我们使用select 仅仅是不阻塞,简单使用FD_ISSET宏去判决是否有数据达到,如果我们没有收到数据,我们就直接返回。
为了简单使用程序,我们封装一个class来使用接收和发送
class c_ws_class //:public TThreadRunable
{
thread v_thread;
std::mutex v_mutex;
std::condition_variable v_cond;
WebSocket v_ws;
int v_stop = 1;
string v_url;
callback_message_recv v_recv = NULL;
//已经
//bool v_is_working = false;
public:
static int InitSock()
{
#ifdef _WIN32
INT rc;
WSADATA wsaData;
rc = WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2, 2), &wsaData);
if (rc) {
printf("WSAStartup Failed.\n");
return -1;
}
#endif
return 0;
}
static void UnInitSock()
{
WSACleanup();
}
c_ws_class()
{}
~c_ws_class()
{
v_ws.close();
}
public:
void set_url(const char * url)
{
v_url = url;
}
int connect()
{
if (v_url.empty())
return -1;
return v_ws.connect(v_url);
}
void Start(callback_message_recv recv)
{
//because we will connect all over the time, so v_stop is zero
v_stop = 0;
v_ws.initSize(0, 0);
v_recv = recv;
v_thread = std::thread(std::bind(&c_ws_class::Run, this));
}
bool send(const char * str)
{
if (str != NULL)
{
if (v_ws.getReadyState() != CLOSED)
{
v_ws.send(str);
v_ws.pollSend(10);
return true;
}
return false;
}
return false;
}
void sendBinary(uint8_t *data, int len)
{
if (v_ws.getReadyState() != CLOSED)
{
v_ws.sendBinary(data, len);
v_ws.pollSend(5);
}
}
void Stop()
{
v_stop = 1;
}
int isStop()
{
return v_stop;
}
void Join()
{
if (v_thread.joinable())
v_thread.join();
}
void Run()
{
while (v_stop == 0) {
//WebSocket::pointer wsp = &*ws; // <-- because a unique_ptr cannot be copied into a lambda
if (v_stop == 1)
break;
if (v_ws.getReadyState() == CLOSED)
{
//断线重连
if (connect() != 0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100));
if (v_stop == 1)
break;
}
}
}
else
{
v_ws.pollRecv(10);
v_ws.dispatch(v_recv);
}
}
v_ws.close();
//std::cout << "server exit" << endl;
v_stop = 1;
}
void WaitForSignal()
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> ul(v_mutex);
v_cond.wait(ul);
}
void Notify()
{
v_cond.notify_one();
}
};
以上为封装的外层线程代码,里面同时也封装了断线重连。
我们常常使用python或者使用nodejs来做测试,这里使用nodejs写一个简单的服务器程序,接收到数据以后发回。
const WebSocket = require('ws');
const wss = new WebSocket.Server({ port: 8000 });
wss.on('connection', function connection(ws) {
ws.on('message', function incoming(message) {
console.log('received: %s', message);
ws.send('recv:'+message);
});//当收到消息时,在控制台打印出来,并回复一条信息
});
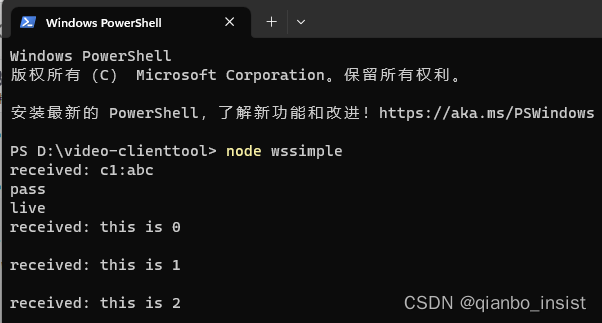
测试结果
服务端nodejs显示
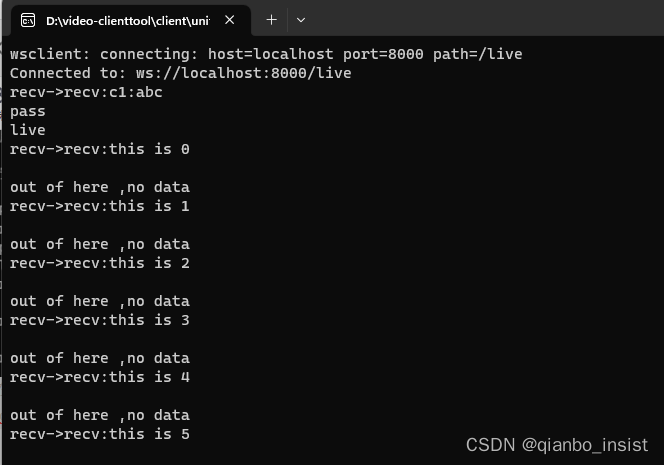
客户端链接后显示
整个的头文件代码和测试代码在gitee上面
gitee地址

![[svg-icon]引入vue项目后,use标签为0,已解决](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0f3c2f769e604847beaa5f15829cd06e.png)