目录
A. TubeTube Feed(签到)
题意:
思路:
代码:
B. Karina and Array(签到)
题意:
思路:
代码:
C. Bun Lover(结论)
题意:
思路:
代码:
D. Super-Permutation(思维)
题意:
思路:
代码:
E. Making Anti-Palindromes(思维)
题意:
思路:
代码:
F. Gardening Friends(图dfs)
题意:
思路:
代码:
G2. Magic Triples (Hard Version)(二分 / 枚举)
题意:
思路:
代码:
A. TubeTube Feed(签到)
Mushroom Filippov cooked himself a meal and while having his lunch, he decided to watch a video on TubeTube. He can not spend more than t seconds for lunch, so he asks you for help with the selection of video.
The TubeTube feed is a list of n videos, indexed from 1 to n. The i-th video lasts ai seconds and has an entertainment value bi. Initially, the feed is opened on the first video, and Mushroom can skip to the next video in 11 second (if the next video exists). Mushroom can skip videos any number of times (including zero).
Help Mushroom choose one video that he can open and watch in t seconds. If there are several of them, he wants to choose the most entertaining one. Print the index of any appropriate video, or −1 if there is no such.
Input
The first line of the input data contains a single integer q (1≤q≤1000) — the number of test cases in the test.
The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of a test case contains two integers n and t (1≤n≤50, 1≤t≤200) — the number of videos in the feed and seconds for lunch, respectively.
The second line of a test case contains n integers a1,a2,a3,…,an(1≤ai≤100) — durations of videos.
The third line of a test case contains n integers b1,b2,b3,…,bn(1≤bi≤100) — entertainment values of videos.
Output
Output q integers, each of which is the answer to the corresponding test case. As an answer, output the index of the most entertaining video that Mushroom will have time to watch. If there are several answers, you are allowed to output any of them. Output −1−1, if there is no video he can watch during his lunch break.
Example
input
5
5 9
1 5 7 6 6
3 4 7 1 9
4 4
4 3 3 2
1 2 3 4
5 7
5 5 5 5 5
2 1 3 9 7
4 33
54 71 69 96
42 24 99 1
2 179
55 66
77 88
output
3 2 3 -1 2
题意:
给定n个电视剧和时间T
每个电视剧需要ti秒看完,好看值ai,打开需要i-1秒,求T秒内能看到最好看的电视剧
思路:
枚举一遍
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,t;
void solve(){
cin>>n>>t;
vector<int>a(n+1),b(n+1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
}
int ans=-1;
int pos=-1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>b[i];
if(b[i]>ans){
if(a[i]+i-1<=t){
ans=b[i];
pos=i;
}
}
}
cout<<pos<<endl;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}B. Karina and Array(签到)
Karina has an array of n integers a1,a2,a3,…,an. She loves multiplying numbers, so she decided that the beauty of a pair of numbers is their product. And the beauty of an array is the maximum beauty of a pair of adjacent elements in the array.
For example, for n=4, a=[3,5,7,4], the beauty of the array is max(3⋅5, 5⋅7, 7⋅4) = max(15, 35, 28) = 35.
Karina wants her array to be as beautiful as possible. In order to achieve her goal, she can remove some elements (possibly zero) from the array. After Karina removes all elements she wants to, the array must contain at least two elements.
Unfortunately, Karina doesn't have enough time to do all her tasks, so she asks you to calculate the maximum beauty of the array that she can get by removing any number of elements (possibly zero).
Input
The first line of the input contains an integer t (1≤t≤104) — the number of test cases.
The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of a test case contains an integer n (2≤n≤2⋅105) — the length of the array a.
The second line of a test case contains n integers a1,a2,a3,…,an (−109≤ai≤109) — the elements of the array a.
The sum of all values of n across all test cases does not exceed 2⋅1052⋅105.
Output
Output t integers, each of which is the answer to the corresponding test case — the maximum beauty of the array that Karina can get.
Example
input
7
4
5 0 2 1
3
-1 1 0
5
2 0 -1 -4 0
6
-8 4 3 7 1 -9
6
0 3 -2 5 -4 -4
2
1000000000 910000000
7
-1 -7 -2 -5 -4 -6 -3
output
10 0 4 72 16 910000000000000000 42
Note
In the first test case of the example, to get the maximum beauty, you need to remove the 22-nd element.
In the second and third test cases of the example, there is no need to remove any elements to achieve maximum beauty.
In the fourth test case of the example, you need to leave only the first and last elements.
题意:
给一个数组a,可以删去任意个元素,求相邻两个元素乘积的最大值
思路:
要么是两个最大数的积,要么是两个最小数的积
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
void solve(){
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<ll>a(n);
for(auto &i:a)cin>>i;
sort(a.begin(),a.end());
cout<<max(a[0]*a[1],a[n-1]*a[n-2])<<endl;
return;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int T=1;
cin>>T;
while(T--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
C. Bun Lover(结论)
Tema loves cinnabon rolls — buns with cinnabon and chocolate in the shape of a "snail".
Cinnabon rolls come in different sizes and are square when viewed from above. The most delicious part of a roll is the chocolate, which is poured in a thin layer over the cinnabon roll in the form of a spiral and around the bun, as in the following picture:
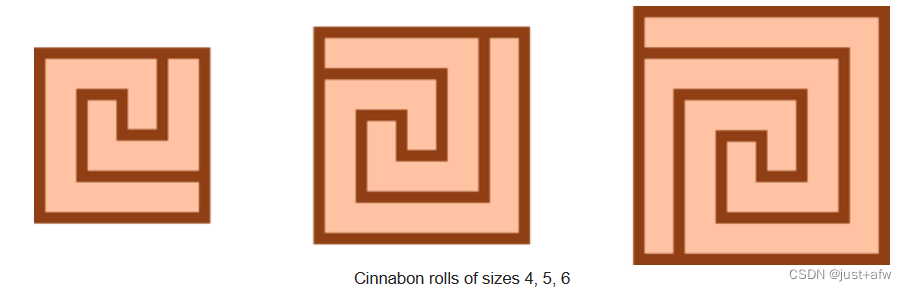
For a cinnabon roll of size n, the length of the outer side of the square is n, and the length of the shortest vertical chocolate segment in the central part is one.
Formally, the bun consists of two dough spirals separated by chocolate. A cinnabon roll of size n+1 is obtained from a cinnabon roll of size n by wrapping each of the dough spirals around the cinnabon roll for another layer.
It is important that a cinnabon roll of size n is defined in a unique way.
Tema is interested in how much chocolate is in his cinnabon roll of size n. Since Tema has long stopped buying small cinnabon rolls, it is guaranteed that n≥4.
Answer this non-obvious question by calculating the total length of the chocolate layer.
Input
The first line of the input contains a single integer t (1≤t≤105) — the number of test cases.
The following t lines describe the test cases.
Each test case is described by a single integer n (4≤n≤109) — the size of the cinnabon roll.
Output
Output t integers. The i-th of them should be equal to the total length of the chocolate layer in the i-th test case.
Example
input
4
4
5
6
179179179
output
26 37 50 32105178545472401
题意:
给一个蛇形图,求所有边的长度和
思路:
找规律发现是(n+1)^2+1,
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
void solve(){
ll n;
cin>>n;
n++;
ll ans=n*n;
cout<<ans+1<<endl;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int T=1;
cin>>T;
while(T--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}D. Super-Permutation(思维)
A permutation is a sequence n integers, where each integer from 1 to n appears exactly once. For example, [1], [3,5,2,1,4], [1,3,2] are permutations, while [2,3,2], [4,3,1], [0] are not.
Given a permutation a, we construct an array b, where bi=(a1+a2+ … +ai)modn.
A permutation of numbers [a1,a2,…,an]is called a super-permutation if [b1+1,b2+1,…,bn+1] is also a permutation of length n.
Grisha became interested whether a super-permutation of length n exists. Help him solve is non-trivial problem. Output any super-permutation of length n, if it exists. Otherwise, output −1−1.
Input
The first line contains a single integer t (1≤t≤104) — the number of test cases. The description of the test cases follows.
Each test case consists of a single line containing one integer n (1≤n≤2⋅105) — the length of the desired permutation.
The sum of n over all test cases does not exceed 2⋅1052⋅105.
Output
For each test case, output in a separate line:
- n integers — a super-permutation of length n, if it exists.
- −1, otherwise.
If there are several suitable permutations, output any of them.
Example
input
4
1
2
3
6
output
1 2 1 -1 6 5 2 3 4 1
题意:
若一个排列a,根据 bi=((a1+a2+ … +ai)mod n)+1 重构一个数组 b
找到一个排列a,使它的重构数组也是一个排列
思路:
手玩,发现奇数不可能构成这样的排列
偶数可以证明 n , 1 , n-2 , 3 , n-4 , 5 ...这样的排列的重组排列也是排列
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
void solve(){
int n;
cin>>n;
if(n==1){
cout<<1<<endl;
return;
}
if(n%2==1){
cout<<-1<<endl;
return;
}
for(int i=n;i>0;i-=2){
cout<<i<<' '<<n+1-i<<' ';
}
cout<<endl;
return;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int T=1;
cin>>T;
while(T--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}E. Making Anti-Palindromes(思维)
You are given a string s, consisting of lowercase English letters. In one operation, you are allowed to swap any two characters of the string s.
A string s of length n is called an anti-palindrome, if s[i]≠s[n−i+1] for every i (1≤i≤n. For example, the strings "codeforces", "string" are anti-palindromes, but the strings "abacaba", "abc", "test" are not.
Determine the minimum number of operations required to make the string s an anti-palindrome, or output −1, if this is not possible.
Input
The first line contains a single integer t (1≤t≤104) — the number of test cases. The description of the test cases follows.
Each test case consists of two lines. The first line contains a single integer n (1≤n≤2⋅105) — the length of the string s.
The second line contains the string s, consisting of n lowercase English letters.
The sum of n over all test cases does not exceed 2⋅105.
Output
For each test case, output a single integer — the minimum number of operations required to make the string s an anti-palindrome, or −1 if this is not possible.
Example
input
10
10
codeforces
3
abc
10
taarrrataa
10
dcbdbdcccc
4
wwww
12
cabbaccabaac
10
aadaaaaddc
14
aacdaaaacadcdc
6
abccba
12
dcbcaebacccd
output
0 -1 1 1 -1 3 -1 2 2 2
Note
In the first test case, the string "codeforces" is already an anti-palindrome, so the answer is 00.
In the second test case, it can be shown that the string "abc" cannot be transformed into an anti-palindrome by performing the allowed operations, so the answer is −1−1.
In the third test case, it is enough to swap the second and the fifth characters of the string "taarrrataa", and the new string "trararataa" will be an anti-palindrome, so the answer is 11.
题意:
给一次字符串,问几次操作后会变成反回文字符串
思路:
奇数长度字符串一定不是反回文
统计所有字母出现次数,若有大于n/2的,一定不可能反回文
统计反回文位置,一次交换操作可以消去两个位置(除了只剩一种字母的情况),若一次交换操作只能消去一个位置时,这种字符最多,必须全部消除,直接两种情况取最差即可
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int cnt[26];
void solve(){
int n;
string s;
cin>>n>>s;
if(n%2==1){ //奇数长度不行
cout<<-1<<endl;
return;
}
s=' '+s;
memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cnt[s[i]-'a']++;
if(cnt[s[i]-'a']>n/2){ //若某字符大于n/2
cout<<-1<<endl;
return;
}
}
memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt));
int tot=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n/2;i++){
if(s[i]==s[n+1-i]){
cnt[s[i]-'a']++; //字母次数
tot++; //统计次数
}
}
sort(cnt,cnt+26);
int ans=0;
int tmp=0;
cout<<max((tot+1)/2,*max_element(cnt,cnt+26))<<endl;
return;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int T=1;
cin>>T;
while(T--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}F. Gardening Friends(图dfs)
Two friends, Alisa and Yuki, planted a tree with n vertices in their garden. A tree is an undirected graph without cycles, loops, or multiple edges. Each edge in this tree has a length of k. Initially, vertex 11 is the root of the tree.
Alisa and Yuki are growing the tree not just for fun, they want to sell it. The cost of the tree is defined as the maximum distance from the root to a vertex among all vertices of the tree. The distance between two vertices u and v is the sum of the lengths of the edges on the path from u to v.
The girls took a course in gardening, so they know how to modify the tree. Alisa and Yuki can spend c coins to shift the root of the tree to one of the neighbors of the current root. This operation can be performed any number of times (possibly zero). Note that the structure of the tree is left unchanged; the only change is which vertex is the root.
The friends want to sell the tree with the maximum profit. The profit is defined as the difference between the cost of the tree and the total cost of operations. The profit is cost of the tree minus the total cost of operations.
Help the girls and find the maximum profit they can get by applying operations to the tree any number of times (possibly zero).
Input
The first line of the input contains one integer t (1≤t≤104) — the number of test cases.
The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains integers n, k, c (2≤n≤2⋅105; 1≤k,c≤109) — the number of vertices in the tree, the length of each edge, and the cost of the operation.
The next n−1 lines of the test case contain pairs of integers ui, vi (1≤ui,vi≤n) — the edges of the graph. These edges form a tree.
The sum of the values of n over all test cases does not exceed 2⋅1052⋅105.
Output
For each test case, output a single integer — the maximum profit that Yuki and Alisa can get.
Example
input
4
3 2 3
2 1
3 1
5 4 1
2 1
4 2
5 4
3 4
6 5 3
4 1
6 1
2 6
5 1
3 2
10 6 4
1 3
1 9
9 7
7 6
6 4
9 2
2 8
8 5
5 10
output
2 12 17 32
题意:
给一棵树,可以花费c元使 根往旁边移动一位,树的价值为 深度*k,输出 能赚的最多的钱
思路:
两遍dfs找出树上最长的链,不管根在何处,深度一定是到 链两端距离的最大值
dfs预处理出每个点到起始根的距离,然后枚举根的所有位置,更新答案即可
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll n,k,c;
vector<int>edge[200005];
vector<int>dis,dis1,dis2,dis3;
void dfs(int x,int f){
for(auto i:edge[x]){
if(i==f)continue;
dis[i]=dis[x]+1;
dfs(i,x);
}
}
void solve(){
cin>>n>>k>>c;
int pos;
dis.resize(n+1,0);
dis1.resize(n+1,0);
dis2.resize(n+1,0);
dis3.resize(n+1,0);
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
edge[u].push_back(v);
edge[v].push_back(u);
}
dis[1]=0;
dfs(1,-1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ //到初始根的距离
dis1[i]=dis[i];
}
pos=max_element(dis1.begin()+1,dis1.end())-dis1.begin();
dis[pos]=0;
dfs(pos,-1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ //到一端的距离
dis2[i]=dis[i];
}
pos=max_element(dis2.begin()+1,dis2.end())-dis2.begin();
dis[pos]=0;
dfs(pos,-1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ //到另一端的距离
dis3[i]=dis[i];
}
ll ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
ans=max(ans,k*max(dis2[i],dis3[i])-c*dis1[i]);
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
edge[i].clear();
}
return;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int T=1;
cin>>T;
while(T--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}G2. Magic Triples (Hard Version)(二分 / 枚举)
This is the hard version of the problem. The only difference is that in this version, ai≤109.
For a given sequence of n integers a, a triple (i,j,k) is called magic if:
- 1≤i,j,k≤n.
- i, j, k are pairwise distinct.
- there exists a positive integer b such that ai⋅b=aj and aj⋅b=ak.
Kolya received a sequence of integers a as a gift and now wants to count the number of magic triples for it. Help him with this task!
Note that there are no constraints on the order of integers i, j and k.
Input
The first line contains a single integer t (1≤t≤104) — the number of test cases. The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of the test case contains a single integer n (3≤n≤2⋅105) — the length of the sequence.
The second line of the test contains n integers a1,a2,a3,…,an (1≤ai≤109) — the elements of the sequence a.
The sum of n over all test cases does not exceed 2⋅105.
Output
For each test case, output a single integer — the number of magic triples for the sequence a.
Example
input
7
5
1 7 7 2 7
3
6 2 18
9
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
4
1000 993 986 179
7
1 10 100 1000 10000 100000 1000000
8
1 1 2 2 4 4 8 8
9
1 1 1 2 2 2 4 4 4
output
6 1 3 0 9 16 45
Note
In the first example, there are 6 magic triples for the sequence a — (2,3,5),(2,5,3), (3,2,5), (3,5,2), (5,2,3), (5,3,2).
In the second example, there is a single magic triple for the sequence a — (2,1,3).
题意:
给一个数组a,找出 i , j , k,是a[i],a[j],a[k]是等比数列,问有一个三元组
思路:
现将数组去重排序,然后枚举等比数列首项,再枚举公比,判断能否组成即可
如果某项个数 >=3 ,则三个自身可以组成等比数列
枚举公比时,二分查找第二项第三项,如果不符合则更新公比继续循环
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
void solve(){
int n;
cin>>n;
map<ll,ll>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
ll x;
cin>>x;
if(m.find(x)==m.end())m[x]=1;
else m[x]++;
}
ll maxn=0;
ll ans=0;
for(auto it:m){
maxn=max(maxn,it.first);
if(it.second>=3)ans+=(it.second)*(it.second-1)*(it.second-2);
}
for(auto it:m){
ll q=2;
ll a=it.first;
while(1){
if(a*q*q>maxn)break;
auto j=m.lower_bound(a*q);
if((j->first)*q>maxn)break;
if(j->first%a!=0){
q=j->first/a+1;
continue;
}
q=j->first/a;
auto k=m.lower_bound(a*q*q);
if(k->first!=a*q*q){
q++;
continue;
}
q++;
ans+=k->second*it.second*j->second;
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int T=1;
cin>>T;
while(T--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}