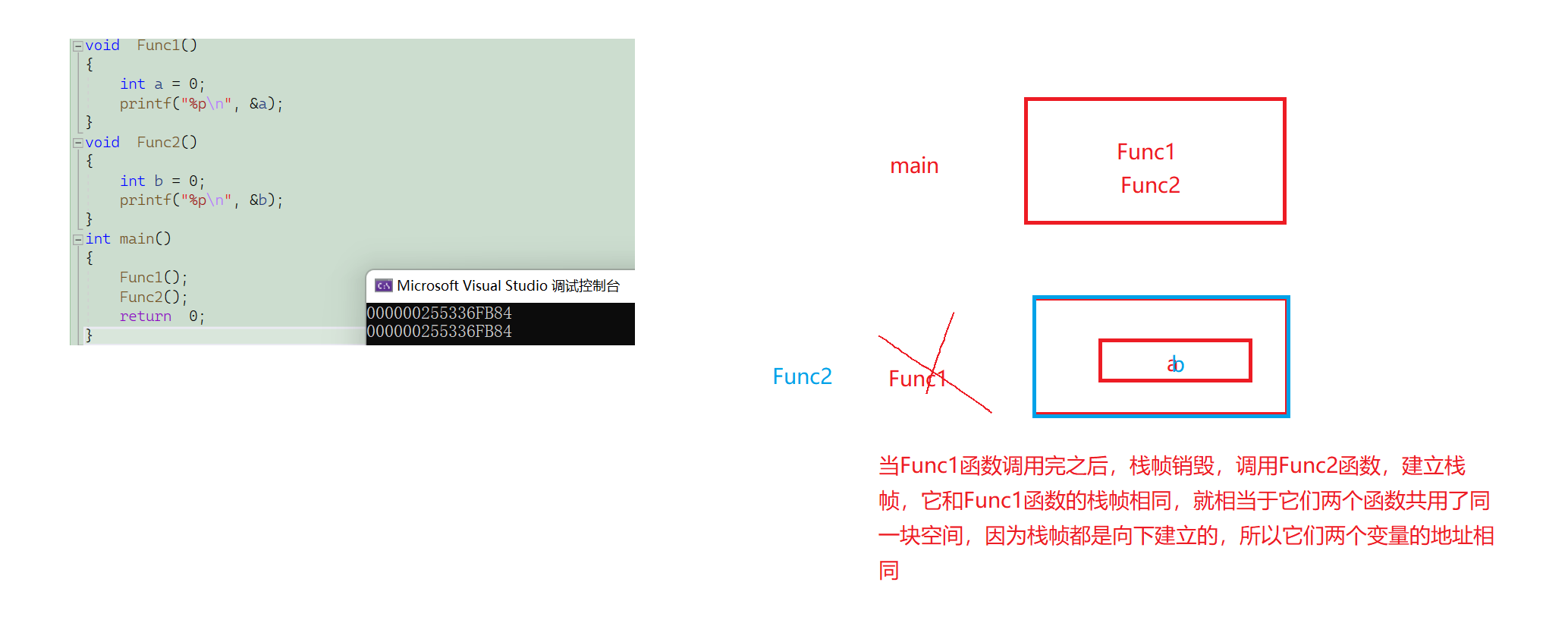
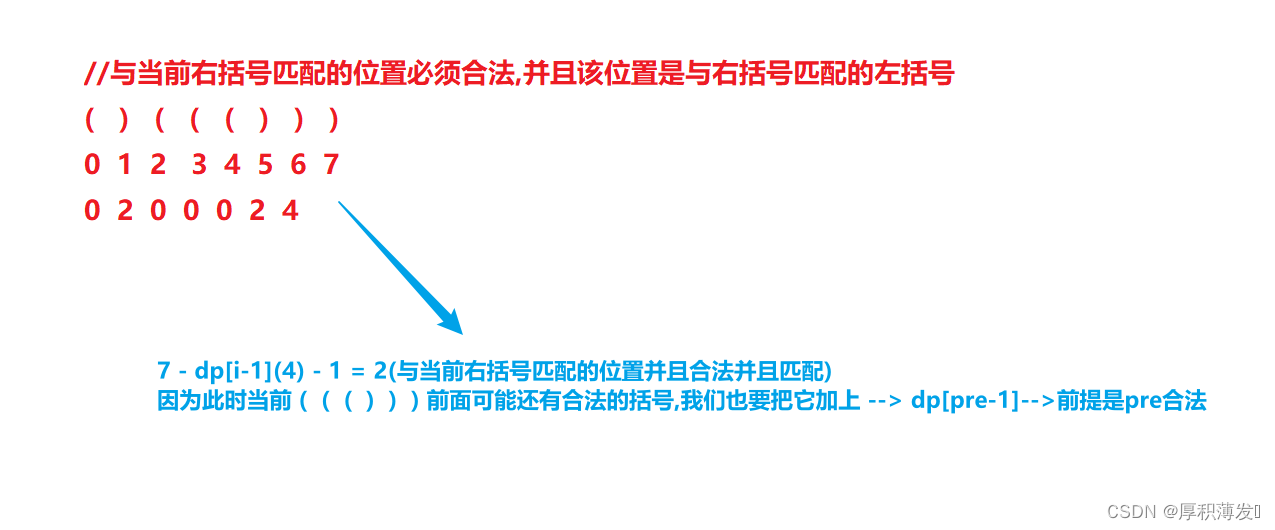
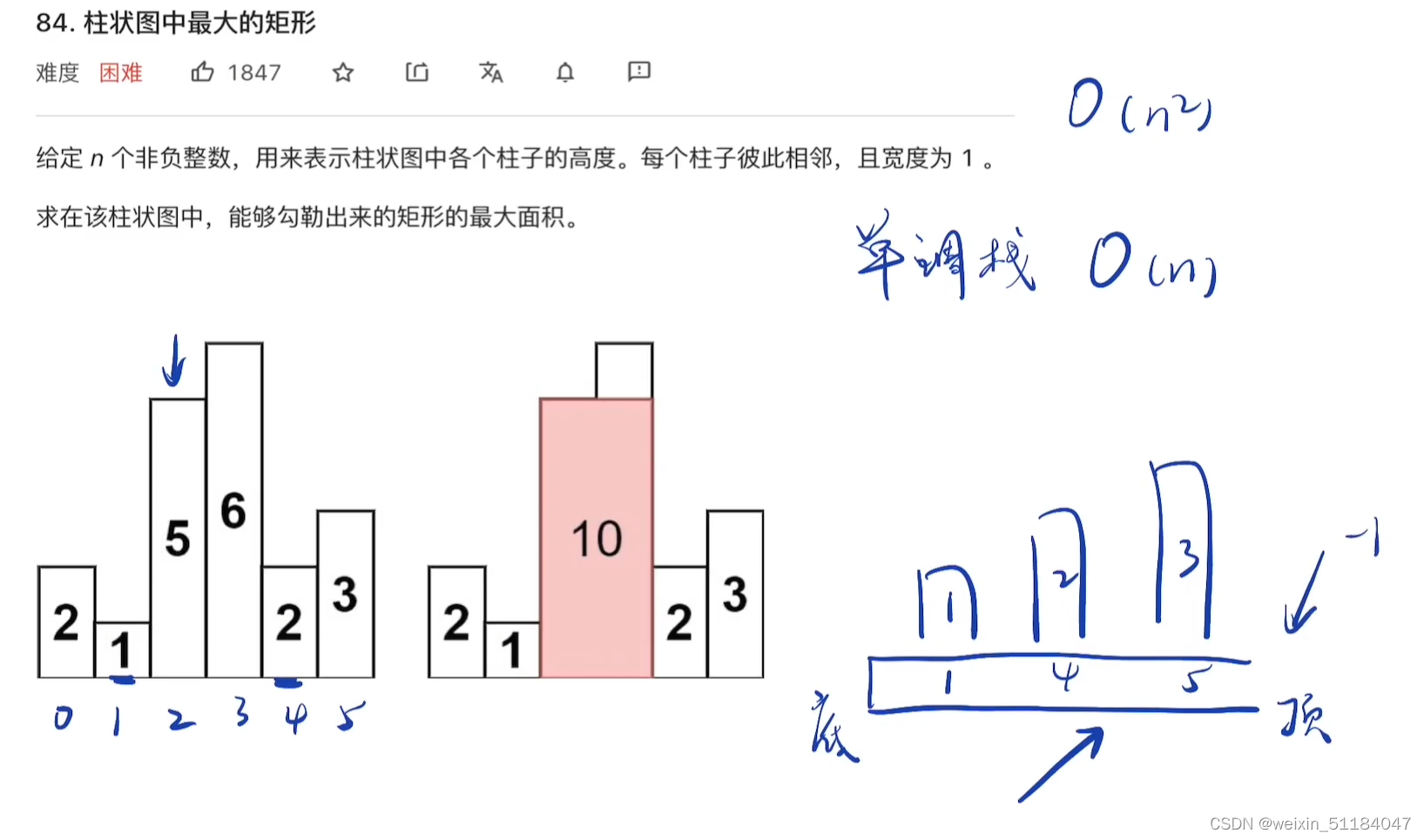
通过手撸这个类的实现,我们可以学习到构造、析构、运算符重载,拷贝构造等面向对象中重要的知识。
首先先看头文件中类的定义:
class Date
{
public:
// 获取某年某月的天数
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month);
// 全缺省的构造函数
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
// 拷贝构造函数
// d2(d1)
//Date(const Date& d);可使用默认生成的拷贝构造
// 赋值运算符重载
// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)
//Date& operator=(const Date& d);
// 析构函数
//~Date();
// 日期+=天数
Date& operator+=(int day);
// 日期+天数
Date operator+(int day);
// 日期-天数
Date operator-(int day);
// 日期-=天数
Date& operator-=(int day);
// 前置++
Date& operator++();
// 后置++
Date operator++(int);
// 后置--
Date operator--(int);
// 前置--
Date& operator--();
// >运算符重载
bool operator>(const Date& d);
// ==运算符重载
bool operator==(const Date& d);
// >=运算符重载
bool operator >= (const Date& d);
// <运算符重载
bool operator < (const Date& d);
// <=运算符重载
bool operator <= (const Date& d);
// !=运算符重载
bool operator != (const Date& d);
// 日期-日期 返回天数
int operator-(const Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};再来看这个类在源文件中的实现:
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include"iostream"
#include"tt.h"
using namespace std;
//对于关系运算符的重载,如下,只需要写一个<=和==,其他就可以运用互补或相反的逻辑写出
bool Date::operator <= (const Date& d)
{
if (_year > d._year)
return false;
else if (_year == d._year && _month > d._month)
return false;
else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day)
return false;
else
return true;
}
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this <= d);
}
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day;
}
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this == d);
}
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this == d) && (*this <= d);
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d)
{
return (*this > d) || (*this == d);
}
// 获取某年某月的天数
int Date::GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
static int days[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
if (month != 2)
{
return days[month];
}
else
{
//判断是否为闰年
if (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 && year % 400 == 0)
return 29;
else
return 28;
}
}
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_month++;
if (_month == 13)
{
_month = 1;
_year++;
}
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this);
tmp += day;
return tmp;
}
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
while (_day <= day)
{
day -= _day;
_month--;
if (_month == 0)
{
_month = 12;
_year--;
}
_day = GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
if (day != 0)
{
_day -= day;
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this);
tmp -= day;
return tmp;
}
// 前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
// 后置++,规定后置++参数列表有一个int占位,和前置++构成重载
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date tmp(*this);
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}
// 后置--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{
Date tmp(*this);
*this -= 1;
return tmp;
}
// 前置--
Date& Date::operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}
// 日期-日期 返回天数
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{
int cnt = 0;
Date small(*this), big(d);
if (small > big)
{
small = d;
big = *this;
}
//年份相同、月份相同时结束循环(结束的条件取反即为继续的条件)
while (small._year != big._year || small._month != big._month)
{
cnt += GetMonthDay(small._year, small._month);
small += GetMonthDay(small._year, small._month);
}
while (small != big)
{
if (small > big)
{
--small;
cnt--;
}
else
{
++small;
++cnt;
}
}
if (*this < d)
{
cnt = cnt * (-1);
}
return cnt;
}通过以上练习可以总结出如下知识: