文章目录
- 单调栈的应用
- [830. 单调栈 - AcWing题库](https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/832/)
- [P5788 【模板】单调栈 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P5788)
- [84. 柱状图中最大的矩形 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/)
- 思路一
- Code
- 思路二
- Code
- [1575. 盛水最多的容器 - AcWing题库](https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/1577/)
- 双指针算法
- [1574. 接雨水 - AcWing题库](https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/1576/)
- 双指针算法
单调栈的应用
可以用来快速找出左右第一个比 a i a_i ai大或小的数及其下标
830. 单调栈 - AcWing题库
给定一个长度为 N的整数数列,输出每个数左边第一个比它小的数,如果不存在则输出 −1。
Code 如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n;
int stk[N],tt;
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )// 输出左边第一个比他小的数。
{
int x;
cin >> x;
while(tt && stk[tt] >= x) tt--;// 栈是非空的,且栈顶元素大于x, 栈顶弹出。
if(tt) cout << stk[tt] << ' ';
else
cout<<-1 <<' ';
stk[++tt] = x;
}
return 0;
}
# 读取数组
n = int(input())
nums = list(map(int, input().split()))
# 单调栈
deq = []
# 开始处理数据
for i in range(len(nums)):
# 从单调栈中弹出不满足升序的数
while deq and deq[-1] >= nums[i]:
deq.pop()
# 此时要么栈空(没有最小),否则栈顶元素就是最近的最小元素
if len(deq) != 0:
print(deq[-1], end = " ")
else:
print(-1, end = " ")
# 将当前数据加入单调栈中(当前数据一定能够保证单调栈升序)
deq.append(nums[i])
P5788 【模板】单调栈 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
const int N = 3e6+10;
int f[N],a[N];// f 答案, a是原始数组,
stack<int> s;//s是单调栈。
int n,tt;
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i -- )// 输出右边第一大于a【i】 的下标
{
while(!s.empty() && a[s.top()] <= a[i]) s.pop();// 如果栈不为空, 且栈顶元素小于a[i], 则弹出
f[i] = s.empty()? 0 : s.top();
s.push(i);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )printf("%d ",f[i]);
return 0;
}
84. 柱状图中最大的矩形 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
思路一
Code
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& h) {
stack<int> stk;
int n = h.size();
if(n == 1) return h[0];
int ans = 0;
int left[n], right[n];
// 左边第一个比h[i]小的下标letf[i]中;右边第一个比h[i]小的下标right[i]中;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
while(!stk.empty() && h[stk.top()] >= h[i])stk.pop();
if(stk.empty())left[i] = -1;
else left[i] = stk.top();
stk.push(i);
}
stk = stack<int>(); // 清空stk;
for(int i = n-1; i >= 0 ; i--)
{
while(!stk.empty() && h[stk.top()]>=h[i]) stk.pop();
if(stk.empty()) right[i] = n;
else right[i] = stk.top();
stk.push(i);
}
for(int i = 0 ; i<n; i++)
{
ans = max(ans, h[i]*(right[i]-left[i]-1));
}
return ans;
}
};
思路二
Code
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
heights.push_back(-1);
//加入哨兵值,便于原先heights中的最后位置的值弹出
//因为需要比最后一个值小的值,才能把最后一个值卡在
//中间计算面积
stack<int> stacks;
stacks.push(-1);
//栈压入哨兵值,便于heights打头的数组进行操作
//压入-1为方便计算打头位置的面积
int maxs = 0;
for(int i=0;i<heights.size();i++)
{
while(stacks.top() != -1&&heights[stacks.top()] > heights[i])
//栈里面后面比前面大的时候才压入,相当于顺序压入,当
//当前值比栈顶的值小的时候,相当于两个比栈顶小的值把
//栈顶位置的数卡在中间,比如5,6,2,栈顶数为6
//此时可以计算栈顶6围成的矩形面积
{
int nums = stacks.top();
stacks.pop();
maxs = max(maxs,heights[nums]*(i-stacks.top()-1));
//面积计算公式为当前下标值*(左右两边的坐标减去1)
}
stacks.push(i);
//栈前面都为比当前值小的时候,无法将栈顶值卡在中间了
//此时压入当前坐标
}
return maxs;
}
};
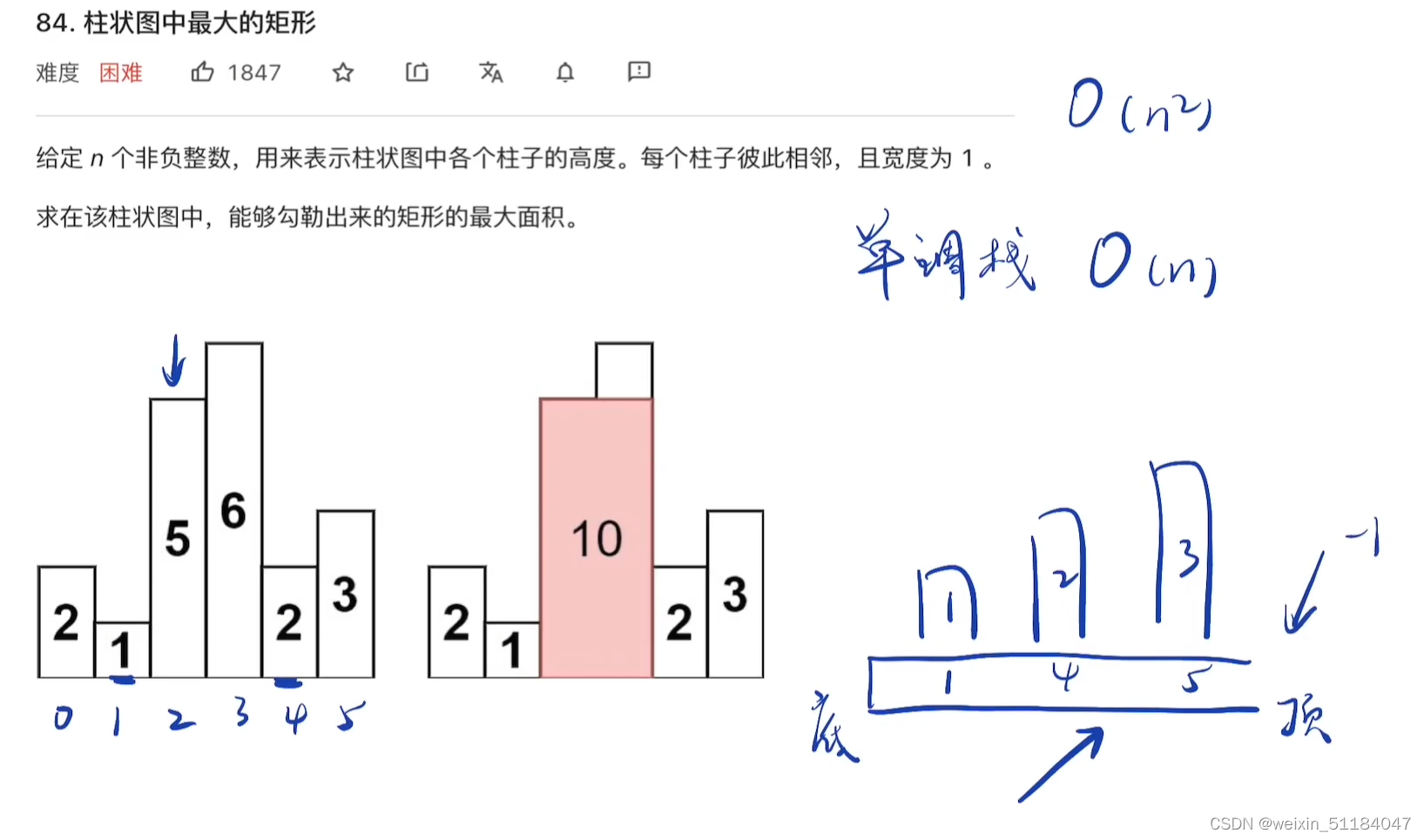
优化思路2
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& h) {
stack<int> stk;
h.push_back(-1); // 为了能让栈清空。 在数组后面放一个-1.
int n = h.size();
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <n; i++)
{
while(stk.size() && h[i]<h[stk.top()])
{
int idx = stk.top();
stk.pop();
int left = stk.empty()? -1 : stk.top();// 比h[idx]小的左边的第一数的下标。
ans = max(ans, (i- left - 1 )* h[idx]);
}
stk.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
};
1575. 盛水最多的容器 - AcWing题库
双指针算法
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a[100100];
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
int ans = 0,l = 1,r = n;
while(l<r)
{
ans = max(ans,(r-l)*min(a[r],a[l]));
if(a[l]<a[r]) l++;
else r--;
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
1574. 接雨水 - AcWing题库
双指针算法
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5+10;
int pre_max[N], suf_max[N], h[N],n;
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
scanf("%d", &h[i]);
pre_max[i] = max(pre_max[i-1], h[i]);
}
for (int i = n; i >= 0; i -- )
{
suf_max[i]= max(suf_max[i+1],h[i]);
}
int ans =0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
ans += min(pre_max[i],suf_max[i]) - h[i];
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
![[Git] Git零基础?带你快速入门,示例练习上手](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/846ce01a535542518c724237577f2968.gif#pic_center)