数据结构中的堆和栈与操作系统内存划分中的堆和栈没有关系
一、堆的定义
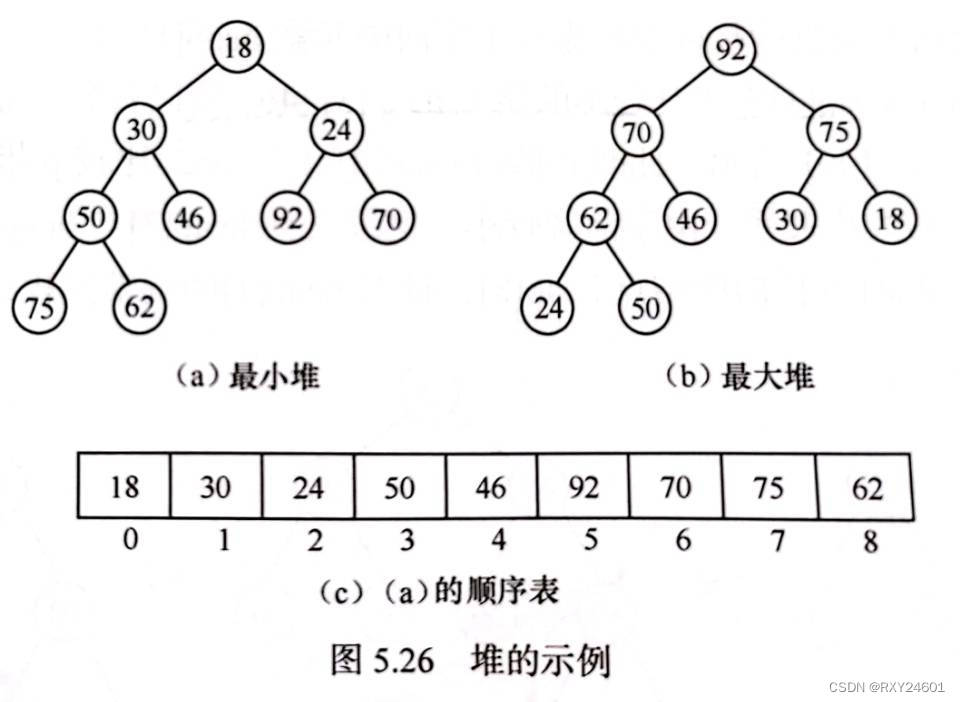
一个大小为n的堆是一棵包含n个结点的完全二叉树,其根节点称为堆顶。
根据堆中亲子结点的大小关系,分为大堆和小堆:
(1)最小堆:树中的每个结点的元素都小于或等于其孩子结点的元素。最小堆中堆顶存储的元素为整棵树中最小的(2)最大堆:树中的每个结点的元素都大于或等于其孩子结点的元素。最大堆中堆顶存储的元素为整棵树中最大的
下列关键字序列为堆的是:(A)
A 100,60,70,50,32,65
B 60,70,65,50,32,100
C 65,100,70,32,50,60
D 70,65,100,32,50,60
E 32,50,100,70,65,60
F 50,100,70,65,60,32
二、堆的存储表示
所有的数组都可以表示成完全二叉树,但是不是所有的数组或完全二叉树都是堆
堆的逻辑结构:逻辑结构为完全二叉树
堆的物理结构:实际上的存储结构是数组
三、建堆运算
向上调整运算思路: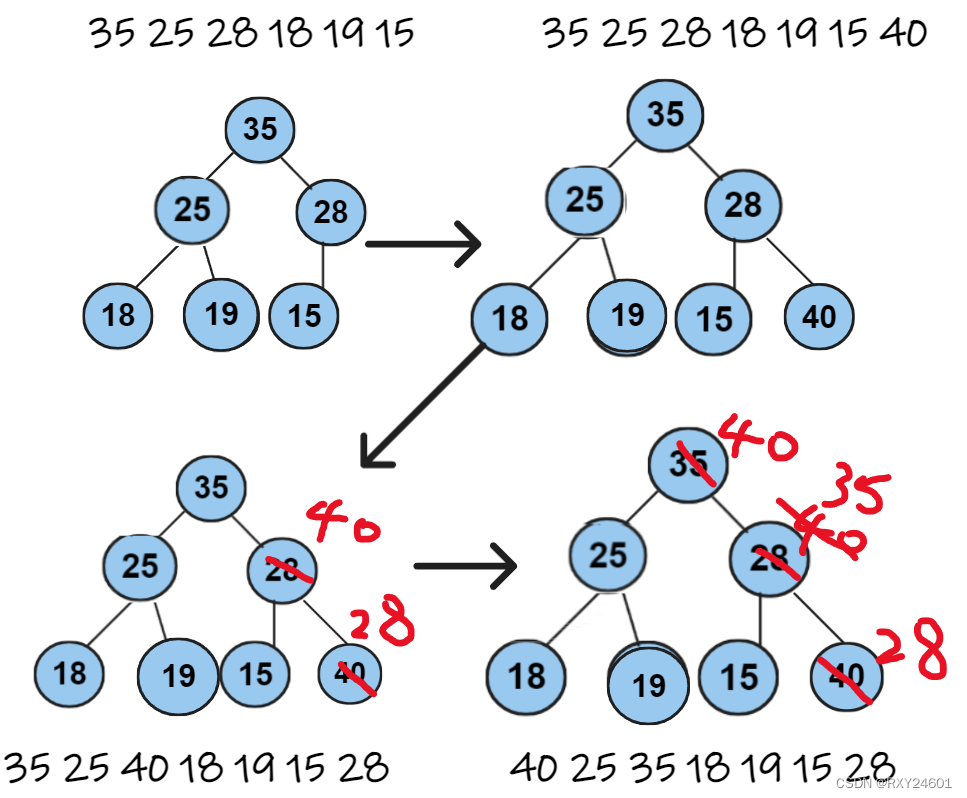
向上调整代码实现:
//n为数组大小,child为新插入的数据位置
void AdjustUp(int *a,int n,int child)//向上调整
{
assert(a);
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child>0)
{
if (a[child] > a[parent])
{
//父子数值交换
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
//更新父子结点
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}向下调整运算思路:
即将其调整成最小堆,向下调整,将根结点与左右孩子中更小的那个交换
结束条件:①父亲<=小的孩子,则停止②调整至叶子结点
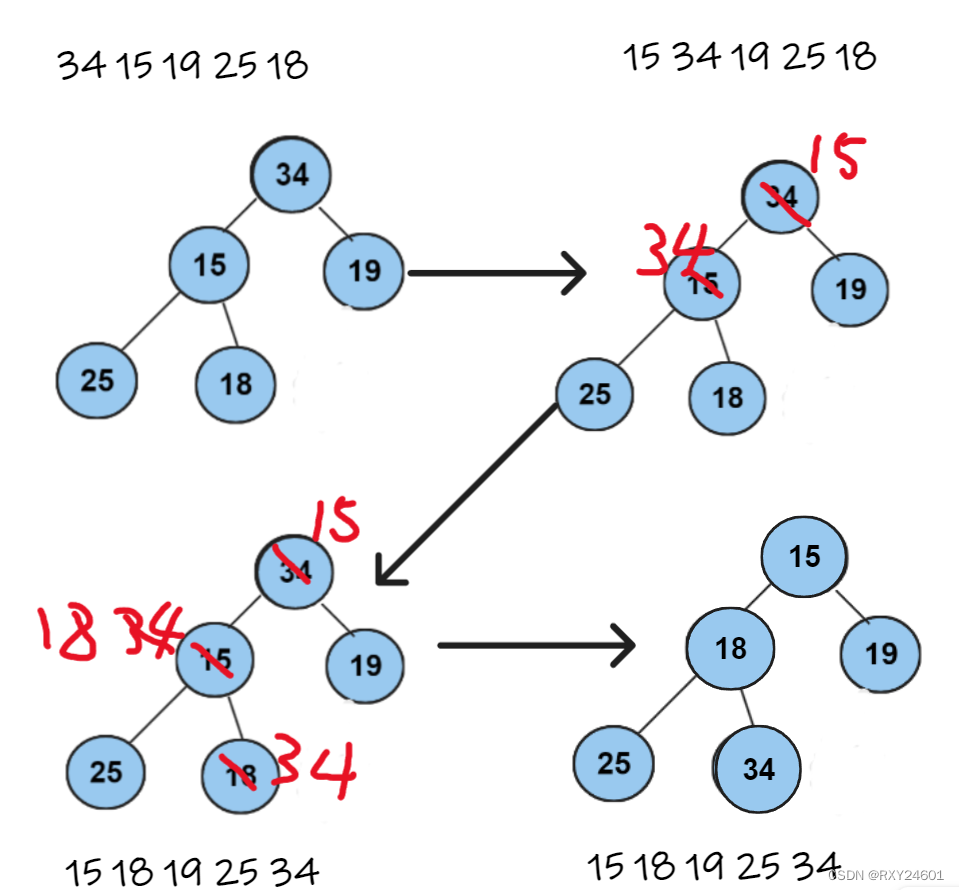
向下调整代码实现:
void AdjustDown(int *a,int n,int parent)
{
assert(a);
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child<n)
{
//选更小的孩子结点
if (child+1<n&&a[child+1]<a[child])
{
child++;
}
//如果小的孩子小于父亲则交换
if (a[child]<a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}建堆运算思路:
这里建堆采用向上调整,删除采用向下调整
建堆运算代码实现:
头文件:
#pragma
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int HPDataType;
typedef struct heap
{
int* a;
int size;
int capacity;
}HP;
void Swap(HPDataType* px, HPDataType* py);//实现数组元素交换
void HeapInit(HP* hp);
void Heapdestory(HP* hp);
void HeapPush(HP* hp,HPDataType x);
void HeapPop(HP* hp);//删除堆顶数据
void HeapPrintf(HP* hp);源文件:
#include"heap.h"
void Swap(HPDataType* px,HPDataType* py)
{
HPDataType* tmp = *px;
*px = *py;
*py = tmp;
}
void HeapInit(HP* hp)
{
assert(hp);
hp->a = NULL;
hp->size = hp->capacity = 0;
}
void Heapdestory(HP* hp)
{
assert(hp);
free(hp->a);
hp->a = NULL;
hp->size = hp->capacity = 0;
}
//n为数组大小,child为新插入的数据位置
void AdjustUp(int *a,int n,int child)//向上调整
{
assert(a);
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child>0)
{
if (a[child] > a[parent])
{
//父子数值交换
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
//更新父子结点
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
//堆插入数据堆其他结点没有影响
//可能会影响它到根节点的路径上的结点关系
void HeapPush(HP* hp, HPDataType x)//向上调整法
{
assert(hp);
if (hp->size==hp->capacity)
{
size_t newcapacity = hp->capacity == 0 ? 4 : hp->capacity * 2;
HPDataType* tmp = realloc(hp->a, sizeof(HPDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp==NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
hp->a = tmp;
hp->capacity = newcapacity;
}
hp->a[hp->size] = x;
hp->size++;
AdjustUp(hp->a, hp->size, hp->size - 1);
}
void AdjustDown(int *a,int n,int parent)
{
assert(a);
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child<n)
{
//选更小的孩子结点
if (child+1<n&&a[child+1]<a[child])
{
child++;
}
//如果小的孩子小于父亲则交换
if (a[child]<a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
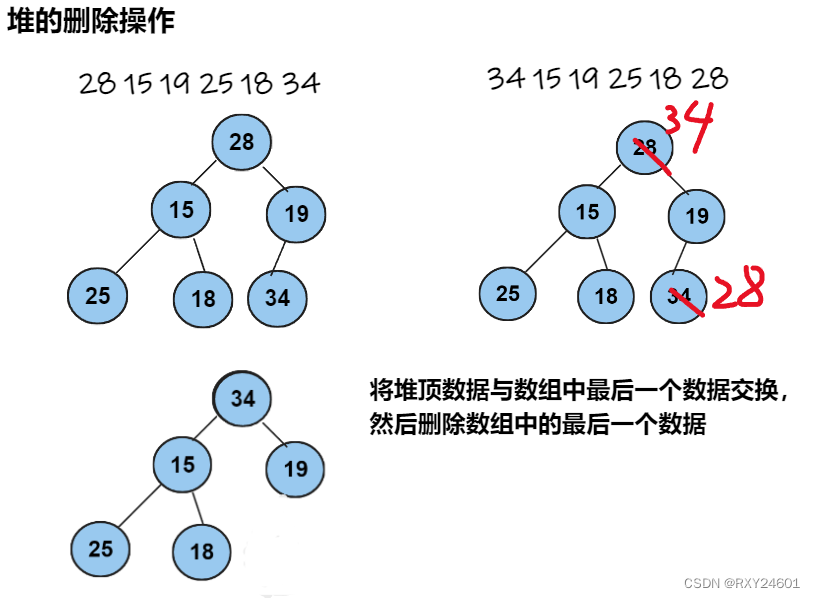
//将堆顶数据与数组中最后一个数据交换,然后删除数组中的最后一个数据
//再进行向下调整算法
void HeapPop(HP* hp)
{
assert(hp);
assert(hp->size > 0);
Swap(&hp->a[0], &hp->a[hp->size - 1]);
hp->size--;
AdjustDown(hp->a, hp->size,0);
}
void HeapPrintf(HP* hp)
{
for(int i=0;i<hp->size;i++)
{
printf("%d ",hp->a[i]);
}
}测试:
#include"heap.h"
int main()
{
int a[] = { 70,56,30,25,15,10,75 };
HP hp;
HeapInit(&hp);
for (int i=0;i<sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]);i++)
{
HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);
}
HeapPrintf(&hp);
return 0;
}