题目:
现有一棵由 n 个节点组成的无向树,节点编号从 0 到 n - 1 ,共有 n - 1 条边。
给你一个二维整数数组 edges ,长度为 n - 1 ,其中 edges[i] = [ai, bi] 表示树中节点 ai 和 bi 之间存在一条边。另给你一个整数数组 restricted 表示 受限 节点。
在不访问受限节点的前提下,返回你可以从节点 0 到达的 最多 节点数目。
注意,节点 0 不 会标记为受限节点。
示例 1:

输入:n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[3,1],[4,0],[0,5],[5,6]], restricted = [4,5]
输出:4
解释:上图所示正是这棵树。
在不访问受限节点的前提下,只有节点 [0,1,2,3] 可以从节点 0 到达。
示例 2:
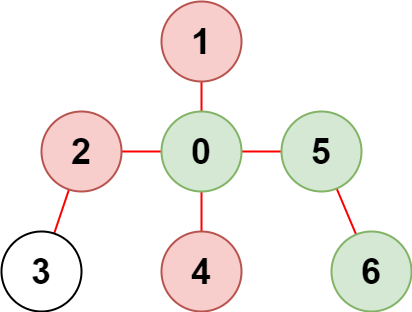
输入:n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,5],[0,4],[3,2],[6,5]], restricted = [4,2,1]
输出:3
解释:上图所示正是这棵树。
在不访问受限节点的前提下,只有节点 [0,5,6] 可以从节点 0 到达。
提示:
2 <= n <= 10^5
edges.length == n - 1
edges[i].length == 2
0 <= ai, bi < n
ai != bi
edges 表示一棵有效的树
1 <= restricted.length < n
1 <= restricted[i] < n
restricted 中的所有值 互不相同
java代码:
class Solution {
public int reachableNodes(int n, int[][] edges, int[] restricted) {
List<Integer>[] adj = new List[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
// 邻接表建图
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i){
adj[edges[i][0]].add(edges[i][1]);
adj[edges[i][1]].add(edges[i][0]);
}
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n];
// 处理restricted数组
for (int num : restricted) vis[num] = true;
Deque<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.addLast(0);
vis[0] = true;
int ans = 1;
while (!q.isEmpty()){
int cur = q.pollFirst();
for (int next : adj[cur]){
if (!vis[next]){
q.addLast(next);
vis[next] = true;
++ans;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}