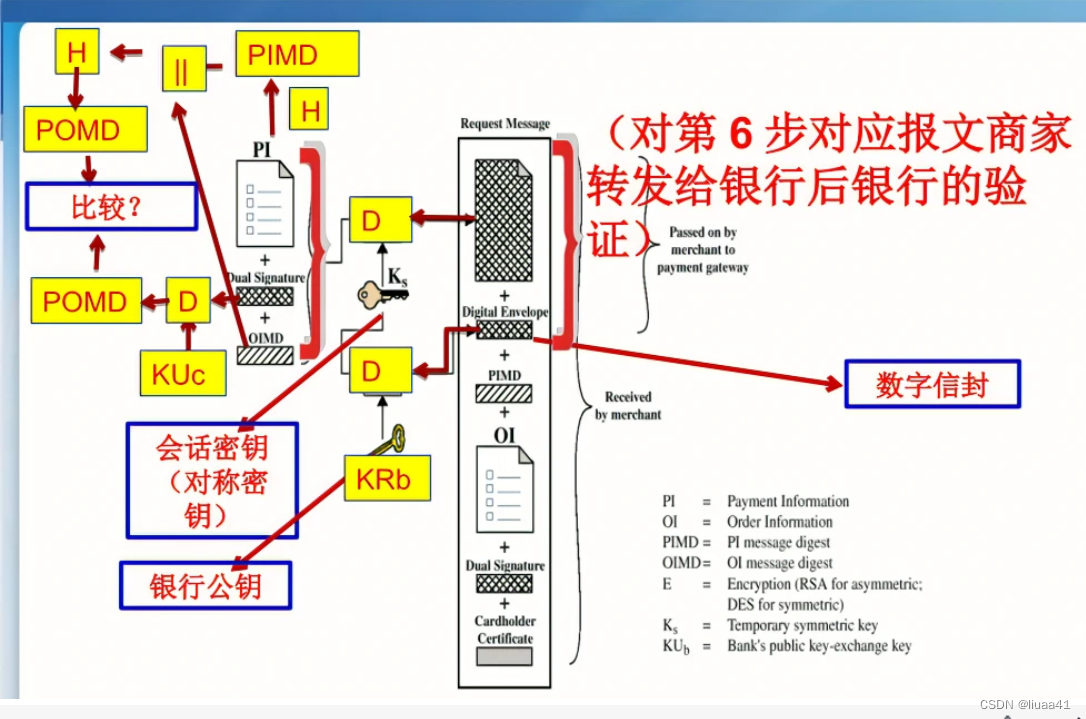
LLM的参数量对于时间和显存要求都带来很大的挑战。现存的两种显著范式:
- 增加adapter:主要问题在于推理时带来的额外计算量和延迟。
- 优化prompt: 前缀微调(Prefix Tuning)较难优化,而且随着参数量增长性能并非单调变化。
那有什么方法可以 解决这个问题么?:图像生成领域 的 lora
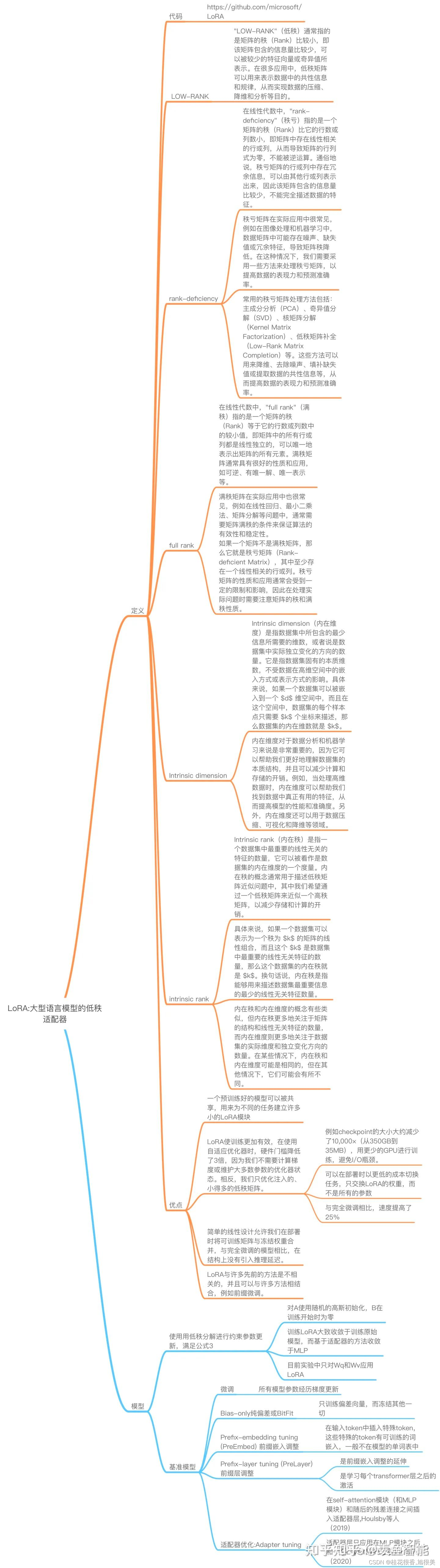
1. 介绍
lora是大模型的低秩适配器,或者就简单的理解为适配器,在图像生成中可以将lora理解为某种图像风格(比如SD社区中的各种漂亮妹子的lora,可插拔式应用,甚至组合式应用实现风格的融合)的适配器,在NLP中可以将其理解为某个任务的适配器(比如最近各种开源chatgpt复现中使用的lora技术,不过限于文本领域的特性,目前组合式应用似乎还不多)。
2. 做法
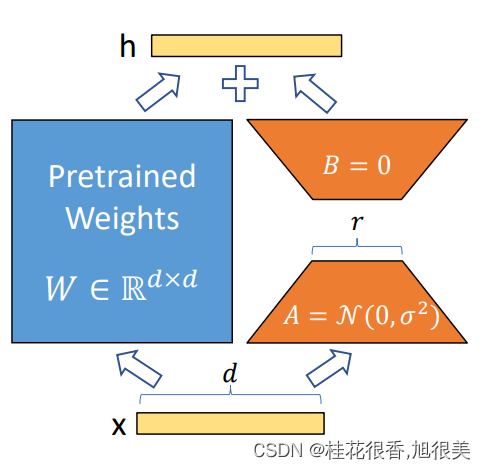
- 在原模型旁边增加一个旁路,通过低秩分解(先降维再升维)来模拟参数的更新量;
- 训练时,原模型固定,只训练降维矩阵A和升维矩阵B;
- 推理时,可将BA加到原参数上,不引入额外的推理延迟;
- 初始化,A采用高斯分布初始化,B初始化为全0,保证训练开始时旁路为0矩阵;
- 可插拔式的切换任务,当前任务W0+B1A1,将lora部分减掉,换成B2A2,即可实现任务切换;
3. 原理
过度参数化的模型实际上位于一个低内在维度的空间,因此lora作者提出假设,微调时权重的变化同样有一个低的"内在维度",因此可以进行低秩矩阵分解。
大模型(LLM)训练微调综述学习
4. 总结
一句话总结 lora:固定大模型,增加低秩分解的矩阵来适配下游任务。
5. 优点
- 一个中心模型服务多个下游任务,节省参数存储量
- 推理阶段不引入额外计算量
- 与其它参数高效微调方法正交,可有效组合
- 训练任务比较稳定,效果比较好
6. 缺点
生成任务上效果 欠佳
7. 总览
8. 实战
安装
pip install loralib
可以选择用loralib中实现的对应层来替换一些层。目前loralib只支持 nn.Linear、nn.Embedding 和 nn.Conv2d。loralib还支持一个 MergedLinear,用于单个 nn.Linear 代表一个以上的层的情况。
# ===== Before =====
# layer = nn.Linear(in_features, out_features)
# ===== After ======
import loralib as lora
# Add a pair of low-rank adaptation matrices with rank r=16
layer = lora.Linear(in_features, out_features, r=16)
在训练之前,设置仅LorA模块的参数可被训练
import loralib as lora
model = BigModel()
# This sets requires_grad to False for all parameters without the string "lora_" in their names
lora.mark_only_lora_as_trainable(model)
# Training loop
for batch in dataloader:
...
在保存checkpoint时,生成一个仅包含LoRA参数的state_dict
# ===== Before =====
# torch.save(model.state_dict(), checkpoint_path)
# ===== After =====
torch.save(lora.lora_state_dict(model), checkpoint_path)
当载入checkpoint时,设置strict为False
# Load the pretrained checkpoint first
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('ckpt_pretrained.pt'), strict=False)
# Then load the LoRA checkpoint
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('ckpt_lora.pt'), strict=False)
lora.MergedLinear的使用
# ===== Before =====
# qkv_proj = nn.Linear(d_model, 3*d_model)
# ===== After =====
# Break it up (remember to modify the pretrained checkpoint accordingly)
q_proj = lora.Linear(d_model, d_model, r=8)
k_proj = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
v_proj = lora.Linear(d_model, d_model, r=8)
# Alternatively, use lora.MergedLinear (recommended)
qkv_proj = lora.MergedLinear(d_model, 3*d_model, r=8, enable_lora=[True, False, True])
可以在调用mark_only_lora_as_trainable时,通过给bias= 传递 "all "或 "lora_only "来标记一些bias为可训练。
# ===== Before =====
# lora.mark_only_lora_as_trainable(model) # Not training any bias vectors
# ===== After =====
# Training all bias vectors associated with modules we apply LoRA to
lora.mark_only_lora_as_trainable(model, bias='lora_only')
# Alternatively, we can train *all* bias vectors in the model, including LayerNorm biases
lora.mark_only_lora_as_trainable(model, bias='all')
# When saving a checkpoint, use the same bias= ('all' or 'lora_only')
torch.save(lora.lora_state_dict(model, bias='all'), checkpoint_path)
Apply to GPT
参见:LoRA/examples/NLG/src/model.py
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, nx, n_ctx, config, scale=False):
super(Attention, self).__init__()
n_state = nx # in Attention: n_state=768 (nx=n_embd)
# [switch nx => n_state from Block to Attention to keep identical to TF implem]
assert n_state % config.n_head == 0
self.register_buffer("bias", torch.tril(torch.ones(n_ctx, n_ctx)).view(1, 1, n_ctx, n_ctx))
self.n_head = config.n_head
self.split_size = n_state
self.scale = scale
self.c_attn = Conv1D(n_state * 3, nx)
self.c_attn = lora.MergedLinear(
nx, n_state * 3,
r=config.lora_attn_dim,
lora_alpha=config.lora_attn_alpha,
lora_dropout=config.lora_dropout,
enable_lora=[True, False, True],
fan_in_fan_out=True,
merge_weights=False
)
self.c_proj = Conv1D(n_state, nx)
self.config = config
源代码解读
总的来说loralib的源代码比较简洁,可以在LORA/loralib/layers.py 查看
Class LoRALayer
class LoRALayer():
def __init__(
self,
r: int,
lora_alpha: int,
lora_dropout: float,
merge_weights: bool,
):
self.r = r
self.lora_alpha = lora_alpha
# Optional dropout
if lora_dropout > 0.:
self.lora_dropout = nn.Dropout(p=lora_dropout)
else:
self.lora_dropout = lambda x: x
# Mark the weight as unmerged
self.merged = False
self.merge_weights = merge_weights
LoRA layer可以添加到任何一个可以有参数训练的层里。但文章中也提到了we only apply LoRA to Wq and Wv in most experiments for simplicity
LoRA Embedding
(注释在代码块中)
“During training, W0 is frozen and does not receive gradient updates, while A and B contain trainable parameters. ”
“We use a random Gaussian initialization for A and zero for B”
class Embedding(nn.Embedding, LoRALayer):
# LoRA implemented in a dense layer
def __init__(
self,
num_embeddings: int,
embedding_dim: int,
r: int = 0,
lora_alpha: int = 1,
merge_weights: bool = True,
**kwargs
):
nn.Embedding.__init__(self, num_embeddings, embedding_dim, **kwargs)
LoRALayer.__init__(self, r=r, lora_alpha=lora_alpha, lora_dropout=0,
merge_weights=merge_weights)
# Lora 部分
# Actual trainable parameters
if r > 0:
self.lora_A = nn.Parameter(self.weight.new_zeros((r, num_embeddings)))
self.lora_B = nn.Parameter(self.weight.new_zeros((embedding_dim, r)))
# scale ∆W x by α/r
self.scaling = self.lora_alpha / self.r
# Freezing the pre-trained weight matrix
#冻结pre-trained 参数
self.weight.requires_grad = False
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self):
nn.Embedding.reset_parameters(self)
if hasattr(self, 'lora_A'):
#初始化
# We use a random Gaussian initialization for A and zero for B, so ∆W = BA is zero at the beginning of training.
# initialize A the same way as the default for nn.Linear and B to zero
nn.init.zeros_(self.lora_A)
nn.init.normal_(self.lora_B)
def train(self, mode: bool = True):
nn.Embedding.train(self, mode)
if self.merge_weights and self.merged:
# self.merged = Ture
# Make sure that the weights are not merged
# weight=weight-B * A * scale 需要剪掉merge的部分
if self.r > 0:
self.weight.data -= (self.lora_B @ self.lora_A).T * self.scaling
self.merged = False
def eval(self):
nn.Linear.eval(self)
if self.merge_weights and not self.merged:
# Merge the weights and mark it
# self.merged= False
if self.r > 0:
self.weight.data += (self.lora_B @ self.lora_A) * self.scaling
self.merged = True
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor):
if self.r > 0 and not self.merged:
# self.merged= False
result = nn.Embedding.forward(self, x)
if self.r > 0:
after_A = F.embedding(
x, self.lora_A.T, self.padding_idx, self.max_norm,
self.norm_type, self.scale_grad_by_freq, self.sparse
) # W0x + BAx
result += (after_A @ self.lora_B.T) * self.scaling
return result
else:
return nn.Embedding.forward(self, x)
Class Linear
kaiming_uniform_ kaiming 初始化
fin in fin out 含义
https://towardsdatascience.com/understand-kaiming-initialization-and-implementation-detail-in-pytorch-f7aa967e9138
因为加了fin in fin out 参数的原因,比之前的embedding层多了一个def T
class Linear(nn.Linear, LoRALayer):
# LoRA implemented in a dense layer
def __init__(
self,
in_features: int,
out_features: int,
r: int = 0,
lora_alpha: int = 1,
lora_dropout: float = 0.,
fan_in_fan_out: bool = False, # Set this to True if the layer to replace stores weight like (fan_in, fan_out)
merge_weights: bool = True,
**kwargs
):
nn.Linear.__init__(self, in_features, out_features, **kwargs)
LoRALayer.__init__(self, r=r, lora_alpha=lora_alpha, lora_dropout=lora_dropout,
merge_weights=merge_weights)
self.fan_in_fan_out = fan_in_fan_out
# Actual trainable parameters
if r > 0:
self.lora_A = nn.Parameter(self.weight.new_zeros((r, in_features)))
self.lora_B = nn.Parameter(self.weight.new_zeros((out_features, r)))
self.scaling = self.lora_alpha / self.r
# Freezing the pre-trained weight matrix
self.weight.requires_grad = False
self.reset_parameters()
if fan_in_fan_out:
self.weight.data = self.weight.data.T
def reset_parameters(self):
nn.Linear.reset_parameters(self)
if hasattr(self, 'lora_A'):
# initialize A the same way as the default for nn.Linear and B to zero
nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(self.lora_A, a=math.sqrt(5))
nn.init.zeros_(self.lora_B)
def train(self, mode: bool = True):
def T(w):
return w.T if self.fan_in_fan_out else w
nn.Linear.train(self, mode)
if self.merge_weights and self.merged:
# Make sure that the weights are not merged
if self.r > 0:
self.weight.data -= T(self.lora_B @ self.lora_A) * self.scaling
self.merged = False
def eval(self):
def T(w):
return w.T if self.fan_in_fan_out else w
nn.Linear.eval(self)
if self.merge_weights and not self.merged:
# Merge the weights and mark it
if self.r > 0:
self.weight.data += T(self.lora_B @ self.lora_A) * self.scaling
self.merged = True
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor):
def T(w):
return w.T if self.fan_in_fan_out else w
#Merge = False
if self.r > 0 and not self.merged:
result = F.linear(x, T(self.weight), bias=self.bias)
if self.r > 0:
result += (self.lora_dropout(x) @ self.lora_A.T @ self.lora_B.T) * self.scaling
return result
#Merge =True
else:
return F.linear(x, T(self.weight), bias=self.bias)
Class MergedLinear
这个针对self- attention模块使用
class MergedLinear(nn.Linear, LoRALayer):
# LoRA implemented in a dense layer
def __init__(
self,
in_features: int,
out_features: int,
r: int = 0,
lora_alpha: int = 1,
lora_dropout: float = 0.,
enable_lora: List[bool] = [False],
fan_in_fan_out: bool = False,
merge_weights: bool = True,
**kwargs
):
nn.Linear.__init__(self, in_features, out_features, **kwargs)
LoRALayer.__init__(self, r=r, lora_alpha=lora_alpha, lora_dropout=lora_dropout,
merge_weights=merge_weights)
assert out_features % len(enable_lora) == 0, \
'The length of enable_lora must divide out_features'
#一个true false list
self.enable_lora = enable_lora
self.fan_in_fan_out = fan_in_fan_out
# Actual trainable parameters
if r > 0 and any(enable_lora):
self.lora_A = nn.Parameter(
self.weight.new_zeros((r * sum(enable_lora), in_features)))
self.lora_B = nn.Parameter(
self.weight.new_zeros((out_features //
len(enable_lora) * sum(enable_lora), r))
) # weights for Conv1D with groups=sum(enable_lora) 计算有几个True
self.scaling = self.lora_alpha / self.r
# Freezing the pre-trained weight matrix
self.weight.requires_grad = False
#因为针对像attention计算中需要Wq Wk Wv 三种linear merge 一起的情况
# Compute the indices
# input (out_features) output (len(enable_lora) , out_features/len(enable_lora))
self.lora_ind = self.weight.new_zeros(
(out_features, ), dtype=torch.bool
).view(len(enable_lora), -1)
#对应的那一行就设为True
self.lora_ind[enable_lora, :] = True
self.lora_ind = self.lora_ind.view(-1)
self.reset_parameters()
if fan_in_fan_out:
self.weight.data = self.weight.data.T
def reset_parameters(self):
nn.Linear.reset_parameters(self)
if hasattr(self, 'lora_A'):
# initialize A the same way as the default for nn.Linear and B to zero
nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(self.lora_A, a=math.sqrt(5))
nn.init.zeros_(self.lora_B)
def zero_pad(self, x):
result = x.new_zeros((*x.shape[:-1], self.out_features))
result = result.view(-1, self.out_features)
result[:, self.lora_ind] = x.reshape(
-1, self.out_features // len(self.enable_lora) * sum(self.enable_lora)
)
return result.view((*x.shape[:-1], self.out_features))
def train(self, mode: bool = True):
def T(w):
return w.T if self.fan_in_fan_out else w
nn.Linear.train(self, mode)
if self.merge_weights and self.merged:
# Make sure that the weights are not merged
if self.r > 0 and any(self.enable_lora):
delta_w = F.conv1d(
self.lora_A.data.unsqueeze(0),
self.lora_B.data.unsqueeze(-1),
groups=sum(self.enable_lora)
).squeeze(0)
self.weight.data -= self.zero_pad(T(delta_w * self.scaling))
self.merged = False
def eval(self):
def T(w):
return w.T if self.fan_in_fan_out else w
nn.Linear.eval(self)
if self.merge_weights and not self.merged:
# Merge the weights and mark it
if self.r > 0 and any(self.enable_lora):
delta_w = F.conv1d(
self.lora_A.data.unsqueeze(0),
self.lora_B.data.unsqueeze(-1),
groups=sum(self.enable_lora)
).squeeze(0)
self.weight.data += self.zero_pad(T(delta_w * self.scaling))
self.merged = True
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor):
def T(w):
return w.T if self.fan_in_fan_out else w
if self.merged:
return F.linear(x, T(self.weight), bias=self.bias)
else:
result = F.linear(x, T(self.weight), bias=self.bias)
if self.r > 0:
after_A = F.linear(self.lora_dropout(x), self.lora_A)
after_B = F.conv1d(
after_A.transpose(-2, -1),
self.lora_B.unsqueeze(-1),
groups=sum(self.enable_lora)
).transpose(-2, -1)
result += self.zero_pad(after_B) * self.scaling
return result
参考
LORA: LOW-RANK ADAPTATION OF LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS
Intrinsic Dimensionality Explains the Effectiveness of Language Model Fine-Tuning
Measuring the Intrinsic Dimension of Objective Landscapes.
peft/tuners/lora.py
microsoft/LoRA
LoRA:大模型的低秩适配-最近大火的lora到底是什么东西?为啥stable diffusion和开源ChatGPT复现都在用?
论文阅读:LORA-大型语言模型的低秩适应
LLaMA模型详解-当前开源ChatGPT复现中使用最多的基础模型
论文速读:LORA: LOW-RANK ADAPTATION OF LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS
论文阅读:LORA-大型语言模型的低秩适应
微软LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models 代码解读