API(application programming interface)是JDK的重要组成部分,API提供了Java程序与运行它的系统软件(Java虚拟机)之间的接口,可以帮助开发者方便、快捷地开发Java程序
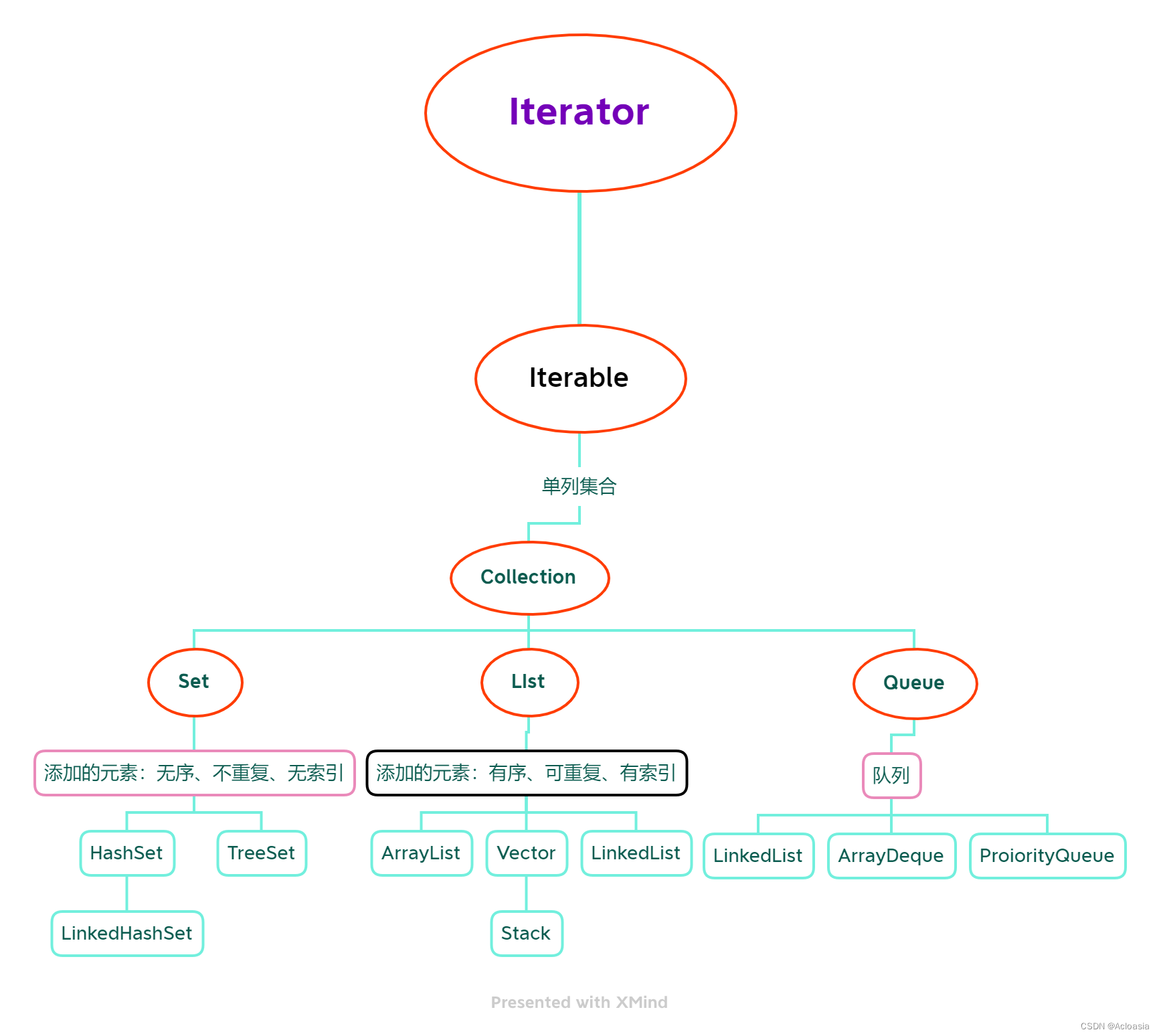
集合在程序设计中是一种重要的是数据结构,Java中提供了有关集合的类库称为Collection API
目录
1.Collection
1.1 Collection 集合概述和使用
1.2 Collection集合常用方法
1.3 Collection集合的遍历
1.3.1 迭代器遍历
1.3.2 增强for遍历
1.3.3 lambda表达式遍历
1.Collection
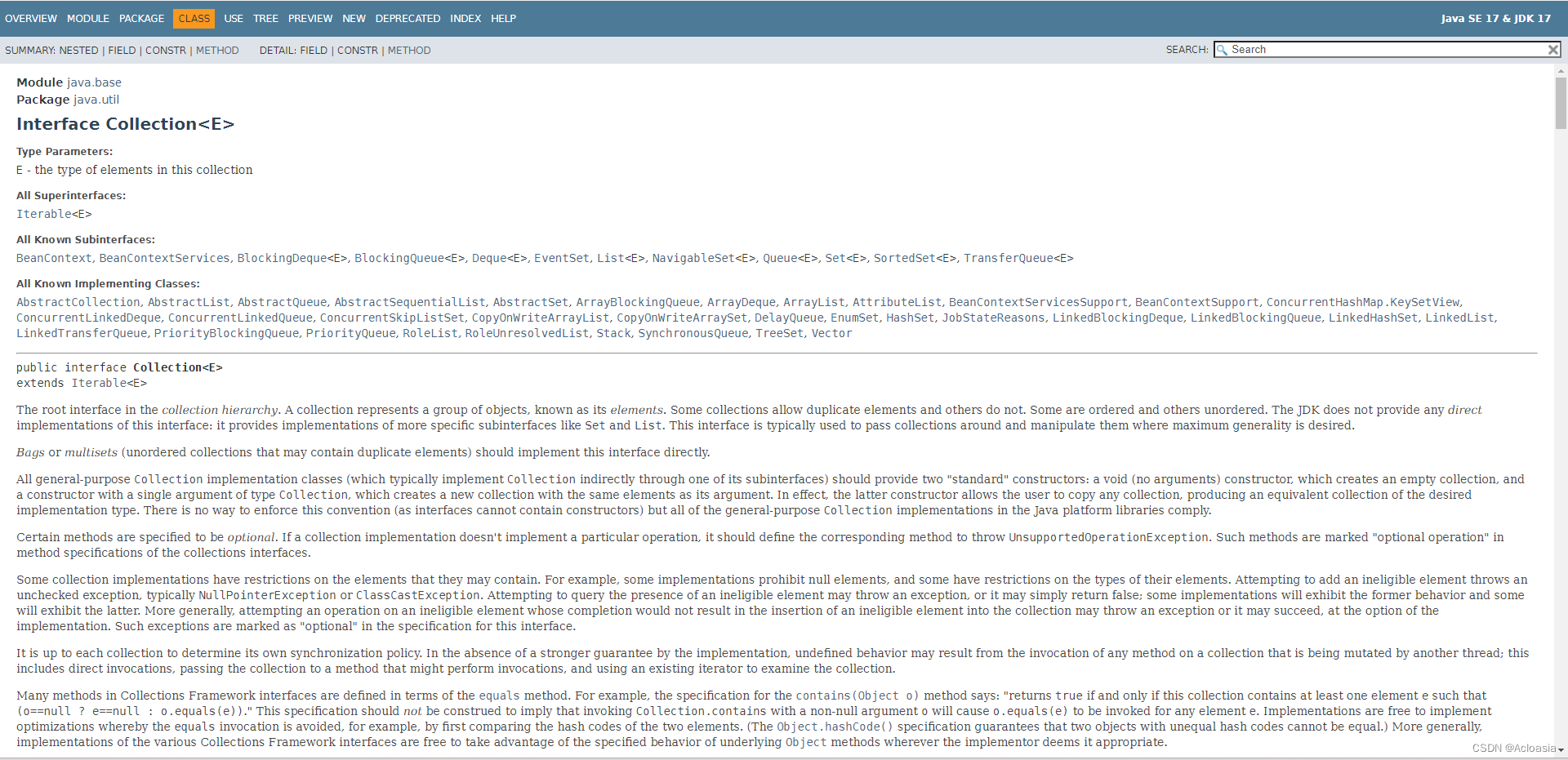
【摘自JDK17】
The root interface in the collection hierarchy. A collection represents a group of objects, known as its elements. Some collections allow duplicate elements and others do not. Some are ordered and others unordered. The JDK does not provide any direct implementations of this interface: it provides implementations of more specific subinterfaces like Set and List. This interface is typically used to pass collections around and manipulate them where maximum generality is desired.
集合层次结构中的根接口。集合表示一组对象,称为其元素。有些集合允许重复元素,而另一些则不允许。有些是有序的,有些是无序的。JDK不提供该接口的任何直接实现:它提供了更具体的子接口(如Set和List)的实现。这个接口通常用于传递集合,并在需要最大通用性的地方对它们进行操作。
1.1 Collection 集合概述和使用
Collection集合概述
是单例集合的顶层接口,它表示一组对象,这些对象也称为Collection的元素
JDK 不提供此接口的任何直接实现.它提供更具体的子接口(如Set和List)实现
创建Collection集合的对象
多态的方式
具体的实现类ArrayList
1.2 Collection集合常用方法
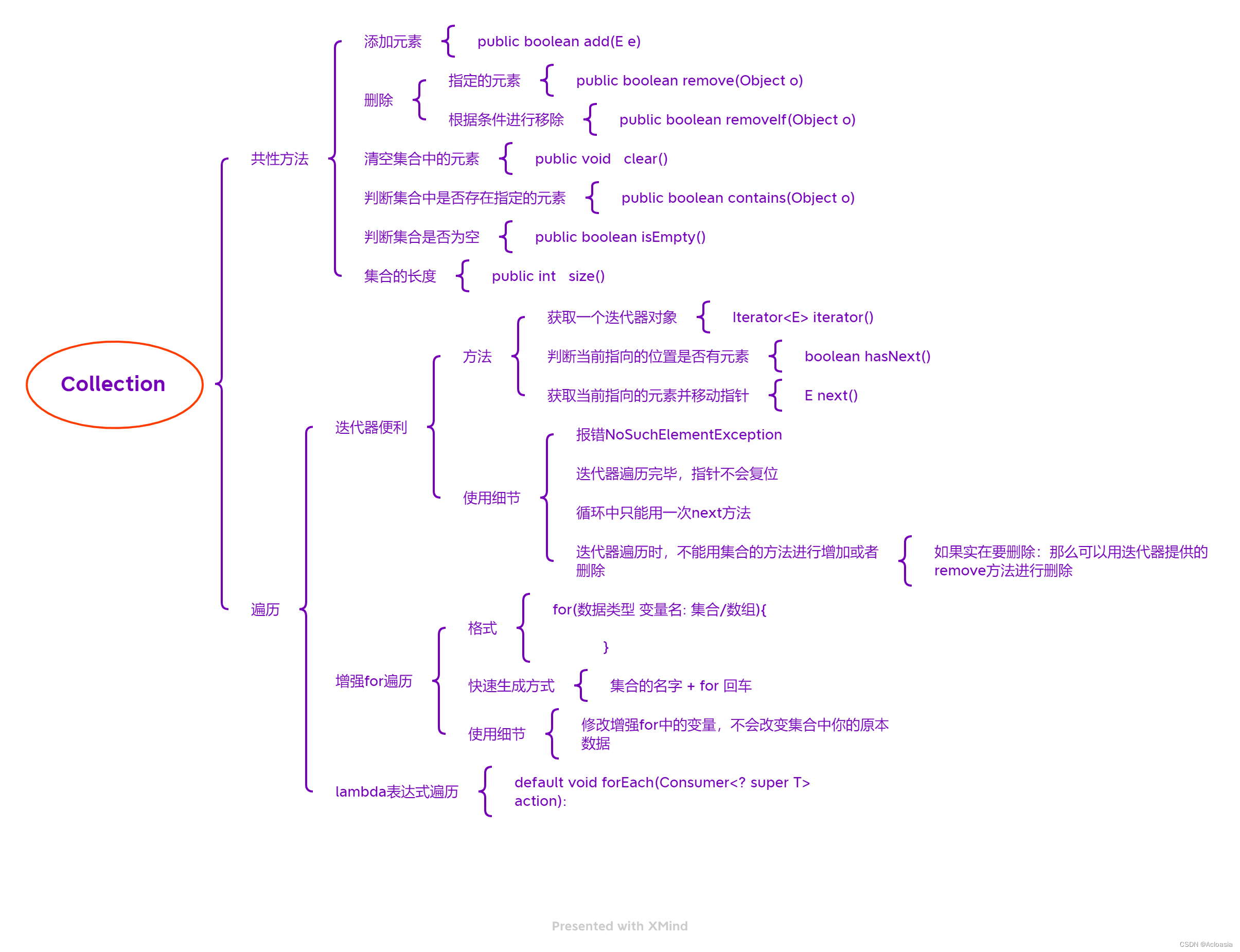
方法名 说明 boolean add(E e) 添加元素 boolean remove(Object o) 从集合中移除指定的元素 boolean removeIf(Object o) 根据条件进行移除 void clear() 清空集合中的元素 boolean contains(Object o) 判断集合中是否存在指定的元素 boolean isEmpty() 判断集合是否为空 int size() 集合的长度,也就是集合中元素的个数 1.3 Collection集合的遍历
Collection系列集合三种通用的遍历方式:
1.迭代器遍历
2.增强for遍历
3.lambda表达式遍历1.3.1 迭代器遍历
public static void main(String[] args) { /* Collection系列集合三种通用的遍历方式: 1.迭代器遍历 2.增强for遍历 3.lambda表达式遍历 迭代器的细节注意点: 1.报错NoSuchElementException 2.迭代器遍历完毕,指针不会复位 3.循环中只能用一次next方法 4.迭代器遍历时,不能用集合的方法进行增加或者删除 如果实在要删除:那么可以用迭代器提供的remove方法进行删除。 如果要添加,暂时没有办法。 */ //1.创建集合并添加元素 Collection<String> Coll = new ArrayList<>(); Coll.add("zhangsan"); Coll.add("lisi"); Coll.add("wangwu"); Coll.add("zhaoliu"); //2.获取迭代器对象 //迭代器就好比是一个箭头,默认指向集合的0索引处 Iterator<String> it = Coll.iterator(); //3.利用循环不断的去获取集合中的每一个元素 while(it.hasNext()){ //4.next方法的两件事情:获取元素并移动指针 String str = it.next(); System.out.println(str); } }1.3.2 增强for遍历
public static void main(String[] args) { /* Collection系列集合三种通用的遍历方式: 1.迭代器遍历 2.增强for遍历 3.lambda表达式遍历 增强for格式: for(数据类型 变量名: 集合/数组){ } 快速生成方式: 集合的名字 + for 回车 */ //1.创建集合并添加元素 Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>(); coll.add("zhangsan"); coll.add("lisi"); coll.add("wangwu"); //2.利用增强for进行遍历 //注意点: //s其实就是一个第三方变量,在循环的过程中依次表示集合中的每一个数据 for(String s : coll){ s = "hello world"; } System.out.println(coll);//zhangsan lisi wangwu }1.3.3 lambda表达式遍历
public static void main(String[] args) { /* Collection系列集合三种通用的遍历方式: 1.迭代器遍历 2.增强for遍历 3.lambda表达式遍历 lambda表达式遍历: default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action): */ //1.创建集合并添加元素 Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>(); coll.add("zhangsan"); coll.add("lisi"); coll.add("wangwu"); //lambda表达式 coll.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s) ); }
未完,待更新