文章目录
- day36 领接表
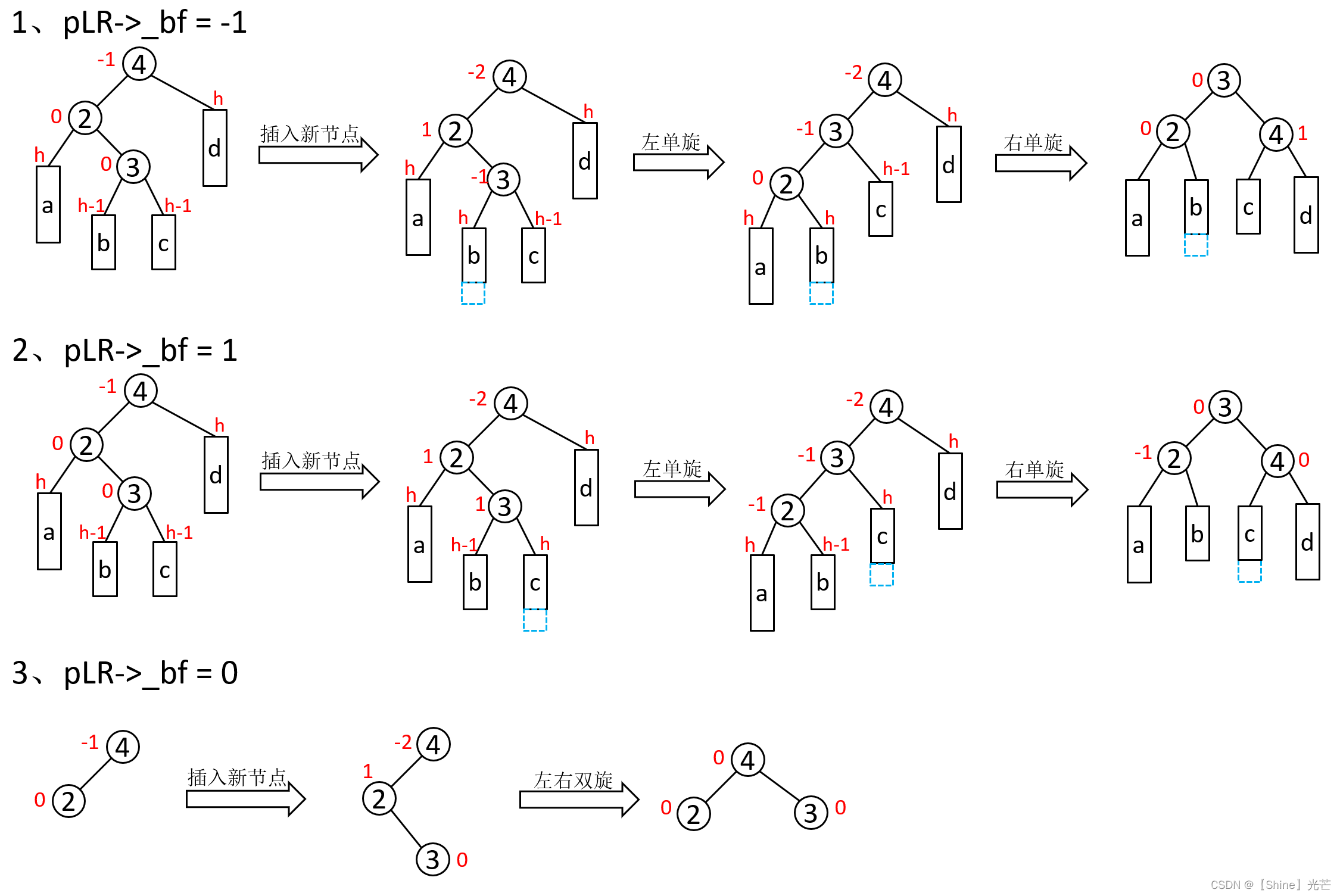
- 1. 领接表知识点
- 2.结合上图去抽象一个邻接表结点的对象
- 3.广度优先遍历
- 4.深度优先遍历
#说明
闵老师的文章链接: 日撸 Java 三百行(总述)_minfanphd的博客-CSDN博客
自己也把手敲的代码放在了github上维护:https://github.com/fulisha-ok/sampledata
day36 领接表
1. 领接表知识点
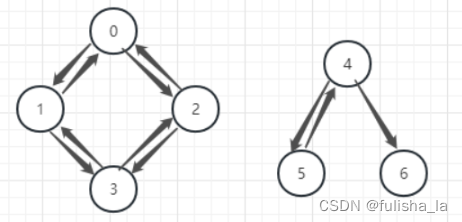
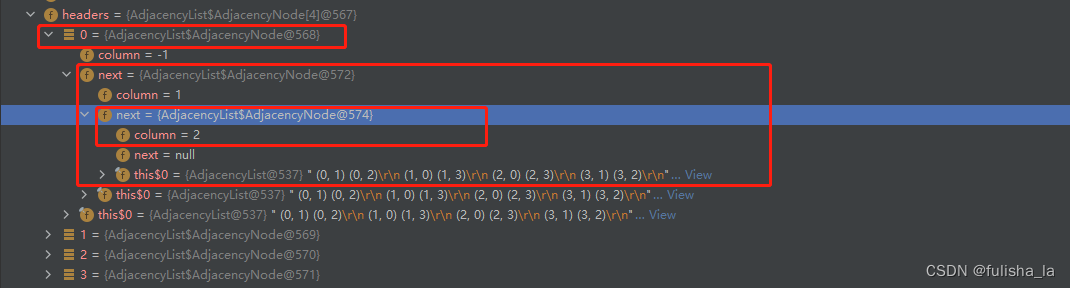
领接表也是图的一种存储结构,之前的存储是领接矩阵。领接表是数组和链表的结合,其中有一个顶点数组和边表组成,如下图所示。对于稀疏图,如果用领接矩阵,有10个节点,则需要10*10的空间,但利用率很低,但是对于邻接表的存储可能需要的空间更少。
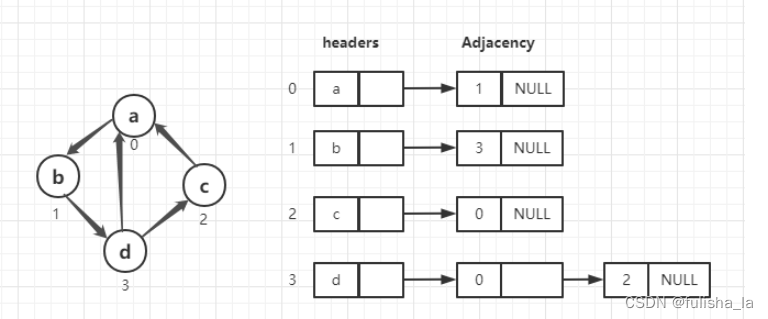
2.结合上图去抽象一个邻接表结点的对象
- 对于顶点数组中,每个结点存的是结点的值,而在边表中的每个结点存储的是顶点数组的下标位置所以对结点的抽象数据就有一个column和一个next
class AdjacencyNode {
/**
* The column index.
*/
int column;
/**
* The next adjacent node.
*/
AdjacencyNode next;
/**
* The first constructor.
* @param paraColumn
*/
public AdjacencyNode(int paraColumn) {
column = paraColumn;
next = null;
}
}
- 对于一个邻接表的构造,从代码中可以知道,对于headers数组的colum设置 为-1,并没有存放数据。在这个构造函数中,tempPreviousNode和tempNode两个变量让顶点数组和边表连接起来了
public AdjacencyList(int[][] paraMatrix) {
numNodes = paraMatrix.length;
// Step 1. Initialize. The data in the headers are not meaningful.
AdjacencyNode tempPreviousNode, tempNode;
headers = new AdjacencyNode[numNodes];
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
headers[i] = new AdjacencyNode(-1);
tempPreviousNode = headers[i];
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
if (paraMatrix[i][j] == 0) {
continue;
}
tempNode = new AdjacencyNode(j);
tempPreviousNode.next = tempNode;
tempPreviousNode = tempNode;
}
}
}
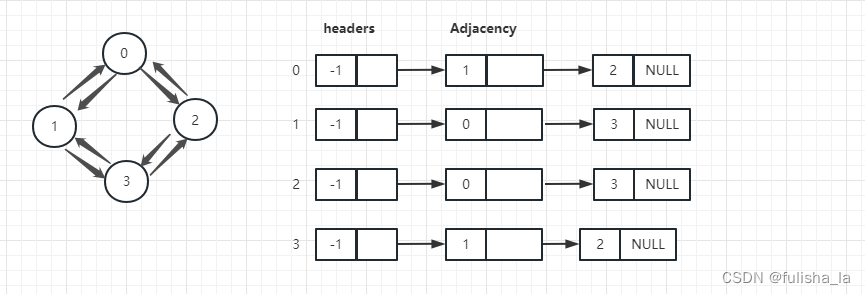
一下数组在初始化后的存储结构,这个.打断点看headers数据结构
int[][] tempMatrix = { { 0, 1, 1, 0 }, { 1, 0, 0, 1 }, { 1, 0, 0, 1 }, { 0, 1, 1, 0 } };
3.广度优先遍历
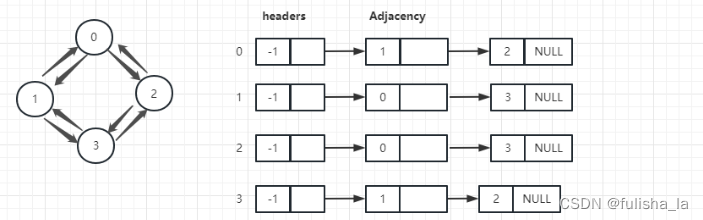
- 邻接表的广度优先也会借助队列实现(以索引2开始)
访问头节点2,将2的边表结点(0,3)访问完并入队列,然后出队列0访问其边结点1,2(并判断是否已经被访问过)依次来访问所有结点
 $$
$$ - 邻接矩阵
访问结点2,并判断其他所有结点与2之间有相连(则横向看2与0,3相连,则把0,3入队列),1,2跳过;之后又0出队列,并判断其他所有结点与0之间有相连等,以这样的方式来进行广度遍历
Δ 0 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 2 1 0 0 1 3 0 1 1 0 \begin{array}{c} % 总表格 \begin{array}{c|cccc} % 第二行 Delta 值数组 \Delta & 0 & 1 & 2 & 3 \\ \hline 0 & 0 & 1 & 1 & 0 \\ 1 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\ 2 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 1\\ 3 & 0 &1 & 1 & 0 \\ \end{array} % 第二行表格结束 \end{array} % 总表格结束 Δ012300110110012100130110 - 从邻接表和邻接矩阵实现广度遍历的过程中,我们可以发现,邻接表在判断结点的相邻结点时更容易,只需要访问其边表结点即可,而邻接矩阵要遍历所有的结点,所以当数据量很大的时候,邻接表的效率会高点。所以从代码上来看,邻接矩阵和邻接表的到差不差,主要区别在于遍历结点方式上。领接矩阵是for循环了所有结点,而邻接矩阵是while当前访问头结点的边表结点即可。
public String breadthFirstTraversal(int paraStartIndex) {
CircleObjectQueue tempQueue = new CircleObjectQueue();
String resultString = "";
boolean[] tempVisitedArray = new boolean[numNodes];
tempVisitedArray[paraStartIndex] = true;
// Initialize the queue.
// Visit before enqueue.
tempVisitedArray[paraStartIndex] = true;
resultString += paraStartIndex;
tempQueue.enqueue(new Integer(paraStartIndex));
// Now visit the rest of the graph.
int tempIndex;
Integer tempInteger = (Integer) tempQueue.dequeue();
AdjacencyNode tempNode;
while (tempInteger != null) {
tempIndex = tempInteger.intValue();
// Enqueue all its unvisited neighbors. The neighbors are linked
// already.
tempNode = headers[tempIndex].next;
while (tempNode != null) {
if (!tempVisitedArray[tempNode.column]) {
// Visit before enqueue.
tempVisitedArray[tempNode.column] = true;
resultString += tempNode.column;
tempQueue.enqueue(new Integer(tempNode.column));
} // Of if
tempNode = tempNode.next;
} // Of for i
// Take out one from the head.
tempInteger = (Integer) tempQueue.dequeue();
} // Of while
return resultString;
}
4.深度优先遍历
-
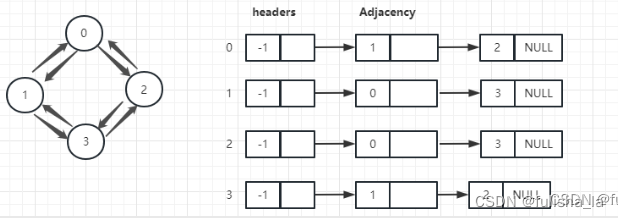
邻接表的深度优先借助栈实现(以索引2开始)
访问头节点2,将2的边表结点(0)访问完并入栈,然后接着访问头结点为0的边表结点1,访问完1再将1入栈,头节点为1的边表结点0,发现已经被访问过则跳过,访问3并将3入栈,然后访问3的边表结点都访问过就回溯。
-
邻接矩阵
访问结点2,将2结点入栈,判断2结点以外的所有结点是否被访问过且是否与2结点相邻,发现0结点符合条件则跳出循环,将0结点入栈,接着又开始判断0结点的条件,以此类推。
Δ 0 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 2 1 0 0 1 3 0 1 1 0 \begin{array}{c} % 总表格 \begin{array}{c|cccc} % 第二行 Delta 值数组 \Delta & 0 & 1 & 2 & 3 \\ \hline 0 & 0 & 1 & 1 & 0 \\ 1 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\ 2 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 1\\ 3 & 0 &1 & 1 & 0 \\ \end{array} % 第二行表格结束 \end{array} % 总表格结束 Δ012300110110012100130110 -
从邻接表和邻接矩阵实现深度遍历的过程中,主要区别也是在访问相邻结点区别上。如下代码
public String depthFirstTraversal(int paraStartIndex) {
ObjectStack tempStack = new ObjectStack();
String resultString = "";
boolean[] tempVisitedArray = new boolean[numNodes];
tempVisitedArray[paraStartIndex] = true;
resultString += paraStartIndex;
tempStack.push(new Integer(paraStartIndex));
System.out.println("Push " + paraStartIndex);
System.out.println("Visited " + resultString);
int tempIndex = paraStartIndex;
int tempNext;
Integer tempInteger;
AdjacencyNode tempNode;
while (true) {
tempNext = -1;
// Find an unvisited neighbor and push
tempNode = headers[tempIndex].next;
while (tempNode != null) {
if (!tempVisitedArray[tempNode.column]) {
// Visit before enqueue.
tempVisitedArray[tempNode.column] = true;
resultString += tempNode.column;
tempStack.push(new Integer(tempNode.column));
System.out.println("Push " + tempNode.column);
tempNext = tempNode.column;
break;
} // Of if
tempNode = tempNode.next;
}
if (tempNext == -1) {
//there is no neighbor node, pop
tempInteger = (Integer) tempStack.pop();
System.out.println("Pop " + tempInteger);
if (tempStack.isEmpty()) {
//No unvisited neighbor。Backtracking to the last one stored in the stack
break;
} else {
tempInteger = (Integer) tempStack.pop();
tempIndex = tempInteger.intValue();
tempStack.push(tempInteger);
}
} else {
tempIndex = tempNext;
}
}
return resultString;
}
##5.代码
package graph;
import datastructure.queue.CircleObjectQueue;
import datastructure.stack.ObjectStack;
/**
* @author: fulisha
* @date: 2023/4/24 11:34
* @description:
*/
public class AdjacencyList {
/**
* An inner class for adjacent node.
*/
class AdjacencyNode {
/**
* The column index.
*/
int column;
/**
* The next adjacent node.
*/
AdjacencyNode next;
/**
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraColumn
*/
public AdjacencyNode(int paraColumn) {
column = paraColumn;
next = null;
}
}
int numNodes;
AdjacencyNode[] headers;
public AdjacencyList(int[][] paraMatrix) {
numNodes = paraMatrix.length;
// Step 1. Initialize. The data in the headers are not meaningful.
AdjacencyNode tempPreviousNode, tempNode;
headers = new AdjacencyNode[numNodes];
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
headers[i] = new AdjacencyNode(-1);
tempPreviousNode = headers[i];
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
if (paraMatrix[i][j] == 0) {
continue;
}
tempNode = new AdjacencyNode(j);
tempPreviousNode.next = tempNode;
tempPreviousNode = tempNode;
}
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String resultString = "";
AdjacencyNode tempNode;
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
tempNode = headers[i].next;
while (tempNode != null) {
resultString += " (" + i + ", " + tempNode.column + ")";
tempNode = tempNode.next;
} // Of while
resultString += "\r\n";
}
return resultString;
}
boolean[] tempVisitedArray;
String resultString = "";
public String breadthFirstTraversal(int paraStartIndex) {
CircleObjectQueue tempQueue = new CircleObjectQueue();
String resultString = "";
tempVisitedArray = new boolean[numNodes];
tempVisitedArray[paraStartIndex] = true;
// Initialize the queue.
// Visit before enqueue.
tempVisitedArray[paraStartIndex] = true;
resultString += paraStartIndex;
tempQueue.enqueue(new Integer(paraStartIndex));
// Now visit the rest of the graph.
int tempIndex;
Integer tempInteger = (Integer) tempQueue.dequeue();
AdjacencyNode tempNode;
while (tempInteger != null) {
tempIndex = tempInteger.intValue();
// Enqueue all its unvisited neighbors. The neighbors are linked
// already.
tempNode = headers[tempIndex].next;
while (tempNode != null) {
if (!tempVisitedArray[tempNode.column]) {
// Visit before enqueue.
tempVisitedArray[tempNode.column] = true;
resultString += tempNode.column;
tempQueue.enqueue(new Integer(tempNode.column));
} // Of if
tempNode = tempNode.next;
} // Of for i
// Take out one from the head.
tempInteger = (Integer) tempQueue.dequeue();
} // Of while
return resultString;
}
public String depthFirstTraversal(int paraStartIndex) {
ObjectStack tempStack = new ObjectStack();
resultString = "";
tempVisitedArray = new boolean[numNodes];
tempVisitedArray[paraStartIndex] = true;
resultString += paraStartIndex;
tempStack.push(new Integer(paraStartIndex));
System.out.println("Push " + paraStartIndex);
System.out.println("Visited " + resultString);
int tempIndex = paraStartIndex;
int tempNext;
Integer tempInteger;
AdjacencyNode tempNode;
while (true) {
tempNext = -1;
// Find an unvisited neighbor and push
tempNode = headers[tempIndex].next;
while (tempNode != null) {
if (!tempVisitedArray[tempNode.column]) {
// Visit before enqueue.
tempVisitedArray[tempNode.column] = true;
resultString += tempNode.column;
tempStack.push(new Integer(tempNode.column));
System.out.println("Push " + tempNode.column);
tempNext = tempNode.column;
break;
} // Of if
tempNode = tempNode.next;
}
if (tempNext == -1) {
//there is no neighbor node, pop
tempInteger = (Integer) tempStack.pop();
System.out.println("Pop " + tempInteger);
if (tempStack.isEmpty()) {
//No unvisited neighbor。Backtracking to the last one stored in the stack
break;
} else {
tempInteger = (Integer) tempStack.pop();
tempIndex = tempInteger.intValue();
tempStack.push(tempInteger);
}
} else {
tempIndex = tempNext;
}
}
return resultString;
}
public boolean breadthTraversal(int paraStartIndex) {
tempVisitedArray = new boolean[numNodes];
resultString = "";
breadthFirstTraversal(paraStartIndex);
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++){
if (!tempVisitedArray[i]){
breadthFirstTraversal(i);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean depthTraversal(int paraStartIndex){
tempVisitedArray = new boolean[numNodes];
resultString = "";
depthFirstTraversal(paraStartIndex);
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++){
if (!tempVisitedArray[i]){
depthFirstTraversal(i);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void breadthFirstTraversalTest() {
// Test an undirected graph.
int[][] tempMatrix = { { 0, 1, 1, 0 }, { 1, 0, 0, 1 }, { 1, 0, 0, 0}, { 0, 1, 0, 0} };
// int[][] tempMatrix = { { 0, 1, 1, 0 , 0}, { 1, 0, 0, 1, 0 }, { 1, 0, 0, 1, 0}, { 0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0} };
// int[][] tempMatrix = { { 0, 1, 1, 0 , 0, 0, 0}, { 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 }, { 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0}, { 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1}, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0}, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0} };
Graph tempGraph = new Graph(tempMatrix);
System.out.println(tempGraph);
AdjacencyList tempAdjList = new AdjacencyList(tempMatrix);
String tempSequence = "";
try {
// tempSequence = tempAdjList.breadthFirstTraversal(2);
tempGraph.breadthTraversal(0);
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println(ee);
} // Of try.
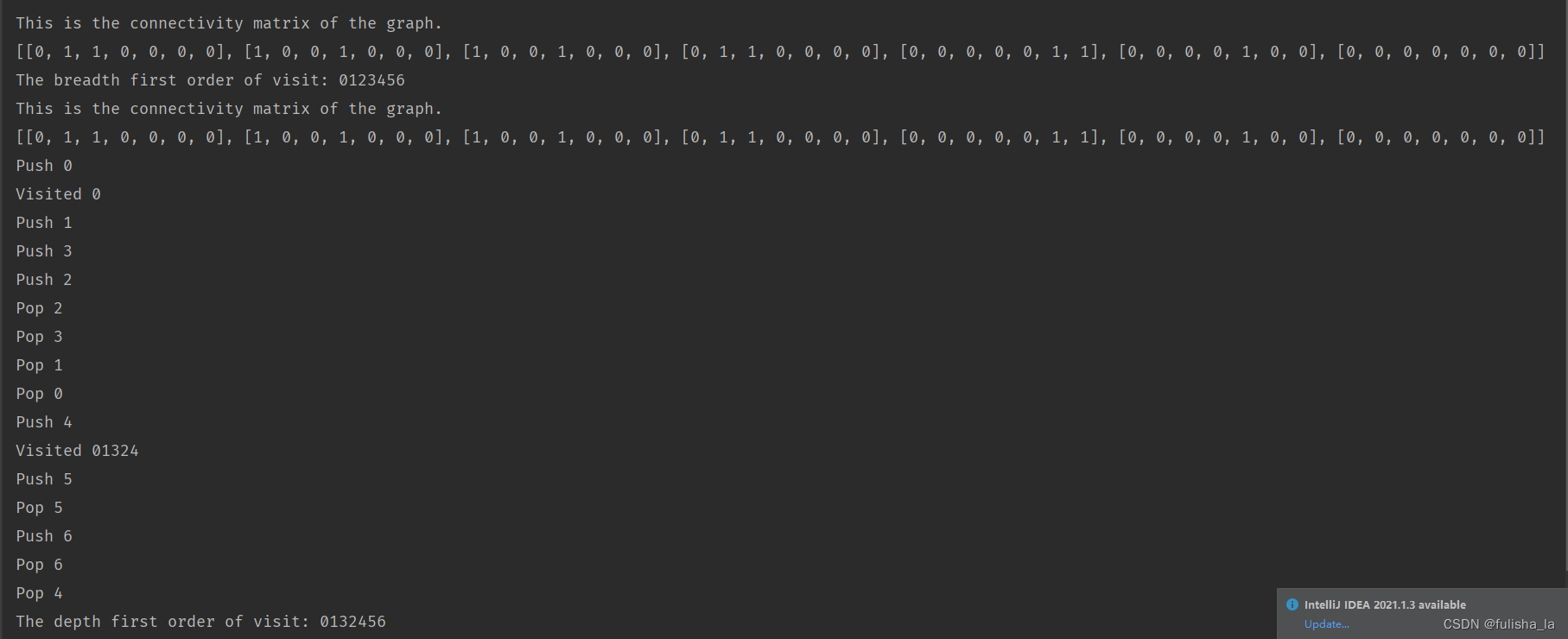
System.out.println("The breadth first order of visit: " + tempGraph.resultString);
}
public static void depthFirstTraversalTest() {
// Test an undirected graph.
int[][] tempMatrix = { { 0, 1, 1, 0 }, { 1, 0, 0, 1 }, { 1, 0, 0, 0}, { 0, 1, 0, 0} };
//int[][] tempMatrix = { { 0, 1, 1, 0 , 0}, { 1, 0, 0, 1, 0 }, { 1, 0, 0, 1, 0}, { 0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0} };
//int[][] tempMatrix = { { 0, 1, 1, 0 , 0, 0, 0}, { 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 }, { 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0}, { 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1}, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0}, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0} };
Graph tempGraph = new Graph(tempMatrix);
System.out.println(tempGraph);
AdjacencyList tempAdjList = new AdjacencyList(tempMatrix);
String tempSequence = "";
try {
tempGraph.depthTraversal(0);
// tempSequence = tempAdjList.depthFirstTraversal(2);
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println(ee);
} // Of try.
System.out.println("The depth first order of visit: " + tempGraph.resultString);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[][] tempMatrix = { { 0, 1, 0 }, { 1, 0, 1 }, { 0, 1, 0 } };
AdjacencyList tempTable = new AdjacencyList(tempMatrix);
System.out.println("The data are:\r\n" + tempTable);
breadthFirstTraversalTest();
depthFirstTraversalTest();
}
}
- 单元测试1
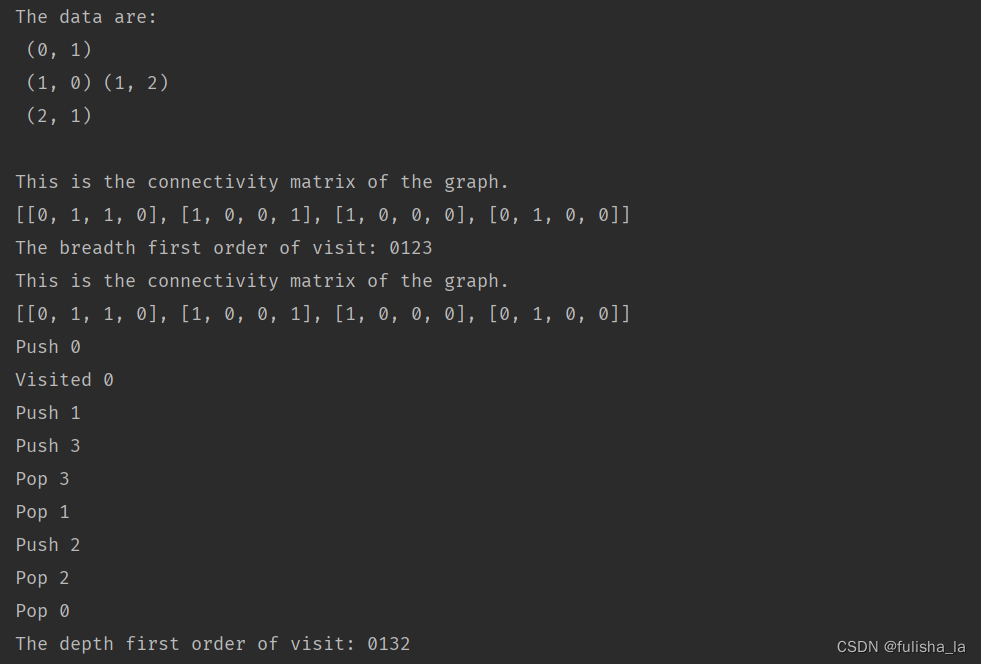
- 单元测试2
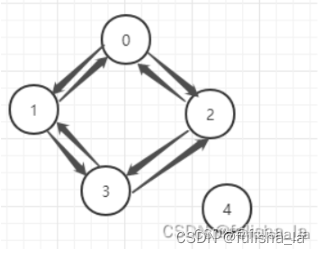
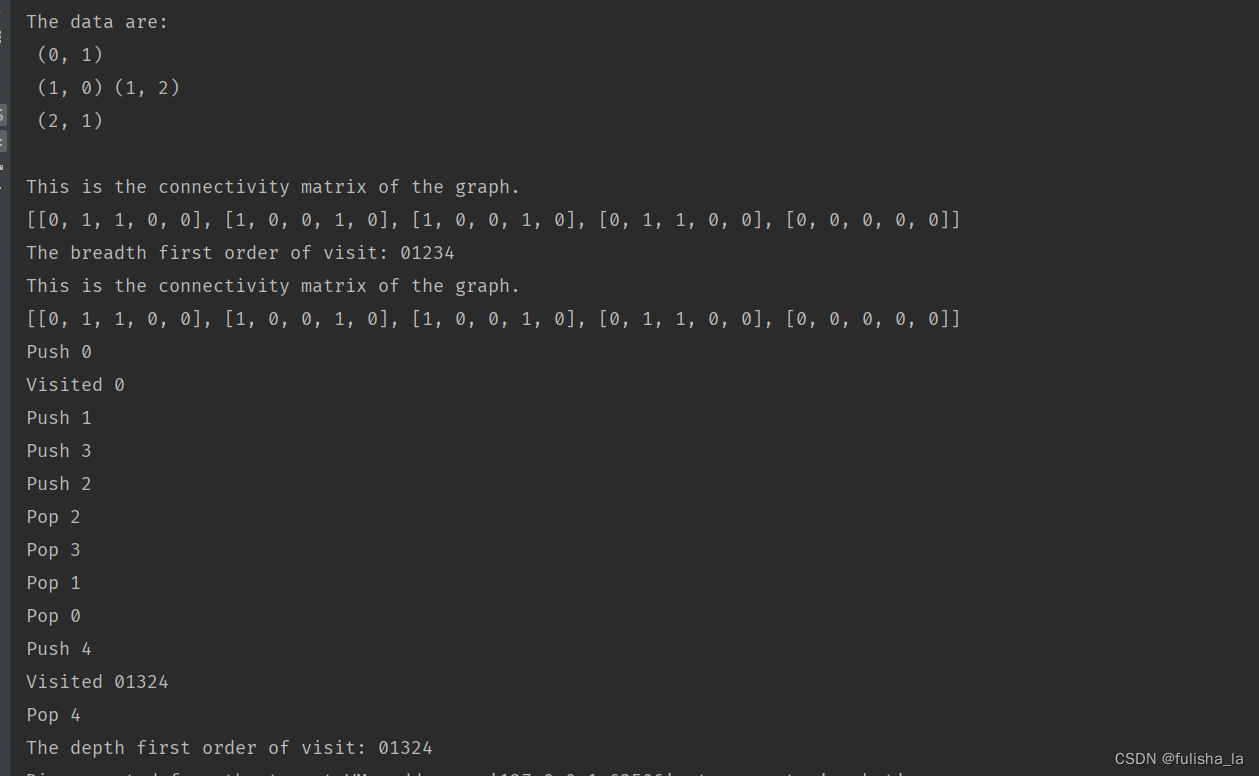
- 单元测试3