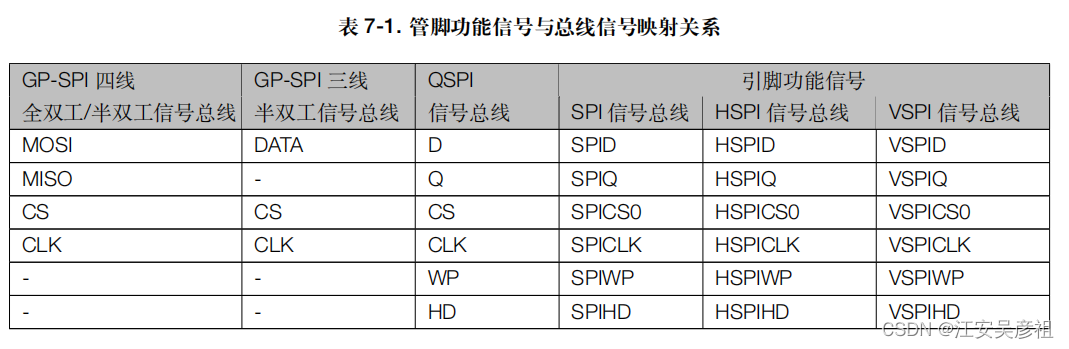
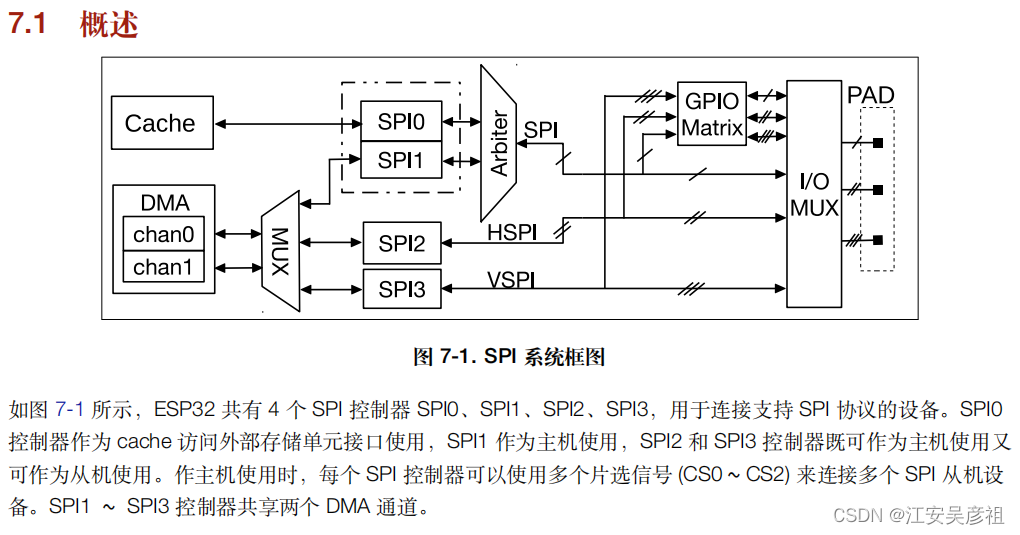
说明
SPI共有4根线,MOSI、MISO、CS、CLK,在ESP32中对应规则如下表:
ESP32共有4个SPI,但是用户能够使用的只有2个SPI,分为VSPI和HSPI。
引脚接口
在ESP32的数据手册中,说明了VSPI和HSPI对应的引脚:
- VSPI:
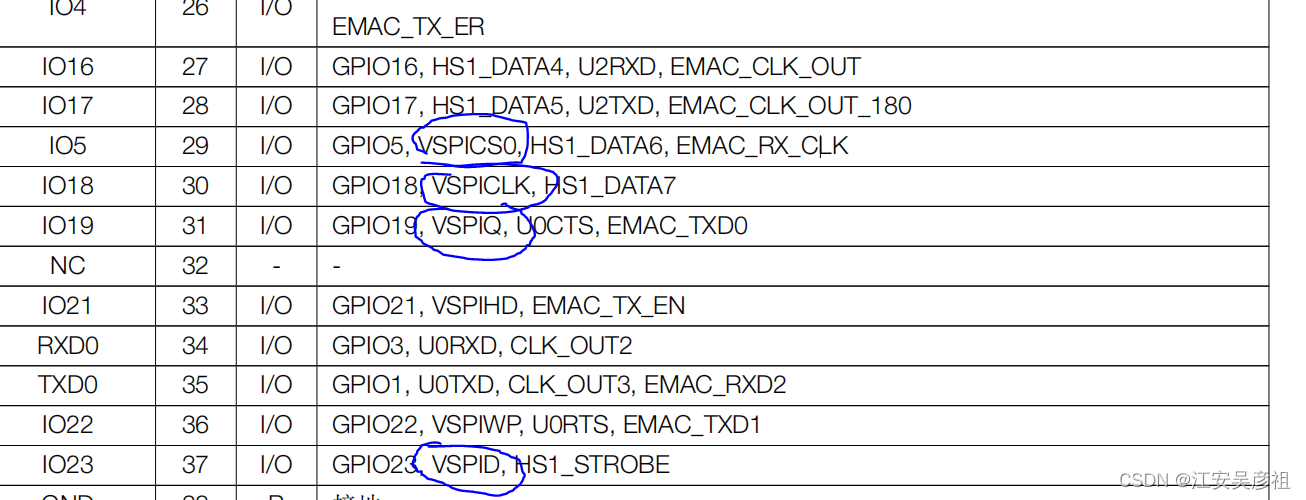
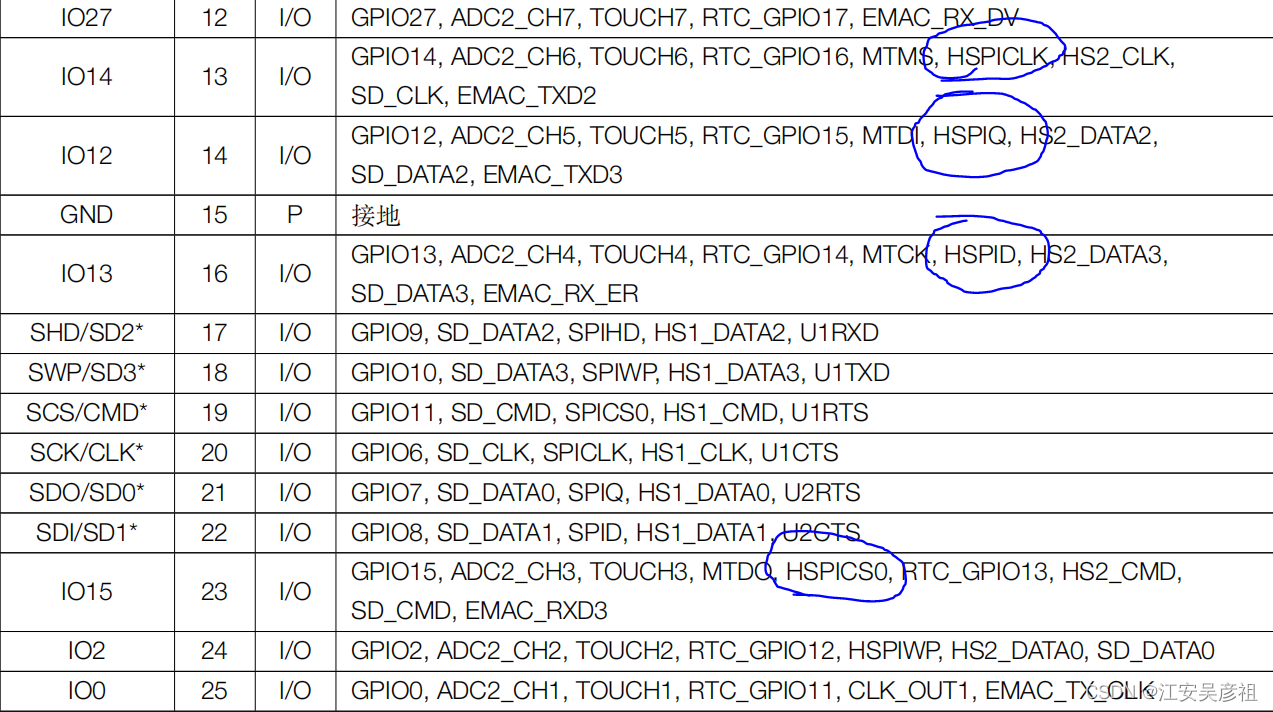
- HSPI:
但是比较麻烦的是,ESP官方不知道犯了什么SB毛病,非弄出来个没有丝毫用途的Strapping 管脚,稍不注意,上电瞬间Strapping管脚电平不对,就没法正常启动,导致但凡是有Strapping管脚功能的引脚,大家都不敢使用。
在SPI中也是这样,VSPI和HSPI默认的引脚中,都有作为Strapping管脚的引脚。我们要格外格外的小心。

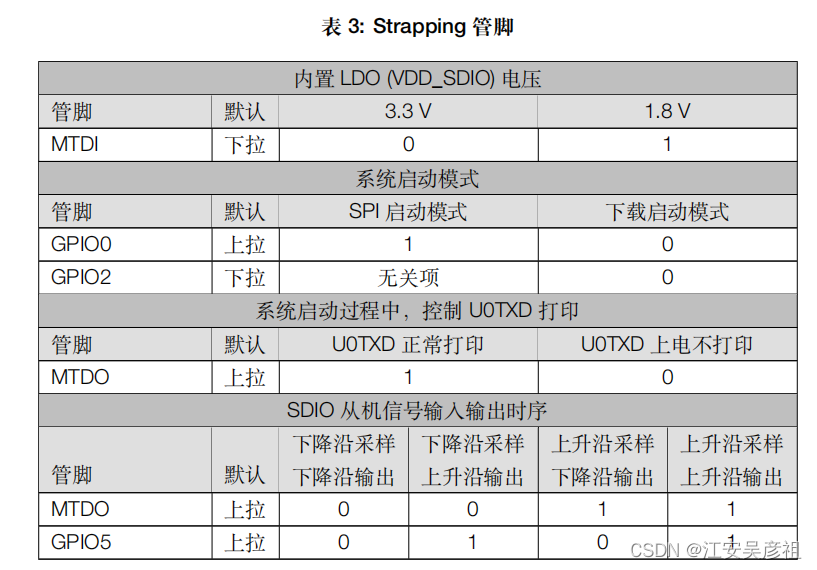
结合Strapping管脚,将引脚对应整理如下表:
- VSPI
| 引脚 | 功能 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| IO23 | MOSI | |
| IO19 | MISO | |
| IO18 | CLK | |
| IO5 | CS | Strapping管脚,上电瞬间必须保证上拉 |
- HSPI
| 引脚 | 功能 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| IO13 | MOSI | |
| IO12 | MISO | Strapping管脚,上电瞬间必须保证下拉 |
| IO14 | CLK | |
| IO15 | CS | Strapping管脚,上电瞬间必须保证上拉 |
更改Auduino框架中SPI默认的引脚
在用arduino框架时,其默认的SPI引脚如下:
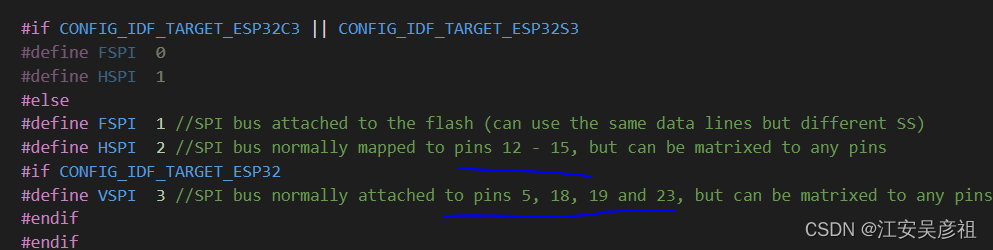
除了使用默认的引脚之外,还可以使用其他方式更改默认引脚。官方给出的示例如下:
/* The ESP32 has four SPi buses, however as of right now only two of
* them are available to use, HSPI and VSPI. Simply using the SPI API
* as illustrated in Arduino examples will use VSPI, leaving HSPI unused.
*
* However if we simply intialise two instance of the SPI class for both
* of these buses both can be used. However when just using these the Arduino
* way only will actually be outputting at a time.
*
* Logic analyser capture is in the same folder as this example as
* "multiple_bus_output.png"
*
* created 30/04/2018 by Alistair Symonds
*/
#include <SPI.h>
// Define ALTERNATE_PINS to use non-standard GPIO pins for SPI bus
#ifdef ALTERNATE_PINS
#define VSPI_MISO 2
#define VSPI_MOSI 4
#define VSPI_SCLK 0
#define VSPI_SS 33
#define HSPI_MISO 26
#define HSPI_MOSI 27
#define HSPI_SCLK 25
#define HSPI_SS 32
#else
#define VSPI_MISO MISO
#define VSPI_MOSI MOSI
#define VSPI_SCLK SCK
#define VSPI_SS SS
#define HSPI_MISO 12
#define HSPI_MOSI 13
#define HSPI_SCLK 14
#define HSPI_SS 15
#endif
#if CONFIG_IDF_TARGET_ESP32S2 || CONFIG_IDF_TARGET_ESP32S3
#define VSPI FSPI
#endif
static const int spiClk = 1000000; // 1 MHz
//uninitalised pointers to SPI objects
SPIClass * vspi = NULL;
SPIClass * hspi = NULL;
void setup() {
//initialise two instances of the SPIClass attached to VSPI and HSPI respectively
vspi = new SPIClass(VSPI);
hspi = new SPIClass(HSPI);
//clock miso mosi ss
#ifndef ALTERNATE_PINS
//initialise vspi with default pins
//SCLK = 18, MISO = 19, MOSI = 23, SS = 5
vspi->begin();
#else
//alternatively route through GPIO pins of your choice
vspi->begin(VSPI_SCLK, VSPI_MISO, VSPI_MOSI, VSPI_SS); //SCLK, MISO, MOSI, SS
#endif
#ifndef ALTERNATE_PINS
//initialise hspi with default pins
//SCLK = 14, MISO = 12, MOSI = 13, SS = 15
hspi->begin();
#else
//alternatively route through GPIO pins
hspi->begin(HSPI_SCLK, HSPI_MISO, HSPI_MOSI, HSPI_SS); //SCLK, MISO, MOSI, SS
#endif
//set up slave select pins as outputs as the Arduino API
//doesn't handle automatically pulling SS low
pinMode(vspi->pinSS(), OUTPUT); //VSPI SS
pinMode(hspi->pinSS(), OUTPUT); //HSPI SS
}
// the loop function runs over and over again until power down or reset
void loop() {
//use the SPI buses
spiCommand(vspi, 0b01010101); // junk data to illustrate usage
spiCommand(hspi, 0b11001100);
delay(100);
}
void spiCommand(SPIClass *spi, byte data) {
//use it as you would the regular arduino SPI API
spi->beginTransaction(SPISettings(spiClk, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0));
digitalWrite(spi->pinSS(), LOW); //pull SS slow to prep other end for transfer
spi->transfer(data);
digitalWrite(spi->pinSS(), HIGH); //pull ss high to signify end of data transfer
spi->endTransaction();
}