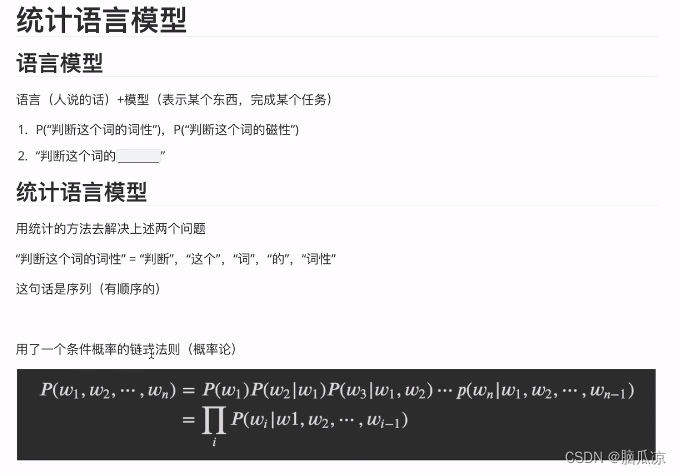
本篇文章承接上文,主要阐述代码,分布的成果等工作。识别结果为单帧图片,每一张图片识别完之后,放在一起,就可以连续播放单帧文件,变成视频,或者直接在matlab图窗里面播放。关于这个函数的功能我会在下一篇文章中进行介绍,感兴趣可以点个关注,去我主页看,或者直接下载资源:传送门。偶尔在平台上回复不及时,可以来找我咨询或下载
注意,要成功复现本项目需要准备好matlab2020a以上版本以及python3.0环境,最好准备好cuda环境,可以大幅度降低大数据训练的时间,没有也没关系,准备好后可以进行接下来的内容啦。
开始正文
数据准备
准备训练集和数据集,训练集包括以下文件:

如果你下载的是我准备好的200个测试文件,那么应该包含如下内容:

测试集如下所示,你可以从训练集随机选取一些作为测试集,也可以使用我打包好的文件。

对于calib的标签文件,我选择了一个放在里面,感兴趣的可以选其他的calib放在里面,当然,你也可以去德国图宾根官网下载数据,同样适用于我们的项目!(前提是要会ladder,想要更多数据的可以联系我q2504953121,路况包括不限于田野,交通路口,高架桥,高校校园等复杂路况。)
数据集可视化
clc; clear; close all;
file = '000264'; % 文件编号
fid=fopen(['./training/velodyne/',file,'.bin'],'rb');
[a,count]=fread(fid,'float32');
fclose(fid);
x = a(1:4:end);
y = a(2:4:end);
z = a(3:4:end);
reflectivity = a(4:4:end);
point_cloud = [x,y,z,reflectivity];
data = pointCloud([x y z]);
figure(11);
pcshow(data);hold on;
label = importdata(['./training/label/',file,'.txt']);
obsName = label.textdata;
data_label = label.data;
obsNum = size(data_label,1); % 包含DontCare类障碍物的总个数
obsCount = 0; % 初始化不包含DontCare类障碍物个数为0
data_calib = importdata(['./training/calib/',file,'.txt']);
Tr_velo_to_cam = reshape(data_calib.data(end-1,:),[4,3])';
Tr_velo_to_cam = [Tr_velo_to_cam;0 0 0 1];
pos = {}; % 创建一个cell数组用于存储障碍物坐标
for i = 1:obsNum
if obsName{i} == "DontCare"
continue;
end
obsCount = obsCount + 1;
la = data_label(i,:);
obsPos = la(11:13)';
[h,w,l] = deal(la(8),la(9),la(10));
r_y = la(end);
% obsPos_velo = Tr_cam_to_velo*[obsPos;1];
% obsPos_velo = obsPos_velo(1:3)
% t1~t8为障碍物坐标系下的坐标(不考虑障碍物旋转,默认长边与x-axis平行)
t1 = [l/2,0,w/2];
t2 = [l/2,0,-w/2];
t3 = [l/2,-h,w/2];
t4 = [l/2,-h,-w/2];
t5 = [-l/2,0,w/2];
t6 = [-l/2,0,-w/2];
t7 = [-l/2,-h,w/2];
t8 = [-l/2,-h,-w/2];
% 考虑障碍物旋转角度r_y,对x,z方向进行更新
T = [t1;t2;t3;t4;t5;t6;t7;t8];
R = [cos(r_y),-sin(r_y);sin(r_y),cos(r_y)];
T(:,[1,3]) = (R*T(:,[1,3])')';
% 考虑障碍物坐标系与相机坐标系坐标位移
T(:,1) = T(:,1) + obsPos(1);
T(:,2) = T(:,2) + obsPos(2);
T(:,3) = T(:,3) + obsPos(3);
% 将相机坐标系转化到激光雷达坐标系
velo_pos = Tr_velo_to_cam\[T';1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1];
velo_pos = velo_pos(1:3,:);
% 记录障碍Box坐标
pos{i} = velo_pos;
% 绘制12根线构成3D-Box
temp = [velo_pos(:,3),velo_pos(:,4),velo_pos(:,7),velo_pos(:,8)];
[~,j] = max([velo_pos(1,3),velo_pos(1,4),velo_pos(1,7),velo_pos(1,8)]);
textPoint = temp(:,j);
text(textPoint(1),textPoint(2),textPoint(3)+0.5,obsName{i},'Color','white');
plot3(velo_pos(1,[1,2,6,5,1]),velo_pos(2,[1,2,6,5,1]),velo_pos(3,[1,2,6,5,1]),'Color','r');
plot3(velo_pos(1,[3,4,8,7,3]),velo_pos(2,[3,4,8,7,3]),velo_pos(3,[3,4,8,7,3]),'Color','r');
plot3(velo_pos(1,[1,3]),velo_pos(2,[1,3]),velo_pos(3,[1,3]),'Color','r');
plot3(velo_pos(1,[2,4]),velo_pos(2,[2,4]),velo_pos(3,[2,4]),'Color','r');
plot3(velo_pos(1,[6,8]),velo_pos(2,[6,8]),velo_pos(3,[2,4]),'Color','r');
plot3(velo_pos(1,[5,7]),velo_pos(2,[5,7]),velo_pos(3,[5,7]),'Color','r');
end
结果如下:主要实现的功能是选取一个训练集可视化,看一下标签,即机动车是什么类型的车,并把点云数据标红。

障碍物点云提取
figure(2);
row = ceil(obsCount / 3);
[n,~] = size(point_cloud);
for k = 1:obsCount
[max_x,~] = max(pos{k}(1,[1,2,5,6]));
[min_x,~] = min(pos{k}(1,[1,2,5,6]));
[max_y,~] = max(pos{k}(2,[1,2,5,6]));
[min_y,~] = min(pos{k}(2,[1,2,5,6]));
point_selected = [];
for i = 1:n
if point_cloud(i,1)>min_x && point_cloud(i,1)<max_x...
&& point_cloud(i,2)>min_y && point_cloud(i,2)<max_y
point_selected = [point_selected;point_cloud(i,:)];
end
end
subplot(row,3,k);
data = pointCloud([point_selected(:,1),point_selected(:,2),point_selected(:,3)]);
pcshow(data);hold on;
title(obsName{k});
end
结果如下:主要实现的功能是把此数据集中包含的车辆拿出来,就像在橱窗里面展示玩具车一样。

非地面点云分割
这里对点云分割有两种方法
第一种 RANSAC算法去除地面点云
options.epsilon = 1e-6;
options.P_inlier = 0.90;
options.sigma = 0.01;
options.T_noise_squared = 0.002;
options.est_fun = @estimate_plane;
options.man_fun = @error_plane;
options.mode = 'MSAC';
options.Ps = [];
options.notify_iters = [];
options.min_iters = 1000;
options.fix_seed = false;
options.reestimate = true;
options.stabilize = false;
processed_point_cloud = point_cloud((point_cloud(:,3)<-1)&(point_cloud(:,3)>-2.5),:);
temp = 1:size(point_cloud,1);
index = temp(point_cloud(:,3)<0);
[results, options] = RANSAC(processed_point_cloud', options);
ind = results.CS;
plane_cloud_point = processed_point_cloud(ind,:);
figure(3);
data = pointCloud([plane_cloud_point(:,1),plane_cloud_point(:,2),plane_cloud_point(:,3)]);
pcshow(data);hold on;
title('The plane point cloud')
figure(4);
temp1 = index(ind);
temp2 = 1:size(point_cloud,1);
temp2(temp1) = [];
not_plane_cloud_point = point_cloud(temp2,:);
data = pointCloud([not_plane_cloud_point(:,1),not_plane_cloud_point(:,2),not_plane_cloud_point(:,3)]);
pcshow(data);hold on;
title('The point cloud without plane')
第二种 直接按照高度去除地面点云
figure(5);
processed_point_cloud = point_cloud(point_cloud(:,3)>-1.5,:);
data = pointCloud(processed_point_cloud(:,1:3));
pcshow(data);hold on;
两种的得到的效果类似(英文题目为ransac效果,中文题目为直接按照高度去除),如下:主要实现的功能是把此数据集中包含的地面反射的点云去除,否则十分影响我们的车辆识别。
-
地上的点云

上下图不是一个时刻的文件

-
去除地面后的点云


点云栅格化
xmin = -20; xmax = 20; ymin = -10; ymax = 10;
d = 0.5; % 1m*1m栅格尺寸 需要整除xmin and xmax and ymin and ymax
gridcell = cell((xmax-xmin)/d,(ymax-ymin)/d); % 定义栅格存储cell
for i = 1:size(processed_point_cloud,1)
point = processed_point_cloud(i,:);
if point(1)>=xmax || point(1)<=xmin || point(2)>=ymax || point(2)<=ymin
continue;
end
xgrid = ceil((point(1)-xmin)/d);
ygrid = ceil((point(2)-ymin)/d);
gridcell{xgrid,ygrid} = [gridcell{xgrid,ygrid};point];
end
% 判断有障碍物的栅格将其保留,其余删除
threshold_deltaZ = 0.3;
threshold_point_num = 10;
for i = 1:(xmax-xmin)/d
for j = 1:(ymax-ymin)/d
if isempty(gridcell{i,j})
continue;
end
cell_point_count = size(gridcell{i,j},1);
deltaZ = max(gridcell{i,j}(:,3))-min(gridcell{i,j}(:,3));
if deltaZ < threshold_deltaZ || cell_point_count < threshold_point_num
gridcell{i,j} = [];
end
end
end
figure(6);
for i = 1:(xmax-xmin)/d
for j = 1:(ymax-ymin)/d
if isempty(gridcell{i,j})
continue;
end
scatter(gridcell{i,j}(:,1),gridcell{i,j}(:,2),1,'r.'); hold on;
end
end
title('经过栅格化并去除多余点后的二维点云图')
set(gca,'XTick',xmin:d:xmax,'YTick',ymin:d:ymax); % 绘制网格
grid on;
得到的结果如下:主要实现的功能是把此数据集中非地面点云的数据按照一定尺寸(我用的是40*20)将点云栅格化,并呈现在二维图中。


非地面栅格点云聚类
我们利用密度聚类(DBSCAN)
cellIndexNotEmpty = []; % 保存非空的cell的(i,j)
ub = [(xmax-xmin)/d,(ymax-ymin)/d];
lb = [1,1];
for i = 1:ub(1)
for j = 1:ub(2)
if isempty(gridcell{i,j})
continue;
end
cellIndexNotEmpty = [cellIndexNotEmpty;i,j 0]; %第三个分量表示栅格是否被访问
end
end
C = {}; % 聚类类别的cell数组
MinPts = 45; % DBSCAN 参数,领域最小对象数
while any(cellIndexNotEmpty(:,3)==0)
unvisited_grids = cellIndexNotEmpty(cellIndexNotEmpty(:,3)==0,:);
random_index = randperm(size(unvisited_grids,1),1);
p = unvisited_grids(random_index,1:2);
cellIndexNotEmpty(cellIndexNotEmpty(:,1)==p(1)&cellIndexNotEmpty(:,2)==p(2),3) = 1; % 标记被访问
neighborhood = [p(1)+1,p(2);p(1)-1,p(2);p(1),p(2)-1;p(1),p(2)+1;...
p(1)-1,p(2)-1;p(1)-1,p(2)+1;p(1)+1,p(2)-1;p(1)+1,p(2)+1];
point_num = 0;
delete_index = [];
for i = 1:size(neighborhood,1)
flag_ub = neighborhood(i,:)>ub;
flag_lb = neighborhood(i,:)<lb;
if any(flag_lb+flag_ub)
delete_index = [delete_index,i];
continue;
end
if isempty(gridcell{neighborhood(i,1),neighborhood(i,2)})
delete_index = [delete_index,i];
continue;
end
neighbor = neighborhood(i,:);
point_num = point_num + size(gridcell{neighbor(1),neighbor(2)},1);
end
neighborhood(delete_index,:) = [];
if point_num >= MinPts
if isempty(C)
C = {p};
else
C{end+1} = p;
end
while ~isempty(neighborhood)
neighbor = neighborhood(1,:);
neighborhood(1,:) = [];
if cellIndexNotEmpty(cellIndexNotEmpty(:,1)==neighbor(1)&...
cellIndexNotEmpty(:,2)==neighbor(2),3) == 0
cellIndexNotEmpty(cellIndexNotEmpty(:,1)==neighbor(1)&...
cellIndexNotEmpty(:,2)==neighbor(2),3) = 1; % 标记被访问
neighborhood_ = [neighbor(1)+1,neighbor(2);neighbor(1)-1,neighbor(2);...
neighbor(1),neighbor(2)-1;neighbor(1),neighbor(2)+1;...
neighbor(1)-1,neighbor(2)-1;neighbor(1)-1,neighbor(2)+1;...
neighbor(1)+1,neighbor(2)-1;neighbor(1)+1,neighbor(2)+1];
point_num = 0;
delete_index = [];
for k = 1:size(neighborhood_,1)
flag_ub = neighborhood_(k,:)>ub;
flag_lb = neighborhood_(k,:)<lb;
if any(flag_lb+flag_ub)
delete_index = [delete_index,k];
continue;
end
if isempty(gridcell{neighborhood_(k,1),neighborhood_(k,2)})
delete_index = [delete_index,k];
continue;
end
neighbor_ = neighborhood_(k,:);
point_num = point_num + size(gridcell{neighbor_(1),neighbor_(2)},1);
end
neighborhood_(delete_index,:) = [];
if point_num >= MinPts
neighborhood = [neighborhood;neighborhood_];
flag = false;
for m = 1:size(C,2)
temp = C{m};
if any(temp(:,1)==neighbor(1)&temp(:,2)==neighbor(2))
flag = true;
break;
end
end
if ~flag
C{end} = [C{end};neighbor];
end
end
end
end
end
end
cluster = {}; % 存放不同类别点云坐标
figure(7);
for i = 1:size(C,2)
temp = C{i};
t2 = [];
for j = 1:size(temp,1)
t = temp(j,:);
x_lb = (t(1)-1)*d+xmin; x_ub = t(1)*d+xmin;
y_lb = (t(2)-1)*d+ymin; y_ub = t(2)*d+ymin;
t1 = point_cloud(:,1)>=x_lb & point_cloud(:,1)<=x_ub...
& point_cloud(:,2)>=y_lb & point_cloud(:,2)<=y_ub...
& point_cloud(:,3)>-1.5;
t2 = [t2;point_cloud(t1,:)];
end
if isempty(cluster)
cluster = {t2};
else
cluster{end+1} = t2;
end
scatter(t2(:,1),t2(:,2),1); hold on;
text(max(t2(:,1)),max(t2(:,2)),num2str(i))
end
cluster % 显示聚类结果
结果如下:主要实现的功能是二维把点聚类,就是把接近的放在一堆,要不就是一堆散的点了,你们看,效果还是十分不错的,当然还有另外两种聚类方法,如果你使用成功的话欢迎给我留言或@我。


用python训练模型
为了方便你们使用,我已经新建好了项目,可以直接使用Visual Studio打开,或者直接用VScode打开main.py即可,我的Visual Studio版本为2017。
- 先在matlab中获取好要训练的点云数据
我的文件里已经批量处理好了。
files = dir("./training/velodyne/*.bin");
car_point = {}; % 存储car障碍点云元胞
pedestrian_point = {}; % 存储pedestrain障碍点云元胞
cyclist_point = {}; % 存储cyclist障碍点云元胞
misc_point = {}; % 存储杂项障碍点云元胞
load_file_num = 200; % 读取的点云文件数
for k = 1:load_file_num
filename = files(k).name;
fid=fopen(['./training/velodyne/',filename],'rb');
[a,count]=fread(fid,'float32');
fclose(fid);
x = a(1:4:end);
y = a(2:4:end);
z = a(3:4:end);
reflectivity = a(4:4:end); % 反射率
point_cloud = [x,y,z,reflectivity];
label = importdata(['./training/label/',filename(1:6),'.txt']);
data_label = label.data;
obsName = label.textdata;
data_calib = importdata(['./training/calib/',filename(1:6),'.txt']);
Tr_velo_to_cam = reshape(data_calib.data(end-1,:),[4,3])';
Tr_velo_to_cam = [Tr_velo_to_cam;0 0 0 1];
pos = {}; % 创建一个cell数组用于存储障碍物坐标
obsNum = size(obsName,1); % 包含DontCare类障碍物的总个数
for i = 1:obsNum
if obsName{i} == "DontCare"
continue;
end
la = data_label(i,:);
obsPos = la(11:13)';
[h,w,l] = deal(la(8),la(9),la(10));
r_y = la(end);
% t1~t8为障碍物坐标系下的坐标(不考虑障碍物旋转,默认长边与x-axis平行)
t1 = [l/2,0,w/2];
t2 = [l/2,0,-w/2];
t3 = [l/2,-h,w/2];
t4 = [l/2,-h,-w/2];
t5 = [-l/2,0,w/2];
t6 = [-l/2,0,-w/2];
t7 = [-l/2,-h,w/2];
t8 = [-l/2,-h,-w/2];
% 考虑障碍物旋转角度r_y,对x,z方向进行更新
T = [t1;t2;t3;t4;t5;t6;t7;t8];
R = [cos(r_y),-sin(r_y);sin(r_y),cos(r_y)];
T(:,[1,3]) = (R*T(:,[1,3])')';
% 考虑障碍物坐标系与相机坐标系坐标位移
T(:,1) = T(:,1) + obsPos(1);
T(:,2) = T(:,2) + obsPos(2);
T(:,3) = T(:,3) + obsPos(3);
% 将相机坐标系转化到激光雷达坐标系
velo_pos = Tr_velo_to_cam\[T';1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1];
velo_pos = velo_pos(1:3,:);
% 记录障碍Box坐标
pos{i} = velo_pos;
end
[n,~] = size(point_cloud);
for i = 1:obsNum
if obsName{i} == "DontCare"
continue;
end
[max_x,~] = max(pos{i}(1,[1,2,5,6]));
[min_x,~] = min(pos{i}(1,[1,2,5,6]));
[max_y,~] = max(pos{i}(2,[1,2,5,6]));
[min_y,~] = min(pos{i}(2,[1,2,5,6]));
la = data_label(i,:);
[h,w,l] = deal(la(8),la(9),la(10));
point_selected = [];
for j = 1:n
if point_cloud(j,1)>min_x && point_cloud(j,1)<max_x...
&& point_cloud(j,2)>min_y && point_cloud(j,2)<max_y && point_cloud(j,3)>-1.5
point_selected = [point_selected;point_cloud(j,:)];
end
end
point_selected = [l,w,h,0;point_selected]; % 数据集第一行数据为[l w h 0],0只是占位
if obsName{i} == "Car" && size(point_selected,1)>200
if isempty(car_point)
car_point = {point_selected};
else
car_point{end+1} = point_selected;
end
end
if obsName{i} == "Pedestrian" && size(point_selected,1)>100
if isempty(pedestrian_point)
pedestrian_point = {point_selected};
else
pedestrian_point{end+1} = point_selected;
end
end
if obsName{i} == "Cyclist" && size(point_selected,1)>100
if isempty(cyclist_point)
cyclist_point = {point_selected};
else
cyclist_point{end+1} = point_selected;
end
end
if obsName{i} == "Misc" && size(point_selected,1)>40
if isempty(misc_point)
misc_point = {point_selected};
else
misc_point{end+1} = point_selected;
end
end
end
end
figure(8);
pcshow(pointCloud(misc_point{3}(2:end,1:3)))
for i = 1:size(car_point,2)
writematrix(car_point{i},['./training/car/',num2str(i),'.csv']);
end
for i = 1:size(pedestrian_point,2)
writematrix(pedestrian_point{i},['./training/pedestrian/',num2str(i),'.csv']);
end
for i = 1:size(cyclist_point,2)
writematrix(cyclist_point{i},['./training/cyclist/',num2str(i),'.csv']);
end
for i = 1:size(misc_point,2)
writematrix(misc_point{i},['./training/misc/',num2str(i),'.csv']);
end
结果如图:
- 测试神经网络分类器(保存聚类结果csv供Python测试)
% cluster点云存储
for i = 1:size(cluster,2)
temp = cluster{i};
max_x = max(temp(:,1));
min_x = min(temp(:,1));
max_y = max(temp(:,2));
min_y = min(temp(:,2));
h = max(temp(:,3)) - min(temp(:,3));
if max_x - min_x > max_y - min_y
l = max_x - min_x;
w = max_y - min_y;
else
l = max_y - min_y;
w = max_x - min_x;
end
writematrix([l,w,h,0;temp],['./testing/cluster/',num2str(i),'.csv']);
end
- 在python中训练识别模型,并评估其效果
设置了400代,在训练中得到model_state_dict.pkl,并有两个测试函数。
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
"""
Date: 2023.4.23
Author: A-Kang
"""
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
from torch import nn
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import os
feature_dim = 按需求设置
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
def feature_extract(filename):
data = pd.read_csv(filename,header=None).to_numpy(dtype=float)
point_cloud = data[1:,0:3]
ref = data[1:,3]
[l,w,h,_] = data[0,:]
max_x,min_x = np.max(point_cloud[:,0]),np.min(point_cloud[:,0])
max_y, min_y = np.max(point_cloud[:,1]), np.min(point_cloud[:,1])
# f1 = np.array([l,w,h]) # 第一个特征
f1 = np.array([h]) # 仅用h效果好些
slices_num = 10
if max_x-min_x > max_y-min_y:
t = np.linspace(min_x,max_x,slices_num+1) # slices_num+1个值构成slices_num个区间
flag = 0
else:
t = np.linspace(min_y, max_y, slices_num+1)
flag = 1
f2 = []
for i in range(len(t)-1):
lb,ub = t[i],t[i+1]
sum_h,num = 0,0
for point in point_cloud:
if lb < point[flag] < ub:
sum_h += point[2]
num += 1
f2.append(sum_h/num if num!=0 else 0)
f2 = np.array(f2) # 第二个特征
f3 = np.array([(max_x-min_x if flag==1 else max_y-min_y)/h]) # 第三个特征
f4 = np.array([np.mean(ref),np.std(ref)]) # 第四个特征
num1,num2 = 0,0
for r in ref:
if 0<=r<0.2:
num1 += 1
if 0.2<=r<0.4:
num2 += 1
f5 = np.array([(num1 - num2) / point_cloud.shape[0]]) # 第五个特征
feature = np.concatenate((f1,f2,f3,f4,f5))
return feature
def load_data():
data_car = np.array([[]],dtype=float).reshape(-1,feature_dim)
for file in os.listdir('./training/car'):
data_car = np.concatenate((data_car,feature_extract('./training/car/'+file).reshape(1,-1)),axis=0)
label_car = np.zeros((data_car.shape[0],),dtype=float) # car标记为0
data_pedestrian = np.array([[]], dtype=float).reshape(-1, feature_dim)
for file in os.listdir('./training/pedestrian'):
data_pedestrian = np.concatenate((data_pedestrian, feature_extract('./training/pedestrian/' + file).reshape(1, -1)), axis=0)
label_pederstian = 1+np.zeros((data_pedestrian.shape[0],), dtype=float) # pedestrian标记为1
data_cyclist = np.array([[]], dtype=float).reshape(-1, feature_dim)
for file in os.listdir('./training/cyclist'):
data_cyclist = np.concatenate((data_cyclist, feature_extract('./training/cyclist/' + file).reshape(1, -1)),axis=0)
label_cyclist = 1+np.zeros((data_cyclist.shape[0],), dtype=float) # cyclist标记为2
data_others = np.array([[]], dtype=float).reshape(-1, feature_dim)
for file in os.listdir('./training/others'):
data_others = np.concatenate((data_others, feature_extract('./training/others/' + file).reshape(1, -1)),axis=0)
label_others = 1 + np.zeros((data_others.shape[0],), dtype=float) # others标记为3
total_data = np.concatenate((data_car,data_pedestrian,data_cyclist,data_others),axis=0)
total_label = np.concatenate((label_car,label_pederstian,label_cyclist,label_others))
train_x,test_x,train_y,test_y = train_test_split(total_data,total_label)
train_x = torch.from_numpy(train_x).type(torch.float32).to(device)
train_y = torch.from_numpy(train_y).type(torch.LongTensor).to(device)
test_x = torch.from_numpy(test_x).type(torch.float32).to(device)
test_y = torch.from_numpy(test_y).type(torch.LongTensor).to(device)
class Mydataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, features, labels):
self.features = features
self.labels = labels
def __getitem__(self, index):
feature = self.features[index]
label = self.labels[index]
return feature, label
def __len__(self):
return len(self.features)
train_ds = Mydataset(train_x, train_y)
test_ds = Mydataset(test_x, test_y)
BTACH_SIZE = 256
train_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
train_ds,
batch_size=BTACH_SIZE,
shuffle=True)
test_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
test_ds,
batch_size=BTACH_SIZE,
shuffle=True)
print('=====load data finished!+=====')
return train_dl,test_dl,(train_ds,test_ds)
def get_model():
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,dim):
super().__init__()
self.liner_1 = nn.Linear(dim,256)
self.liner_2 = nn.Linear(256,256)
self.liner_3 = nn.Linear(256,2)
self.relu = nn.LeakyReLU()
def forward(self,feature):
x = self.liner_1(feature)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.liner_2(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.liner_3(x)
return x
model = Model(feature_dim).to(device)
opt = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr=1e-4)
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
return model,opt,loss_fn
def save_model_para(model):
import scipy.io as scio
var_name = list()
for name,para in model.named_parameters():
x = name.split(".")
para_name = x[0] + "_" + x[1]
exec(para_name + '=para.cpu().data.numpy()')
print(name)
var_name.append(para.cpu().data.numpy())
data_file = 'para_save_open.mat'
scio.savemat(data_file,
{'l1_weight': var_name[0], 'l1_bias': var_name[1], 'l2_weight': var_name[2], 'l2_bias': var_name[3],
'l3_weight': var_name[4], 'l3_bias': var_name[5],
})
def test():
model = get_model()[0]
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('model_state_dict.pkl',map_location='cpu'))
test_feature = np.array([[]], dtype=float).reshape(-1, feature_dim)
test_data = list()
for file in os.listdir('./testing/cluster'):
data = pd.read_csv("".join(['./testing/cluster/',file]), header=None).to_numpy(dtype=float)
test_data.append(data)
feature = feature_extract("".join(['./testing/cluster/',file]))
test_feature = np.concatenate((test_feature,feature.reshape(1,-1)),axis=0)
test_x = torch.from_numpy(test_feature).type(torch.float32).to(device)
model.eval()
plt.figure(2)
plt.scatter(0,0,s=20)
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(test_x)
y_pred = torch.argmax(output,dim=1).cpu().detach().numpy()
# points_dict = {'Car':np.array([]),'Pedestrian':np.array([]),'Cyclist':np.array([]),'Others':np.array([])}
# category_list = ['Car','Pedestrian','Cyclist','Others']
points_dict = {'Car':np.array([]),'Others':np.array([])}
category_list = ['Car','Others']
for i,val in enumerate(y_pred):
points_dict[category_list[val]] = np.append(points_dict[category_list[val]],test_data[i][1:,0:3])
for ca in category_list:
points = points_dict[ca].reshape(-1,3)
plt.scatter(points[:,0],points[:,1],s=np.ones(len(points),))
leg = ['Coordinate origin of lidar']
leg.extend(category_list)
plt.legend(leg)
plt.show()
def test2():
model = get_model()[0]
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('model_state_dict.pkl',map_location='cpu'))
test_feature = np.array([[]], dtype=float).reshape(-1, feature_dim)
test_data = list()
for file in os.listdir('./training/pedestrian'):
data = pd.read_csv("".join(['./training/pedestrian/', file]), header=None).to_numpy(dtype=float)
test_data.append(data)
feature = feature_extract("".join(['./training/pedestrian/', file]))
test_feature = np.concatenate((test_feature, feature.reshape(1, -1)), axis=0)
test_x = torch.from_numpy(test_feature).type(torch.float32).to(device)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(test_x)
y_pred = torch.argmax(output, dim=1).cpu().detach().numpy()
print((y_pred==np.ones(len(y_pred),).mean()))
def main():
train_dl,test_dl,(train_ds,test_ds) = load_data()
model,opt,loss_fn = get_model()
def accuracy(y_pred,y_true):
y_pred = torch.argmax(y_pred,dim=1)
acc = (y_pred == y_true).float().mean()
return acc
epochs = 400
loss_list = []
accuracy_list = []
test_loss_list = []
test_accuarcy_list = []
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
for x, y in train_dl:
if torch.cuda.is_available():
x, y = x.to('cuda'), y.to('cuda')
y_pred = model(x)
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y)
opt.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
opt.step()
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
epoch_accuracy = accuracy(model(train_ds.features), train_ds.labels)
epoch_loss = loss_fn(model(train_ds.features), train_ds.labels).data
epoch_test_accuracy = accuracy(model(test_ds.features), test_ds.labels)
epoch_test_loss = loss_fn(model(test_ds.features), test_ds.labels).data
loss_list.append(round(epoch_loss.item(), 3))
accuracy_list.append(round(epoch_accuracy.item(), 3))
test_loss_list.append(round(epoch_test_loss.item(), 3))
test_accuarcy_list.append(round(epoch_test_accuracy.item(), 3))
print('epoch: ', epoch, 'loss: ', round(epoch_loss.item(), 3),
'accuracy:', round(epoch_accuracy.item(), 3),
'test_loss: ', round(epoch_test_loss.item(), 3),
'test_accuracy:', round(epoch_test_accuracy.item(), 3)
)
save_model_para(model)
torch.save(model.state_dict(),'model_state_dict.pkl')
plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(range(0, epochs), loss_list, 'r', label='Training loss')
plt.plot(range(0, epochs), accuracy_list, 'g', label='Training accuracy')
plt.plot(range(0, epochs), test_loss_list, 'b', label='Test loss')
plt.plot(range(0, epochs), test_accuarcy_list, 'k', label='Test accuracy')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
def setup_seed(seed):
torch.manual_seed(seed)
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)
np.random.seed(seed)
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
setup_seed(自己按需求设置)
main()
test()
结果可以看到在200代的时候基本识别精度已经99%了。

这是识别后的py可视化:

运行过程:

利用训练好的模型在matlab中识别
加载Python得到的模型参数-前向传播,在matlab中运行
load('para_save_open.mat');
figure(9);
data = pointCloud(point_cloud(:,1:3));
pcshow(data);hold on;
figure(10);
for i = 1:size(cluster,2)
temp = cluster{i};
max_x = max(temp(:,1));
min_x = min(temp(:,1));
max_y = max(temp(:,2));
min_y = min(temp(:,2));
h = max(temp(:,3)) - min(temp(:,3));
if max_x - min_x > max_y - min_y
l = max_x - min_x;
w = max_y - min_y;
else
l = max_y - min_y;
w = max_x - min_x;
end
f = feature_extract([l,w,h,0;temp]);%%
res = policy_net_sign_bankangle(f');
[~,index] = max(res,[],1);
if index == 1
figure(9);
scatter3(temp(:,1),temp(:,2),temp(:,3),1,'r.');
figure(10);
bar1 = scatter(temp(:,1),temp(:,2),1,'r.'); hold on;
elseif index == 2
figure(10);
bar2 = scatter(temp(:,1),temp(:,2),1,'b.');hold on;
end
end
figure(9);
title("最终分类结果(红点表示Car点云)")
figure(10);
legend([bar1,bar2],["Car","Others"]);
title('检测结果')
结果如下:主要实现的功能是识别结果可视化,把点云数据标红。


我们学校某路段结果:


查看训练结果在物理世界是什么样子的
figure()
Image = imread(['./training/image_2/',file,'.png']);
imshow(Image); hold on;
P2 = reshape(data_calib.data(3,:),[4,3])';
R0_rect = reshape(data_calib.data(5,1:end-3),[3,3])';
R0_rect = [R0_rect,[0;0;0];[0,0,0,1]];
for i = 1:obsNum
if obsName{i} == "DontCare"
continue;
end
la = data_label(i,:);
obsPos = la(11:13)';
[h,w,l] = deal(la(8),la(9),la(10));
r_y = la(end);
% t1~t8为障碍物坐标系下的坐标(不考虑障碍物旋转,默认长边与x-axis平行)
t1 = [l/2,0,w/2];
t2 = [l/2,0,-w/2];
t3 = [l/2,-h,w/2];
t4 = [l/2,-h,-w/2];
t5 = [-l/2,0,w/2];
t6 = [-l/2,0,-w/2];
t7 = [-l/2,-h,w/2];
t8 = [-l/2,-h,-w/2];
% 考虑障碍物旋转角度r_y,对x,z方向进行更新
T = [t1;t2;t3;t4;t5;t6;t7;t8];
R = [cos(r_y),-sin(r_y);sin(r_y),cos(r_y)];
T(:,[1,3]) = (R*T(:,[1,3])')';
% 考虑障碍物坐标系与相机坐标系坐标位移
T(:,1) = T(:,1) + obsPos(1);
T(:,2) = T(:,2) + obsPos(2);
T(:,3) = T(:,3) + obsPos(3);
T = [T';1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1];
res = P2*R0_rect*T; % 从参考相机坐标系到左彩色相机图像坐标
for j = 1:size(res,2)
res(:,j) = res(:,j)/res(3,j);
end
res = res(1:2,:);
% 绘制12根线构成3D-Box
temp = res(:,[3,4,8,7]);
[~,j] = min(res(2,[3,4,8,7]));
textPoint = temp(:,j);
text(textPoint(1),textPoint(2)-10,obsName{i},'Color','green');
plot(res(1,[1,2,6,5,1]),res(2,[1,2,6,5,1]),'Color','r');
plot(res(1,[3,4,8,7,3]),res(2,[3,4,8,7,3]),'Color','r');
plot(res(1,[1,3]),res(2,[1,3]),'Color','r');
plot(res(1,[2,4]),res(2,[2,4]),'Color','r');
plot(res(1,[6,8]),res(2,[6,8]),'Color','r');
plot(res(1,[5,7]),res(2,[5,7]),'Color','r');
end
结果如下:

补充的特征提取函数,要加在主文件夹下
function f = feature_extract(data) %%f = feature_extract([l,w,h,0;temp])
point_cloud = data(2:end,1:3);
ref = data(2:end,4);
h = data(1,3);
w = data(1,2);
max_x = max(point_cloud(:,1));
min_x = min(point_cloud(:,1));
max_y = max(point_cloud(:,2));
min_y = min(point_cloud(:,2));
f1 = [h];% f1 = [w,h];
slices_num = 10;
if max_x - min_x > max_y - min_y
t = linspace(min_x,max_x,slices_num+1);
flag = 1;
else
t = linspace(min_y,max_y,slices_num+1);
flag = 2;
end
f2 = [];
for i = 1:size(t,2)-1
lb = t(i); ub = t(i+1);
sum_h = 0; num = 0;
for j = 1:size(point_cloud,1)
point = point_cloud(j,:);
if point(flag)<ub && point(flag)>lb
sum_h = sum_h + point(3);
num = num + 1;
end
end
if num == 0
f2 = [f2,0];
else
f2 = [f2,sum_h/num];
end
end
if flag == 1
f3 = (max_y-min_y)/h;
else
f3 = (max_x-min_x)/h;
end
f4 = [mean(ref),std(ref)];
num1 = 0; num2 = 0;
for i = 1:size(ref)
if ref(i)>=0 && ref(i)<0.2
num1 = num1 + 1;
end
if ref(i)>=0.2 && ref(i)<0.4
num2 = num2 + 1;
end
end
f5 = (num1-num2)/size(point_cloud,1);
f = [f1,f2,f3,f4,f5];
end
看到这里点个赞再走吧!!!!!!!!!!!!
编写不易,求个点赞!!!!!!!
“你是谁?”
“一个看帖子的人。”
“看帖子不点赞啊?”
“你点赞吗?”
“当然点了。”
“我也会点。”
“谁会把经验写在帖子里。”
“写在帖子里的那能叫经验贴?”
“上流!”
cheer!!!