IO流读取
文本内容
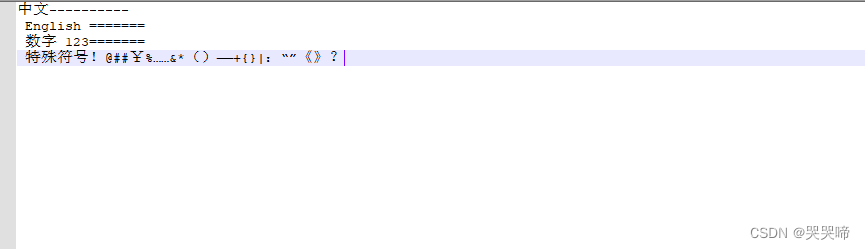
按行读取文件内容
指定编码格式(推荐)
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
read("D:\\test.txt");
}
public static void read(String path) {
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(path), "UTF-8"));
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}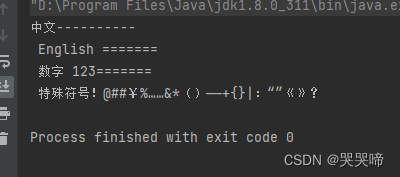
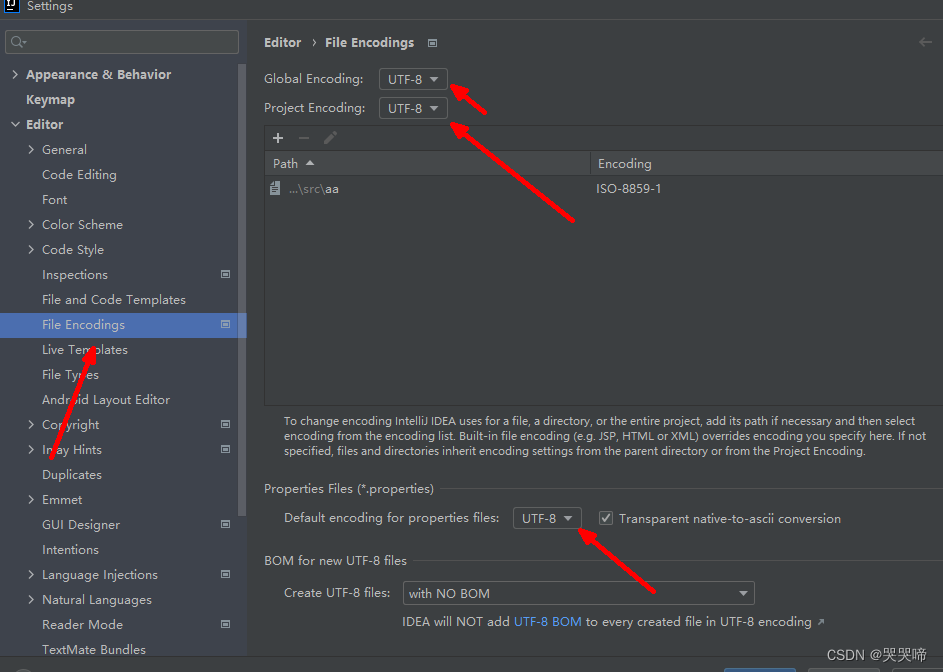
注意,如果控制台输出为乱码,需要度idea进行配置,依次选择file-Setting-editor-File Encoding
不指定编码格式
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
read("D:\\test.txt");
}
public static void read(String path) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path));
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null)
{
System.out.println(line);
}
reader.close();
}可能出现乱码。
按字符读取文件内容
public static void read(String path) throws IOException {
Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(path));
int tempchar;
while ((tempchar = reader.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) tempchar);
}
reader.close();
}按字节读取文件内容
常用于读取图片,声音,影像等
单字节读取
public static void read(String path) throws IOException {
FileInputStream reader = new FileInputStream(path);
int tempchar;
while ((tempchar = reader.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) tempchar);
}
reader.close();
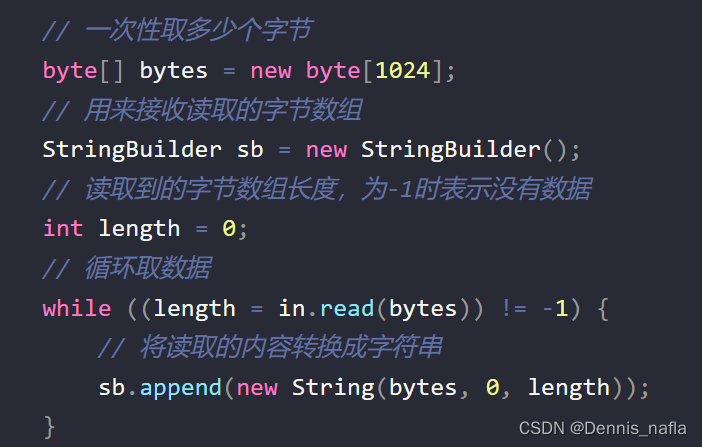
}多字节读取
public static void read(String path) throws IOException {
FileInputStream reader = new FileInputStream(path);
byte[] tempByte = new byte[1024];
int len = 0 ;
while((len = reader.read(tempByte))!= -1){
for (int i = 0; i <len; i++) {
System.out.print((char)tempByte[i]);
}
}
reader.close();
}Scanner
第一种方式是Scanner,从JDK1.5开始提供的API,特点是可以按行读取、按分割符去读取文件数据,既可以读取String类型,也可以读取Int类型、Long类型等基础数据类型的数据。
public static void read(String path) throws IOException {
try (Scanner sc = new Scanner(new FileReader(path))) {
while (sc.hasNextLine()) { //按行读取字符串
String line = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(line);
}
}
}JDK1.7提供的NIO读取文件
小文件
public static void read(String path) throws IOException {
final String CHARSET_NAME = "UTF-8";
List<String> content = new ArrayList<>(0);
try {
content = Files.readAllLines(Paths.get(path), Charset.forName(CHARSET_NAME));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
content.forEach(System.out::println);
}大文件
public static void read(String path) throws IOException {
final String CHARSET_NAME = "UTF-8";
List<String> content = new ArrayList<>(0);
try (BufferedReader br = Files.newBufferedReader(Paths.get(path), Charset.forName(CHARSET_NAME))) {
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
content.add(line);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
content.forEach(System.out::println);
}
JDK1.4提供的NIO读取文件(适用于超大文件)
public static void read(String path) throws IOException {
final String CHARSET_NAME = "UTF-8";
final int ASCII_LF = 10; // 换行符
final int ASCII_CR = 13; // 回车符
List<String> content = new ArrayList<>();
try (FileChannel fileChannel = new RandomAccessFile(path, "r").getChannel()) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024 * 100);
byte[] lineByte;
byte[] temp = new byte[0];
while (fileChannel.read(byteBuffer) != -1) {
// 获取缓冲区位置,即读取长度
int readSize = byteBuffer.position();
// 将读取位置置0,并将读取位置标为废弃
byteBuffer.rewind();
// 读取内容
byte[] readByte = new byte[readSize];
byteBuffer.get(readByte);
// 清除缓存区
byteBuffer.clear();
// 读取内容是否包含一整行
boolean hasLF = false;
int startNum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < readSize; i++) {
if (readByte[i] == ASCII_LF) {
hasLF = true;
int tempNum = temp.length;
int lineNum = i - startNum;
// 数组大小已经去掉换行符
lineByte = new byte[tempNum + lineNum];
System.arraycopy(temp, 0, lineByte, 0, tempNum);
temp = new byte[0];
System.arraycopy(readByte, startNum, lineByte, tempNum, lineNum);
String line = new String(lineByte, 0, lineByte.length, CHARSET_NAME);
content.add(line);
// 过滤回车符和换行符
if (i + 1 < readSize && readByte[i + 1] == ASCII_CR) {
startNum = i + 2;
} else {
startNum = i + 1;
}
}
}
if (hasLF) {
temp = new byte[readByte.length - startNum];
System.arraycopy(readByte, startNum, temp, 0, temp.length);
} else {
// 单次读取的内容不足一行的情况
byte[] toTemp = new byte[temp.length + readByte.length];
System.arraycopy(temp, 0, toTemp, 0, temp.length);
System.arraycopy(readByte, 0, toTemp, temp.length, readByte.length);
temp = toTemp;
}
}
// 最后一行
if (temp.length > 0) {
String lastLine = new String(temp, 0, temp.length, CHARSET_NAME);
content.add(lastLine);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
content.forEach(System.out::println);
}
JDK1.7 Files.readAllBytes
public static void read(String path) throws IOException {
byte[] bytes = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(path));
String content = new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println(content);
}JDK1.8 Stream流
可能会出现内存溢出问题 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError
Files.lines
public static void read(String path) throws IOException {
// 读取文件内容到Stream流中,按行读取
Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(Paths.get(path));
// 随机行顺序进行数据处理
lines.forEach(System.out::println);
}
forEach获取Stream流中的行数据不能保证顺序,但速度快。如果你想按顺序去处理文件中的行数据,可以使用forEachOrdered,但处理效率会下降。
lines.forEachOrdered(System.out::println);或者利用CPU多和的能力,进行数据的并行处理parallel(),适合比较大的文件
lines.parallel().forEachOrdered(System.out::println);Files.readAllLines
public static void read(String path) throws IOException {
// 读取文件内容到Stream流中,按行读取
List<String> lines = Files.readAllLines(Paths.get(path),
StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// 随机行顺序进行数据处理
lines.forEach(System.out::println);
}
JDK 11 Files.readString()
文件不能超过2G,同时要注意你的服务器及JVM内存。这种方法适合快速读取小文本文件。
System.out.println(Files.readString(Paths.get(path))); 依赖hutool
IoUtil工具类
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-core</artifactId>
<version>5.8.10</version>
</dependency>
或者:
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.8.10</version>
</dependency> public static void read(String path) throws IOException {
final String CHARSET_NAME = "UTF-8";
List<String> content = new ArrayList<>();
try {
IoUtil.readLines(new FileInputStream(path), CharsetUtil.charset(CHARSET_NAME), content);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
content.forEach(System.out::println);
}FileUtil工具类
public static void fileOfHutool() {
final String CHARSET_NAME = "UTF-8";
List<String> content = FileUtil.readLines(path, CHARSET_NAME);
content.forEach(System.out::println);
}依赖cmmons-io
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.11.0</version>
</dependency>FileUtils工具类
public static void read(String path) throws IOException {
final String CHARSET_NAME = "UTF-8";
List<String> content = new ArrayList<>(0);
try {
content = FileUtils.readLines(new File(fileName), CHARSET_NAME);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
content.forEach(System.out::println);
}IOUtils工具类
public static void read(String path) throws IOException {
final String CHARSET_NAME = "UTF-8";
List<String> content = new ArrayList<>(0);
try {
content = IOUtils.readLines(new FileInputStream(fileName), CHARSET_NAME);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
content.forEach(System.out::println);
}