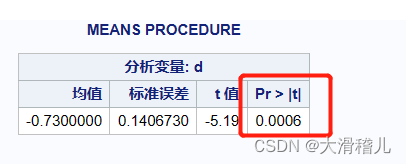
目录
认证
AuthenticationManager
ProviderManager
AuthenticationProvider
Authentication
SecurityContextHolder
授权
AccessDecisionManager
AccessDecisionVoter
RoleVoter
AuthenticatedVoter
Custom Voters
ConfigAttribute
在SpringSecurity的架构中,认证跟授权是分开的,无论采用什么样的认证方式,都不会影响授权,这是两个独立的存在。

认证
官方文档:Servlet Authentication Architecture :: Spring Security
AuthenticationManager
在 Spring Security中,认证是由该接口来负责的
AuthenticationManager is the API that defines how Spring Security’s Filters perform authentication. The Authentication that is returned is then set on the SecurityContextHolder by the controller (that is, by Spring Security’s Filters instances) that invoked the AuthenticationManager. If you are not integrating with Spring Security’s Filters instances, you can set the SecurityContextHolder directly and are not required to use an AuthenticationManager.While the implementation of AuthenticationManager could be anything, the most common implementation is ProviderManager.
public interface AuthenticationManager {
/**
* 返回 Authentication 表示认证成功
* 抛出 AuthenticationException 表示认证失败
*/
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException;
}ProviderManager
ProviderManager is the most commonly used implementation of AuthenticationManager. ProviderManager delegates to a List of AuthenticationProvider instances. Each AuthenticationProvider has an opportunity to indicate that authentication should be successful, fail, or indicate it cannot make a decision and allow a downstream AuthenticationProvider to decide. If none of the configured AuthenticationProvider instances can authenticate, authentication fails with a ProviderNotFoundException, which is a special AuthenticationException that indicates that the ProviderManager was not configured to support the type of Authentication that was passed into it.


In practice each AuthenticationProvider knows how to perform a specific type of authentication. For example, one AuthenticationProvider might be able to validate a username/password, while another might be able to authenticate a SAML assertion. This lets each AuthenticationProvider do a very specific type of authentication while supporting multiple types of authentication and expose only a single AuthenticationManager bean.
ProviderManageralso allows configuring an optional parentAuthenticationManager, which is consulted in the event that noAuthenticationProvidercan perform authentication. The parent can be any type ofAuthenticationManager, but it is often an instance ofProviderManager

In fact, multiple ProviderManager instances might share the same parent AuthenticationManager. This is somewhat common in scenarios where there are multiple
SecurityFilterChain instances that have some authentication in common (the shared parent AuthenticationManager), but also different authentication mechanisms (the different ProviderManager instances).

AuthenticationProvider
You can inject multiple
AuthenticationProviders instances into
ProviderManager. Each AuthenticationProvider performs a specific type of authentication. For example,
DaoAuthenticationProvider supports username/password-based authentication, while JwtAuthenticationProvider supports authenticating a JWT token.
AuthenticationManager 主要实现类为 ProviderManager,在 ProviderManager中管理了众多 AuthenticationProvider 实例。在⼀次完整的认证流程中, Spring Security 允许存在多个 AuthenticationProvider ,⽤来实现多种认证⽅式,这些 AuthenticationProvider 都是由 ProviderManager 进⾏统⼀管理的
Authentication
The Authentication interface serves two main purposes within Spring Security:
- An input to AuthenticationManager to provide the credentials a user has provided to authenticate. When used in this scenario, isAuthenticated() returns false.
- Represent the currently authenticated user. You can obtain the current Authentication from the SecurityContext.
The Authentication contains:
- principal: Identifies the user. When authenticating with a username/password this is often an instance of UserDetails.
- credentials: Often a password. In many cases, this is cleared after the user is authenticated, to ensure that it is not leaked.
- authorities: The GrantedAuthority instances are high-level permissions the user is granted. Two examples are roles and scopes.

SecurityContextHolder
The SecurityContext is obtained from the SecurityContextHolder. The SecurityContext contains an Authentication object.
The SecurityContextHolder is where Spring Security stores the details of who is authenticated. Spring Security does not care how the SecurityContextHolder is populated. If it contains a value, it is used as the currently authenticated user.

By default, SecurityContextHolder uses a ThreadLocal to store these details, which means that the SecurityContext is always available to methods in the same thread, even if the SecurityContext is not explicitly passed around as an argument to those methods. Using a ThreadLocal in this way is quite safe if you take care to clear the thread after the present principal’s request is processed. Spring Security’s
FilterChainProxy ensures that the SecurityContext is always cleared.
SecurityContextHolder ⽤来获取登录之后⽤户信息。 Spring Security 会将登录⽤户数据保存在 Session 中。但是,为了使⽤⽅便,Spring Security在此基础上还做了⼀些改进,其中最主要的⼀个变化就是线程绑定。当⽤户登录成功后,Spring Security 会将登录成功的⽤户信息保存到 SecurityContextHolder 中。
SecurityContextHolder 中的数据保存默认是通过ThreadLocal 来实现的,使⽤ThreadLocal 创建的变量只能被当前线程访问,不能被其他线程访问和修改,也就是⽤户数据和请求线程绑定在⼀起。当登录请求处理完毕后, Spring Security 会将SecurityContextHolder 中的数据拿出来保存到 Session 中,同时将SecurityContexHolder 中的数据清空。以后每当有请求到来时, Spring Security就会先从 Session 中取出⽤户登录数据,保存到 SecurityContextHolder 中,⽅便在该请求的后续处理过程中使⽤,同时在请求结束时将SecurityContextHolder 中的数 据拿出来保存到 Session 中,然后将 Security SecurityContextHolder 中的数据清空。这⼀策略⾮常⽅便⽤户在 Controller、 Service 层以及任何代码中获取当前登录⽤户数据。
授权
官方文档:Authorization Architecture :: Spring Security
AccessDecisionManager
AccessDecisionManager (访问决策管理器),⽤来决定此次访问是否被允许
The AccessDecisionManager is called by the AbstractSecurityInterceptor and is responsible for making final access control decisions.

The decide method of the AccessDecisionManager is passed all the relevant information it needs to make an authorization decision. In particular, passing the secure Object lets those arguments contained in the actual secure object invocation be inspected. For example, assume the secure object is a MethodInvocation. You can query the MethodInvocation for any Customer argument and then implement some sort of security logic in the AccessDecisionManager to ensure the principal is permitted to operate on that customer. Implementations are expected to throw an AccessDeniedException if access is denied.
The supports(ConfigAttribute) method is called by the AbstractSecurityInterceptor at startup time to determine if the AccessDecisionManager can process the passed ConfigAttribute. The supports(Class) method is called by a security interceptor implementation to ensure the configured AccessDecisionManager supports the type of secure object that the security interceptor presents
AccessDecisionVoter
AccessDecisionVoter (访问决定投票器),投票器会检查⽤户是否具备应有的⻆⾊,进⽽投出赞成、反对或者弃权票

While users can implement their own AccessDecisionManager to control all aspects of authorization, Spring Security includes several AccessDecisionManager implementations that are based on voting. Voting Decision Manager describes the relevant classes.
By using this approach, a series of AccessDecisionVoter implementations are polled on an authorization decision. The AccessDecisionManager then decides whether or not to throw an AccessDeniedException based on its assessment of the votes.

Concrete implementations return an int, with possible values being reflected in the AccessDecisionVoter static fields named ACCESS_ABSTAIN, ACCESS_DENIED and ACCESS_GRANTED. A voting implementation returns ACCESS_ABSTAIN if it has no opinion on an authorization decision. If it does have an opinion, it must return either ACCESS_DENIED or ACCESS_GRANTED.
There are three concrete AccessDecisionManager implementations provided with Spring Security to tally the votes. The ConsensusBased implementation grants or denies access based on the consensus of non-abstain votes. Properties are provided to control behavior in the event of an equality of votes or if all votes are abstain. The AffirmativeBased implementation grants access if one or more ACCESS_GRANTED votes were received (in other words, a deny vote will be ignored, provided there was at least one grant vote). Like the ConsensusBased implementation, there is a parameter that controls the behavior if all voters abstain. The UnanimousBased provider expects unanimous ACCESS_GRANTED votes in order to grant access, ignoring abstains. It denies access if there is any ACCESS_DENIED vote. Like the other implementations, there is a parameter that controls the behavior if all voters abstain.
You can implement a custom AccessDecisionManager that tallies votes differently. For example, votes from a particular AccessDecisionVoter might receive additional weighting, while a deny vote from a particular voter may have a veto effect.

AccesDecisionVoter 和 AccessDecisionManager 都有众多的实现类,在AccessDecisionManager 中会换个遍历 AccessDecisionVoter,进⽽决定是否允许⽤户访问,因⽽ AaccesDecisionVoter 和 AccessDecisionManager 两者的关系类似于 AuthenticationProvider 和 ProviderManager 的关系。
RoleVoter
The most commonly used AccessDecisionVoter provided with Spring Security is the RoleVoter, which treats configuration attributes as role names and votes to grant access if the user has been assigned that role.
It votes if any ConfigAttribute begins with the ROLE_ prefix. It votes to grant access if there is a GrantedAuthority that returns a String representation (from the getAuthority() method) exactly equal to one or more ConfigAttributes that start with the ROLE_ prefix. If there is no exact match of any ConfigAttribute starting with ROLE_, RoleVoter votes to deny access. If no ConfigAttribute begins with ROLE_, the voter abstains.
AuthenticatedVoter
Another voter which we have implicitly seen is the AuthenticatedVoter, which can be used to differentiate between anonymous, fully-authenticated, and remember-me authenticated users. Many sites allow certain limited access under remember-me authentication but require a user to confirm their identity by logging in for full access.When we have used the IS_AUTHENTICATED_ANONYMOUSLY attribute to grant anonymous access, this attribute was being processed by the AuthenticatedVoter. For more information, see AuthenticatedVoter.
Custom Voters
You can also implement a custom AccessDecisionVoter and put just about any access-control logic you want in it. It might be specific to your application (business-logic related) or it might implement some security administration logic. For example, on the Spring web site, you can find a blog article that describes how to use a voter to deny access in real-time to users whose accounts have been suspended.

Like many other parts of Spring Security, AfterInvocationManager has a single concrete implementation, AfterInvocationProviderManager, which polls a list of AfterInvocationProviders. Each AfterInvocationProvider is allowed to modify the return object or throw an AccessDeniedException. Indeed multiple providers can modify the object, as the result of the previous provider is passed to the next in the list.
Please be aware that if you’re using AfterInvocationManager, you will still need configuration attributes that allow the MethodSecurityInterceptor's AccessDecisionManager to allow an operation. If you’re using the typical Spring Security included AccessDecisionManager implementations, having no configuration attributes defined for a particular secure method invocation will cause each AccessDecisionVoter to abstain from voting. In turn, if the AccessDecisionManager property “allowIfAllAbstainDecisions” is false, an AccessDeniedException will be thrown. You may avoid this potential issue by either (i) setting “allowIfAllAbstainDecisions” to true (although this is generally not recommended) or (ii) simply ensure that there is at least one configuration attribute that an AccessDecisionVoter will vote to grant access for. This latter (recommended) approach is usually achieved through a ROLE_USER or ROLE_AUTHENTICATED configuration attribute.
ConfigAttribute
ConfigAttribute,⽤来保存授权时的⻆⾊信息
在 Spring Security 中,⽤户请求⼀个资源(通常是⼀个接⼝或者⼀个 Java ⽅法)需要的⻆⾊会被封装成⼀个 ConfigAttribute 对象,在 ConfigAttribute 中只有⼀个getAttribute⽅法,该⽅法返回⼀个 String 字符串,就是⻆⾊的名称。⼀般来说,⻆⾊名称都带有⼀个 ROLE_ 前缀,投票器 AccessDecisionVoter 所做的事情,其实就是⽐较⽤户所具各的⻆⾊和请求某个资源所需的 ConfigAtuibute 之间的关系。