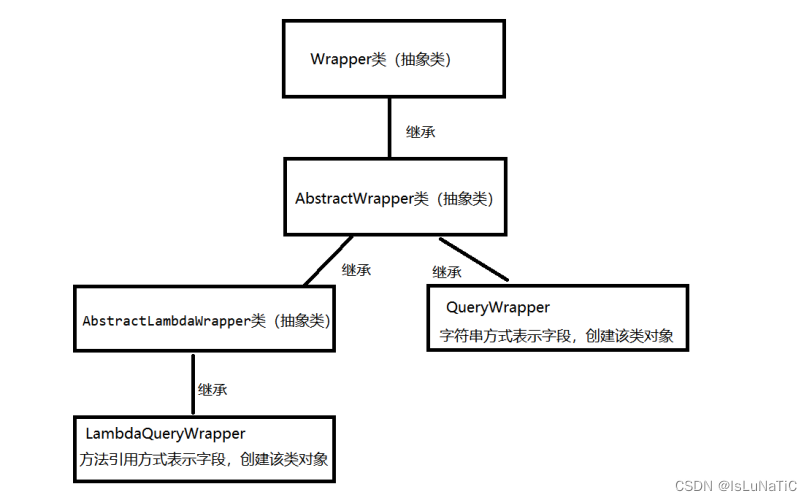
文章目录
- 前言
- 一. RecyclerView中使用Glide出现加载图片闪烁
- 1.1 提出问题
- 1.2 查看源码
- 1.3 ViewTarget和SimpleTarget
- 二. CustomTarget和CustomViewTarget
- 2.1 onResourceCleared和onLoadCleared
- 2.2 onLoadStarted和onResourceLoading
- 结束
前言
最近在项目中使用RecyclerView+Glide发现了一些bug,在此记录一下。
一. RecyclerView中使用Glide出现加载图片闪烁
1.1 提出问题

如上图所示,在使用RecyclerView+Glide的时候会出现,图片多次叠加的问题。首先看下代码:
// 用了BaseQuickAdapter
@Override
protected void convert(BaseViewHolder holder, Bean bean) {
// loading加载
final View loading = holder.getView(R.id.loading);
loading.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
// 省略业务代码...
Glide.with(getContext())
.load(url) // 加载数据的URL
.override(Target.SIZE_ORIGINAL, Target.SIZE_ORIGINAL) // 图片使用原始尺寸
.into(new SimpleTarget<Drawable>() { // SimpleTarget已经过时
@Override
public void onResourceReady(@NonNull Drawable resource,
@Nullable Transition<? super Drawable> transition)
{
// 图片加载完成就隐藏loading
loading.setVisibility(View.GONE);
imageView.setImageDrawable(resource);
}
});
}
由于业务上要求需要显示loading,目前所做的是将loading的View置于ImageView下面,如果图片加载完成,那么就需要将loading给隐藏。
经过分析,之所以会上面图片所示的问题,主要还是由于RecyclerView的复用机制导致的。当我快速滑动到顶部的时候,顶部的那些View是复用被移出列表的itemView,但是这些被复用的itemView可能还在加载之前的数据,同时这些itemView还要加载当前位置上需要加载的数据,这就导致加载的时候会先出现被复用之前需要加载的数据,然后再加载复用之后需要加载的数据。
如果将上面的SimpleTarget改为直接into(imageView),就不会出现该问题!那么为什么会出现这种情况呢?
1.2 查看源码
首先看一下Glide在直接into的时候做了啥?
Glide源码:
@NonNull
public ViewTarget<ImageView, TranscodeType> into(@NonNull ImageView view) {
// 省略代码...
// 主要看buildImageViewTarget
return into(
glideContext.buildImageViewTarget(view, transcodeClass),
/*targetListener=*/ null,
requestOptions,
Executors.mainThreadExecutor());
}
继续跟进:
buildImageViewTarget方法
@NonNull
public <X> ViewTarget<ImageView, X> buildImageViewTarget(
@NonNull ImageView imageView, @NonNull Class<X> transcodeClass) {
return imageViewTargetFactory.buildTarget(imageView, transcodeClass);
}
跟进到buildTarget里面
ImageViewTargetFactory类
@NonNull
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <Z> ViewTarget<ImageView, Z> buildTarget(
@NonNull ImageView view, @NonNull Class<Z> clazz) {
if (Bitmap.class.equals(clazz)) {
return (ViewTarget<ImageView, Z>) new BitmapImageViewTarget(view);
} else if (Drawable.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
return (ViewTarget<ImageView, Z>) new DrawableImageViewTarget(view);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Unhandled class: " + clazz + ", try .as*(Class).transcode(ResourceTranscoder)");
}
}
到这里就一目了然了,直接into(imageView),里面使用的是ViewTarget回调加载的图片!
那么ViewTarget和SimpleTarget有啥区别导致的这个情况呢?
1.3 ViewTarget和SimpleTarget
首先看看SimpleTarget:
@Deprecated
public abstract class SimpleTarget<Z> extends BaseTarget<Z> {
private final int width;
private final int height;
/**
* Constructor for the target that uses {@link Target#SIZE_ORIGINAL} as the target width and
* height.
*/
// Public API.
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")
public SimpleTarget() {
this(SIZE_ORIGINAL, SIZE_ORIGINAL);
}
/**
* Constructor for the target that takes the desired dimensions of the decoded and/or transformed
* resource.
*
* @param width The width in pixels of the desired resource.
* @param height The height in pixels of the desired resource.
*/
// Public API.
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")
public SimpleTarget(int width, int height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
/**
* Immediately calls the given callback with the sizes given in the constructor.
*
* @param cb {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public final void getSize(@NonNull SizeReadyCallback cb) {
if (!Util.isValidDimensions(width, height)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Width and height must both be > 0 or Target#SIZE_ORIGINAL, but given"
+ " width: "
+ width
+ " and height: "
+ height
+ ", either provide dimensions in the constructor"
+ " or call override()");
}
cb.onSizeReady(width, height);
}
@Override
public void removeCallback(@NonNull SizeReadyCallback cb) {
// Do nothing, we never retain a reference to the callback.
}
}
SimpleTarget的代码相当简单,继承自BaseTarget抽象类
BaseTarget类
@Deprecated
public abstract class BaseTarget<Z> implements Target<Z> {
private Request request;
@Override
public void setRequest(@Nullable Request request) {
this.request = request;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Request getRequest() {
return request;
}
// 很重要后面会讲到
@Override
public void onLoadCleared(@Nullable Drawable placeholder) {
// Do nothing.
}
@Override
public void onLoadStarted(@Nullable Drawable placeholder) {
// Do nothing.
}
@Override
public void onLoadFailed(@Nullable Drawable errorDrawable) {
// Do nothing.
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
// Do nothing.
}
@Override
public void onStop() {
// Do nothing.
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
// Do nothing.
}
}
BaseTarget是Target接口的实现。
下面我们来看看ViewTarget的源码:
@Deprecated
public abstract class ViewTarget<T extends View, Z> extends BaseTarget<Z> {
private static final String TAG = "ViewTarget";
private static boolean isTagUsedAtLeastOnce;
private static int tagId = R.id.glide_custom_view_target_tag;
protected final T view;
private final SizeDeterminer sizeDeterminer;
@Nullable private OnAttachStateChangeListener attachStateListener;
private boolean isClearedByUs;
private boolean isAttachStateListenerAdded;
public ViewTarget(@NonNull T view) {
this.view = Preconditions.checkNotNull(view);
sizeDeterminer = new SizeDeterminer(view);
}
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess") // Public API
@Deprecated
public ViewTarget(@NonNull T view, boolean waitForLayout) {
this(view);
if (waitForLayout) {
waitForLayout();
}
}
// 省略代码...
private void setTag(@Nullable Object tag) {
isTagUsedAtLeastOnce = true;
view.setTag(tagId, tag);
}
@Nullable
private Object getTag() {
return view.getTag(tagId);
}
/**
* Stores the request using {@link View#setTag(Object)}.
*
* @param request {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void setRequest(@Nullable Request request) {
setTag(request);
}
/**
* Returns any stored request using {@link android.view.View#getTag()}.
*
* <p>For Glide to function correctly, Glide must be the only thing that calls {@link
* View#setTag(Object)}. If the tag is cleared or put to another object type, Glide will not be
* able to retrieve and cancel previous loads which will not only prevent Glide from reusing
* resource, but will also result in incorrect images being loaded and lots of flashing of images
* in lists. As a result, this will throw an {@link java.lang.IllegalArgumentException} if {@link
* android.view.View#getTag()}} returns a non null object that is not an {@link
* com.bumptech.glide.request.Request}.
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public Request getRequest() {
Object tag = getTag();
Request request = null;
if (tag != null) {
if (tag instanceof Request) {
request = (Request) tag;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"You must not call setTag() on a view Glide is targeting");
}
}
return request;
}
// 省略代码...
}
这里最重要的是getRequest和setRequest,它们内部分别调用了getTag和setTag,内部又分别调用了View的setTag和getTag方法,通过setTag和getTag将Request对象和View绑定起来。
我们再来看看getRequest和setRequest方法是在哪里调用的。
RequestBuilder类
private <Y extends Target<TranscodeType>> Y into(@NonNull Y target,@Nullable RequestListener<TranscodeType> targetListener,BaseRequestOptions<?> options,Executor callbackExecutor) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(target);
if (!isModelSet) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You must call #load() before calling #into()");
}
Request request = buildRequest(target, targetListener, options, callbackExecutor);
// 调用ViewTarget的getRequest,也就是获取View里面的Request
Request previous = target.getRequest();
// 将新的Request和View中的Request对比,如果不一样,就取消View里面的Request
if (request.isEquivalentTo(previous)
&& !isSkipMemoryCacheWithCompletePreviousRequest(options, previous)) {
// If the request is completed, beginning again will ensure the result is re-delivered,
// triggering RequestListeners and Targets. If the request is failed, beginning again will
// restart the request, giving it another chance to complete. If the request is already
// running, we can let it continue running without interruption.
if (!Preconditions.checkNotNull(previous).isRunning()) {
// Use the previous request rather than the new one to allow for optimizations like skipping
// setting placeholders, tracking and un-tracking Targets, and obtaining View dimensions
// that are done in the individual Request.
previous.begin();
}
return target;
}
// 清除旧的Request
requestManager.clear(target);
// 设置新的Request
target.setRequest(request);
requestManager.track(target, request);
return target;
}
上面的代码的意思就是,将新的Request和View中的Request对比,如果不一样,就取消View里面的Request,去加载新的Request。这样做就可以解决前面的问题,被复用的旧的Request会被取消,而去加载新的Request。
至此,搞清楚了为啥直接into(imageView)不会出现图片多次叠加的问题。
修改的代码如下:
Glide.with(getContext())
.load(url)
.override(Target.SIZE_ORIGINAL, Target.SIZE_ORIGINAL) // 图片使用原始尺寸
.listener(new RequestListener<Drawable>() {
@Override
public boolean onLoadFailed(@Nullable GlideException e,Object model, Target<Drawable> target, boolean isFirstResource){
loading.setVisibility(View.GONE);
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean onResourceReady(Drawable resource, Object model, Target<Drawable> target, DataSource dataSource, boolean isFirstResource) {
loading.setVisibility(View.GONE);
return false;
}
})
.into(imageView);
需要注意的是由于使用了ViewTarget,会自动改变Bitmap的大小,我们的业务逻辑是不改变Bitmap大小,所以需要加上override(Target.SIZE_ORIGINAL, Target.SIZE_ORIGINAL)使用图片原始尺寸。
修改后:

二. CustomTarget和CustomViewTarget
2.1 onResourceCleared和onLoadCleared
在解决问题的过程中,会发现Glide4.0后SimpleTarget和ViewTarget都被废弃掉了,被CustomTarget和CustomViewTarget替代掉了。其实它们内部的主要逻辑和SimpleTarget和ViewTarget基本上都差不多的。只不过这两个回调需要强制实现onLoadCleared和onResourceReady,onResourceReady在onLoadCleared里面被调用。
当Glide的内存缓存池满掉后,就会释放多余的bitmap,而被释放的bitmap,会被主动recycle,可能会使用已经被recycle的图片,导致如下的bug:
Canvas: trying to use a recycled bitmap android.graphics.Bitmap@XXXX
所以Glide4.0后要求我们强制实现这个方法,当然只实现该方法是不行的,还需要给imageView设置为null。
// CustomViewTarget的onResourceCleared
@Override
protected void onResourceCleared(@Nullable Drawable placeholder) {
// 必须在onResourceCleared中给ImageView设置默认图片或者null.
imageView.setImageDrawable(null);
}
2.2 onLoadStarted和onResourceLoading
当我尝试用CustomViewTarget解决加载图片闪烁的问题的时候,发现显示加载的View,有的时候会不显示。
出问题的代码如下:
@Override
protected void convert(BaseViewHolder holder, Bean bean) {
// loading加载
final View loading = holder.getView(R.id.loading);
loading.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
// 省略代码...
Glide.with(getContext())
.load(url)
.into(new CustomViewTarget<View, Drawable>(imageView) {
@Override
public void onLoadFailed(@Nullable Drawable errorDrawable) {
loading.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
@Override
public void onResourceReady(@NonNull Drawable resource, @Nullable Transition<? super Drawable> transition) {
loading.setVisibility(View.GONE);
imageView.setImageDrawable(resource);
}
@Override
protected void onResourceCleared(@Nullable Drawable placeholder) {
// 必须在onResourceCleared中给ImageView设置默认图片或者null.
imageView.setImageDrawable(null);
loading.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
});
}
通过查看CustomViewTarget的API发现了onResourceLoading,我尝试将loading.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);放到onResourceLoading里面,解决掉了该问题。
代码上可以看到onResourceLoading被onLoadStarted调用了
// 通知图片开始加载
@Override
public final void onLoadStarted(@Nullable Drawable placeholder) {
maybeAddAttachStateListener();
onResourceLoading(placeholder);
}
最后的解决代码:
@Override
protected void convert(BaseViewHolder holder, Bean bean) {
// loading加载
final View loading = holder.getView(R.id.loading);
// 省略代码...
Glide.with(getContext())
.load(url)
.into(new CustomViewTarget<View, Drawable>(imageView) {
@Override
protected void onResourceLoading(@Nullable Drawable placeholder) {
super.onResourceLoading(placeholder);
// loading需要放在该回调中,要不然会出现loading数据错乱的问题
loading.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
@Override
public void onLoadFailed(@Nullable Drawable errorDrawable) {
loading.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
@Override
public void onResourceReady(@NonNull Drawable resource, @Nullable Transition<? super Drawable> transition) {
loading.setVisibility(View.GONE);
imageView.setImageDrawable(resource);
}
@Override
protected void onResourceCleared(@Nullable Drawable placeholder) {
// 必须在onResourceCleared中给ImageView设置默认图片或者null.
imageView.setImageDrawable(null);
loading.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
});
}
结束
以上就是在使用Recycler+Glide的时候出现的一些bug,以及对这些bug的分析和解决思路。