目录
- 1.PSO算法主要步骤🌱
- 2.PSO更新方法🌾
- 3.PSO求解TSP问题🌴
粒子群算法(Particle Swarm Optimization,简称PSO)是一种优化算法,模拟了鸟群或鱼群等群体生物行为的优化思想。
其基本思想是将待求解问题看成一个在多维空间中寻找最优解的优化问题,将每个可能的解看成多维空间中的一个粒子,并将它们随机散布在搜索空间中。
粒子的位置表示一个可行解,粒子的速度表示更新时的变化量。通过给每个粒子分配一个随机的速度向量,指导每个粒子进行探索。同时,使用全局最优和局部最优导引粒子的搜索方向。全局最优即全局最优解的位置,局部最优为某个粒子在个体搜索阶段找到的最优解。将这些信息作为粒子的引导方向,逐渐逼近全局最优解,达到最优化的目的。
1.PSO算法主要步骤🌱
-
设定粒子群
种群大小、目标函数及搜索空间。
初始化粒子群:每个粒子的位置和速度都要设置随机初值,并计算其个体适应度。 -
更新每个粒子的
速度和位置:对于第i个粒子,分别计算其个体和全局最优解的影响,然后更新该粒子的速度和位置。 -
重新计算每个粒子的
适应度。 -
判断是否满足停止条件,若
满足停止条件,则输出当前种群中最优的粒子。
否则,返回第3步进行迭代。
PSO算法的优点是可以适应任意目标函数,复杂度不高,具有较好的搜索能力。根据个体最优和全局最优的影响参数的设置不同会影响算法收敛性和导致算法陷入局部最优。PSO算法由于其具有较强的随机性,导致其搜索过程缺乏自适应能力,可能会在搜索过程中出现较大波动。同时,在高维空间中表现欠佳,并且对于复杂问题,需要精细地调节参数才能取得良好的效果。
2.PSO更新方法🌾
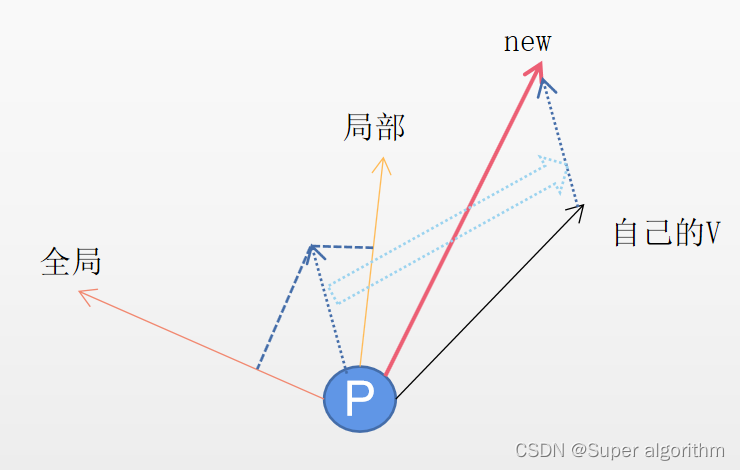
粒子群算法的核心就在于更新粒子的速度和位置,从而不断搜索搜寻空间寻找最优解。其速度和位置的更新公式包括两个部分:个体最优引导和全局最优引导。
以下是粒子群算法的速度和位置更新公式:
-
速度更新公式:
v i , d ( t + 1 ) = w v i , d ( t ) + c 1 r 1 ( p b e s t i , d − x i , d ( t ) ) + c 2 r 2 ( g b e s t d − x i , d ( t ) ) v_{i,d}(t+1) = wv_{i,d}(t) + c_{1}r_{1}(pbest_{i,d}-x_{i,d}(t)) + c_{2}r_{2}(gbest_{d}-x_{i,d}(t)) vi,d(t+1)=wvi,d(t)+c1r1(pbesti,d−xi,d(t))+c2r2(gbestd−xi,d(t))
其中, v i , d ( t ) v_{i,d}(t) vi,d(t) 表示第 i 个粒子在第 d 维的速度, t t t表示迭代次数, w w w表示惯性权重, c 1 c_1 c1和 c 2 c_2 c2 表示粒子个体和群体认知系数, r 1 r_1 r1 和 r 2 r_2 r2 是 0 到 1 之间的随机数, p b e s t i , d pbest_{i,d} pbesti,d 表示第 i 个粒子在第 d 维度的个体最优位置, g b e s t d gbest_{d} gbestd 表示全局最优位置在第 d 维度的取值, x i , d ( t ) x_{i,d}(t) xi,d(t) 是第 i 个粒子在第 d 维度的位置。 p b e s t pbest pbest是于该粒子之前最优的解, g b e s t gbest gbest是于所有粒子之前最优的解。
公式中第一项是粒子本身的惯性,第二项是粒子向个体最优点的引力,第三项是粒子向全局最优点的引力。 -
位置更新公式:
x i , d ( t + 1 ) = x i , d ( t ) + v i , d ( t + 1 ) x_{i,d}(t+1) = x_{i,d}(t) + v_{i,d}(t+1) xi,d(t+1)=xi,d(t)+vi,d(t+1)
其中 x i , d ( t ) x_{i,d}(t) xi,d(t) 表示第 i 个粒子在维度 d 上的位置, v i , d ( t + 1 ) v_{i,d}(t+1) vi,d(t+1) 表示第 i 个粒子在维度 d 上的速度。通过以上公式,粒子群不断迭代,直到达到所要求的精度或者达到最大迭代次数。
在实际应用中,惯性权重 w 是一个非常重要的参数,控制着算法的局部变化和全局探索的平衡。在迭代过程中,w 的值通常逐渐递减。同时,也需要通过多次实验和调整,确定其他参数的合理取值,以获得更好的优化结果。

3.PSO求解TSP问题🌴
实现粒子群算法求解TSP问题的代码:
定义一个 Particle 类用于存储粒子的相关信息;
initialize() 方法来初始化种群;
updatePBest()方法用于更新个体历史最优路径;
updateVelocity() 方法更新粒子速度;
updatePosition()方法更新粒子位置;
定义了 calculateFitness() 方法用于计算适应度(路径长度)。
在 main() 方法中,我们首先调用 initialize() 方法初始化种群,然后通过迭代不断更新粒子的速度、位置、适应度等相关参数,更新个体最优路径和全局最优路径
最终输出最优解路径和路径长度。
public class PSOTSP {
// 城市集合,第i号城市的编码为i
public static int[][] coordinates = {
{200, 40}, {180, 80}, {160, 100}, {140, 120}, {160, 140},
{180, 160}, {200, 200}, {220, 160}, {240, 140}, {260,120},
{240, 100}, {220, 60}, {200, 20}, {240, 20}, {260, 40}
};
// 城市数目
public static int cityNum = coordinates.length;
// 种群规模
public static int populationSize = 50;
// 最大迭代次数
public static int maxGeneration = 200;
// 学习因子,用于控制粒子速度和位置的更新
public static double learningFactor = 0.7;
// 粒子群
public static Particle[] particles = new Particle[populationSize];
// 全局最优解
public static int[] gbest = new int[cityNum];
// 全局最优解路径长度
public static double gbestValue = Double.MAX_VALUE;
// 计算城市间距离,采用欧氏距离
public static double[][] distanceMatrix = new double[cityNum][cityNum];
static {
for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < cityNum; j++) {
int xDistance = coordinates[i][0] - coordinates[j][0];
int yDistance = coordinates[i][1] - coordinates[j][1];
distanceMatrix[i][j] = Math.sqrt(xDistance * xDistance + yDistance * yDistance);
distanceMatrix[j][i] = distanceMatrix[i][j];
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
initialize();
for (int g = 0; g < maxGeneration; g++) {
for (int i = 0; i < populationSize; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cityNum; j++) {
particles[i].updateVelocity(gbest, learningFactor);
particles[i].updatePosition();
particles[i].calculateFitness(distanceMatrix);
}
// 更新个体最优解
particles[i].updatePBest();
// 更新全局最优解
if (particles[i].getPBestValue() < gbestValue) {
gbestValue = particles[i].getPBestValue();
System.arraycopy(particles[i].getPBest(), 0, gbest, 0, cityNum);
}
}
}
System.out.print("最优解路径: ");
for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) {
System.out.print(gbest[i] + 1 + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("最短路径长度: " + gbestValue);
}
public static void initialize() {
// 初始化粒子
for (int i = 0; i < populationSize; i++) {
particles[i] = new Particle(cityNum);
particles[i].initialize();
particles[i].calculateFitness(distanceMatrix);
// 更新全局最优解
if (particles[i].getPBestValue() < gbestValue) {
gbestValue = particles[i].getPBestValue();
System.arraycopy(particles[i].getPBest(), 0, gbest, 0, cityNum);
}
}
}
// 定义粒子实体类
public static class Particle {
// 存储粒子经过的路径,初始化为-1
private int[] path;
// 存储粒子历史最优路径
private int[] pbest;
// 粒子当前位置的适应度值
private double fitness;
// 粒子历史最优位置的适应度值
private double pbestValue;
// 存储粒子当前速度
private double[] velocity;
// 最大速度
private static double vmax = 5;
public Particle(int length) {
path = new int[length];
pbest = new int[length];
velocity = new double[length];
}
// 随机初始化粒子位置和速度
public void initialize() {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < path.length; i++) {
list.add(i);
path[i] = -1;
velocity[i] = 0;
}
Collections.shuffle(list);
for (int i = 0; i < path.length; i++) {
path[i] = list.get(i);
}
System.arraycopy(path, 0, pbest, 0, path.length);
pbestValue = fitness;
}
// 计算当前位置的适应度值
public void calculateFitness(double[][] distanceMatrix) {
double pathLength = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < path.length - 1; i++) {
pathLength += distanceMatrix[path[i]][path[i + 1]];
}
pathLength += distanceMatrix[path[path.length - 1]][path[0]];
fitness = pathLength;
}
// 更新个体历史最优位置
public void updatePBest() {
if (fitness < pbestValue) {
System.arraycopy(path, 0, pbest, 0, path.length);
pbestValue = fitness;
}
}
// 更新粒子速度
public void updateVelocity(int[] gbest, double learningFactor) {
// 计算个体和全局最优差距
double[] deltaPbest = new double[path.length];
double[] deltaGbest = new double[path.length];
for (int i = 0; i < path.length; i++) {
deltaPbest[i] = pbest[i] - path[i];
deltaGbest[i] = gbest[i] - path[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < path.length; i++) {
// 估算粒子的局部最优解和全局最优解的距离占所有点之间距离的比值
double alpha = Math.random() * learningFactor;
// 更新速度
velocity[i] = alpha * velocity[i] + deltaPbest[i] * Math.random()
+ (1 - alpha) * deltaGbest[i] * Math.random();
// 控制速度不超过最大限制
if (velocity[i] > vmax) {
velocity[i] = vmax;
} else if (velocity[i] < -vmax) {
velocity[i] = -vmax;
}
}
}
// 更新粒子位置
public void updatePosition() {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < path.length; i++) {
list.add(path[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < path.length; i++) {
int index = list.indexOf(i);
int moveLength = (int) Math.round(velocity[i]);
int newPosition = (index + moveLength + path.length) % path.length;
if (newPosition < list.size() && newPosition > 0) {
list.add(newPosition, i);
list.remove(index < 0 ? list.size() - 1 : index);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < path.length; i++) {
path[i] = list.get(i);
}
}
public double getPBestValue() {
return pbestValue;
}
public int[] getPBest() {
return pbest;
}
}
}
☕物有本末,事有终始,知所先后。🍭
🍎☝☝☝☝☝我的CSDN☝☝☝☝☝☝🍓



![[Linux]环境变量](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/94dbb11cf7c642f39cd0254a90275532.png)