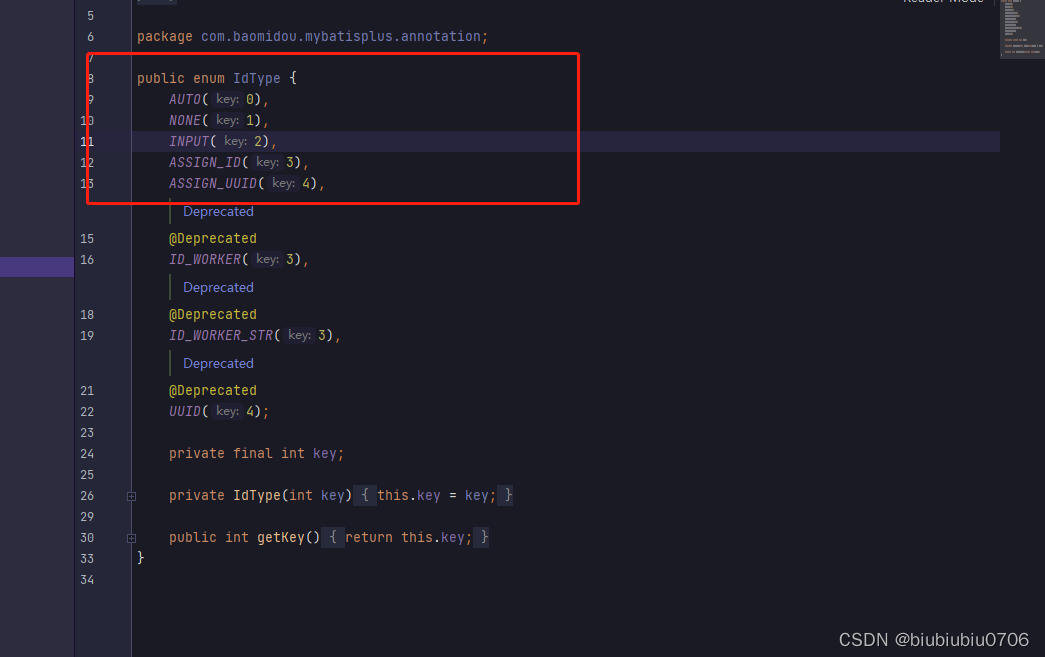
Walt 算法
WALT负载统计原理_walt算法_森森浅浅笙笙的博客-CSDN博客
CPU负载均衡之WALT学习【转】_mb5fdcad0be2e90的技术博客_51CTO博客
1、A task’s demand is the maximum of its contribution to the most recently completed window and its average demand over the past N windows.
WALT “forgets” blocked time entirely:即只统计runable和running time,可以对于Task的实际耗时有更准确的统计,可以通过demand预测;更新demand 通过函数account_busy_for_task_demand判断

linux/sched/walt.h
struct walt_task_struct {
...
}
2、CPU busy time - The sum of execution times of all tasks in the most recently completed window;WALT “forgets” cpu utilization as soon as tasks are taken off of the runqueue;
更新通过account_busy_for_cpu_time函数判断
struct walt_task_struct 、struct walt_rq 内嵌到tast_struct 和 struct rq 里面
walt_update_task_ravg 更新demand 和 cpu busy time
kernel-5.10/kernel_platform/msm-kernel/kernel/sched/walt/walt.c
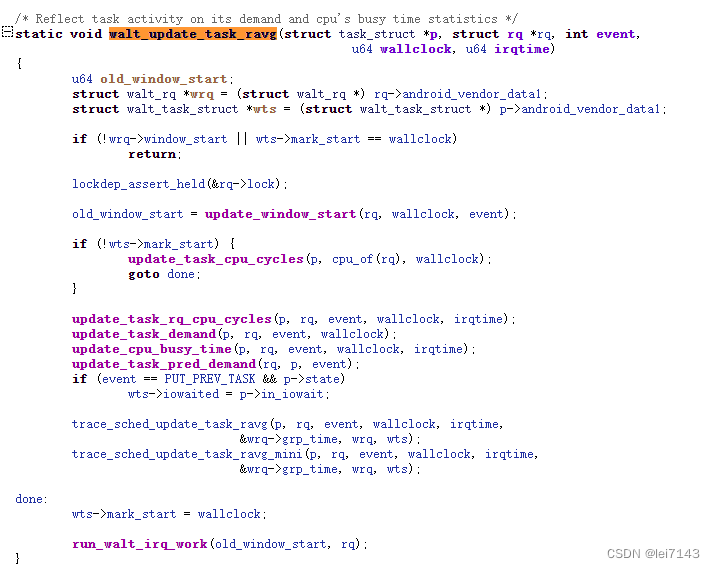
1、
old_window_start = update_window_start(rq, wallclock, event);

根据当前时间wallclock 更新walt_rq 中当前窗口起始时间;
如果wallclock 和 walt_rq->window_start 间隔N(N>=1)个窗口周期,就需要walt_rq->window_start 向前偏移N个窗口周期;prev_window_size 赋值为窗口周期;
2、
2243 if (!wts->mark_start) {
2244 update_task_cpu_cycles(p, cpu_of(rq), wallclock);
2245 goto done;
2246 }
任务标记时间还没有开始,则根据cpu 周期更新rq 周期,再赋值给walt_task_struct 周期;


cycles cup周期;更新cycles 时时间last_cc_update (即为wallclock)
3、更新rq 和 task 运行时钟周期及窗口负载(执行算力*时间/理论最大执行算力*时间)

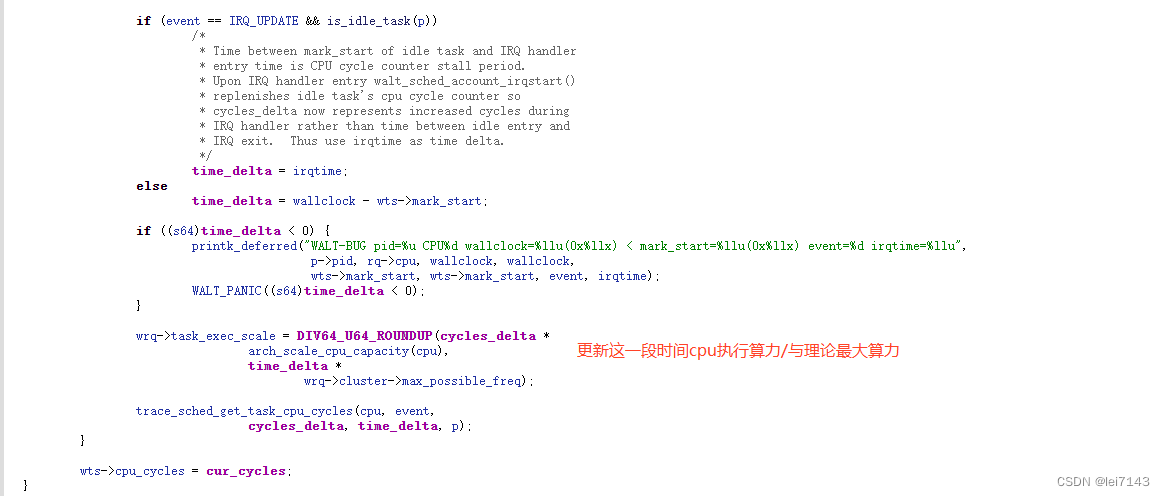
4、update_task_demand(p, rq, event, wallclock);
参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/lingjiajun/p/12317090.html
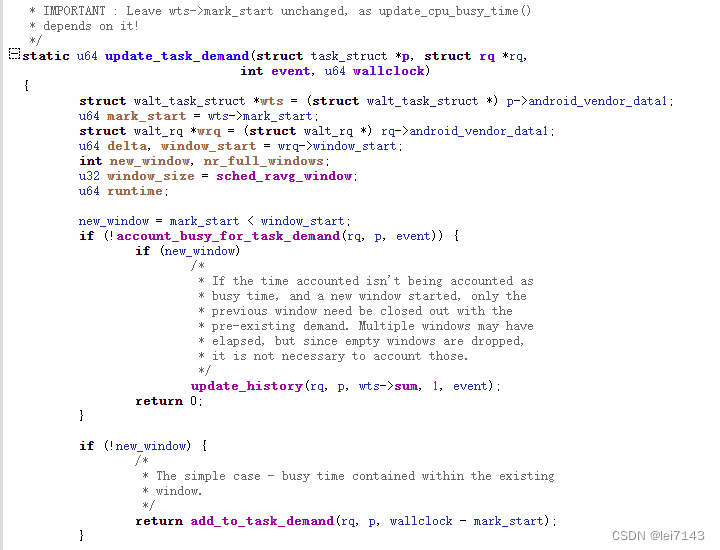
如果不是新的窗口,执行add_to_task_demand ,等效这段时间中,满算力执行的时间,更新wts->sum

update_history(rq, p, wts->sum, 1, event);
第一部分

类似上面这个图
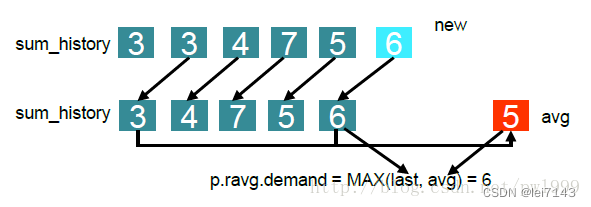
walt 算法5 个窗口,这里将
hist[3] => 赋值给hist[4]
hist[2] => 赋值给hist[3]
...
hist[1] => 赋值给hist[2]
再将runtime 赋值给到hist[1]
sum 为 更新后hist数组和,max 为更新后hist数组最大值
再根据配置,获取demand(等效最近5个窗口计算出来的负载)
第二部分
参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/lingjiajun/p/12317090.html
这里是核心的部分,有时间再慢慢看

pred_demand 用于EAS
第三部分
直接根据结果更新walt_rq->walt_sched_stats

337 stats->cumulative_runnable_avg_scaled + demand_scaled_delta;
338 s64 pred_demands_sum_scaled =
339 stats->pred_demands_sum_scaled + pred_demand_scaled_delta;

第四部分
更新

Sched_Boost小结
调度器分支之RTG_内核工匠的博客-CSDN博客
在后续的kernel版本升级及代码演进中,又进行了一些功能的调整,比如在5.4内核上,引入skip_min来替代perferredcluster,并通过sched_min_task_util_for_colocation来过滤掉负载较低的任务,当任务负载低于sched_min_task_util_for_colocation时,其选核时的优先调度大核任然可以持续维持sched_task_unfilter_period的时间(这个名字也很有趣,不过滤的时间周期,迟滞一段时间)。整体功能并没有发生大的变化。
第六部分
这里就是完整窗口了及剩下的最后一个窗口
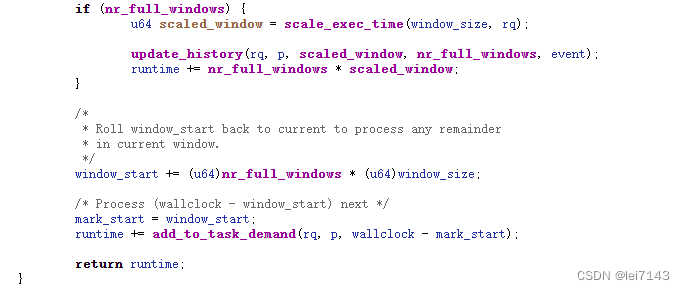
5、
update_cpu_busy_time(p, rq, event, wallclock, irqtime);
第一部分
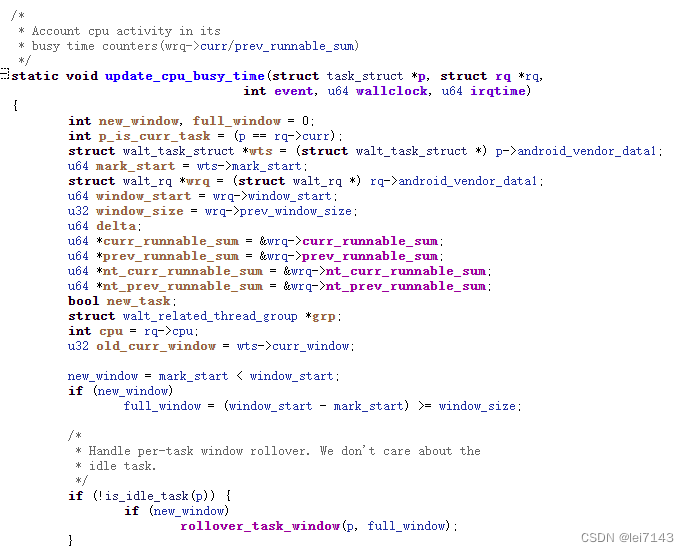
一个新的窗口

第二部分
当前任务到了一个新窗口,需要更新prev 到curr ,curr 清零,不是当前任务不需要



第三部分
不是当前任务,更新,由于第二部分没有 更新prev 到curr ,curr 清零
if (!p_is_curr_task) {
...
}
是当前任务,更新,由于第二部分已经 更新prev 到curr ,curr 清零
.....
第四部分,有时间再慢慢看
1853 done:
1854 if (!is_idle_task(p))
1855 update_top_tasks(p, rq, old_curr_window,
1856 new_window, full_window);
6、有时间再慢慢看

不同算法对比:
cfs eas
task placement task load (pelt) task demand(walt)
balance task load(pelt) task load(pelt)
cupfreq task utility (pelt) task utility(walt)