主打一手结果导向;
一、背景
在系统中,异步执行任务,是很常见的功能逻辑,但是在不同的场景中,又存在很多细节差异;
有的任务只强调「执行过程」,并不需要追溯任务自身的「执行结果」,这里并不是指对系统和业务产生的效果,比如定时任务、消息队列等场景;
但是有些任务即强调「执行过程」,又需要追溯任务自身的「执行结果」,在流程中依赖某个异步结果,判断流程是否中断,比如「并行」处理;
【串行处理】整个流程按照逻辑逐步推进,如果出现异常会导致流程中断;
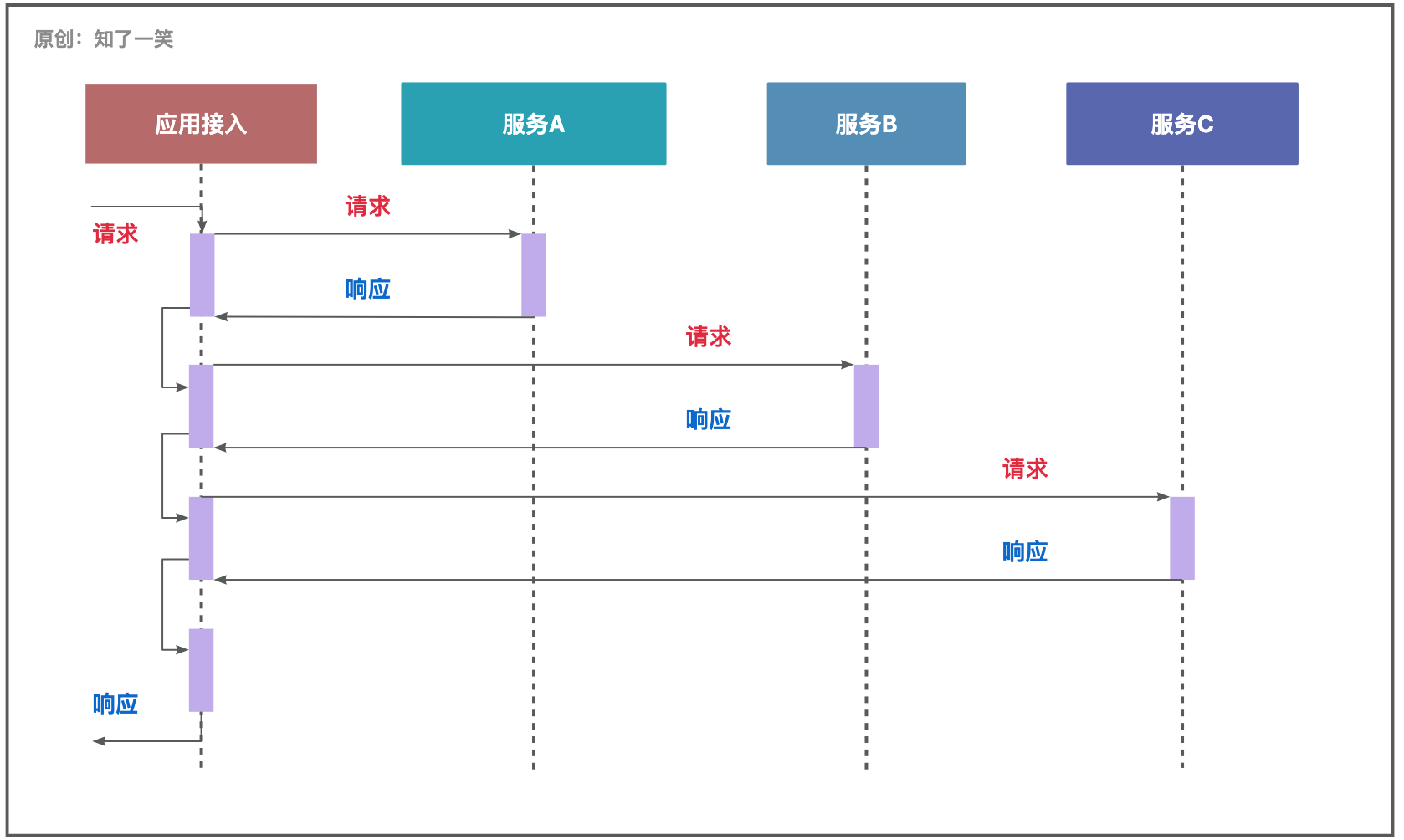
【并行处理】主流程按照逻辑逐步推进,其他「异步」交互的流程执行完毕后,将结果返回到主流程,如果「异步」流程异常,会影响部分结果;
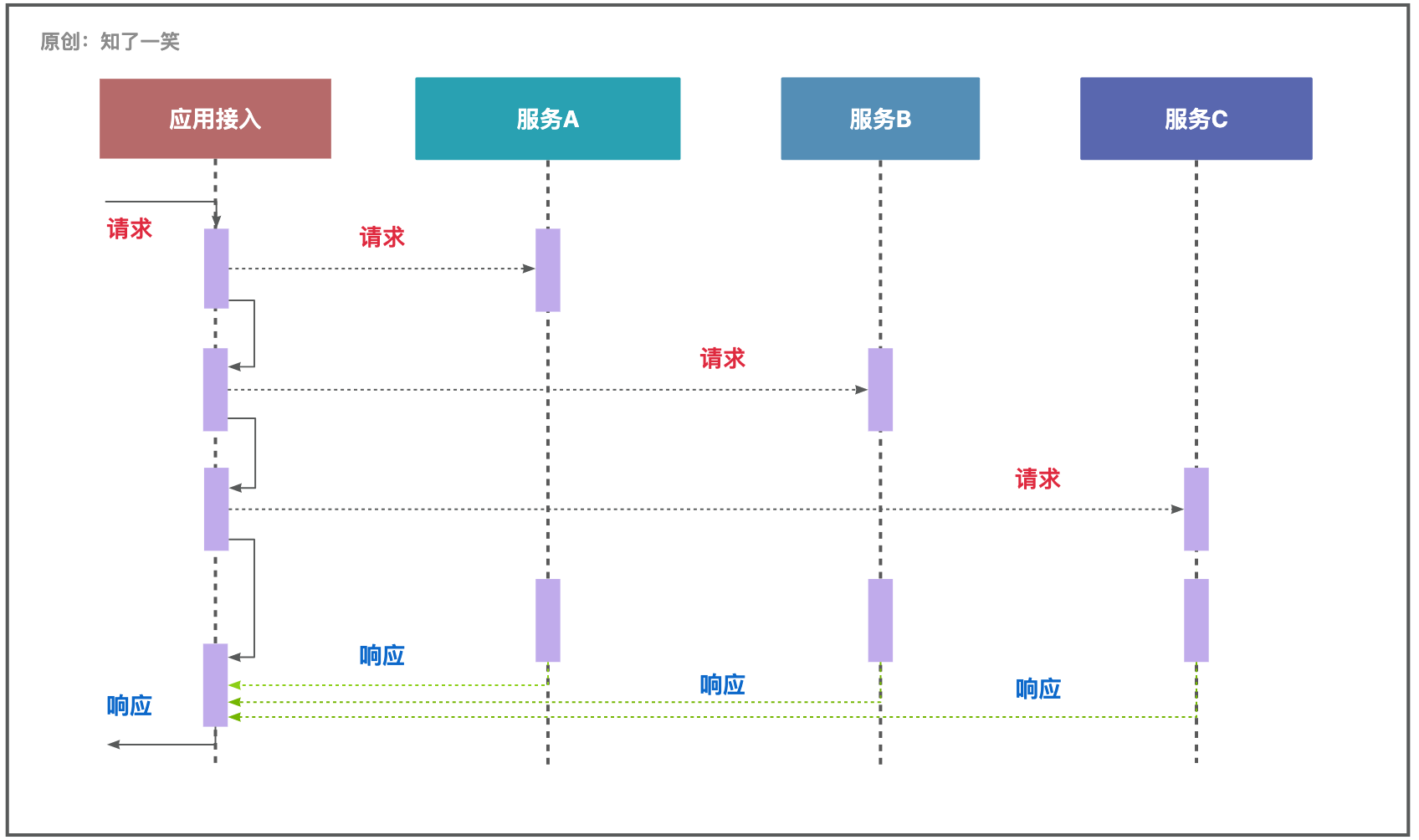
此前在《「订单」业务》的内容中,聊过关于「串行」和「并行」的应用对比,即在订单详情的加载过程中,通过「并行」的方式读取:商品、商户、订单、用户等信息,提升接口的响应时间;
二、Future接口
1、入门案例
异步是对流程的解耦,但是有的流程中又依赖异步执行的最终结果,此时就可以使用「Future」接口来达到该目的,先来看一个简单的入门案例;
public class ServerTask implements Callable<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(2000);
return 3;
}
}
public class FutureBase01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TimeInterval timer = DateUtil.timer();
// 线程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// 批量任务
List<ServerTask> serverTasks = new ArrayList<>() ;
for (int i=0;i<3;i++){
serverTasks.add(new ServerTask());
}
List<Future<Integer>> taskResList = executor.invokeAll(serverTasks) ;
// 结果输出
for (Future<Integer> intFuture:taskResList){
System.out.println(intFuture.get());
}
// 耗时统计
System.out.println("timer...interval = "+timer.interval());
}
}
这里模拟一个场景,以线程池批量执行异步任务,在任务内线程休眠2秒,以并行的方式最终获取全部结果,只耗时2秒多一点,如果串行的话耗时肯定超过6秒;
2、Future接口
Future表示异步计算的结果,提供了用于检查计算是否完成、等待计算完成、以及检索计算结果的方法。
【核心方法】
get():等待任务完成,获取执行结果,如果任务取消会抛出异常;get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit):指定等待任务完成的时间,等待超时会抛出异常;isDone():判断任务是否完成;isCancelled():判断任务是否被取消;cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning):尝试取消此任务的执行,如果任务已经完成、已经取消或由于其他原因无法取消,则此尝试将失败;
【基础用法】
public class FutureBase02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 线程池执行任务
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new Callable<String>() {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(3000);
return "task...OK";
}
}) ;
executor.execute(futureTask);
// 任务信息获取
System.out.println("是否完成:"+futureTask.isDone());
System.out.println("是否取消:"+futureTask.isCancelled());
System.out.println("获取结果:"+futureTask.get());
System.out.println("尝试取消:"+futureTask.cancel(Boolean.TRUE));
}
}
【FutureTask】
Future接口的基本实现类,提供了计算的启动和取消、查询计算是否完成以及检索计算结果的方法;
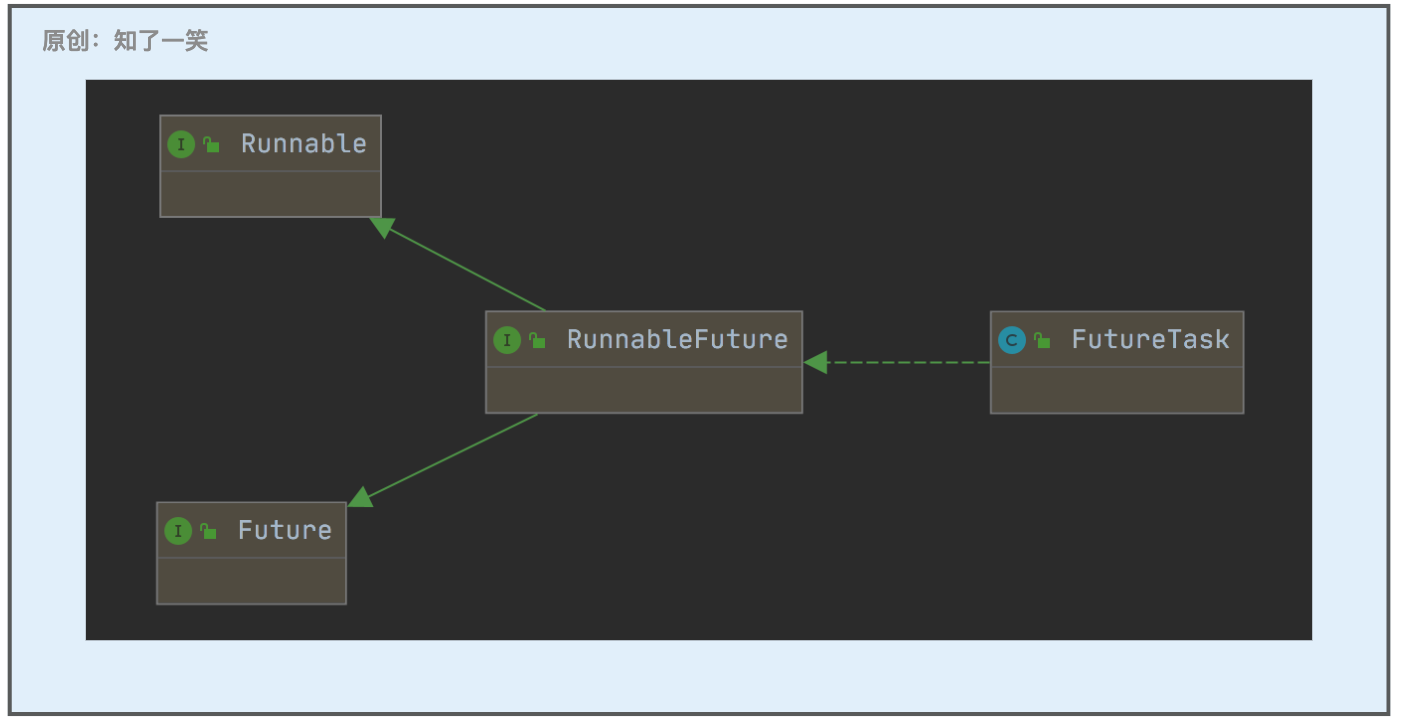
在「FutureTask」类中,可以看到线程异步执行任务时,其中的核心状态转换,以及最终结果写出的方式;
虽然「Future」从设计上,实现了异步计算的结果获取,但是通过上面的案例也可以发现,流程的主线程在执行get()方法时会阻塞,直到最终获取结果,显然对于程序来说并不友好;
在JDK1.8提供「CompletableFuture」类,对「Future」进行优化和扩展;
三、CompletableFuture类
1、基础说明
「CompletableFuture」类提供函数编程的能力,可以通过回调的方式处理计算结果,并且支持组合操作,提供很多方法来实现异步编排,降低异步编程的复杂度;

「CompletableFuture」实现「Future」和「CompletionStage」两个接口;
- Future:表示异步计算的结果;
- CompletionStage:表示异步计算的一个步骤,当一个阶段计算完成时,可能会触发其他阶段,即步骤可能由其他CompletionStage触发;
【入门案例】
public class CompletableBase01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 线程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// 任务执行
CompletableFuture<String> cft = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "Res...OK";
}, executor);
// 结果输出
System.out.println(cft.get());
}
}
2、核心方法
2.1 实例方法
public class Completable01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 线程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// 1、创建未完成的CompletableFuture,通过complete()方法完成
CompletableFuture<Integer> cft01 = new CompletableFuture<>() ;
cft01.complete(99) ;
// 2、创建已经完成CompletableFuture,并且给定结果
CompletableFuture<String> cft02 = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("given...value");
// 3、有返回值,默认ForkJoinPool线程池
CompletableFuture<String> cft03 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return "OK-3";});
// 4、有返回值,采用Executor自定义线程池
CompletableFuture<String> cft04 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return "OK-4";},executor);
// 5、无返回值,默认ForkJoinPool线程池
CompletableFuture<Void> cft05 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {});
// 6、无返回值,采用Executor自定义线程池
CompletableFuture<Void> cft06 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(()-> {}, executor);
}
}
2.2 计算方法
public class Completable02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 线程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture<String> cft01 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "OK";
},executor);
// 1、计算完成后,执行后续处理
// cft01.whenComplete((res, ex) -> System.out.println("Result:"+res+";Exe:"+ex));
// 2、触发计算,如果没有完成,则get设定的值,如果已完成,则get任务返回值
// boolean completeFlag = cft01.complete("given...value");
// if (completeFlag){
// System.out.println(cft01.get());
// } else {
// System.out.println(cft01.get());
// }
// 3、开启新CompletionStage,重新获取线程执行任务
cft01.whenCompleteAsync((res, ex) -> System.out.println("Result:"+res+";Exe:"+ex),executor);
}
}
2.3 结果获取方法
public class Completable03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 线程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture<String> cft01 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "Res...OK";
},executor);
// 1、阻塞直到获取结果
// System.out.println(cft01.get());
// 2、设定超时的阻塞获取结果
// System.out.println(cft01.get(4, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
// 3、非阻塞获取结果,如果任务已经完成,则返回结果,如果任务未完成,返回给定的值
// System.out.println(cft01.getNow("given...value"));
// 4、get获取抛检查异常,join获取非检查异常
System.out.println(cft01.join());
}
}
2.4 任务编排方法
public class Completable04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 线程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture<String> cft01 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("OK-1");
return "OK";
},executor);
// 1、cft01任务执行完成后,执行之后的任务,此处不关注cft01的结果
// cft01.thenRun(() -> System.out.println("task...run")) ;
// 2、cft01任务执行完成后,执行之后的任务,可以获取cft01的结果
// cft01.thenAccept((res) -> {
// System.out.println("cft01:"+res);
// System.out.println("task...run");
// });
// 3、cft01任务执行完成后,执行之后的任务,获取cft01的结果,并且具有返回值
// CompletableFuture<Integer> cft02 = cft01.thenApply((res) -> {
// System.out.println("cft01:"+res);
// return 99 ;
// });
// System.out.println(cft02.get());
// 4、顺序执行cft01、cft02
// CompletableFuture<String> cft02 = cft01.thenCompose((res) -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// System.out.println("cft01:"+res);
// return "OK-2";
// }));
// cft02.whenComplete((res,ex) -> System.out.println("Result:"+res+";Exe:"+ex));
// 5、对比任务的执行效率,由于cft02先完成,所以取cft02的结果
// CompletableFuture<String> cft02 = cft01.applyToEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// System.out.println("run...cft02");
// try {
// Thread.sleep(3000);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// return "OK-2";
// }),(res) -> {
// System.out.println("either...result:" + res);
// return res;
// });
// System.out.println("finally...result:" + cft02.get());
// 6、两组任务执行完成后,对结果进行合并
// CompletableFuture<String> cft02 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "OK-2") ;
// String finallyRes = cft01.thenCombine(cft02,(res1,res2) -> {
// System.out.println("res1:"+res1+";res2:"+res2);
// return res1+";"+res2 ;
// }).get();
// System.out.println(finallyRes);
CompletableFuture<String> cft02 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("OK-2");
return "OK-2";
}) ;
CompletableFuture<String> cft03 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("OK-3");
return "OK-3";
}) ;
// 7、等待批量任务执行完返回
// CompletableFuture.allOf(cft01,cft02,cft03).get();
// 8、任意一个任务执行完即返回
System.out.println("Sign:"+CompletableFuture.anyOf(cft01,cft02,cft03).get());
}
}
2.5 异常处理方法
public class Completable05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 线程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture<String> cft01 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
if (1 > 0){
throw new RuntimeException("task...exception");
}
return "OK";
},executor);
// 1、捕获cft01的异常信息,并提供返回值
String finallyRes = cft01.thenApply((res) -> {
System.out.println("cft01-res:" + res);
return res;
}).exceptionally((ex) -> {
System.out.println("cft01-exe:" + ex.getMessage());
return "error" ;
}).get();
System.out.println("finallyRes="+finallyRes);
CompletableFuture<String> cft02 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "OK-2";
},executor);
// 2、如果cft02未完成,则get时抛出指定异常信息
boolean exeFlag = cft02.completeExceptionally(new RuntimeException("given...exception"));
if (exeFlag){
System.out.println(cft02.get());
} else {
System.out.println(cft02.get());
}
}
}
3、线程池问题
- 在实践中,通常不使用
ForkJoinPool#commonPool()公共线程池,会出现线程竞争问题,从而形成系统瓶颈; - 在任务编排中,如果出现依赖情况或者父子任务,尽量使用多个线程池,从而避免任务请求同一个线程池,规避死锁情况发生;
四、CompletableFuture原理
1、核心结构
在分析「CompletableFuture」其原理之前,首先看一下涉及的核心结构;

【CompletableFuture】
在该类中有两个关键的字段:「result」存储当前CF的结果,「stack」代表栈顶元素,即当前CF计算完成后会触发的依赖动作;从上面案例中可知,依赖动作可以没有或者有多个;
【Completion】
依赖动作的封装类;
【UniCompletion】
继承Completion类,一元依赖的基础类,「executor」指线程池,「dep」指依赖的计算,「src」指源动作;
【BiCompletion】
继承UniCompletion类,二元或者多元依赖的基础类,「snd」指第二个源动作;
2、零依赖
顾名思义,即各个CF之间不产生依赖关系;
public class DepZero {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture<String> cft1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()-> "OK-1",executor);
CompletableFuture<String> cft2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()-> "OK-2",executor);
System.out.println(cft1.get()+";"+cft2.get());
}
}
3、一元依赖
即CF之间的单个依赖关系;这里使用「thenApply」方法演示,为了看到效果,使「cft1」长时间休眠,断点查看「stack」结构;
public class DepOne {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture<String> cft1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(30000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "OK-1";
},executor);
CompletableFuture<String> cft2 = cft1.thenApply(res -> {
System.out.println("cft01-res"+res);
return "OK-2" ;
});
System.out.println("cft02-res"+cft2.get());
}
}
断点截图:
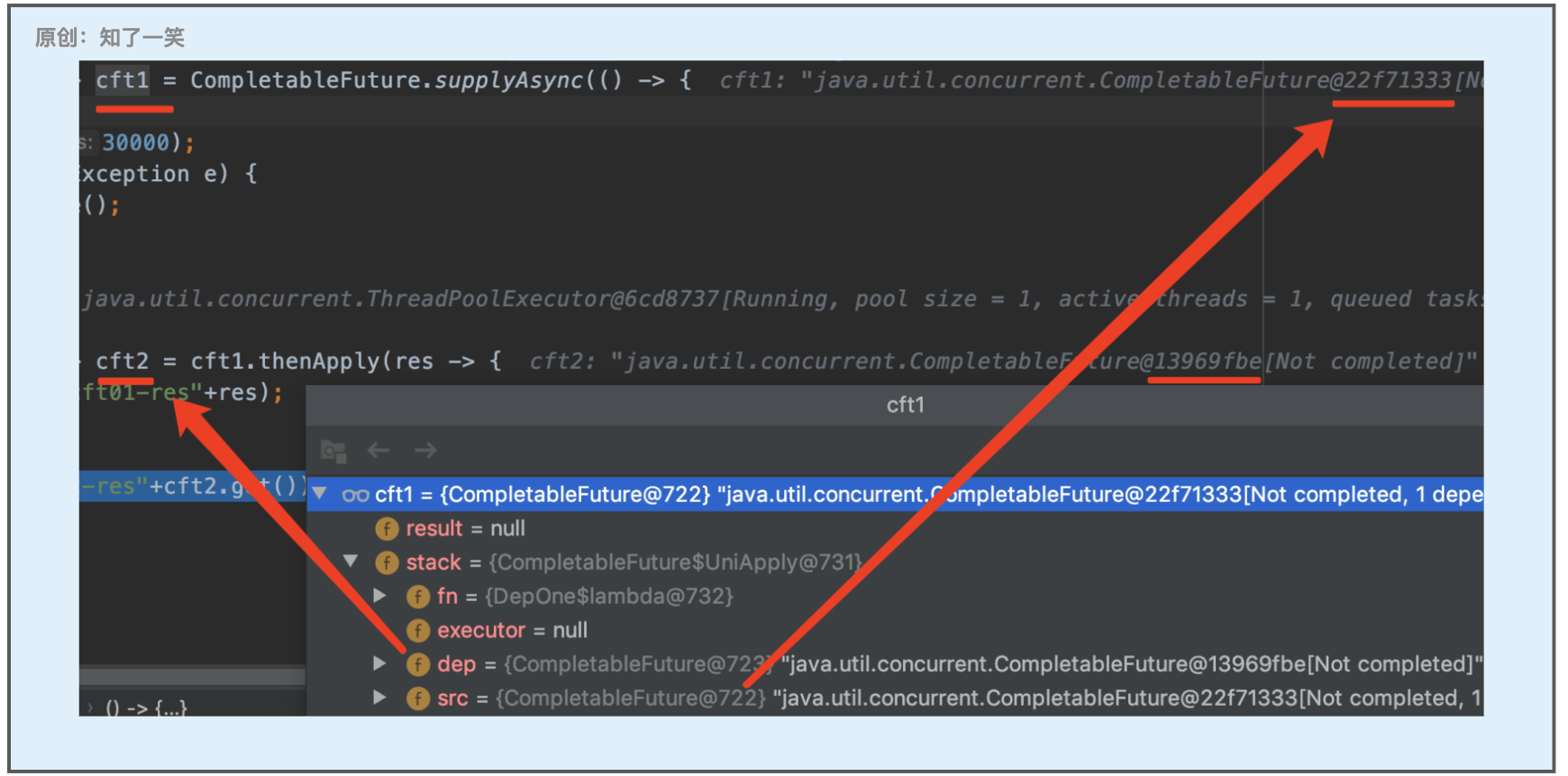
原理分析:
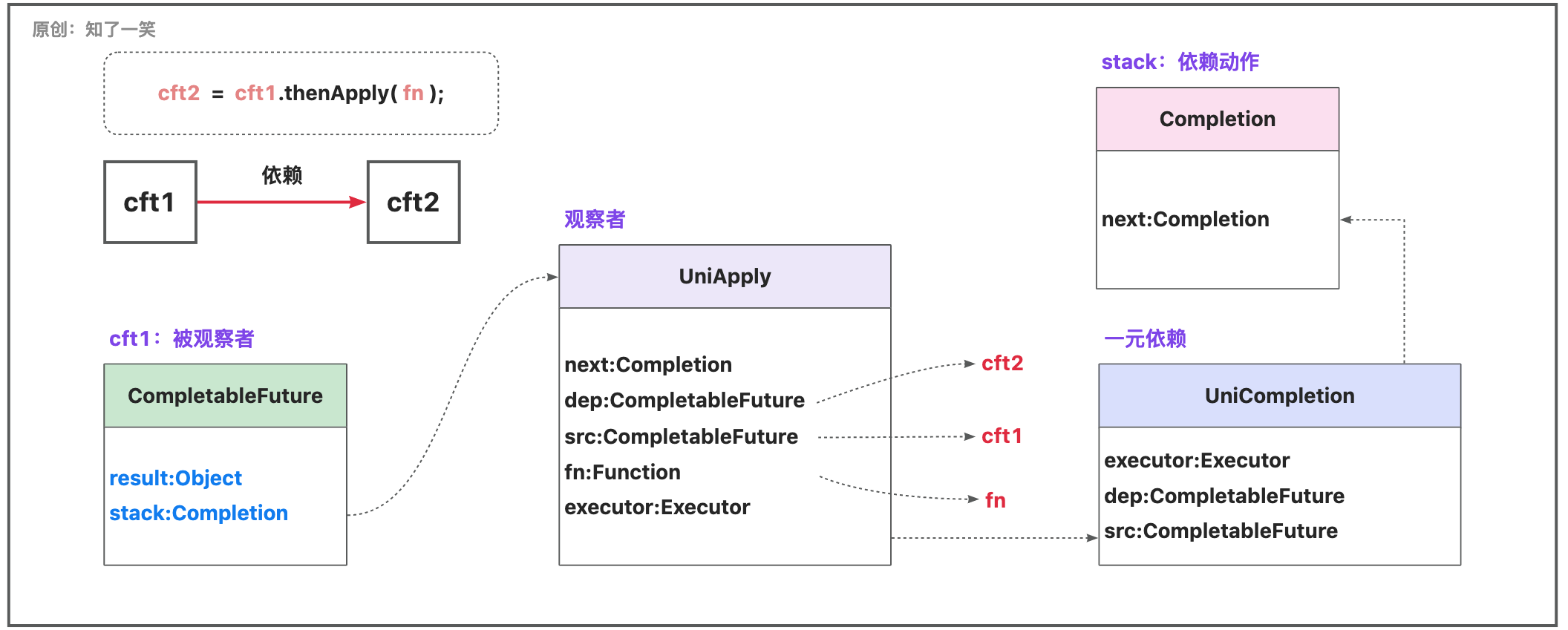
观察者Completion注册到「cft1」,注册时会检查计算是否完成,未完成则观察者入栈,当「cft1」计算完成会弹栈;已完成则直接触发观察者;
可以调整断点代码,让「cft1」先处于完成状态,再查看其运行时结构,从而分析完整的逻辑;
4、二元依赖
即一个CF同时依赖两个CF;这里使用「thenCombine」方法演示;为了看到效果,使「cft1、cft2」长时间休眠,断点查看「stack」结构;
public class DepTwo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture<String> cft1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(30000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "OK-1";
},executor);
CompletableFuture<String> cft2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(30000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "OK-2";
},executor);
// cft3 依赖 cft1和cft2 的计算结果
CompletableFuture<String> cft3 = cft1.thenCombine(cft2,(res1,res2) -> {
System.out.println("cft01-res:"+res1);
System.out.println("cft02-res:"+res2);
return "OK-3" ;
});
System.out.println("cft03-res:"+cft3.get());
}
}
断点截图:
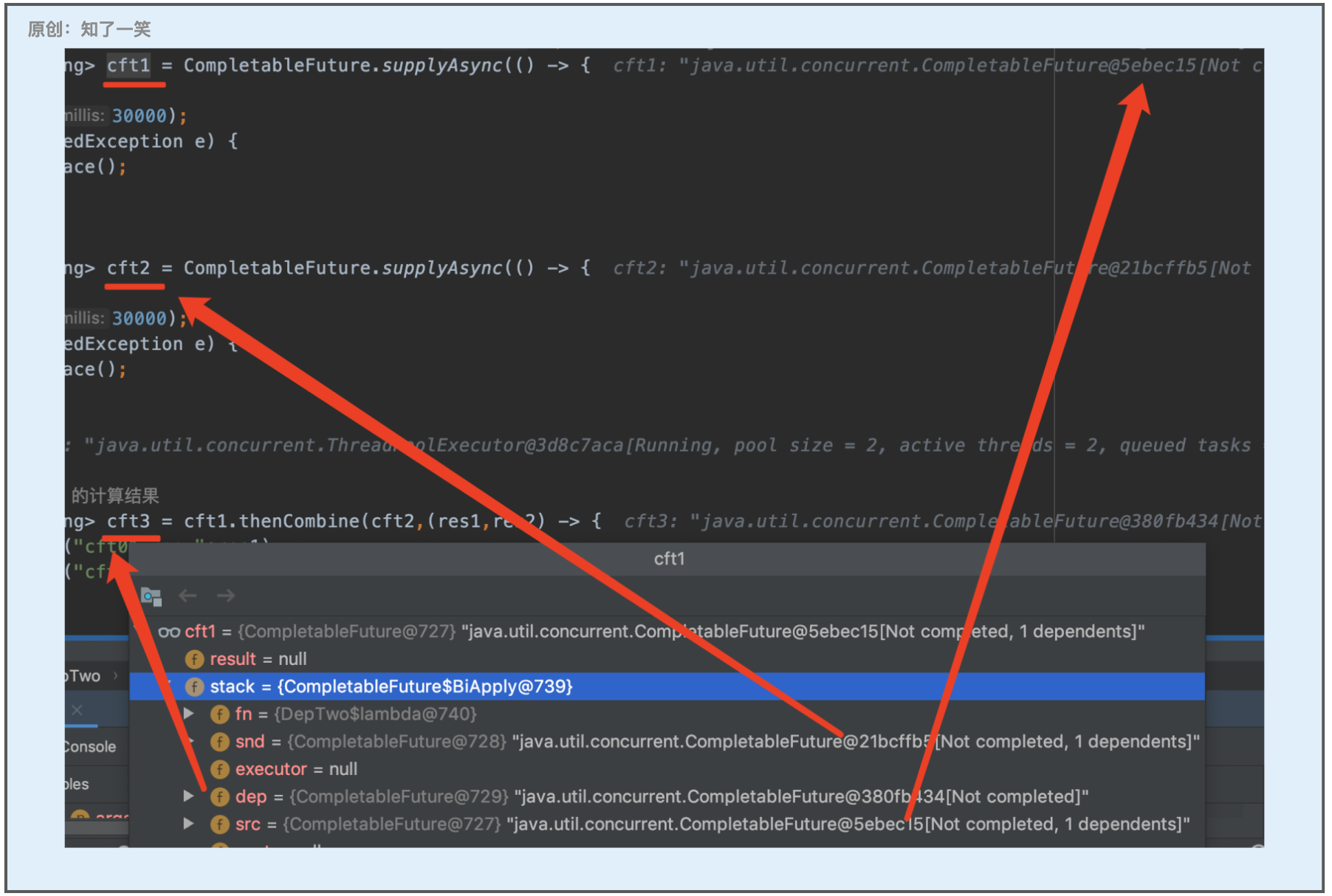
原理分析:
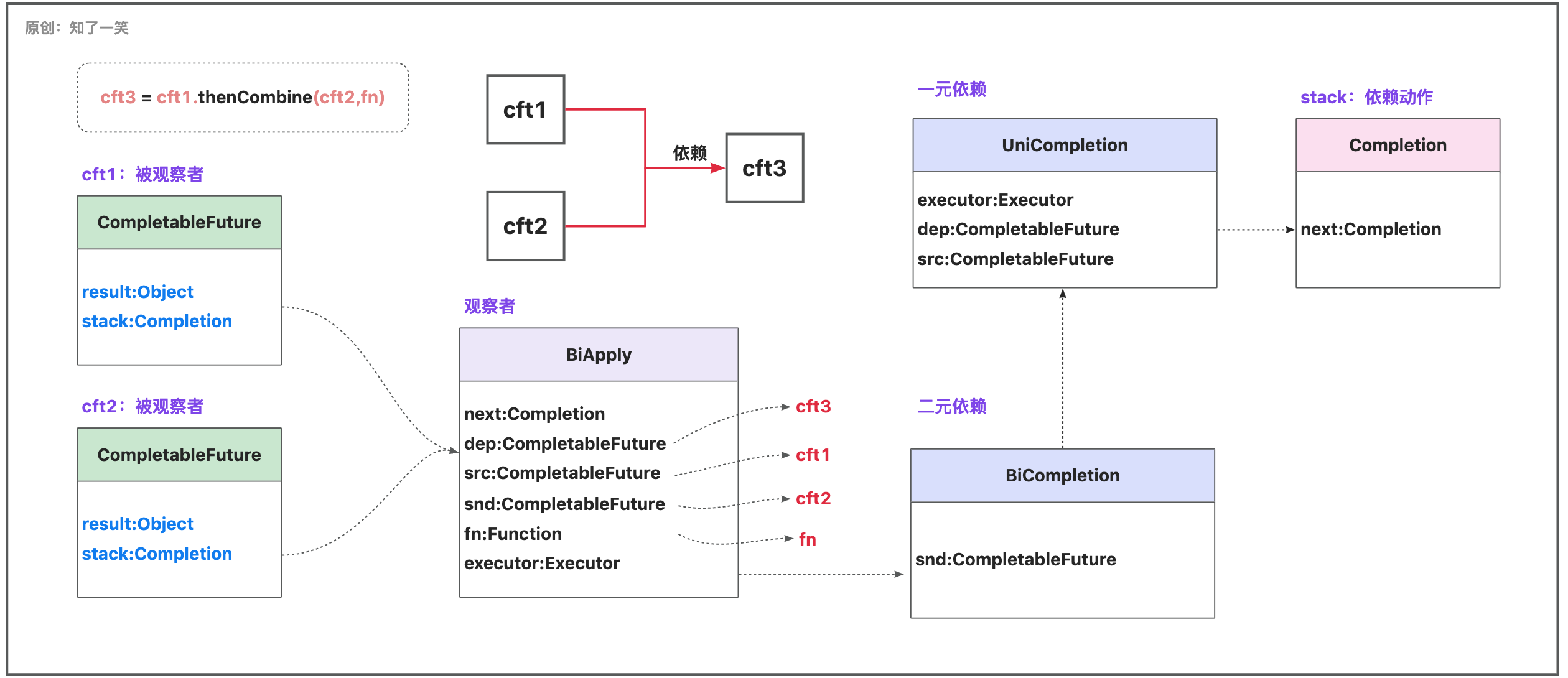
在「cft1」和「cft2」未完成的状态下,尝试将BiApply压入「cft1」和「cft2」两个栈中,任意CF完成时,会尝试触发观察者,观察者检查「cft1」和「cft2」是否都完成,如果完成则执行;
5、多元依赖
即一个CF同时依赖多个CF;这里使用「allOf」方法演示;为了看到效果,使「cft1、cft2、cft3」长时间休眠,断点查看「stack」结构;
public class DepMore {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture<String> cft1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(30000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "OK-1";
},executor);
CompletableFuture<String> cft2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(30000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "OK-2";
},executor);
CompletableFuture<String> cft3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(30000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "OK-3";
},executor);
// cft4 依赖 cft1和cft2和cft3 的计算结果
CompletableFuture<Void> cft4 = CompletableFuture.allOf(cft1,cft2,cft3);
CompletableFuture<String> finallyRes = cft4.thenApply(tm -> {
System.out.println("cft01-res:"+cft1.join());
System.out.println("cft02-res:"+cft2.join());
System.out.println("cft03-res:"+cft3.join());
return "OK-4";
});
System.out.println("finally-res:"+finallyRes.get());
}
}
断点截图:
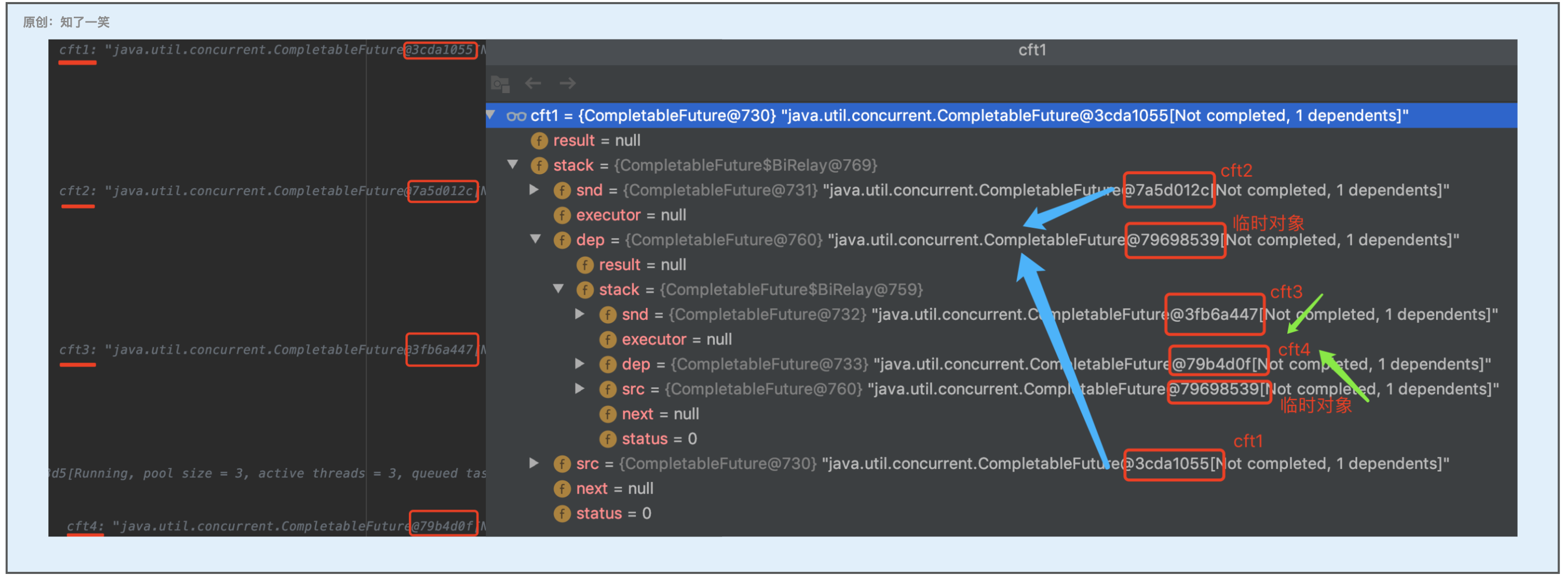
原理分析:

多元依赖的回调方法除了「allOf」还有「anyOf」,其实现原理都是将依赖的多个CF补全为平衡二叉树,从断点图可知会按照树的层级处理,核心结构参考二元依赖即可;
五、参考源码
编程文档:
https://gitee.com/cicadasmile/butte-java-note
应用仓库:
https://gitee.com/cicadasmile/butte-flyer-parent