目录
1.前言
2.实现过程
2.1目录
2.2文件介绍
3.核心逻辑分步骤详解
4.总结
1.前言
最近火爆全网的羊了个羊小程序,背景是根据官方介绍,“羊了个羊”是一款闯关消除小游戏,通关率不到0.1%。主要玩法为重叠的各类方块,需要在下方7个栏内完成消除(3个同类消除),其特点就是“极难”,也因此成为热门挑战。我也颇感兴趣,去玩了2把,的确很有乐趣,整理了一下思路,决定搞个vue3版本的网页版本,我看网上有react版本的了,vue3版本还没有,下面分别给出设计思路,实现方式,和玩法
设计思路:
1,先来一张背景图,网上搜一张草地图片
2,最底部设置七个槽位,有三个连续相同的就消除,槽位满了的话,挑战失败
3,中间的图层区域使用重叠的方式,可能是半重叠,可能是全重叠,只有第一层可以移入槽位,全部消除时,表示挑战成功!后续挑战是变化关卡的布局方式(多种排列方式)
4,点击事件的思路(内层不能点击,前置点击如果槽位满了还没有消除完,关卡的消除,消除动作 和 添加爆炸效果,进入下一关,挑战失败)
5,辅助类函数:判断是否过关,消除函数,实现爆炸💥效果,控制关卡
实现方式:
vue3配合pinia实现数据驱动页面
玩法:
使用关卡模式,从第1关简单到2困难,3关复杂,这里的关卡只是数据的多少变化而已,可以设计出无数关卡,这里前端模拟json数据,使用对象json
效果演示:
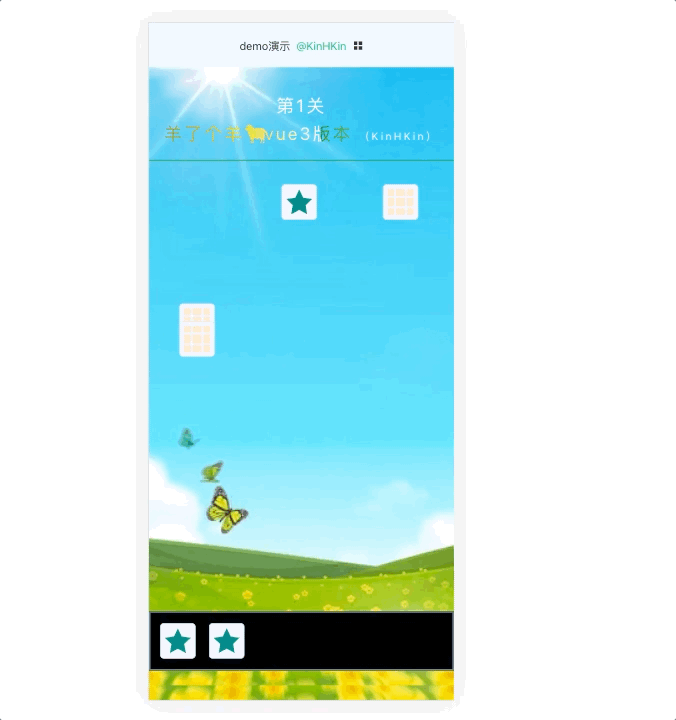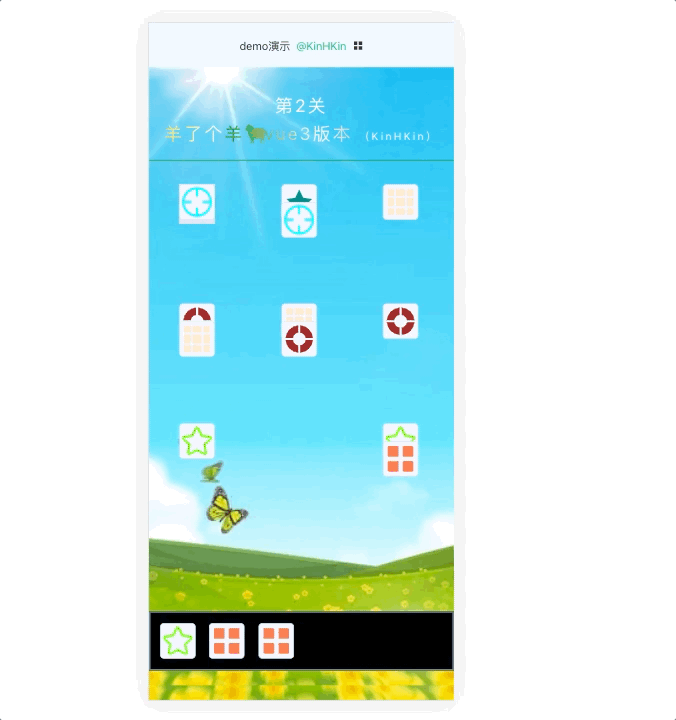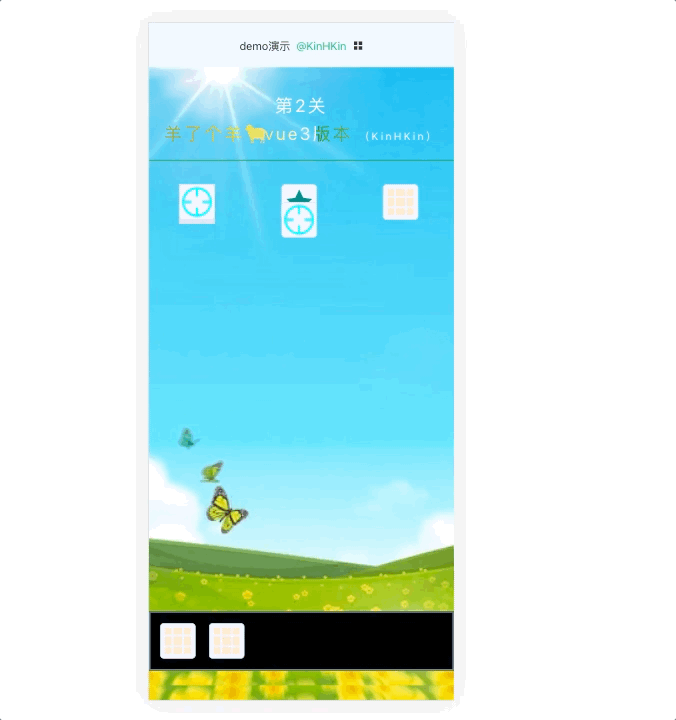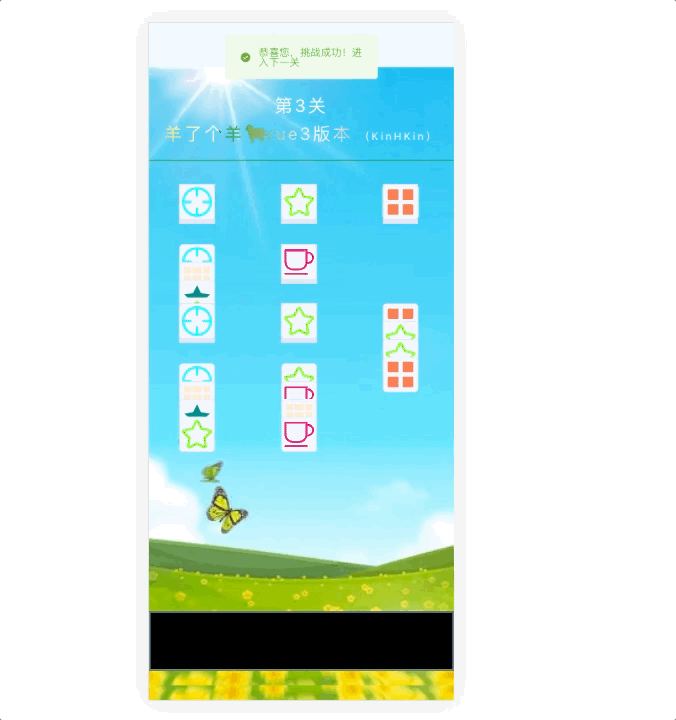
在线体验 :
KinHKinhttps://rondsjinhuajin.github.io/DemoVue/#/
源码地址:
在github欢迎follow和star,感谢可爱的各位看官大佬~❤️
2.实现过程
2.1目录

2.2文件介绍
入口文件index.vue,设计背景色
<script setup lang='ts'>
import Header from "./components/Header.vue";
import Main from "./components/Main.vue";
</script>
<template>
<div class="sheep-wrap">
<div class="sheep">
<div class="sheep-wrap">
<div class="sheep">
<Header />
<Main />
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped lang='less'>
.sheep-wrap {
.sheep {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
padding-bottom: 20px;
}
width: 100%;
height: calc(100vh - 60px);
background: url("../../assets/images/sheep.png") center no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
}
</style>Header.vue文件,文字动效,配合pinia显示第几关
<script lang='ts' setup>
import { useSheepStore } from "@/stores/sheep";
const store = useSheepStore();
</script>
<template>
<div class="sheep-header">
<div>第{{ store.step + 1 }}关</div>
<div>
<span class="l">羊了个羊🐑vue3版本</span
><span
style="font-size: 14px;font-family: 'Times New Roman', Times, serif';"
>(KinHKin)</span
>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped lang="less">
.flex-center {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
.sheep-header {
padding-top: 2rem;
text-align: center;
letter-spacing: 0.2rem;
font-size: 1.5rem;
color: #fff;
border-bottom: 1px solid #1d9614;
padding-bottom: 1rem;
margin-bottom: 2rem;
div .l {
background-image: -webkit-linear-gradient(
left,
#1d9614,
#fff 25%,
#666 50%,
#e6d205 75%,
#fff
);
-webkit-text-fill-color: transparent;
-webkit-background-clip: text;
-webkit-background-size: 200% 100%;
-webkit-animation: maskedAnimation 4s infinite linear;
padding-right: 8px;
}
}
@keyframes maskedAnimation {
0% {
background-position: 0 0;
}
100% {
background-position: -100% 0;
}
}
</style>
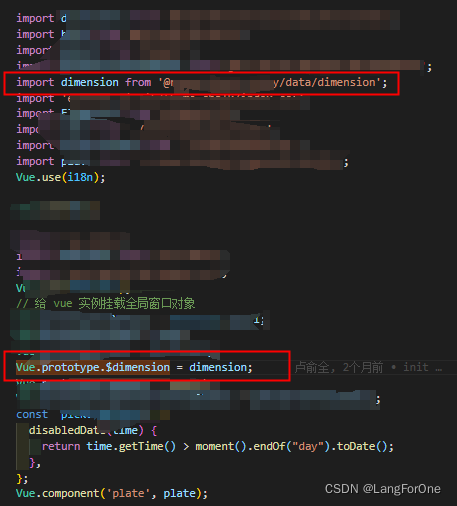
Main.vue文件是核心文件,作用是引入颜色,控制关卡,设置关卡数据,如何消除,增加爆炸动效,控制交互逻辑等。
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, type Ref } from "vue";
import { ElMessage, ElMessageBox } from "element-plus";
import { useSheepStore } from "@/stores/sheep";
// 关卡数据
import data from "./data.json";
// 颜色
import constants from "./constants";
// pinia 控制关卡
const store = useSheepStore();
// 七个槽位
// const footerList = ref([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]);
const footerList: Ref<Array<any> | [any]> = ref([]);
const colors = ref(constants.colors);
// 关卡响应式
const totalList: Ref<Array<any> | [any]> = ref([]);
totalList.value = data["list1"]; // 默认第一关
// 控制动画效果结束才能点击
const isNotClick = ref(false);
// 点击控制事件
function handleClick(
i: number,
k: number,
onei: { oneSub: string | Array<string> },
onek: number,
oneiSub: Array<number>,
onekSub: number
) {
console.log(i, k, onei, onek, oneiSub, onekSub, "测试");
if (isNotClick.value) {
return false;
}
// 内层不能点击
if (onekSub !== onei.oneSub.length - 1) {
return false;
}
// 前置点击如果槽位满了还没有消除完
fullFun()
// 关卡的消除
let tempList = fixFun(k, onekSub, onek, oneiSub)
// 消除动作 和 添加爆炸效果
if (footerList.value.length > 2) {
isNotClick.value = true
const { list, flag } = eliminationFunction(footerList.value)
footerList.value = list;
if (flag) {
footerList.value = addBoomFunction(footerList.value);
}
setTimeout(() => {
const { list, flag } = eliminationFunction(footerList.value)
footerList.value = list;
isNotClick.value = false
}, 1000);
// 进入下一关
nextFun(tempList)
}
// 挑战失败
failFun(tempList)
console.log(footerList, tempList, "tempList");
}
// full
function fullFun() {
if (footerList.value.length === 7) {
ElMessage.closeAll();
ElMessageBox.alert("挑战失败,点击确定返回!", "Warning", {
confirmButtonText: "确定",
type: "warning",
showClose: false,
}).then(() => {
location.reload();
});
return false;
}
}
// fix
function fixFun(k: number, onekSub: number, onek: number, oneiSub: Array<number>) {
const { value } = totalList;
let tempList = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(value));
for (let i = 0; i < tempList.length; i++) {
const one = tempList[k].one;
for (let j = 0; j < one.length; j++) {
const oneSub = one[onek];
for (let k = 0; k < oneSub.oneSub.length; k++) {
if (onekSub === k) {
const footItem = oneSub.oneSub.splice(onekSub);
break;
}
}
}
}
footerList.value.push(oneiSub);
totalList.value = tempList;
return tempList
}
//fail
function failFun(tempList: any[]) {
setTimeout(() => {
if (footerList.value.length > 0 && !jugeList(tempList)) {
ElMessage.closeAll();
ElMessageBox.alert("挑战失败,点击确定返回!", "Warning", {
confirmButtonText: "确定",
type: "warning",
showClose: false,
}).then(() => {
location.reload();
});
return false;
}
}, 1002)
}
// next
function nextFun(tempList: any[]) {
setTimeout(() => {
if (!footerList.value.length && !jugeList(tempList)) {
// debugger
ElMessage.closeAll();
ElMessage.success("恭喜您,挑战成功!进入下一关");
store.step++;
const inStep: string = "list" + (store.step + 1);
totalList.value = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(data))[inStep];
footerList.value = [];
}
}, 1001)
}
// 判断是否过关
function jugeList(list: any[]) {
let temp: any = [];
list?.forEach((oeni: { one: any }) => {
oeni?.one?.forEach((sub: { oneSub: any }) => {
temp = [...temp, ...sub.oneSub];
});
});
return temp.length;
}
// 消除函数
function eliminationFunction(list: any[]) {
let flag: boolean = false;
for (let k = 0; k < list.length - 2; k++) {
const temp = list;
const arr = temp.slice(k, k + 3);
console.log(k, arr);
if (arr[0] === arr[1] && arr[1] === arr[2] && arr[0] === arr[2]) {
list.splice(k + 2);
list.splice(k + 1);
list.splice(k, 1);
flag = true
break;
}
}
return { list, flag };
}
// 实现爆炸💥效果
function addBoomFunction(list: any[]) {
const temp = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify([...list, ...['boom', 'boom', 'boom']]))
return temp;
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="sheep-main">
<div class="sheep-main-wrap">
<template v-for="(i, k) in totalList" :key="'i' + k">
<el-row v-if="i.one">
<el-col :span="8" v-for="(onei, onek) in i.one" :key="'i' + onek">
<div class="pic-list">
<div class="pic-list-item" v-for="(oneiSub, onekSub) in onei.oneSub"
:style="!onei.full ? `--i:${onekSub}` : `--i:0`"
:class="onei.full && onei.oneSub.length > 1 ? 'true' : ''" :key="'i' + onekSub"
@click="handleClick(i, k, onei, onek, oneiSub, onekSub)">
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 0">
<StarFilled :color="colors[0]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 1">
<Aim :color="colors[1]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 2">
<Grid :color="colors[2]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 3">
<HelpFilled :color="colors[3]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 4">
<Star :color="colors[4]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 5">
<Menu :color="colors[5]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 6">
<Camera :color="colors[6]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 7">
<Bicycle :color="colors[7]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 8">
<IceTea :color="colors[8]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 9">
<ColdDrink :color="colors[9]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 10">
<CoffeeCup :color="colors[10]" />
</el-icon>
</div>
</div>
</el-col>
</el-row>
</template>
</div>
<div class="sheep-footer flex-center">
<div v-for="(ii, k) in footerList" :key="'ii' + k" class="sheep-footer-items">
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="ii === 0">
<StarFilled :color="colors[0]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="ii === 1">
<Aim :color="colors[1]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="ii === 2">
<Grid :color="colors[2]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="ii === 3">
<HelpFilled :color="colors[3]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="ii === 4">
<Star :color="colors[4]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="ii === 5">
<Menu :color="colors[5]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="ii === 6">
<Camera :color="colors[6]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="ii === 7">
<Bicycle :color="colors[7]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="ii === 8">
<IceTea :color="colors[8]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="ii === 9">
<ColdDrink :color="colors[9]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="ii === 10">
<CoffeeCup :color="colors[10]" />
</el-icon>
<div class="boom-class" v-if="ii === 'boom'">💥</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped lang="less">
.flex-center {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
.el-row {
// margin-top: 3rem;
height: 28%;
}
.fz {
font-size: 3rem;
border: 1px solid #dfe5f9;
// box-shadow: 2px 2px 10px #f3f6fe;
background: #f3f6fe;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.pic-list {
position: relative;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
&-item {
position: absolute;
left: 10vw;
cursor: pointer;
transition: all 0.3s;
&:nth-child(1n) {
top: calc(var(--i) * 1.5rem);
}
&.true {
box-shadow: 0 -55px 0 0 #dfe5f9 inset;
}
// &:nth-child(even) {
// top: 2rem;
// }
}
}
.sheep-main {
flex: 1;
&-wrap {
height: calc(100% - 80px);
}
}
.sheep-footer {
height: 80px;
width: 100%;
// border: 2px solid #298df9;
border: 2px solid #778899;
background: #010206;
.sheep-footer-items {
height: 80px;
width: calc(100% / 7);
margin-left: 8px;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
.boom-class {
font-size: 3rem;
animation: myMove 3s ease-in-out infinite;
}
@keyframes myMove {
0% {
opacity: 1;
}
100% {
opacity: 0;
}
}
// border-right: 1px solid #dfe5f9;
}
}
</style>
3.核心逻辑分步骤详解
import { ref, type Ref } from "vue";
import { ElMessage, ElMessageBox } from "element-plus";
import { useSheepStore } from "@/stores/sheep";
// 关卡数据
import data from "./data.json";
// 颜色
import constants from "./constants";
// pinia 控制关卡
const store = useSheepStore();
首先引入data.json数据是渲染中间的页面内容,即是:

中间的就叫卡片区域吧,卡片分为半个遮挡和整个遮挡,在data数据里面配置:
"full": true
默认是半个遮挡,配置了"full": true就表示这块的卡片是全遮挡的效果:
:style="!onei.full ? `--i:${onekSub}` : `--i:0`"
:class="onei.full && onei.oneSub.length > 1 ? 'true' : ''" :key="'i' + onekSub"
css: 使用了var的变量形式,来控制是否需要top下移,&.true来控制是否有下一级的卡片的样式
&:nth-child(1n) {
top: calc(var(--i) * 1.5rem);
}
&.true {
box-shadow: 0 -55px 0 0 #dfe5f9 inset;
}
data.json里面的数据oneSub的选值范围是:0-10
这和dom渲染层的息息相关:卡片使用的是简单的icon也可以是其他类型的元素,你觉得好看即可。
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 0">
<StarFilled :color="colors[0]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 1">
<Aim :color="colors[1]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 2">
<Grid :color="colors[2]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 3">
<HelpFilled :color="colors[3]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 4">
<Star :color="colors[4]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 5">
<Menu :color="colors[5]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 6">
<Camera :color="colors[6]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 7">
<Bicycle :color="colors[7]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 8">
<IceTea :color="colors[8]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 9">
<ColdDrink :color="colors[9]" />
</el-icon>
<el-icon class="fz" v-if="oneiSub === 10">
<CoffeeCup :color="colors[10]" />
</el-icon>这里只提供11中卡片的效果,可以扩展添加,需要修改代码。
接下来是:
// 七个槽位
// const footerList = ref([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]);
const footerList: Ref<Array<any> | [any]> = ref([]);
const colors = ref(constants.colors);
// 关卡响应式
const totalList: Ref<Array<any> | [any]> = ref([]);
totalList.value = data["list1"]; // 默认第一关
// 控制动画效果结束才能点击
const isNotClick = ref(false);
7个槽位在底部需要变化展示,做成响应式。totalList是动态变化的卡片数据集。totalList.value = data["list1"] ,默认第一关。爆炸💥的电话效果有延迟,需要控制在结束之后才能进行卡片的点击。
然后就是核心的卡片点击事件,需要做哪些逻辑控制呢?先看源代码,已经提前做了备注:
// 点击控制事件
function handleClick(
i: number,
k: number,
onei: { oneSub: string | Array<string> },
onek: number,
oneiSub: Array<number>,
onekSub: number
) {
console.log(i, k, onei, onek, oneiSub, onekSub, "测试");
if (isNotClick.value) {
return false;
}
// 内层不能点击
if (onekSub !== onei.oneSub.length - 1) {
return false;
}
// 前置点击如果槽位满了还没有消除完
fullFun()
// 关卡的消除
let tempList = fixFun(k, onekSub, onek, oneiSub)
// 消除动作 和 添加爆炸效果
if (footerList.value.length > 2) {
isNotClick.value = true
const { list, flag } = eliminationFunction(footerList.value)
footerList.value = list;
if (flag) {
footerList.value = addBoomFunction(footerList.value);
}
setTimeout(() => {
const { list, flag } = eliminationFunction(footerList.value)
footerList.value = list;
isNotClick.value = false
}, 1000);
// 进入下一关
nextFun(tempList)
}
// 挑战失败
failFun(tempList)
console.log(footerList, tempList, "tempList");
}首先是函数的签名,接受最上层级的i对象,k索引,然后是中层的onei对象,onek索引,最后是父级的oneiSub对象,onekSub索引。判断条件需要前置,判断能否点击isNotClick,内层不能点击
if (isNotClick.value) {
return false;
}
// 前置点击如果槽位满了还没有消除完
fullFun()函数判断如果槽位满了还没有消除完,就是挑战失败
function fullFun() {
if (footerList.value.length === 7) {
ElMessage.closeAll();
ElMessageBox.alert("挑战失败,点击确定返回!", "Warning", {
confirmButtonText: "确定",
type: "warning",
showClose: false,
}).then(() => {
location.reload();
});
return false;
}
}如何添加爆炸💥效果:
思路是在三个相同消除之后添加,添加在totalList数据之中 ,效果展示完成之后立即进行totalList数据重置操作。
// 关卡的消除
let tempList = fixFun(k, onekSub, onek, oneiSub)
// 消除动作 和 添加爆炸效果
if (footerList.value.length > 2) {
isNotClick.value = true
const { list, flag } = eliminationFunction(footerList.value)
footerList.value = list;
if (flag) {
footerList.value = addBoomFunction(footerList.value);
}
setTimeout(() => {
const { list, flag } = eliminationFunction(footerList.value)
footerList.value = list;
isNotClick.value = false
}, 1000);
// 进入下一关
nextFun(tempList)
}css 添加的方法:
.boom-class {
font-size: 3rem;
animation: myMove 3s ease-in-out infinite;
}
@keyframes myMove {
0% {
opacity: 1;
}
100% {
opacity: 0;
}
}消除函数eliminationFunction逻辑的控制,flag用来进行是否成功消除:
// 消除函数
function eliminationFunction(list: any[]) {
let flag: boolean = false;
for (let k = 0; k < list.length - 2; k++) {
const temp = list;
const arr = temp.slice(k, k + 3);
console.log(k, arr);
if (arr[0] === arr[1] && arr[1] === arr[2] && arr[0] === arr[2]) {
list.splice(k + 2);
list.splice(k + 1);
list.splice(k, 1);
flag = true
break;
}
}
return { list, flag };
}添加addBoomFunction爆炸函数:
// 实现爆炸💥效果
function addBoomFunction(list: any[]) {
const temp = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify([...list, ...['boom', 'boom', 'boom']]))
return temp;
}挑战失败如何判断呢?
//fail
function failFun(tempList: any[]) {
setTimeout(() => {
if (footerList.value.length > 0 && !jugeList(tempList)) {
ElMessage.closeAll();
ElMessageBox.alert("挑战失败,点击确定返回!", "Warning", {
confirmButtonText: "确定",
type: "warning",
showClose: false,
}).then(() => {
location.reload();
});
return false;
}
}, 1002)
}jugeList函数是对目前存在的卡片集合进行长度判断,如何卡片不存在,但是槽位的数据不为空的情况下,说明没有消除完,就判断要重新开始挑战:
// 判断是否过关
function jugeList(list: any[]) {
let temp: any = [];
list?.forEach((oeni: { one: any }) => {
oeni?.one?.forEach((sub: { oneSub: any }) => {
temp = [...temp, ...sub.oneSub];
});
});
return temp.length;
}最后是挑战成功就可以进行下一关:
// next
function nextFun(tempList: any[]) {
setTimeout(() => {
if (!footerList.value.length && !jugeList(tempList)) {
// debugger
ElMessage.closeAll();
ElMessage.success("恭喜您,挑战成功!进入下一关");
store.step++;
const inStep: string = "list" + (store.step + 1);
totalList.value = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(data))[inStep];
footerList.value = [];
}
}, 1001)
}如何卡片不存在,但是槽位的数据为空的情况下,说明消除完了,就可以进入下一关进行挑战,难度也将升级!
4.总结
最近是由于玩了羊了个羊的小程序,有所感悟,思考了这个游戏的整体的玩法,如何去操作,然后想到了可以实现一个前端网页版本的羊了个羊,这里面有一些自己的设计思考是很重要的,花了一个星期左右来实现,中间遇到了如何消除,如何控制挑战失败,成功的问题,并且一一解决了,可以想到如果前端来做这个游戏怎么在最优的方案上,书写可以扩展的dom,来适配很多不同的关卡的元素或者是我们需要什么样的数据结构,方便后续的关卡的升级。这里解决的方案是配合json,数据是数组嵌套类型,元素是需要循环来调用的,什么类型的卡片是需要提前有个范围的,这样是可扩展的。最后的操作,或者撤销,恢复等操作(这里没有实现)本质上也是对于数据的操作。终而言之:数据驱动页面,才是我们追求的。最后,各位同学一起多思考一下背后的实现,让我们用技术来创作更多有趣的事情吧~❤️
个人主页:KinHKin(五年前端)的博客_CSDN博客-vue,css,中秋活动领域博主
在线演示:KinHKin
fllow我的github: rondsjinhuajin (承吾) · GitHub