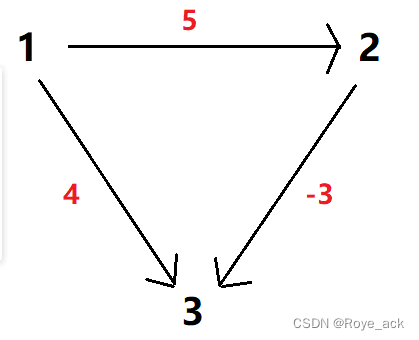
——SPFA 算法是 Bellman-Ford算法 的队列优化算法的别称
单源最短路,且图中没有负环就可以用spfa
目录
spaf求最短路模板
852. spfa判断负环
341. 最优贸易 - spfa + 双向建图
3305. 作物杂交 -
spaf求最短路模板
只有当一个点的前驱结点更新了,该节点才会得到更新
因此只需要创建一个队列每一次加入距离被更新的结点
队列存的是待更新的节点——取出队列里的节点会更新它的后续节点
已经在队列的节点不需要重复入队,可以用st数组标记已入队节点
spfa算法步骤:
- 建立队列,队列初始只有节点1
- 取出队头节点x,取消该点标记,遍历x所有出边(x,y,z),若dist[y]>dist[x]+w,则更新最短路dist[y]=dist[x]+w,若y不在队列中,让y入队并标记
- 重复上述步骤,直到队列为空
- 注:dist[x]存1→x的最短路径长度 st[x]标记x节点是否在队列中
活动 - AcWing
题目:
给定n个点m条边的带权有向图,图中可能存在重边和自环,边权可能为负数
请你求出 1 号点到 n 号点的最短距离,如果无法从 1 号点走到 n 号点,则输出 impossible。
数据保证不存在负权回路。
/*
*道阻且长,行则将至*
author:Roye_ack
*/
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
class Main
{
static PrintWriter wt=new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
static int N=100010;
static int n,m,idx;
static int[] h=new int[N],e=new int[N],ne=new int[N],w=new int[N];
static int[] dist=new int[N];
static int[] st=new int[N];
public static void add(int a,int b,int c)
{
e[idx]=b;w[idx]=c;ne[idx]=h[a];h[a]=idx++;
}
public static int spaf()
{
Queue<Integer> q=new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(1);
Arrays.fill(dist,0x3f3f3f3f);
dist[1]=0;
st[1]=1;
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
var t=q.poll();
st[t]=0;
for(int i=h[t];i!=-1;i=ne[i])
{
int j=e[i];
if(dist[j]>dist[t]+w[i])
{
dist[j]=dist[t]+w[i];
if(st[j]==0) //如果当前队列里不存在该节点 则入队并标记
{
q.offer(j);
st[j]=1;
}
}
}
}
return dist[n];
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
n=rd.nextInt();
m=rd.nextInt();
Arrays.fill(h,-1);
while(m-->0)
{
int a=rd.nextInt(),b=rd.nextInt(),c=rd.nextInt();
add(a,b,c);
}
int res=spaf();
if(res==0x3f3f3f3f) wt.print("impossible");
else wt.print(res);
wt.flush();
}
static class rd
{
static BufferedReader bf=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static StringTokenizer tk=new StringTokenizer("");
static String nextLine() throws IOException
{
return bf.readLine();
}
static String next() throws IOException
{
while(!tk.hasMoreTokens()) tk=new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
return tk.nextToken();
}
static int nextInt() throws IOException
{
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
static double nextDouble() throws IOException
{
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
static long nextLong() throws IOException
{
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
static BigInteger nextBig() throws IOException
{
BigInteger d=new BigInteger(rd.nextLine());
return d;
}
}
}
class PII
{
int x,y;
PII(int x,int y)
{
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
}852. spfa判断负环
活动 - AcWing
题目:
给定一个 n 个点 m 条边的有向图,图中可能存在重边和自环, 边权可能为负数
请你判断图中是否存在负权回路
思路:
在spfa基础上添加一个cnt数组,cnt[x]存1→x经过的边数
边数cnt的更新方式:cnt[x]=cnt[t]+1(1到t的边数+1)
判断负环原理:
- 如果cnt[x]≥n,说明1~x至少经过了n+1个点,由抽屉原理可知至少两个点的编号一样
- 由于只有当dist[x]<dist[t]+w[i]才会更新cnt边数,因此w[i]必定是负数
- 综上可判断图中存在负环
/*
*道阻且长,行则将至*
author:Roye_ack
*/
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
class Main
{
static PrintWriter wt=new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
static int N=100010;
static int n,m,idx;
static int[] h=new int[N],e=new int[N],ne=new int[N],w=new int[N];
static int[] dist=new int[N],cnt=new int[N]; //cnt用于存边数
static int[] st=new int[N];
public static void add(int a,int b,int c)
{
e[idx]=b;w[idx]=c;ne[idx]=h[a];h[a]=idx++;
}
public static boolean spaf()
{
Queue<Integer> q=new LinkedList<>();
//这里不用初始化dist数组为 正无穷/初始化的原因是:如果存在负环,那么dist不管初始化为多少,都会被更新
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) //该题是判断是否存在负环,并非判断是否存在从1开始的负环,因此需要将所有的点都加入队列中,更新周围的点
{
q.offer(i);
st[i]=1;
}
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
var t=q.poll();
st[t]=0;
for(int i=h[t];i!=-1;i=ne[i])
{
int j=e[i];
if(dist[j]>dist[t]+w[i])
{
dist[j]=dist[t]+w[i];
cnt[j]=cnt[t]+1;
if(cnt[j]>=n) return true;
if(st[j]==0)
{
q.offer(j);
st[j]=1;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
n=rd.nextInt();
m=rd.nextInt();
Arrays.fill(h,-1);
while(m-->0)
{
int a=rd.nextInt(),b=rd.nextInt(),c=rd.nextInt();
add(a,b,c);
}
if(spaf()) wt.print("Yes");
else wt.print("No");
wt.flush();
}
static class rd
{
static BufferedReader bf=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static StringTokenizer tk=new StringTokenizer("");
static String nextLine() throws IOException
{
return bf.readLine();
}
static String next() throws IOException
{
while(!tk.hasMoreTokens()) tk=new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
return tk.nextToken();
}
static int nextInt() throws IOException
{
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
static double nextDouble() throws IOException
{
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
static long nextLong() throws IOException
{
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
static BigInteger nextBig() throws IOException
{
BigInteger d=new BigInteger(rd.nextLine());
return d;
}
}
}
class PII
{
int x,y;
PII(int x,int y)
{
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
}341. 最优贸易 - spfa + 双向建图
活动 - AcWing
题目:
n个城市m条边,1代表x到y单向通道,2代表x到y的双向通道
每个城市都有一个商品的价格,一人从1号点出发,在某个城市买一个商品
在另一个城市卖出,该交易只进行一次
问最大赚取的差价为多少?
思路:
为何不能用dijkstra算法?
如果当前 dmin[i] 最小的点是 5,那么有可能存在边 5-> 6, 6-> 7, 7-> 5,假设当前 dmin[5] = 10,则有可能存在 6 的价格是11, 但 7 的价格是3,那么 dmin[5] 的值就应该被更新成3,因此当前最小值也不一定是最终最小值,所以dijkstra算法并不适用,我们只能采用 spfa 算法
dijkstra算法的特性保证后面出现的点都比前面出现的差,不能及时更新最小值
思路总体就是:1~i正向取最小 n~i反向取最大 枚举所有点作为中间点i 求出差值的最大值
- 从 1 走到 i 的过程中,买入水晶球的最低价格 dmin[i];
- 从 i 走到 n 的过程中,卖出水晶球的最高价格 dmax[i];
然后枚举每个城市作为买卖的中间城市,求出 dmax[i] - dmin[i] 的最大值
为什么不能正向求出i号点到n号点求出最大价格?
因为并不是所有点到终点都是可达的,必须保证从1号点走到i号点时,i号点一定能走到n号点
/*
*道阻且长,行则将至*
author:Roye_ack
*/
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
class Main
{
static PrintWriter wt=new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
static int N=100010,M=5*N;
static int n,m,idx;
static int[] h=new int[N],rh=new int[N],e=new int[M],ne=new int[M];
static int[] w=new int[N];
static int[] st=new int[N];
static int[] dmin=new int[N],dmax=new int[N];
public static void add(int[]h,int a,int b)
{
e[idx]=b;ne[idx]=h[a];h[a]=idx++;
}
public static void spfa(int[] d,int start,int[] h,boolean flag)
{
Queue<Integer> q=new LinkedList<>();
if(flag) Arrays.fill(d,0x3f3f3f3f);
q.offer(start);
d[start]=w[start];
st[start]=1;
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
var t=q.poll();
st[t]=0;
for(int i=h[t];i!=-1;i=ne[i])
{
int j=e[i];
if(flag&&d[j]>Math.min(d[t],w[j])||!flag&&d[j]<Math.max(d[t],w[j]))
{
if(flag) d[j]=Math.min(d[t],w[j]);
else d[j]=Math.max(d[t],w[j]);
if(st[j]==0)
{
st[j]=1;
q.offer(j);
}
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
n=rd.nextInt();
m=rd.nextInt();
Arrays.fill(h,-1);
Arrays.fill(rh,-1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) w[i]=rd.nextInt();
while(m-->0)
{
int a=rd.nextInt(),b=rd.nextInt(),c=rd.nextInt();
add(h,a,b); //便于计算1~i点
add(rh,b,a); //便于计算n~i点
if(c==2)
{
add(h,b,a);
add(rh,a,b);
}
}
spfa(dmin,1,h,true);
spfa(dmax,n,rh,false);
int res=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) res=Math.max(res,dmax[i]-dmin[i]);
wt.print(res);
wt.flush();
}
static class rd
{
static BufferedReader bf=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static StringTokenizer tk=new StringTokenizer("");
static String nextLine() throws IOException
{
return bf.readLine();
}
static String next() throws IOException
{
while(!tk.hasMoreTokens()) tk=new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
return tk.nextToken();
}
static int nextInt() throws IOException
{
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
static double nextDouble() throws IOException
{
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
static long nextLong() throws IOException
{
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
static BigInteger nextBig() throws IOException
{
BigInteger d=new BigInteger(rd.nextLine());
return d;
}
}
}
class PII
{
int x,y;
PII(int x,int y)
{
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
}3305. 作物杂交 -
3305. 作物杂交 - AcWing题库
题目:
思路: