通过对webgl和three.js的不断学习与实践,在三维应用场景建设过程中,利用Three.js与webgl配合可以实现大部分三维场景的应用需求,这一篇主要讲述如何利用Three.js加载已有的模型,支持的三维模型格式有.fbx和.obj,同时.obj格式记得将对应的mtl文件放在与obj文件同目录下,名称一致即可。这样就可以加载我们已经建设好的各类三维模型,目前100M之内的模型加载都没问题。Three.js的基础代码请参考其他三篇文章,一般利用Three.js实现三维场景的代码主要内容有:
1.获取canvas元素
2.创建场景scene
3.创建相机camera
4.添加相机控件OrbitControls
5.添加灯光-环境光AmbientLight
6.创建渲染器renderer并设置像素比和场景背景色
7.添加三维物体,一般在另一个js中完成。
8.添加动画函数实现场景的动态循环渲染、添加浏览器窗口变化事件,用于设置随着浏览器窗口大小进行画布大小的调整。
开发环境:vue-2.5.2,Three.js-0.142.0,开发工具webstorm2021.2.3, 前端用chrome109.0.5414.120,其他默认。
以下是实现三维模型加载示例的功能描述和关键代码。
一、功能简述:在浏览器中实现已有三维模型文件的动态加载,不需要安装插件,支持旋转、放大缩小、移动,场景扫描和烟雾预警等。
二、实现效果:
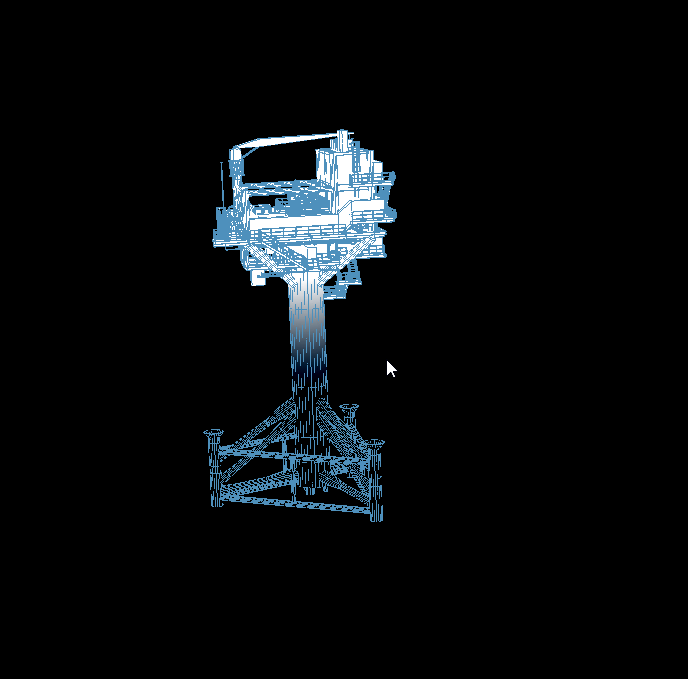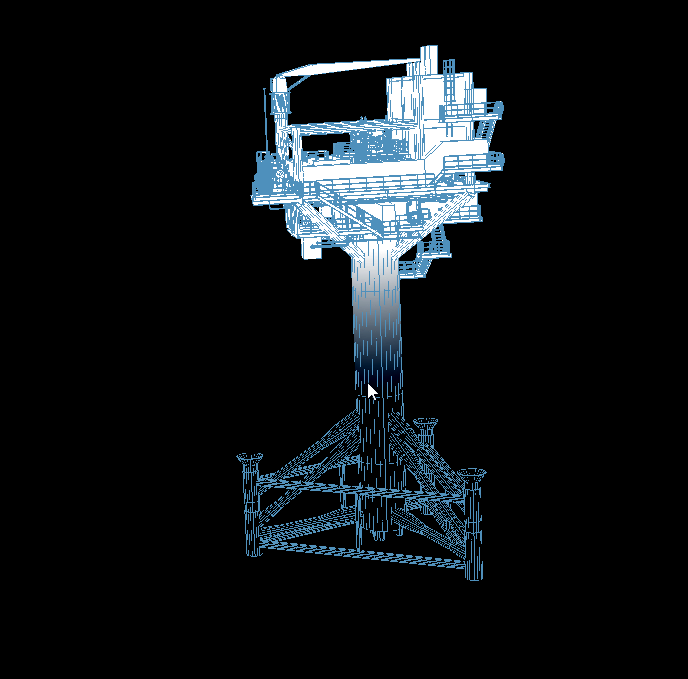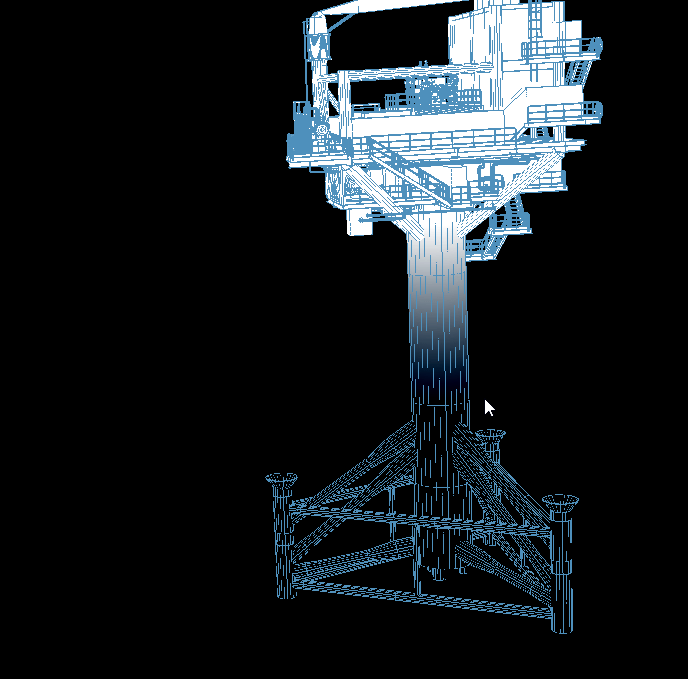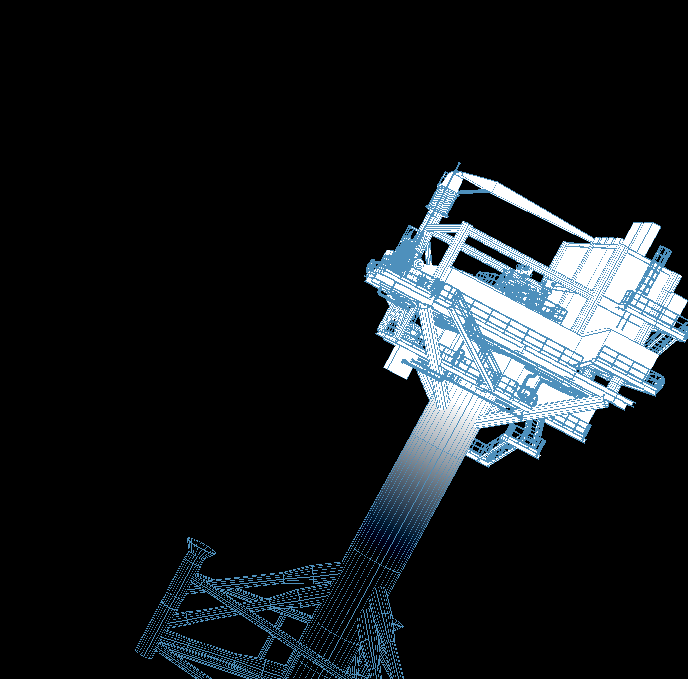

三、关键代码如下(相机platform下的src/enter目录下的index.js和addComponent.js文件):
1.index.js文件中需要引入加载各个三维组件对应的js。
import { AddComponent } from './addComponent.js'
export const initPlatform = () => {
//添加三维场景的各个组件,相当于加载各种三维模型
const plat = new AddComponent(scene, camera, controls);
const clock = new THREE.Clock();
const start = () => {
plat.start(clock.getDelta());
//记得更新相机位置
controls.update();
// 渲染场景
renderer.render(scene, camera)
requestAnimationFrame(start)
}
start();
//设置随着浏览器窗口大小进行画布大小的调整
window.addEventListener('resize', () => {
// 更新宽高比
camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight
// 更新相机的投影矩阵
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
// 设置像素比
renderer.setPixelRatio(Math.min(window.devicePixelRatio, 2))
})
}2.addComponent.js文件中引入加载模型后的处理js和加载fbx和obj文件的js,每个组件是一个类。
import { SurroundLine } from '../effect/surroundLine.js'
import { loadFBX } from '../utils'
import { loadOBJ } from '../utils'
export class AddComponent {
constructor(scene, camera, controls) {
this.scene = scene;
this.camera = camera;
this.controls = controls;
this.loadModel('fbx');
}
// 加载模型,并且渲染到画布上
loadModel(fileType) {
if(fileType=='fbx'){
loadFBX('/src/model/NB352-3D.fbx').then(object => {
object.rotation.z = Math.PI / 2;//模型旋转90度
object.traverse((child) => {
if (child.isMesh) {
new SurroundLine(this.scene, child, this.height, this.time);
}
})
this.initEffect();
})
}else if(fileType=='obj'){
loadOBJ('/src/model/factory.obj').then(object => {
object.traverse((child) => {
if (child.isMesh) {
new SurroundLine(this.scene, child, this.height, this.time);
}
})
// this.initEffect();
})
}
}
}
3.surroundLine.js完整文件如下:
import * as THREE from "three";
export class SurroundLine {
constructor(scene, child, height, time) {
this.height = height;
this.scene = scene;
this.child = child;
this.time = time;
this.createMesh();
}
computedMesh() {
this.child.geometry.computeBoundingBox();
this.child.geometry.computeBoundingSphere();
}
createMesh() {
this.computedMesh();
const { max, min } = this.child.geometry.boundingBox
// 高度差
const size = max.z - min.z
//利用webgl原始的顶点和片元着色器对模型进行设置。
const material = new THREE.ShaderMaterial({
uniforms: {
// 当前扫描的高度
u_height: this.height,
// 扫描线条的颜色是什么
u_up_color: {
value: new THREE.Color({color:'#5588AA'}),
},
u_city_color: {
// 得需要一个模型颜色 最底部显示的颜色
value: new THREE.Color(color.mesh)
},
u_head_color: {
// 要有一个头部颜色 最顶部显示的颜色
value: new THREE.Color(color.head)
},
u_size: {
value: size,
},
u_time: this.time,
},
//顶点着色器
vertexShader: `
uniform float u_time;
varying vec3 v_position;
void main() {
// 变化的时间
float uMax = 4.0;
v_position = position;
// 变化的比例
float rate = u_time / uMax * 2.0;
// 边界条件
if (rate > 1.0) {
rate = 1.0;
}
float z = position.z * rate;
gl_Position = projectionMatrix * modelViewMatrix * vec4(vec2(position), z, 1.0);
}
`,
//片元着色器
fragmentShader: `
varying vec3 v_position;
uniform vec3 u_city_color;
uniform vec3 u_head_color;
uniform float u_size;
uniform vec3 u_up_color;
uniform float u_height;
void main() {
vec3 base_color = u_city_color;
base_color = mix(base_color, u_head_color, v_position.z / u_size);
// 上升线条的高度是多少
if (u_height > v_position.z && u_height < v_position.z + 6.0) {
float f_index = (u_height - v_position.z) / 3.0;
base_color = mix(u_up_color, base_color, abs(f_index - 1.0));
}
gl_FragColor = vec4(base_color, 1.0);
}
`,
})
const mesh = new THREE.Mesh(this.child.geometry, material);
// 让mesh 继承 child 的旋转、缩放、平移
mesh.position.copy(this.child.position)
mesh.rotation.copy(this.child.rotation)
mesh.scale.copy(this.child.scale)
this.scene.add(mesh);
}
}![English Learning - L2 第1次小组纠音 [ɑː] [ɔː] [uː] 2023.2.25 周六](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2dd7bac83ebb459f908f5b06c89fe968.png)






![[深入理解SSD系列综述 1.5] SSD固态硬盘参数图文解析_选购固态硬盘就像买衣服?](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/0692bee0cbc042e8a32ce5869ca25185.png)