OAuth(二)
原文链接:OAuth 2.0 tutorial | OAuth flows
本文假设您已经看过 OAuth(一)
目录
- OAuth(二)
- OpenId Connect
- OAuth2:令牌自检(Token Introspection)
- 非结构化 Token 必须进行令牌自检
- 结构化 Token,对安全要求不高,资源服务器可以本地自检
- OAuth2:令牌撤销(RFC 7009)
- OAuth2:JWT 概述
- OAuth2:授权请求推送(RFC 9126)
- OAuth2:资源标识(RFC 8707)
- OAuth2:动态客户端注册(RFC 7591)
- OAuth2.0:TLS 与 Bearer token
- TLS
OpenId Connect
OpenlD Connect 1.0 是 OAuth 2.0 协议之上的一个简单身份层 (simple identity layer)。它使客户端能够基于授权服务器验证用户身份,并以交互式 REST-API 的方式暴露用户的基本信息
OpenlD Connect 1.0 is a simple identity layer on top of the OAuth 2.0 protocol. It enables Clients to verifythe identity of the End-User based on the authentication performed by an Authorization Server, as well asto obtain basic profile information about the End-User in an interoperable and REST-like manner.
OAuth 授权码流程可用于,验证 用户 和 客户端 之间身份信息交换
OAuth authorization code grant can be used to approve an approval flow between the resource owner and the client
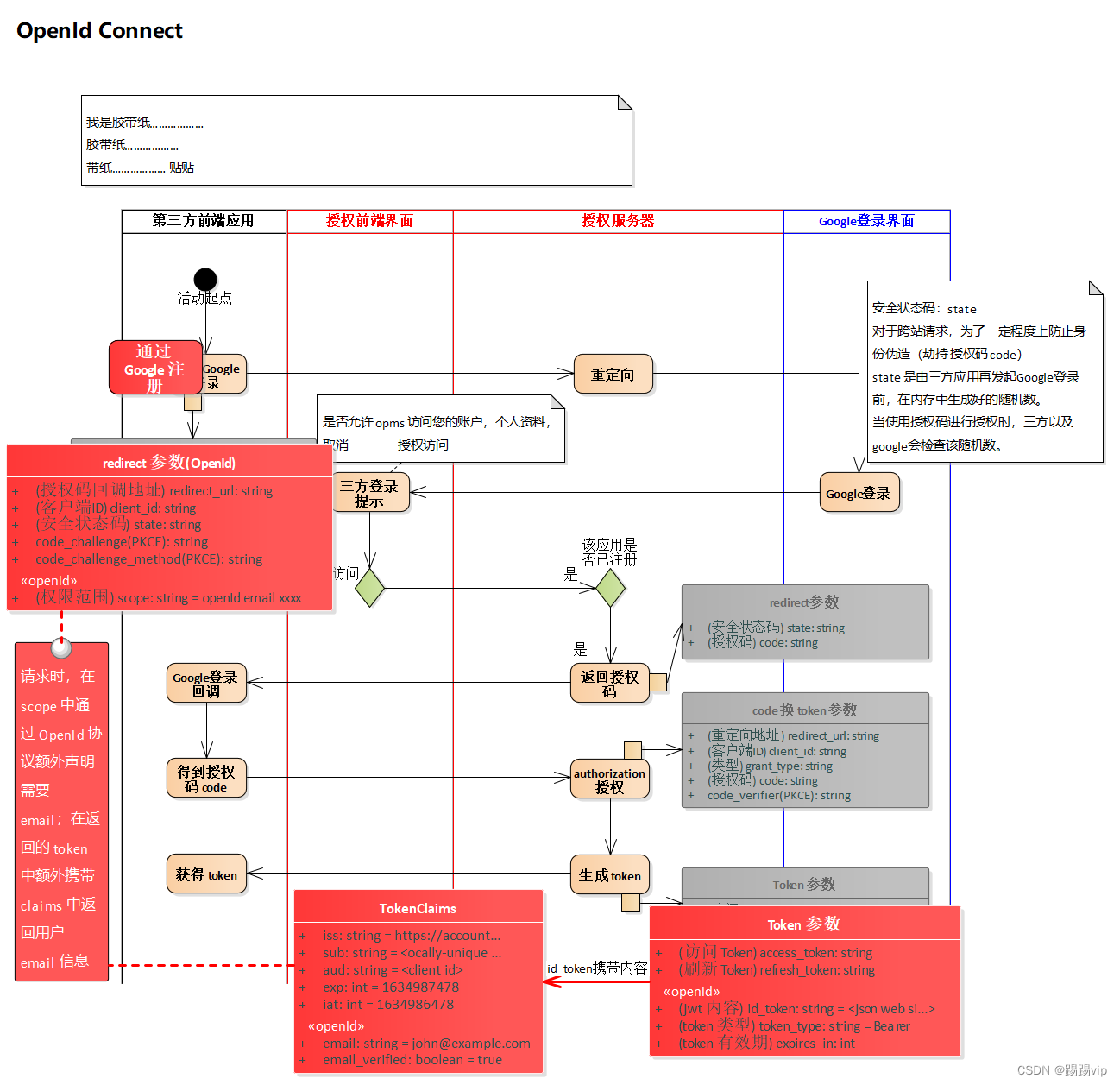
图:通过 OpenId Connect 协议额外获得用户 Email 用于注册
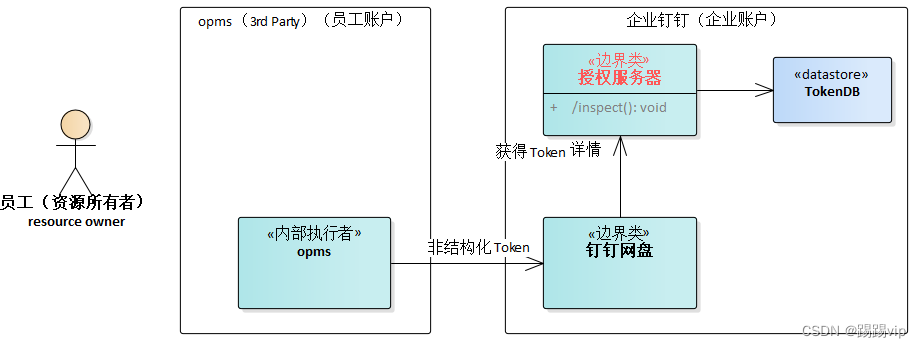
OAuth2:令牌自检(Token Introspection)
令牌自检:定义了一种协议:
授权的受保护的“资源服务器”向授权服务器发送查询请求,得到 OAuth2.0 给定令牌的状态。包括令牌当前是否处于活动状态、令牌具有哪些访问权限以及令牌的授权上下文。
[…] defines a protocol that allows authorized protected resources to query the authorization server to determinethe set of metadata for a given token that was presented to them byan OAuth2.0 client.
This metadata includes whether or not the tokenis currently active […],what rights of access the token carries […]and the authorization context in which the tokenwas granted […]
令牌可以是一些随机的字符串,也可以是结构化的 JWT 令牌。如果令牌只是一个随机字符串,则需要做令牌自检。
假设我们不使用 JWT Token,当用户使用 opaque Token (非结构化 Token) 向资源服务器发送请求时,资源服务器需要向 认证服务器 发起解析 Token 请求。获得 token 的具体信息。
非结构化 Token 必须进行令牌自检
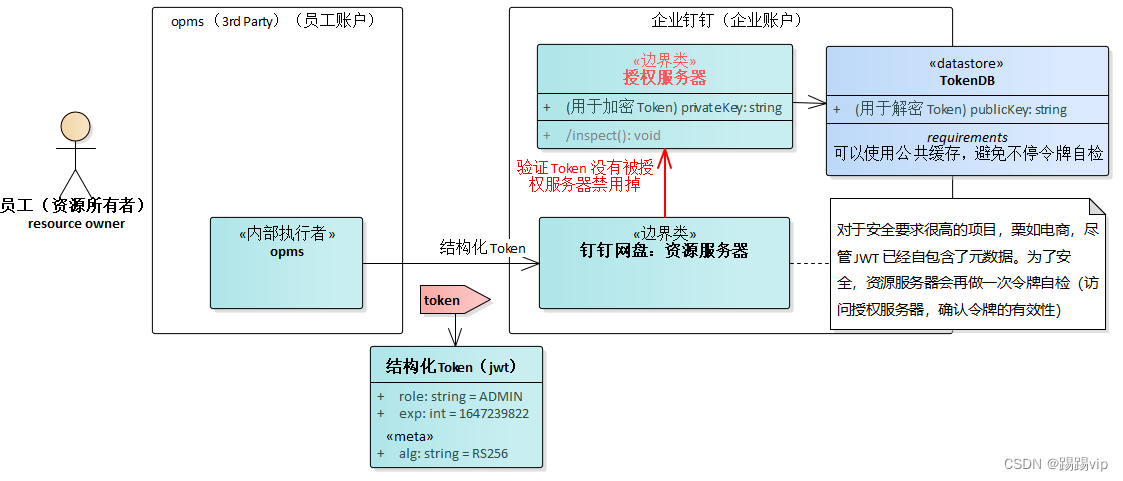
结构化 Token,对安全要求不高,资源服务器可以本地自检
OAuth2:令牌撤销(RFC 7009)
令牌撤销为OAuth授权服务器提出了一个额外的端点,它允许客户端(通过一种安全的方式)通知授权服务器不再需要以前获得的刷新或访问令牌。
proposes an additional endpoint for OAuth authorizationservers,which allows clients to notify the authorization server that a previously obtained refresh or access token is no longer needed.
如果你向 授权服务器 发送请求 撤销 刷新令牌,那么和这个刷新令牌绑定的 访问令牌很可能也会跟着失效。视具体的授权服务器和其配置决定。
OAuth2:JWT 概述
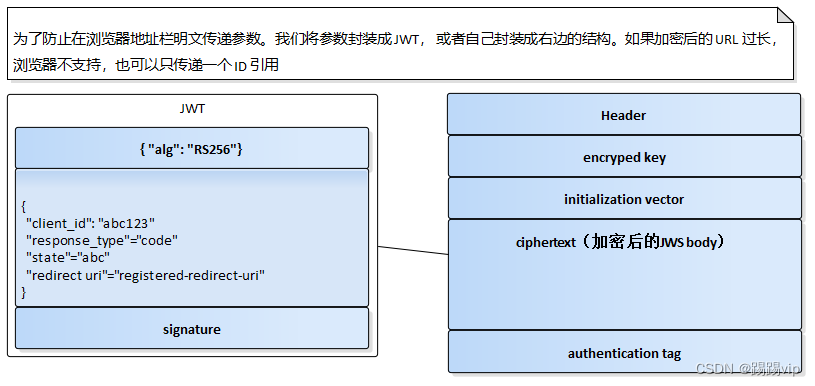
JWT:为了提升授权的安全性。
Redirect 参数加密
GET /authorize?client_id=abc123&response_type=code&state=abc&redirect_url=<registered-redirect-url>&...
通过 JWT 加密成为
GET /authorize?client_id=abc123&request=jwt
OAuth2:授权请求推送(RFC 9126)
将参数提前发送给授权服务器,叫做授权请求推送。
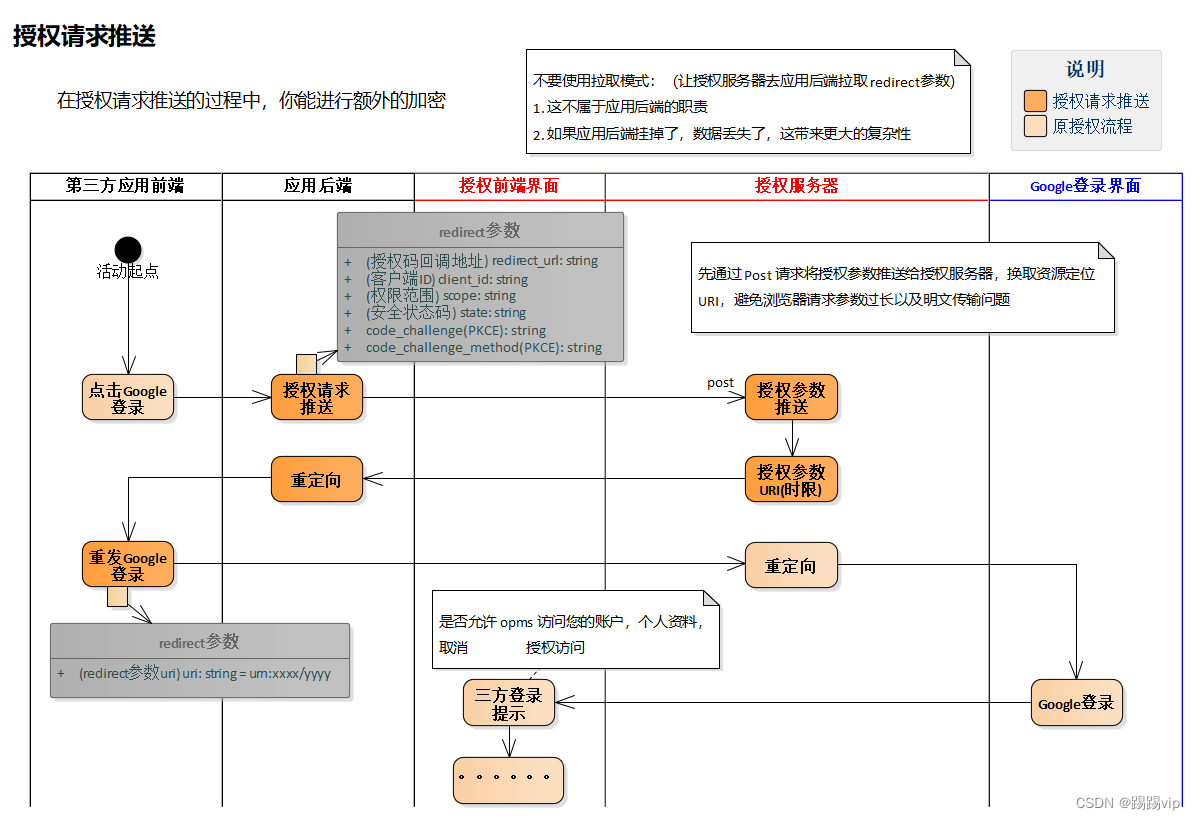
图:授权请求推送流程
OAuth2:资源标识(RFC 8707)
为了防止 两个完全不相干的系统之间 资源标识 相同,造成权限污染,我们在通过授权码换取 token 时额外引入了 resource uri 的概念
PS 博主个人理解: 通过 resource
栗如限定,该 Token 只对 项目1 生效
栗如限定,该 Token 只对 租户1 生效
{
grant_type: 'authorization_code&code=abc',
client_id: 'xxx',
resource=https://rs1.example.com
}
// jwt 中的 aud 代表了 resource 生效范围
{
{
"alg": "ES256"
},
{
// iss = 一般标识客户端ID
"iss": "https://authorization-server.com",
// aud = token 的预期接收者
"aud": "https://rs1.example.com"
},
{signature}
}
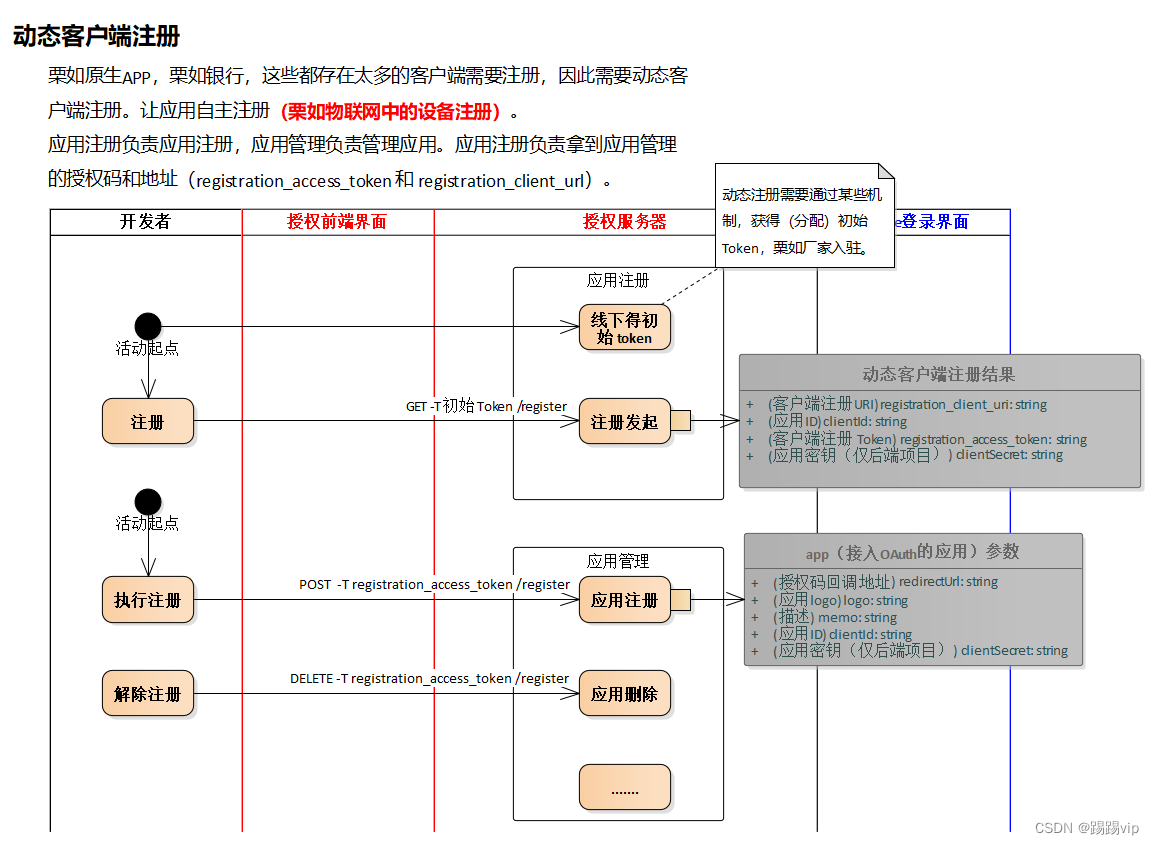
OAuth2:动态客户端注册(RFC 7591)
OAuth2.0:TLS 与 Bearer token
httpHead 中的 Authorization: Bearer 是什么意思:
token 就像是 钱,谁捡到了,都能去商店里头买东西。Bearer token 就是使用 一个使用了 私钥+公钥,只有你能解密出的 token。
以此来证明这是你的钱(路上大风刮来的)。而不是路上捡的。
TLS
客户端 双向-tls 认证和令牌绑定证书(RFC8705)
Oauth 2.0 Mutual-tls Client Authentication and Certificate-boundAccess Tokens ( RFC8705)
看不懂,用于高度安全领域,反正就是两边都有自己的公钥私钥,相互验证
博主个人猜测,应该是在应用注册的是,颁发一些公钥、私钥对之类的,然后对 token 进行 hash,和 token 一起传递,接收方验证 hash 结果一致时,才接收这个 token 之类的(┭┮﹏┭┮ 此处 Harker 的眼泪)
{
"alg": "RS256"
},
{
"iss": "xxx",
"cnf": {
// 可能就是这玩意儿,用 hash 加解密,进行一次公钥 握手呗
"x5t#S256": "<base64url-encoded SHA256 hash of DER encoded X509 certificate>"
}
}