| C++中的双冒号::名解析(Scope Resolution Operator)! |
文章目录
- 1. 访问命名空间中的成员
- 2. 访问类中的静态成员
- 3. 嵌套类访问
- 4. 在类之外定义函数
- 5. 当存在具有相同名称的局部变量时,要访问全局变量
- 6. C++模板参数的自动推导
- 参考文献
- C++中的双冒号名解析(Scope Resolution Operator),也称作作用域运算符,用于指明一个标识符的作用域。双冒号一般用于以下几种情况:
1. 访问命名空间中的成员
- 在C++中,命名空间是将全局作用域分隔为更小的区域,以避免命名冲突的一种机制。可以使用双冒号来访问命名空间中的成员,例如:
namespace ns {
int a;
void foo() {}
}
int main() {
ns::a = 1; // 使用双冒号访问命名空间中的 a
ns::foo(); // 使用双冒号访问命名空间中的 foo 函数
}
2. 访问类中的静态成员
- 在 C++ 中,可以使用类名和双冒号来访问类中的静态成员,例如:
// C++ program to show that :: can be used to access static
// members when there is a local variable with same name
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
static int x;
public:
static int y;
// Local parameter 'a' hides class member
// 'a', but we can access it using ::
void func(int x)
{
// We can access class's static variable
// even if there is a local variable
cout << "Value of static x is " << Test::x;
cout << "\nValue of local x is " << x;
}
};
// In C++, static members must be explicitly defined
// like this
int Test::x = 1;
int Test::y = 2;
int main()
{
Test obj;
int x = 3 ;
obj.func(x);
cout << "\nTest::y = " << Test::y;
return 0;
}
3. 嵌套类访问
- 如果另一个类中存在一个类,我们可以使用嵌套类使用作用域运算符来引用嵌套的类,例如:
// Use of scope resolution class inside another class.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class outside {
public:
int x;
class inside {
public:
int x;
static int y;
int foo();
};
};
int outside::inside::y = 5;
int main() {
outside A;
outside::inside B;
}
- 下面这种情况和下面
std::vector<int>::iterator的情况一样。
// Use of scope resolution class inside another class.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
A() { cout << "constructor" << endl; }
};
class B {
public:
typedef A B_A;
};
int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) {
B::B_A a;
return 0;
}
// constructor
- c++中的标准库vector中,
std::vector<int>::iterator it;给出解释:在这个例子中,std是标准命名空间,vector是std中的一个类,int是vector类的模板参数之一,iterator是vector类中的一个类型定义(type definition)。因此,std::vector::iterator表示vector类的迭代器类型,它的别名为iterator。- 也就是说:当一个类内部定义了一个嵌套类型(nested type),比如 std::vector 内部定义了 iterator 类型,我们可以使用 :: 来访问这个类型。
- 源码中iterator是这样定义的,
typedef __gnu_cxx::__normal_iterator<pointer, vector> iterator;这里的 __gnu_cxx::__normal_iterator 实际上是一个迭代器类,用于在容器中遍历元素。pointer 表示指向元素的指针类型,而 vector 则表示容器类型。- typedef 是 C++ 中的一个关键字,用于给一个已有的数据类型起一个新的名称。它的作用是让程序员可以用一个简短、易懂的名字来代替一个复杂、冗长的数据类型名称,从而提高程序的可读性和可维护性。
# typedef <原类型> <新类型名>;
typedef int myInt;
myInt a = 5;
- 在 C++11 标准中,也可以使用 using 来定义类型别名,如下,这样定义的效果与上述 typedef 的效果相同。
using myInt = int;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int main() {
std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
std::vector<int>::iterator it = vec.begin(); // 使用 :: 访问嵌套类型 iterator
std::cout << *it << std::endl; // 输出 1
return 0;
}
4. 在类之外定义函数
// C++ program to show that scope resolution operator :: is used
// to define a function outside a class
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
// Only declaration
void fun();
};
// Definition outside class using ::
void A::fun()
{
cout << "fun() called";
}
int main()
{
A a;
a.fun();
return 0;
}
5. 当存在具有相同名称的局部变量时,要访问全局变量
// C++ program to show that we can access a global variable
// using scope resolution operator :: when there is a local
// variable with same name
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int x; // Global x
int main()
{
int x = 10; // Local x
cout << "Value of global x is " << ::x;
cout << "\nValue of local x is " << x;
return 0;
}
6. C++模板参数的自动推导
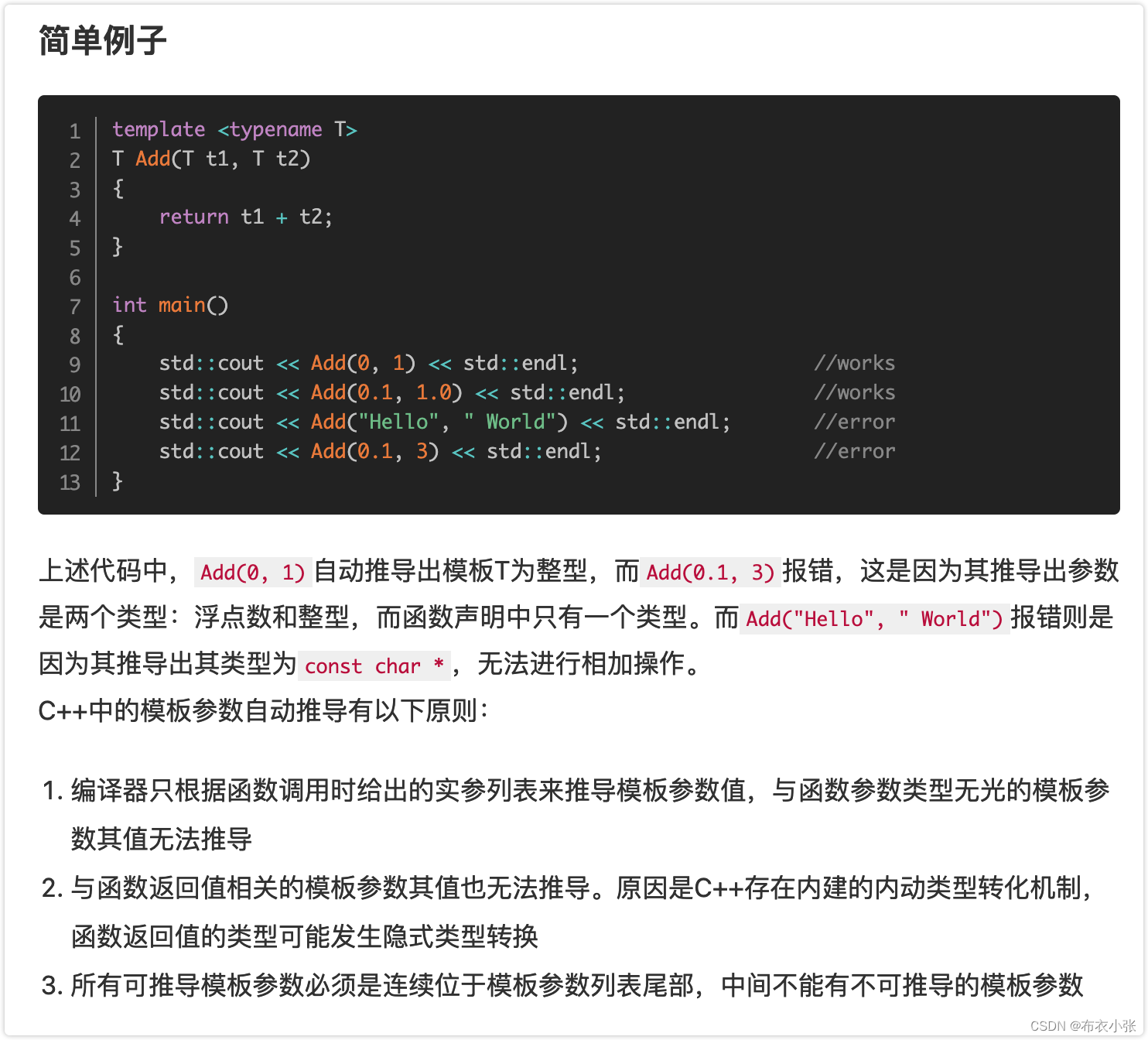

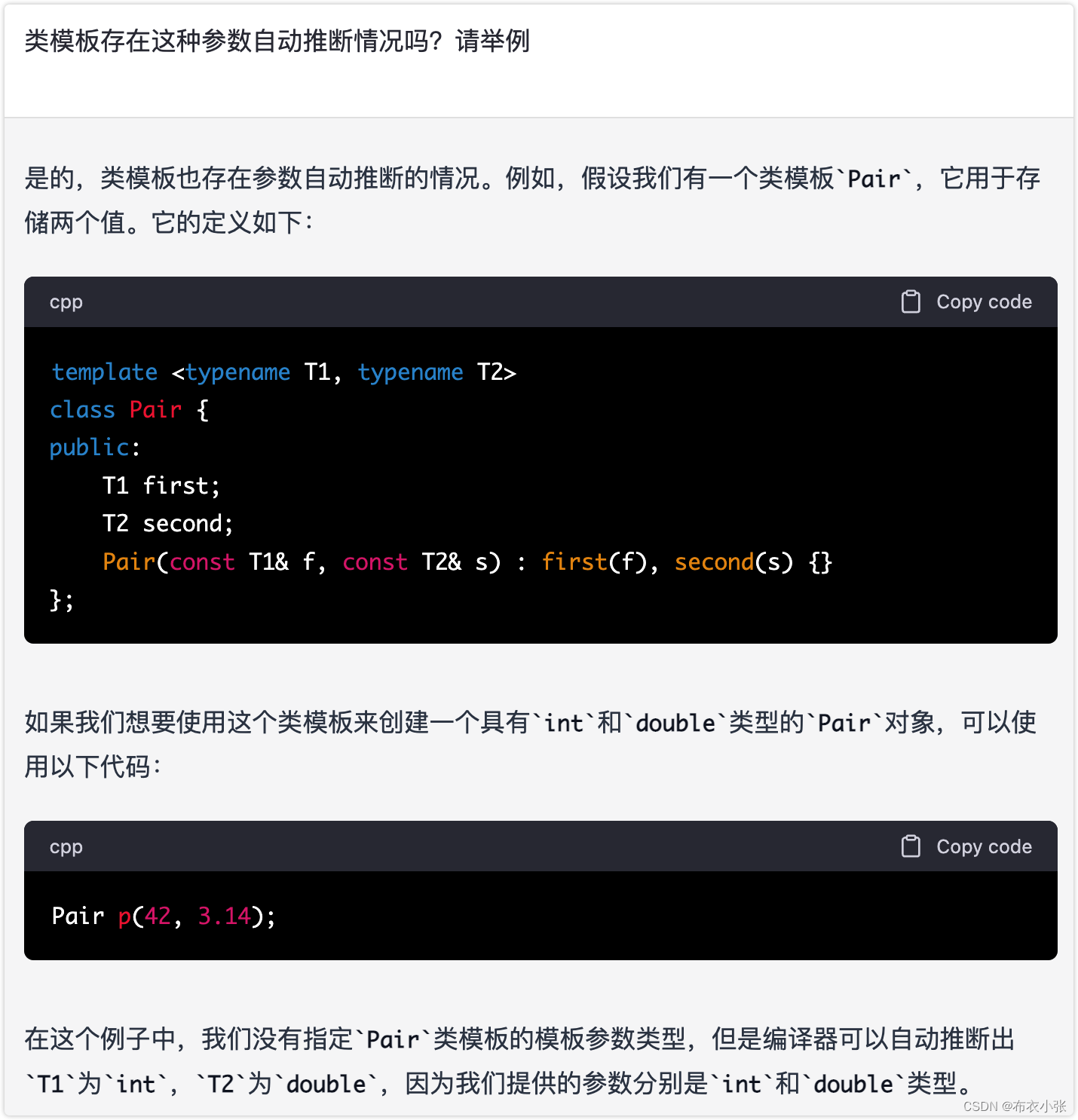
参考文献
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/137383328
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/75968bf24fe7