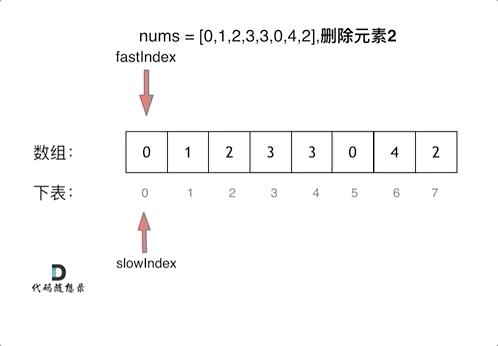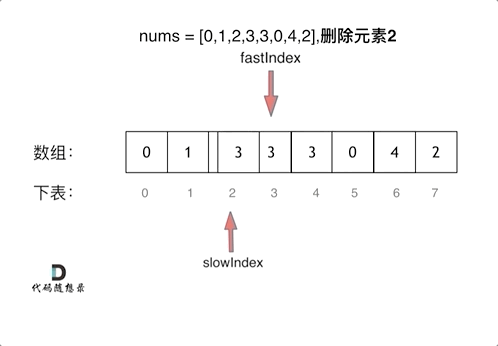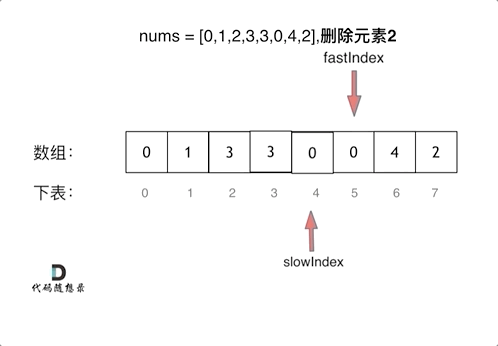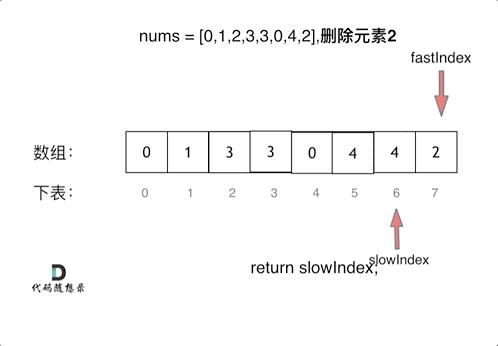
上一章,我们讲到了Vue初始化做的一些操作,那么我们这一章来讲一个Vue核心概念响应式系统。
我们先来看一下官方对深入响应式系统的解释:
当你把一个普通的 JavaScript 对象传给 Vue 实例的 data 选项,Vue 将遍历此对象所有的属性。
并使用 Object.defineProperty 把这些属性全部转为 getter/setter。
Object.defineProperty 是 ES5 中一个无法 shim 的特性。
这也就是为什么 Vue 不支持 IE8 以及更低版本浏览器的原因。

上图是Vue官方放出的一张图,而且提到核心概念Object.defineProperty,那么我们直接看源码,我们看到的Object.defineProperty在defineReactive函数的内部,而defineReactive函数在walk函数内部,依次找到源头是Observer类
./core/observer/index
export class Observer {
value: any;
dep: Dep;
vmCount: number; // number of vms that has this object as root $data
/** * 生成的Observer实例上挂载三个属性 * 1. value, 即观测数据对象本身 * 2. dep, 用于依赖收集的容器 * 3. vmCount, 直接写死为0 */
constructor (value: any) {
this.value = value
this.dep = new Dep()
this.vmCount = 0
// 在观测数据对象上添加__ob__属性, 是Observer实例的引用
// def相当于Object.defineProperty, 区别是dep里会把__ob__属性设置为不可枚举
// 需要注意的是, value.__ob__.value 显然就是 value 本身, 这里有一个循环引用
def(value, '__ob__', this)
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
const augment = hasProto
? protoAugment
: copyAugment
augment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys)
this.observeArray(value)
} else {
this.walk(value)
}
}
// 用于处理对象类型的观测值, 循环所有的key都调用一次defineReactive
walk (obj: Object) {
const keys = Object.keys(obj)
for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
defineReactive(obj, keys[i])
}
}
// 对数组的每一项进行监听
observeArray (items: Array<any>) {
for (let i = 0, l = items.length; i < l; i++) {
observe(items[i])
}
}
}
value是需要被观察的数据对象,在构造函数中,会给value增加ob属性,作为数据已经被Observer观察的标志。如果value是数组,就使用observeArray遍历value,对value中每一个元素调用observe分别进行观察。如果value是对象,则使用walk遍历value上每个key,对每个key调用defineReactive来获得该key的set/get控制权。
那么说到假如value是数组的话,调用observeArray方法遍历数组,末尾还调用了observe函数,那到底这个函数有什么用呢?我们来一探究竟:
// 用于观测一个数据
export function observe (value: any, asRootData: ?boolean): Observer | void {
// 对于不是object或者是vnode实例的数据, 直接返回, 不会进行观测
if (!isObject(value) || value instanceof VNode) {
return
}
let ob: Observer | void
// 如果数据上已有__ob__属性, 说明该数据已经被观测, 不再重复处理
if (hasOwn(value, '__ob__') && value.__ob__ instanceof Observer) {
ob = value.__ob__
// 要观测一个数据需要满足以下条件:
// 1. shouldObserve为true, 这是一个标志位, 默认为true, 某些特殊情况下会改成false
// 2. !isServerRendering(), 不能是服务端渲染
// 3. Array.isArray(value) || isPlainObject(value), 要观测的数据必须是数组或者对象
// 4. Object.isExtensible(value). 要观测的数据必须是可扩展的
// 5. !value._isVue, 所有vue实例的_isVue属性都为true, 避免观测vue实例对象
} else if (
shouldObserve &&
!isServerRendering() &&
(Array.isArray(value) || isPlainObject(value)) &&
Object.isExtensible(value) &&
!value._isVue
) {
ob = new Observer(value)
}
if (asRootData && ob) {
ob.vmCount++
}
return ob
}
可以见得observe函数的作用是:检查对象上是否有ob属性,如果存在,则表明该对象已经处于Observer的观察中,如果不存在,则new Observer来观察对象。
回到上文,数组说完了,那么来说对象的函数walk调用,我们看到直接是调用了defineReactive函数,那我们来一探究竟:
// 定义响应式对象, 给对象动态添加get set拦截方法,
export function defineReactive (
obj: Object,
key: string,
val: any,
customSetter?: ?Function,
shallow?: boolean
) {
const dep = new Dep()
const property = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, key)
if (property && property.configurable === false) {
return
}
// cater for pre-defined getter/setters
const getter = property && property.get
if (!getter && arguments.length === 2) {
val = obj[key]
}
const setter = property && property.set
let childOb = !shallow && observe(val)
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter () {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend()
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend()
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
}
}
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
/* eslint-disable no-self-compare */
// 判断NaN的情况
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
/* eslint-enable no-self-compare */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && customSetter) {
customSetter()
}
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal)
} else {
val = newVal
}
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal)
dep.notify()
}
})
}
可以见得defineReactive函数的作用是:通过Object.defineProperty设置对象的key属性,使得能够捕获到该属性值的set/get操作,且observe函数深度遍历,所以把所有的属性都添加到了Observe上面了,也就是说,咱们对数据的读写就会触发getter/setter,再者我们可以看到get方法里面有Dep.target这个变量,dep.depend,dependArray,set方法里面有dep.notify这些方法,可想而知,我们依赖了Dep这个文件:
参考 前端进阶面试题详细解答
export default class Dep {
// target是一个全局唯一的Watcher
static target: ?Watcher;
id: number;
subs: Array<Watcher>;
// 生成每个实例唯一的uid, subs用于存储watcher
constructor () {
this.id = uid++
this.subs = []
}
// 添加一个watcher
addSub (sub: Watcher) {
this.subs.push(sub)
}
// 删除一个watcher
removeSub (sub: Watcher) {
remove(this.subs, sub)
}
// 将自身加入到全局的watcher中
depend () {
if (Dep.target) {
Dep.target.addDep(this)
}
}
// 通知所有订阅者
notify () {
// stabilize the subscriber list first
const subs = this.subs.slice()
for (let i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) {
subs[i].update()
}
}
}
观察dep文件,我们可以看到一个Dep类,其中有几个方法:
addSub:接收的参数为Watcher实例,并把Watcher实例存入记录依赖的数组中removeSub:与addSub对应,作用是将Watcher实例从记录依赖的数组中移除depend:Dep.target上存放这当前需要操作的Watcher实例,调用depend会调用该Watcher实例的addDep方法。notify:通知依赖数组中所有的watcher进行更新操作
而且创造了一个subs用来存储订阅者。
分析完了之后,我们就总结出一句话,dep是一个用来存储所有订阅者watcher的对象,他的notify方法就是去遍历通知所有的Watcher订阅者数据源发生了改变需要去更新视图了。
那么我们再来看一下Watcher的结构是咋样的:
export default class Watcher {
vm: Component;
expression: string;
cb: Function;
id: number;
deep: boolean;
user: boolean;
lazy: boolean;
sync: boolean;
dirty: boolean;
active: boolean;
deps: Array<Dep>;
newDeps: Array<Dep>;
depIds: SimpleSet;
newDepIds: SimpleSet;
getter: Function;
value: any;
constructor (
vm: Component,
expOrFn: string | Function,
cb: Function,
options?: ?Object,
isRenderWatcher?: boolean
) {
this.vm = vm
if (isRenderWatcher) {
vm._watcher = this
}
vm._watchers.push(this)
// options
if (options) {
this.deep = !!options.deep
this.user = !!options.user
this.lazy = !!options.lazy
this.sync = !!options.sync
} else {
this.deep = this.user = this.lazy = this.sync = false
}
this.cb = cb
this.id = ++uid // uid for batching
this.active = true
this.dirty = this.lazy // for lazy watchers
this.deps = []
this.newDeps = []
this.depIds = new Set()
this.newDepIds = new Set()
this.expression = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'
? expOrFn.toString()
: ''
// parse expression for getter
if (typeof expOrFn === 'function') {
this.getter = expOrFn
} else {
this.getter = parsePath(expOrFn)
if (!this.getter) {
this.getter = function () {}
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
`Failed watching path: "${expOrFn}" ` +
'Watcher only accepts simple dot-delimited paths. ' +
'For full control, use a function instead.',
vm
)
}
}
this.value = this.lazy
? undefined
: this.get()
}
/** * Evaluate the getter, and re-collect dependencies. */
get () {
pushTarget(this)
let value
const vm = this.vm
try {
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)
} catch (e) {
if (this.user) {
handleError(e, vm, `getter for watcher "${this.expression}"`)
} else {
throw e
}
} finally {
// "touch" every property so they are all tracked as
// dependencies for deep watching
if (this.deep) {
traverse(value)
}
popTarget()
this.cleanupDeps()
}
return value
}
/** * 接收参数`dep(Dep实例)`,让当前`watcher`订阅`dep` */
addDep (dep: Dep) {
const id = dep.id
if (!this.newDepIds.has(id)) {
this.newDepIds.add(id)
this.newDeps.push(dep)
if (!this.depIds.has(id)) {
dep.addSub(this)
}
}
}
/** * 清除`newDepIds和newDep`上记录的对dep的订阅信息 */
cleanupDeps () {
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
const dep = this.deps[i]
if (!this.newDepIds.has(dep.id)) {
dep.removeSub(this)
}
}
let tmp = this.depIds
this.depIds = this.newDepIds
this.newDepIds = tmp
this.newDepIds.clear()
tmp = this.deps
this.deps = this.newDeps
this.newDeps = tmp
this.newDeps.length = 0
}
/** * 立刻运行`watcher`或者将`watcher`加入队列中等待统一`flush` */
update () {
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (this.lazy) {
this.dirty = true
} else if (this.sync) {
this.run()
} else {
queueWatcher(this)
}
}
/** * 运行`watcher`,调用`this.get()`求值,然后触发回调 */
run () {
if (this.active) {
const value = this.get()
if (
value !== this.value ||
// Deep watchers and watchers on Object/Arrays should fire even
// when the value is the same, because the value may
// have mutated.
isObject(value) ||
this.deep
) {
// set new value
const oldValue = this.value
this.value = value
if (this.user) {
try {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, this.vm, `callback for watcher "${this.expression}"`)
}
} else {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue)
}
}
}
}
/** *调用`this.get()`求值 */
evaluate () {
this.value = this.get()
this.dirty = false
}
/** * 遍历`this.deps`,让当前`watcher`实例订阅所有`dep` */
depend () {
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
this.deps[i].depend()
}
}
/** *去除当前`watcher`实例所有的订阅 */
teardown () {
if (this.active) {
// remove self from vm's watcher list
// this is a somewhat expensive operation so we skip it
// if the vm is being destroyed.
if (!this.vm._isBeingDestroyed) {
remove(this.vm._watchers, this)
}
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
this.deps[i].removeSub(this)
}
this.active = false
}
}
}
我们看到了一个Watcher类,并且有一些方法:
get:将Dep.target设置为当前watcher实例,在内部调用this.getter,如果此时某个被Observer观察的数据对象被取值了,那么当前watcher实例将会自动订阅数据对象的Dep实例addDep:接收参数dep(Dep实例),让当前watcher订阅depcleanupDeps:清除newDepIds和newDep上记录的对dep的订阅信息update:立刻运行watcher或者将watcher加入队列中等待统一freshrun:运行watcher,调用this.get()求值,然后触发回调evaluate:调用this.get()求值depend:遍历this.deps,让当前watcher实例订阅所有depteardown:去除当前watcher实例所有的订阅
那么我们知道这么多方法,来梳理一下流程
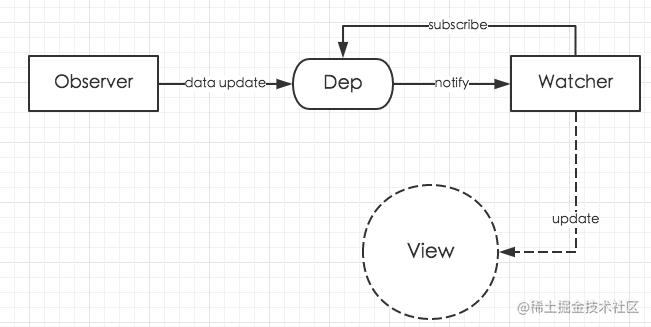
我们的数据发生变化,我们data里面所有的属性都可以看做一个dep,而dep里面的subs就是存放当前属性的地方,当我们数据发生变化的时候就不会被监听到,我们就要通过dep去调用notify方法通知所有的Watcher进行更新视图。
那么问题又来了,这个this.subs是如何添加订阅者的?
get () {
pushTarget(this)
let value
const vm = this.vm
try {
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)
} catch (e) {
if (this.user) {
handleError(e, vm, `getter for watcher "${this.expression}"`)
} else {
throw e
}
} finally {
// "touch" every property so they are all tracked as
// dependencies for deep watching
if (this.deep) {
traverse(value)
}
popTarget()
this.cleanupDeps()
}
return value
}
/** * Add a dependency to this directive. */
addDep (dep: Dep) {
const id = dep.id
if (!this.newDepIds.has(id)) {
this.newDepIds.add(id)
this.newDeps.push(dep)
if (!this.depIds.has(id)) {
dep.addSub(this)
}
}
}
我们在Dep中可以看到Dep在一开始定义了一个全局属性Dep.target,在新建watcher是,这个属性为null,而在watcher的构造函数中最后会执行自己的get()方法,进而执行pushTarget(this)方法:
// 将watcher实例赋值给Dep.target,用于依赖收集。同时将该实例存入target栈中
export function pushTarget (_target: ?Watcher) {
if (Dep.target) targetStack.push(Dep.target)
Dep.target = _target
}
可以看到get()方法,value = this.getter.call(vm, vm),然后popTarget()方法:
// 从target栈取出一个watcher实例
export function popTarget () {
Dep.target = targetStack.pop()
}
Dep.target只是一个标记,存储当前的watcher实例,触发Object.defineProperty中的get拦截,而在Oject.defineProperty中的get那里,我们可以看到dep.depend(),正是在这里将当前的订阅者watcher绑定当Dep上。
也就是说,每个watcher第一次实例化的时候,都会作为订阅者订阅其相应的Dep。
写到这里,相信各位对数据响应式已经有很深刻的理解了吧,那么我们还有一个话题,我们是如何进行初始化渲染更新和二次更新视图的?下章我们讨论一下。






![[架构之路-124]-《软考-系统架构设计师》-操作系统-3-操作系统原理 - IO设备、微内核、嵌入式系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/97265df656e52926a882fff4c1bdb22b.jpeg)