这里写自定义目录标题
- 一、File类
- 1.构造方法
- 2.普通方法
- 二、InputStream
- 1.方法
- 2.FileInputStream
- 3.Scanner类的应用
- 三、OutputStream
- 1.方法
- 2.FileOutputStream
- 3.PrintWriter类的应用
一、File类
1.构造方法
| 签名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| File(File parent, Stringchild) | 根据父目录 + 孩子文件路径,创建一个新的 File 实例 |
| File(String pathname) | 根据文件路径创建一个新的 File 实例,路径可以是绝对路径或者相对路径 |
| File(String parent, Stringchild) | 根据父目录 + 孩子文件路径,创建一个新的 File 实例,父目录用路径表示 |
2.普通方法
getAbsolutePath()和getCanonicalPath():
getAbsolutePath():返回 File 对象的绝对路径
getCanonicalPath():返回 File 对象的修饰过的绝对路径
假设我们创建一个File file = new File(文件地址),若文件地址是绝对路径,则上述两个方法输出结果相同,均为D:\hello-world.txt;若文件地址是相对路径如:File file = new File("..\\hello.txt");则输出会略有不同:
getAbsolutePath()会输出:D:\hello-world.txt;
getCanonicalPath()会输出:D:\.\hello-world.txt;
余下的比较简单,如下:
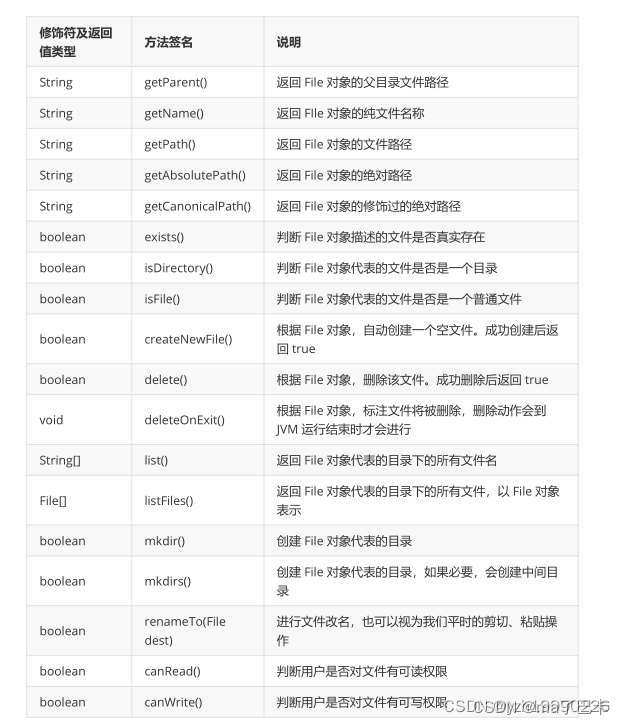
想看全部普通方法的可以自行了解api,给大家贴一个链接:File
二、InputStream
1.方法
| 签名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| read() | 读取一个字节的数据,返回 -1 代表已经完全读完了 |
| read(byte[] b) | 最多读取 b.length 字节的数据到 b 中,返回实际读到的数量;-1 代表以及读完了 |
| read(byte[] b,int off, int len) | 最多读取 len - off 字节的数据到 b 中,放在从 off 开始,返回实际读到的数量;-1 代表以及读完了 |
| close() | 关闭字节流 |
因为InputStream是抽象类,因此我们还需要了解它的具体实现类,在这里我距离文件操作的实现类 FileInputStream。
2.FileInputStream
构造方法:
| 签名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| FileInputStream(File file) | 利用 File 构造文件输入流 |
| FileInputStream(String name) | 利用文件路径构造文件输入流 |
案例:
读取ASCII码字符并显示:
// 需要先在项目目录下准备好一个 hello.txt 的文件,里面填充 "Hello" 的内容
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (InputStream is = new FileInputStream("hello.txt")) {
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while (true) {
len = is.read(buf);
if (len == -1) {
// 代表文件已经全部读完
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
System.out.printf("%c", buf[i]);
}
}
}
}
}
读取汉字并显示:为什么要有这两个案例呢?因为汉字在UTF-8 编码下占三个字符,所以我们需要修改输出,细节如下:
// 需要先在项目目录下准备好一个 hello.txt 的文件,里面填充 "你好中国" 的内容
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (InputStream is = new FileInputStream("hello.txt")) {
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while (true) {
len = is.read(buf);
if (len == -1) {
// 代表文件已经全部读完
break;
}
// 每次使用 3 字节进行 utf-8 解码,得到中文字符
// 利用 String 中的构造方法完成
// 这个方法了解下即可,不是通用的解决办法
for (int i = 0; i < len; i += 3) {
String s = new String(buf, i, 3, "UTF-8");
System.out.printf("%s", s);
}
}
}
}
}
3.Scanner类的应用
上述例子中,我们看到了对字符类型直接使用 InputStream 进行读取是非常麻烦且困难的,所以,我们使用一种我们之前比较熟悉的类来完成该工作,就是 Scanner 类,它可以通过传输一个charset类型,通过编码类型对字符进行自动的调整,是数据正常输出。
| 签名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Scanner(InputStream is, String charset) | 使用 charset 字符集进行 is 的扫描读取 |
案例修改:
// 需要先在项目目录下准备好一个 hello.txt 的文件,里面填充 "你好中国" 的内容
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (InputStream is = new FileInputStream("hello.txt")) {
try (Scanner scanner = new Scanner(is, "UTF-8")) {
while (scanner.hasNext()) {
String s = scanner.next();
System.out.print(s);
}
}
}
}
}
三、OutputStream
1.方法
| 签名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| write(int b) | 写入要给字节的数据 |
| write(byte[]b)) | 将 b 这个字符数组中的数据全部写入 os 中 |
| write(byte[]b, int off,int len) | 将 b 这个字符数组中从 off 开始的数据写入 os 中,一共写 len 个 |
| close() | 关闭字节流 |
| flush() | 我们知道 I/O 的速度是很慢的,所以,大多的 OutputStream 为了减少设备操作的次数,在写数据的时候都会将数据先暂时写入内存的一个指定区域里,直到该区域满了或者其他指定条件时才真正将数据写入设备中,这个区域一般称为缓冲区。但造成一个结果,就是我们写的数据,很可能会遗留一部分在缓冲区中。需要在最后或者合适的位置,调用 flush(刷新)操作,将数据刷到设备中。 |
因为OutputStream是抽象类,因此我们还需要了解它的具体实现类,在这里我距离文件操作的实现类 FileOutputStream。
2.FileOutputStream
构造方法:
| 签名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| FileOutputStream(File file) | 利用 File 构造文件输出流 |
| FileOutputStream(String name) | 利用文件路径构造文件输出流 |
案例:
ASCII码字符案例:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("output.txt")) {
String s = "Nothing";
byte[] b = s.getBytes();
os.write(b);
// 不要忘记 flush
os.flush();
}
}
}
汉字案例:
// 需要先在项目目录下准备好一个 hello.txt 的文件,里面填充 "你好中国" 的内容
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("output.txt")) {
String s = "你好中国";
byte[] b = s.getBytes("utf-8");
os.write(b);
// 不要忘记 flush
os.flush();
}
}
}
3.PrintWriter类的应用
上述,我们其实已经完成输出工作,但总是有所不方便,我们接来下将 OutputStream 处理下,使用PrintWriter 类来完成输出,因为PrintWriter 类中提供了print/println/printf 方法
案例修改:
// 需要先在项目目录下准备好一个 hello.txt 的文件,里面填充 "你好中国" 的内容
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("output.txt")) {
PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(os);
writer.print("你想写入的内容");
// 不要忘记 flush
writer.flush();
}
}
}