Springboot启动过程分析
SpringBoot的版本是v3.0.2,下面进行详细的分析。
一、SpringBoot启动流程的主干
示例程序入口如下所示:
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class StudySpringBootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(StudySpringBootApplication.class, args); // ref-1
}
}
ref-1处代码最终走到的核心代码如下所示:
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 记录开始时间
long startTime = System.nanoTime(); // ref-2
// 创建启动上下文
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext(); // ref-6
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
// 配置无头属性
configureHeadlessProperty(); // ref-7
// 获取监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); //ref-8
// 告知监听器:应用程序已经启动
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 准备环境变量信息
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments); // ref-9
// 打印sping的标题栏
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 创建应用上下文
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
// 准备应用上下文
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); // ref-11
refreshContext(context); // ref-11
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); // ref-15
// 计算应用启动时间
Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup);
}
// 通知监听器:应用已经启动了
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments); // ref-16
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof AbandonedRunException) {
throw ex;
}
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
if (context.isRunning()) {
Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady);
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof AbandonedRunException) {
throw ex;
}
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
接下来我们看看ref-6处的createBootstrapContext()方法,下面是该方法的内容:
// SpringApplication.java文件
private DefaultBootstrapContext createBootstrapContext() {
// 创建默认的上下文
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = new DefaultBootstrapContext();
// 使用初始化器对默认的上下文对象进行初始化
this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers.forEach((initializer) -> initializer.initialize(bootstrapContext));
return bootstrapContext;
}
DefaultBootstrapContext是一个启动上下文,我们来看看它的类层次关系:

ConfigurableBootstrapContext是一个组合性接口,BootstrapRegistry用来注册对象,BootstrapContext用来访问注册的单例对象。
接下来我们继续看ref-7处的configureHeadlessProperty(),详细代码如下:
// SpringApplication.java文件
private void configureHeadlessProperty() {
System.setProperty(SYSTEM_PROPERTY_JAVA_AWT_HEADLESS,
System.getProperty(SYSTEM_PROPERTY_JAVA_AWT_HEADLESS, Boolean.toString(this.headless)));
}
简单讲,这段代码就是在确保属性java.awt.headless的值为true。这个属性叫作无头属性,是用来告知Java图形类库是否有显示器,当它设置为true时,可以保证在命令行情况下部分Java图形控件还是可以正常使用的。
我们再来看ref-8处的代码,如下所示:
// SpringApplication.java文件
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
...... // 省略其他代码
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); // ref-8
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
...... // 省略其他代码
}
ref-8处的代码会获取监听器对象,然后会通知监听器对象应用已经启动了。
我们接着看ref-处9的prepareEnvironment(...)函数内容,代码如下所示:
// SpringApplication.java文件
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment(); // 创建一个环境信息对象
// 配置属性源,并且配置被激活的profile
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// 挂载属性源到环境信息对象
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 通知监听器:环境信息已经准备好了
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
// 将默认的属性源移动到属性源列表的末尾
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
Assert.state(!environment.containsProperty("spring.main.environment-prefix"),
"Environment prefix cannot be set via properties.");
// 绑定"spring.main"属性到环境信息对象
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
// 如果不是定制化的环境信息对象,而且环境信息对象的类型不是指定的类型,那么就要做转换
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
EnvironmentConverter environmentConverter = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader());
// 转换就是把属性源从environment拷贝到指定类型的环境变量对象中。
environment = environmentConverter.convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
// 将环境信息对象中的"configurationProperties"拿出来,然后放入到属性源列表的最后
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 将准备好的环境信息对象返回
return environment;
}
接下来我们继续看ref-10处准备应用上下文的代码:
// SpringApplication.java文件
private void prepareContext(DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
// 为应用上下文设置环境信息
context.setEnvironment(environment);
// 为应用上下文设置bean名称生成器、资源加载器、类加载器和转换服务。
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
// 添加特殊的初始化器 ApplicationContextInitializer
addAotGeneratedInitializerIfNecessary(this.initializers);
// 调用初始化器来初始化这个应用上下文
applyInitializers(context);
// 通知监听器:应用上下文已经准备好
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
// 当应用上下文已经准备好并且启动上下文已经关闭的时候,广播该事件
bootstrapContext.close(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
// 通过日志输出启动信息
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans 设置启动阶段特殊的单例对象
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
// 注册应用参数单例对象
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
// 注册springBootBanner单例对象
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory autowireCapableBeanFactory) {
// 设置是否允许循环依赖
autowireCapableBeanFactory.setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences);
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory listableBeanFactory) {
// 设置是否允许bean定义重载
listableBeanFactory.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
}
// 设置懒初始化
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
// 设置Bean工厂的后置处理器,这个应用上下文刷新的时候,这个后置处理器就会应用到内部的bean工厂,
// 然后bean对象的定义就会被执行。
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new PropertySourceOrderingBeanFactoryPostProcessor(context));
// 预编译技术(AOT)相关
if (!AotDetector.useGeneratedArtifacts()) {
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
// 加载beans到应用上下文中
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
}
// 通知监听器:应用上下文已经加载完成
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
接下来我们就分析ref-11处的应用上下文刷新refreshContext(...)的内容,函数代码如下所示:
// SpringApplication.java文件
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// 注册应用关闭时的钩子
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
shutdownHook.registerApplicationContext(context);
}
// 刷新应用上下文
refresh(context); // ref-12
}
我们继续看ref-12处的应用上下文刷新代码:
// SpringApplication.java文件
/**
* Refresh the underlying {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param applicationContext the application context to refresh
*/
protected void refresh(ConfigurableApplicationjavaContext applicationContext) {
applicationContext.refresh(); // ref-13
}
ref-13处的代码实际执行代码段如下所示:
// org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java文件
@Override
public final void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
try {
super.refresh(); // ref-14
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
if (webServer != null) {
webServer.stop();
}
throw ex;
}
}
ref-14处的代码实际执行代码段如下所示:
// org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.java文件
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
// 启动和关闭时都要加锁
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// 创建代表步骤刷新的StartupStep
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing. 准备刷新该应用上下文
prepareRefresh(); // 设置启动时间、激活标志,以及执行属性源的初始化
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 告诉子类去刷新内部的bean工厂
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 配置bean工厂需要地特征
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// bean工厂加载了所有bean的定义时,这儿方便子类对bean工厂进行后置处理
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 创建代表后置处理步骤的StartupStep
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 调用bean工厂后置处理器
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 注册拦截bean创建的bean后置处理器
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end(); // 后置处理步骤结束
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 初始化消息源,其实就是在获取注册到该应用上下文中的messageSource对象
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 初始化事件广播器,其实就是在获取注册到该应用上下文中的applicationEventMulticaster对象
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 初始化子类中的其他特殊bean
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 添加实现了ApplicationListener接口的bean成为监听器
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 完成bean工厂的初始化,初始化所有剩余的对象
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// 清除资源缓存、初始化这个应用上下文的生命周期处理器、发布应用上下文刷新的事件
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
// 应用上下文步骤结束
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}
接下来我们继续看应用刷新后的处理操作,也就是ref-15处的代码:
// org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.java文件
/**
* Called after the context has been refreshed.
* @param context the application context
* @param args the application arguments
*/
protected void afterRefresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
}
可以看到这个方法是一个空的实现,子类可以重写该方法完成刷新应用上下文之后的操作。
ref-16处的代码会调用ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner,函数细节如下所示:
// org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.java文件
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取所有的ApplicationRunner类型的实例
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
// 获取所有的CommandLineRunner类型的实例
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
// 依据注解上的优先级对runners进行排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
// 执行ApplicationRunner实现类的run(...)方法
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner applicationRunner) {
callRunner(applicationRunner, args);
}
// 执行CommandLineRunner实现类的run(...)方法
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner) {
callRunner(commandLineRunner, args);
}
}
}
到这里,基本已经分析完了SpringBoot启动流程的主干路径。
二、ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner分析
在SpringBoot启动流程的主干路径的最后调用ApplicationRunner和 CommandLineRunner两个接口的实现类。
ApplicationRunner接口定义如下:
// org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner.java文件
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
/**
* Interface used to indicate that a bean should <em>run</em> when it is contained within
* a {@link SpringApplication}. Multiple {@link ApplicationRunner} beans can be defined
* within the same application context and can be ordered using the {@link Ordered}
* interface or {@link Order @Order} annotation.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @since 1.3.0
* @see CommandLineRunner
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationRunner {
/**
* Callback used to run the bean.
* @param args incoming application arguments
* @throws Exception on error
*/
void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception;
}
可以看到就是将启动类的参数传递给run(...)方法。
CommandLineRunner接口定义如下所示:
// org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner.java文件
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
/**
* Interface used to indicate that a bean should <em>run</em> when it is contained within
* a {@link SpringApplication}. Multiple {@link CommandLineRunner} beans can be defined
* within the same application context and can be ordered using the {@link Ordered}
* interface or {@link Order @Order} annotation.
* <p>
* If you need access to {@link ApplicationArguments} instead of the raw String array
* consider using {@link ApplicationRunner}.
*
* @author Dave Syer
* @since 1.0.0
* @see ApplicationRunner
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface CommandLineRunner {
/**
* Callback used to run the bean.
* @param args incoming main method arguments
* @throws Exception on error
*/
void run(String... args) throws Exception;
}
可以看到,基本上和ApplicationRunner差不多。
三、SpringApplicationRunListeners的获取与通知
我们先回顾一下主干流程中关于SpringApplicationRunListeners的部分,代码如下所示:
// SpringApplication.java文件
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
...... // 省略其他代码
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); // ref-8
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
...... // 省略其他代码
}
ref-8代码处的函数如下所示:
// org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.java文件
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
// 创建参数解析器,这个解析器会用来解析工厂类的构造器
ArgumentResolver argumentResolver = ArgumentResolver.of(SpringApplication.class, this);
// 追加可以解析的类型
argumentResolver = argumentResolver.and(String[].class, args);
// 获取监听器
List<SpringApplicationRunListener> listeners = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, argumentResolver); // ref-17
SpringApplicationHook hook = applicationHook.get();
SpringApplicationRunListener hookListener = (hook != null) ? hook.getRunListener(this) : null;
// 将钩子监听器也添加到监听器列表中
if (hookListener != null) {
listeners = new ArrayList<>(listeners);
listeners.add(hookListener);
}
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger, listeners, this.applicationStartup);
}
我们接着看ref-17处的函数是如何获取工厂实例的:
// org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.java文件
private <T> List<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, ArgumentResolver argumentResolver) {
return SpringFactoriesLoader.forDefaultResourceLocation(getClassLoader()).load(type, argumentResolver); // ref-18
}
ref-18处代码中的load(...)方法就是具体获取工厂实例的逻辑。下面是load(...)方法的代码细节:
// org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader.java文件
/**
* Load and instantiate the factory implementations of the given type from
* {@value #FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION}, using the configured class loader
* and the given argument resolver.
* <p>The returned factories are sorted through {@link AnnotationAwareOrderComparator}.
* <p>As of Spring Framework 5.3, if duplicate implementation class names are
* discovered for a given factory type, only one instance of the duplicated
* implementation type will be instantiated.
* @param factoryType the interface or abstract class representing the factory
* @param argumentResolver strategy used to resolve constructor arguments by their type
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if any factory implementation class cannot
* be loaded or if an error occurs while instantiating any factory
* @since 6.0
*/
public <T> List<T> load(Class<T> factoryType, @Nullable ArgumentResolver argumentResolver) {
return load(factoryType, argumentResolver, null); // ref-19
}
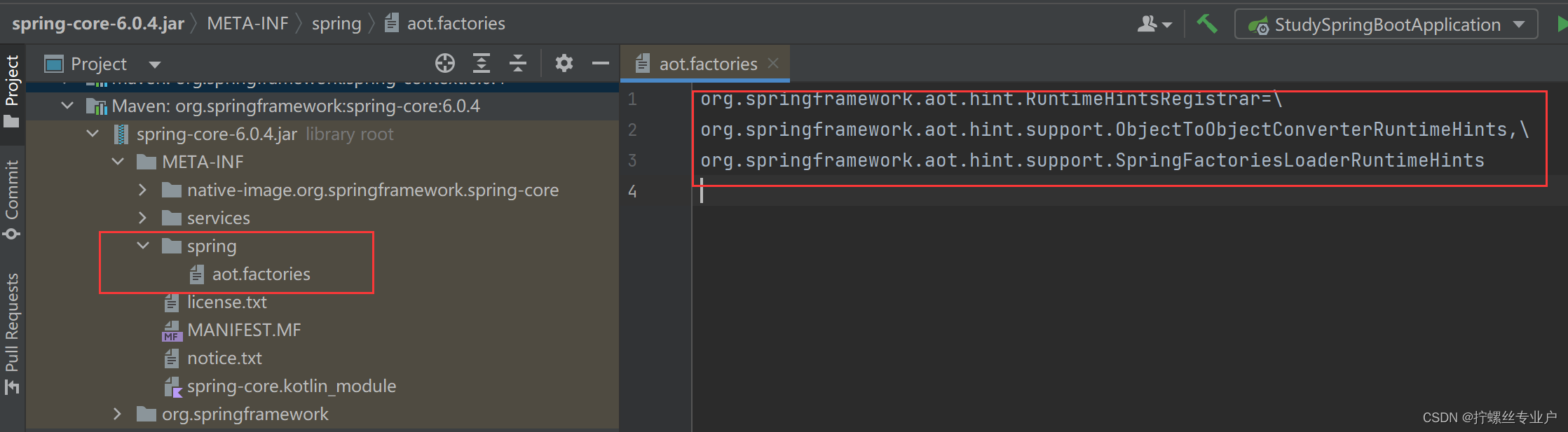
这个load(...)方法的大概意思是通过指定的工厂类型和构造器参数解析器会找到对应的工厂类实现类,具体的工厂类实现类注册在META-INF/spring.factories文件中,下面是该文件的截图:
我们接下来看看ref-19处代码里面具体是怎么加载工厂类实例的:
// org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader.java文件
/**
* Load and instantiate the factory implementations of the given type from
* {@value #FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION}, using the configured class loader,
* the given argument resolver, and custom failure handling provided by the given
* failure handler.
* <p>The returned factories are sorted through {@link AnnotationAwareOrderComparator}.
* <p>As of Spring Framework 5.3, if duplicate implementation class names are
* discovered for a given factory type, only one instance of the duplicated
* implementation type will be instantiated.
* <p>For any factory implementation class that cannot be loaded or error that
* occurs while instantiating it, the given failure handler is called.
* @param factoryType the interface or abstract class representing the factory
* @param argumentResolver strategy used to resolve constructor arguments by their type
* @param failureHandler strategy used to handle factory instantiation failures
* @since 6.0
*/
public <T> List<T> load(Class<T> factoryType, @Nullable ArgumentResolver argumentResolver,
@Nullable FailureHandler failureHandler) {
Assert.notNull(factoryType, "'factoryType' must not be null");
// 加载指定类型的工厂实例的名称
List<String> implementationNames = loadFactoryNames(factoryType);
logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Loaded [%s] names: %s", factoryType.getName(), implementationNames));
List<T> result = new ArrayList<>(implementationNames.size());
FailureHandler failureHandlerToUse = (failureHandler != null) ? failureHandler : THROWING_FAILURE_HANDLER;
for (String implementationName : implementationNames)
// 使用反射工具创建工厂类的实例
T factory = instantiateFactory(implementationName, factoryType, argumentResolver, failureHandlerToUse);
if (factory != null) {
result.add(factory);
}
}
// 对实例列表进行排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(result);
return result;
}
注释里面的大概意思是,会从META-INF/spring.factories中依据指定类型、参数解析器、失败处理器加载工厂实现类。加载完成后还会进行排序。如果有重复工厂实现类定义的话,只会加载一个。