文章目录
- 37. 解数独:
- 样例 1:
- 提示:
- 分析:
- 题解:
- rust
- go
- c++
- c
- python
- java
37. 解数独:
编写一个程序,通过填充空格来解决数独问题。
数独的解法需 遵循如下规则:
数字 1-9 在每一行只能出现一次。
数字 1-9 在每一列只能出现一次。
数字 1-9 在每一个以粗实线分隔的 3x3 宫内只能出现一次。(请参考示例图)
数独部分空格内已填入了数字,空白格用 '.' 表示。
样例 1:
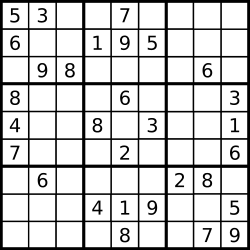
输入:
board = [["5","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."]
,["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."]
,[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."]
,["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"]
,["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"]
,["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"]
,[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."]
,[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"]
,[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]]
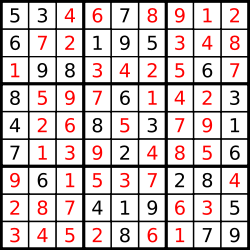
输出:
[["5","3","4","6","7","8","9","1","2"]
,["6","7","2","1","9","5","3","4","8"]
,["1","9","8","3","4","2","5","6","7"]
,["8","5","9","7","6","1","4","2","3"]
,["4","2","6","8","5","3","7","9","1"]
,["7","1","3","9","2","4","8","5","6"]
,["9","6","1","5","3","7","2","8","4"]
,["2","8","7","4","1","9","6","3","5"]
,["3","4","5","2","8","6","1","7","9"]]
解释:
输入的数独如上图所示,唯一有效的解决方案如下所示:
提示:
board.length == 9board[i].length == 9board[i][j]是一位数字或者'.'- 题目数据 保证 输入数独仅有一个解
分析:
- 面对这道算法题目,二当家的陷入了沉思。
- 主要是如何存储行,列,以及3*3宫内出现过的值。
- 方法很多,集合,整形数组,布尔数组都可以,只有1-9,一共9个数,最优化的空间方式应该是仅仅用一个整形,然后用位运算。
题解:
rust
impl Solution {
pub fn solve_sudoku(board: &mut Vec<Vec<char>>) {
let mut line = vec![vec![false; 9]; 9];
let mut column = vec![vec![false; 9]; 9];
let mut block = vec![vec![vec![false; 9]; 3]; 3];
let mut spaces = Vec::new();
(0..9).for_each(|i| {
(0..9).for_each(|j| {
if board[i][j] == '.' {
spaces.push((i, j));
} else {
let digit = board[i][j].to_digit(10).unwrap() as usize - 1;
line[i][digit] = true;
column[j][digit] = true;
block[i / 3][j / 3][digit] = true;
}
});
});
fn dfs(board: &mut Vec<Vec<char>>, spaces: &Vec<(usize, usize)>, line: &mut Vec<Vec<bool>>, column: &mut Vec<Vec<bool>>, block: &mut Vec<Vec<Vec<bool>>>, pos: usize) -> bool {
if pos == spaces.len() {
return true;
}
let (i, j) = spaces[pos];
for digit in 0..9 {
if !line[i][digit] && !column[j][digit] && !block[i / 3][j / 3][digit] {
line[i][digit] = true;
column[j][digit] = true;
block[i / 3][j / 3][digit] = true;
board[i][j] = (digit as u8 + b'1') as char;
if dfs(board, spaces, line, column, block, pos + 1) {
return true;
}
line[i][digit] = false;
column[j][digit] = false;
block[i / 3][j / 3][digit] = false;
}
}
return false;
}
dfs(board, &mut spaces, &mut line, &mut column, &mut block, 0);
}
}
go
func solveSudoku(board [][]byte) {
var line, column [9][9]bool
var block [3][3][9]bool
var spaces [][2]int
for i := 0; i < 9; i++ {
for j := 0; j < 9; j++ {
b := board[i][j]
if b == '.' {
spaces = append(spaces, [2]int{i, j})
} else {
digit := b - '1'
line[i][digit] = true
column[j][digit] = true
block[i/3][j/3][digit] = true
}
}
}
var dfs func(int) bool
dfs = func(pos int) bool {
if pos == len(spaces) {
return true
}
i, j := spaces[pos][0], spaces[pos][1]
for digit := byte(0); digit < 9; digit++ {
if !line[i][digit] && !column[j][digit] && !block[i/3][j/3][digit] {
line[i][digit] = true
column[j][digit] = true
block[i/3][j/3][digit] = true
board[i][j] = digit + '1'
if dfs(pos + 1) {
return true
}
line[i][digit] = false
column[j][digit] = false
block[i/3][j/3][digit] = false
}
}
return false
}
dfs(0)
}
c++
class Solution {
private:
bool dfs(vector<vector<char>> &board, vector<pair<int, int>> &spaces, bool line[9][9], bool column[9][9], bool block[3][3][9], int pos) {
if (pos == spaces.size()) {
return true;
}
auto [i, j] = spaces[pos];
for (int digit = 0; digit < 9; ++digit) {
if (!line[i][digit] && !column[j][digit] && !block[i / 3][j / 3][digit]) {
line[i][digit] = column[j][digit] = block[i / 3][j / 3][digit] = true;
board[i][j] = digit + '1';
if (dfs(board, spaces, line, column, block, pos + 1)) {
return true;
}
line[i][digit] = column[j][digit] = block[i / 3][j / 3][digit] = false;
}
}
return false;
}
public:
void solveSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
bool line[9][9];
bool column[9][9];
bool block[3][3][9];
vector<pair<int, int>> spaces;
memset(line, false, sizeof(line));
memset(column, false, sizeof(column));
memset(block, false, sizeof(block));
for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; ++j) {
if (board[i][j] == '.') {
spaces.emplace_back(i, j);
}
else {
int digit = board[i][j] - '1';
line[i][digit] = column[j][digit] = block[i / 3][j / 3][digit] = true;
}
}
}
dfs(board, spaces, line, column, block, 0);
}
};
c
bool dfs(char **board, int *spaces[81], int spacesSize, bool line[9][9], bool column[9][9], bool block[3][3][9], int pos) {
if (pos == spacesSize) {
return true;
}
int i = spaces[pos][0], j = spaces[pos][1];
for (int digit = 0; digit < 9; ++digit) {
if (!line[i][digit] && !column[j][digit] && !block[i / 3][j / 3][digit]) {
line[i][digit] = column[j][digit] = block[i / 3][j / 3][digit] = true;
board[i][j] = digit + '1';
if (dfs(board, spaces, spacesSize, line, column, block, pos + 1)) {
return true;
}
line[i][digit] = column[j][digit] = block[i / 3][j / 3][digit] = false;
}
}
return false;
}
void solveSudoku(char **board, int boardSize, int *boardColSize) {
bool line[9][9];
bool column[9][9];
bool block[3][3][9];
int *spaces[81];
int spacesSize = 0;
memset(line, 0, sizeof(line));
memset(column, 0, sizeof(column));
memset(block, 0, sizeof(block));
for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; ++j) {
if (board[i][j] == '.') {
spaces[spacesSize] = malloc(sizeof(int) * 2);
spaces[spacesSize][0] = i;
spaces[spacesSize++][1] = j;
} else {
int digit = board[i][j] - '1';
line[i][digit] = column[j][digit] = block[i / 3][j / 3][digit] = true;
}
}
}
dfs(board, spaces, spacesSize, line, column, block, 0);
}
python
class Solution:
def solveSudoku(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
def dfs(pos: int) -> bool:
if pos == len(spaces):
return True
i, j = spaces[pos]
for digit in range(9):
if line[i][digit] == column[j][digit] == block[i // 3][j // 3][digit] == False:
line[i][digit] = column[j][digit] = block[i // 3][j // 3][digit] = True
board[i][j] = str(digit + 1)
if dfs(pos + 1):
return True
line[i][digit] = column[j][digit] = block[i // 3][j // 3][digit] = False
return False
line = [[False] * 9 for _ in range(9)]
column = [[False] * 9 for _ in range(9)]
block = [[[False] * 9 for _a in range(3)] for _b in range(3)]
spaces = list()
for i in range(9):
for j in range(9):
if board[i][j] == ".":
spaces.append((i, j))
else:
digit = int(board[i][j]) - 1
line[i][digit] = column[j][digit] = block[i // 3][j // 3][digit] = True
dfs(0)
java
class Solution {
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
boolean[][] line = new boolean[9][9];
boolean[][] column = new boolean[9][9];
boolean[][][] block = new boolean[3][3][9];
List<int[]> spaces = new ArrayList<int[]>();
for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; ++j) {
if (board[i][j] == '.') {
spaces.add(new int[]{i, j});
} else {
int digit = board[i][j] - '1';
line[i][digit] = column[j][digit] = block[i / 3][j / 3][digit] = true;
}
}
}
dfs(board, spaces, line, column, block, 0);
}
private boolean dfs(char[][] board, List<int[]> spaces, boolean[][] line, boolean[][] column, boolean[][][] block, int pos) {
if (pos == spaces.size()) {
return true;
}
int[] space = spaces.get(pos);
int i = space[0], j = space[1];
for (int digit = 0; digit < 9; ++digit) {
if (!line[i][digit] && !column[j][digit] && !block[i / 3][j / 3][digit]) {
line[i][digit] = column[j][digit] = block[i / 3][j / 3][digit] = true;
board[i][j] = (char) (digit + '1');
if (dfs(board, spaces, line, column, block, pos + 1)) {
return true;
}
line[i][digit] = column[j][digit] = block[i / 3][j / 3][digit] = false;
}
}
return false;
}
}
非常感谢你阅读本文~
欢迎【点赞】【收藏】【评论】~
放弃不难,但坚持一定很酷~
希望我们大家都能每天进步一点点~
本文由 二当家的白帽子:https://le-yi.blog.csdn.net/ 博客原创~