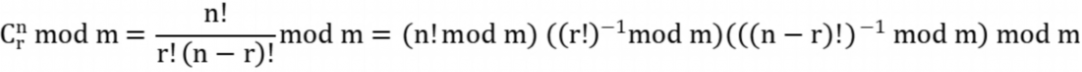解决SpringBean循环依赖为什么需要3级缓存?
回答:1级Map保存单例bean。2级Map 为了保证产生循环引用问题时,每次查询早期引用对象,都拿到同一个对象。3级Map保存ObjectFactory对象。
数据结构
1级Map singletonObjects
2级Map earlySingletonObjects
3级Map singletonFactories
boolean allowCircularReference 是否允许循环引用
源码
DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name to bean instance. */
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
/** Cache of singleton factories: bean name to ObjectFactory. */
private final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> singletonFactories = new HashMap<>(16);
/** Cache of early singleton objects: bean name to bean instance. */
private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);依赖注入理解
走InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessProperties最终还是调用DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBean获取bean实例进行依赖注入。
重点是从Map缓存读取实例逻辑
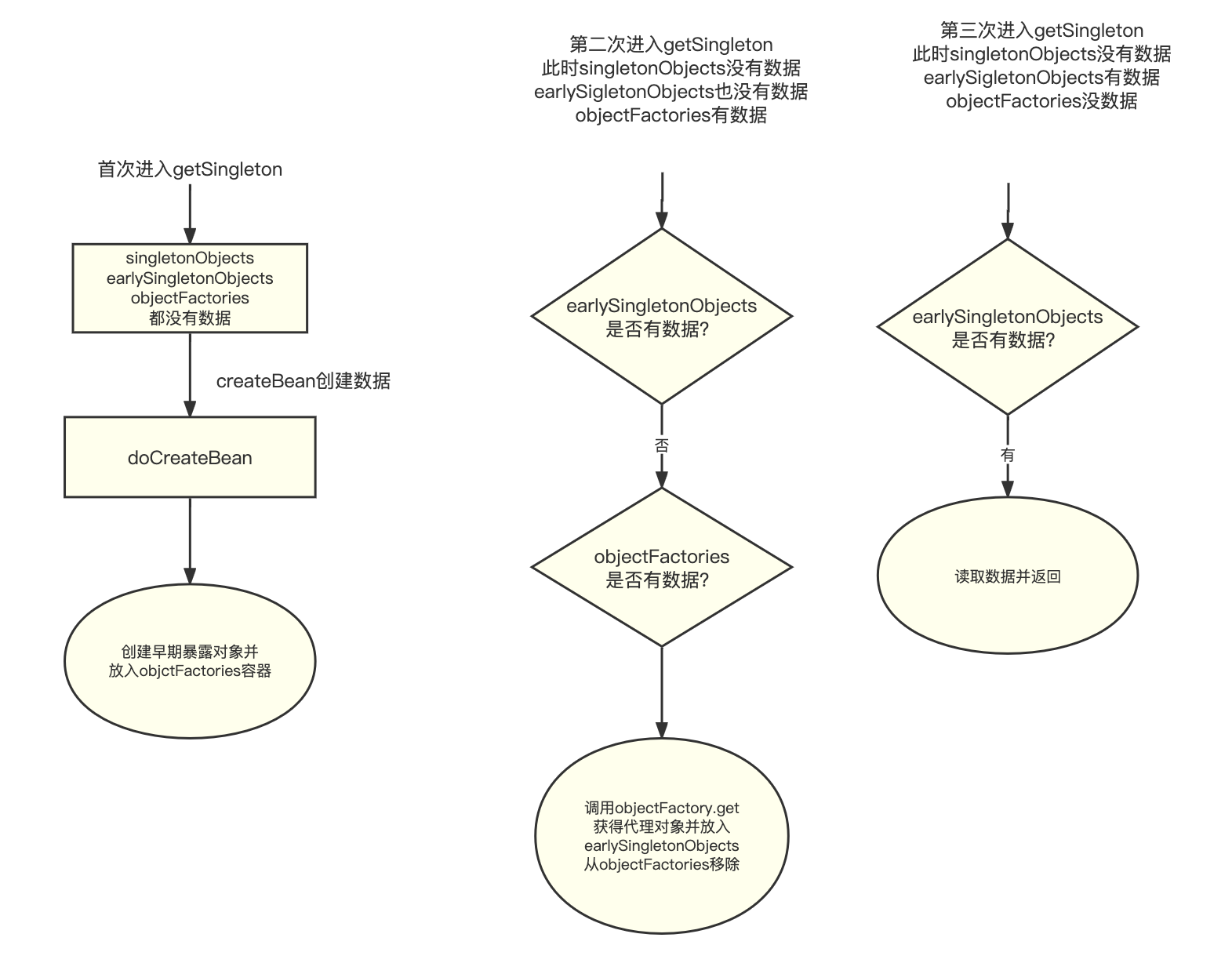
DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#getSingleton
/**
* Return the (raw) singleton object registered under the given name.
* <p>Checks already instantiated singletons and also allows for an early
* reference to a currently created singleton (resolving a circular reference).
* @param beanName the name of the bean to look for
* @param allowEarlyReference whether early references should be created or not
* @return the registered singleton object, or {@code null} if none found
*/
@Nullable
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// Quick check for existing instance without full singleton lock
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// Consistent creation of early reference within full singleton lock
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}AbstractAutowiredCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
}AbstractAutowiredCapableBeanFactory#getEarlyReference
protected Object getEarlyBeanReference(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object bean) {
Object exposedObject = bean;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().smartInstantiationAware) {
exposedObject = bp.getEarlyBeanReference(exposedObject, beanName);
}
}
return exposedObject;
}DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#addSingletonFactory
/**
* Add the given singleton factory for building the specified singleton
* if necessary.
* <p>To be called for eager registration of singletons, e.g. to be able to
* resolve circular references.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param singletonFactory the factory for the singleton object
*/
protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) {
this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
}依赖注入的入口
调用实例化扩展点处理 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessProperties
源码
AbstractAutowiredCapableBeanFactory#populateBean
-->接口 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessProperties
----> 实现类AutowireAnnotationBeanPostProcssor.postProcessProperties
-----> metadata.inject
------> 实现类AutowriedFieldElement.inject
-------> AutowriedFieldElement.resolveFiledValue
--------> beanFactory.resolveDependency
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessProperties
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
//获取bean的依赖注入的元数据
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
//依赖注入
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
return pvs;
}取依赖注入元数据调其inject注入
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}AutowiredFieldElement#inject
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
value = resolveFieldValue(field, bean, beanName);
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(bean, value);
}AutowiredFiledElement#resolveFieldValue
@Nullable
private Object resolveFieldValue(Field field, Object bean, @Nullable String beanName) {
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(1);
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
Object value;
value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
return value;
}DefaultListableBeanFactory#resolveDependency
@Override
@Nullable
public Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String requestingBeanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
descriptor.initParameterNameDiscovery(getParameterNameDiscoverer());
Object result = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary(
descriptor, requestingBeanName);
if (result == null) {
result = doResolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
return result;
}DefaultListableBeanFactory#doResolveDependency
@Nullable
public Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
InjectionPoint previousInjectionPoint = ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(descriptor);
try {
Object shortcut = descriptor.resolveShortcut(this);
if (shortcut != null) {
return shortcut;
}
Class<?> type = descriptor.getDependencyType();
Object value = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getSuggestedValue(descriptor);
if (value != null) {
if (value instanceof String) {
String strVal = resolveEmbeddedValue((String) value);
BeanDefinition bd = (beanName != null && containsBean(beanName) ?
getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName) : null);
value = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(strVal, bd);
}
TypeConverter converter = (typeConverter != null ? typeConverter : getTypeConverter());
try {
return converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getTypeDescriptor());
}
catch (UnsupportedOperationException ex) {
// A custom TypeConverter which does not support TypeDescriptor resolution...
return (descriptor.getField() != null ?
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getField()) :
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getMethodParameter()));
}
}
//处理多类型的bean 比如Steam 、 array、Collection、Map
Object multipleBeans = resolveMultipleBeans(descriptor, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
if (multipleBeans != null) {
return multipleBeans;
}
//查询依赖注入候选bean
Map<String, Object> matchingBeans = findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor);
//若匹配的bean为空则抛出不能找到匹配的bean异常
if (matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
return null;
}
String autowiredBeanName;
Object instanceCandidate;
// 若匹配多个候选bean,按规则(标记Primary的bean 、取PriorityOrder排序取、按字段名注入取),若都未取到抛出获取bean不唯一异常
if (matchingBeans.size() > 1) {
autowiredBeanName = determineAutowireCandidate(matchingBeans, descriptor);
if (autowiredBeanName == null) {
if (isRequired(descriptor) || !indicatesMultipleBeans(type)) {
return descriptor.resolveNotUnique(descriptor.getResolvableType(), matchingBeans);
}
else {
// In case of an optional Collection/Map, silently ignore a non-unique case:
// possibly it was meant to be an empty collection of multiple regular beans
// (before 4.3 in particular when we didn't even look for collection beans).
return null;
}
}
instanceCandidate = matchingBeans.get(autowiredBeanName);
}
else {
// We have exactly one match.
Map.Entry<String, Object> entry = matchingBeans.entrySet().iterator().next();
autowiredBeanName = entry.getKey();
instanceCandidate = entry.getValue();
}
if (autowiredBeanNames != null) {
autowiredBeanNames.add(autowiredBeanName);
}
if (instanceCandidate instanceof Class) {
instanceCandidate = descriptor.resolveCandidate(autowiredBeanName, type, this);
}
Object result = instanceCandidate;
if (result instanceof NullBean) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
result = null;
}
if (!ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(type, result)) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(autowiredBeanName, type, instanceCandidate.getClass());
}
return result;
}
finally {
ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(previousInjectionPoint);
}
}
DefaultListableBeanFactory#findAutowireCandidates
protected Map<String, Object> findAutowireCandidates(
@Nullable String beanName, Class<?> requiredType, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {
String[] candidateNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this, requiredType, true, descriptor.isEager());
Map<String, Object> result = CollectionUtils.newLinkedHashMap(candidateNames.length);
for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object> classObjectEntry : this.resolvableDependencies.entrySet()) {
Class<?> autowiringType = classObjectEntry.getKey();
if (autowiringType.isAssignableFrom(requiredType)) {
Object autowiringValue = classObjectEntry.getValue();
autowiringValue = AutowireUtils.resolveAutowiringValue(autowiringValue, requiredType);
if (requiredType.isInstance(autowiringValue)) {
result.put(ObjectUtils.identityToString(autowiringValue), autowiringValue);
break;
}
}
}
for (String candidate : candidateNames) {
if (!isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) && isAutowireCandidate(candidate, descriptor)) {
addCandidateEntry(result, candidate, descriptor, requiredType);
}
}
if (result.isEmpty()) {
boolean multiple = indicatesMultipleBeans(requiredType);
// Consider fallback matches if the first pass failed to find anything...
DependencyDescriptor fallbackDescriptor = descriptor.forFallbackMatch();
for (String candidate : candidateNames) {
if (!isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) && isAutowireCandidate(candidate, fallbackDescriptor) &&
(!multiple || getAutowireCandidateResolver().hasQualifier(descriptor))) {
addCandidateEntry(result, candidate, descriptor, requiredType);
}
}
if (result.isEmpty() && !multiple) {
// Consider self references as a final pass...
// but in the case of a dependency collection, not the very same bean itself.
for (String candidate : candidateNames) {
if (isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) &&
(!(descriptor instanceof MultiElementDescriptor) || !beanName.equals(candidate)) &&
isAutowireCandidate(candidate, fallbackDescriptor)) {
addCandidateEntry(result, candidate, descriptor, requiredType);
}
}
}
}
return result;
}DefaultListableBeanFactory#addCandidateEntry
/**
* Add an entry to the candidate map: a bean instance if available or just the resolved
* type, preventing early bean initialization ahead of primary candidate selection.
*/
private void addCandidateEntry(Map<String, Object> candidates, String candidateName,
DependencyDescriptor descriptor, Class<?> requiredType) {
if (descriptor instanceof MultiElementDescriptor) {
Object beanInstance = descriptor.resolveCandidate(candidateName, requiredType, this);
if (!(beanInstance instanceof NullBean)) {
candidates.put(candidateName, beanInstance);
}
}
else if (containsSingleton(candidateName) || (descriptor instanceof StreamDependencyDescriptor &&
((StreamDependencyDescriptor) descriptor).isOrdered())) {
Object beanInstance = descriptor.resolveCandidate(candidateName, requiredType, this);
candidates.put(candidateName, (beanInstance instanceof NullBean ? null : beanInstance));
}
else {
candidates.put(candidateName, getType(candidateName));
}
}DefaultListableBeanFactory#resovleCandidate
public Object resolveCandidate(String beanName, Class<?> requiredType, BeanFactory beanFactory)
throws BeansException {
return beanFactory.getBean(beanName);
}