linux线程阻塞中CPU的占用率
一、简介
总所周知Linux系统下,我们编写的程序进入阻塞后,系统把任务挂起,交给内核进行处理,此时我们的进程CPU占用率不高,可以说是占用率0.0%,让CPU资源交给其他进程处理,这样系统执行效率就很高,系统也很安全。
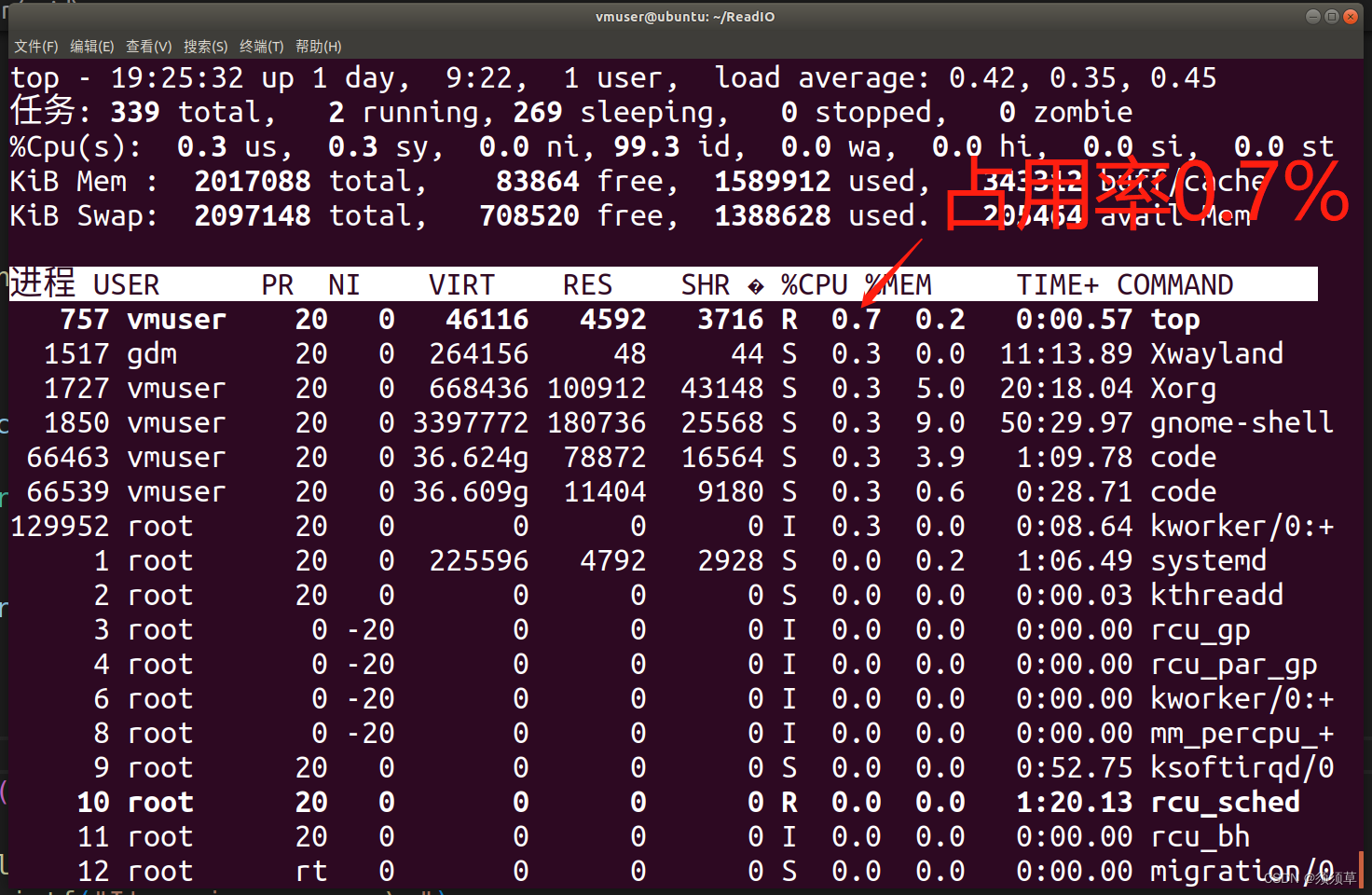
使用top命令产看到列表中,CPU占用率较高的也就是0.7%。
二、线程阻塞sleep
实现秒延时的函数
unsigned int sleep(unsigned int seconds);
现在做一个测试,在mian()加入一个延时sleep()函数,同时创建一个线程也在里面键入延时函数sleep(),测试代码如下。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
unsigned char I_ucRunning = 0;
static void *Timer_routine(void *arg){
//死循环执行
while (I_ucRunning != 0) {
printf("I'm pthread,is running\n");
sleep(1);
/* code */
}
}
int main(void)
{
int k = 0;
//设定线程执行死循环
I_ucRunning = 1;
pthread_t t;
//开启线程
int ret= pthread_create(&t, NULL, Timer_routine, NULL);
if(ret){
exit(ret);
}
//循环处理
for(k = 0;k < 10;k++)
{
sleep(1);
printf("I'm main process.\n");
}
//退出线程中的死循环
I_ucRunning = 0;
//等待退出线程
pthread_join(t, NULL);
//销毁进程
exit(0);
}
先来看看执行效果!!
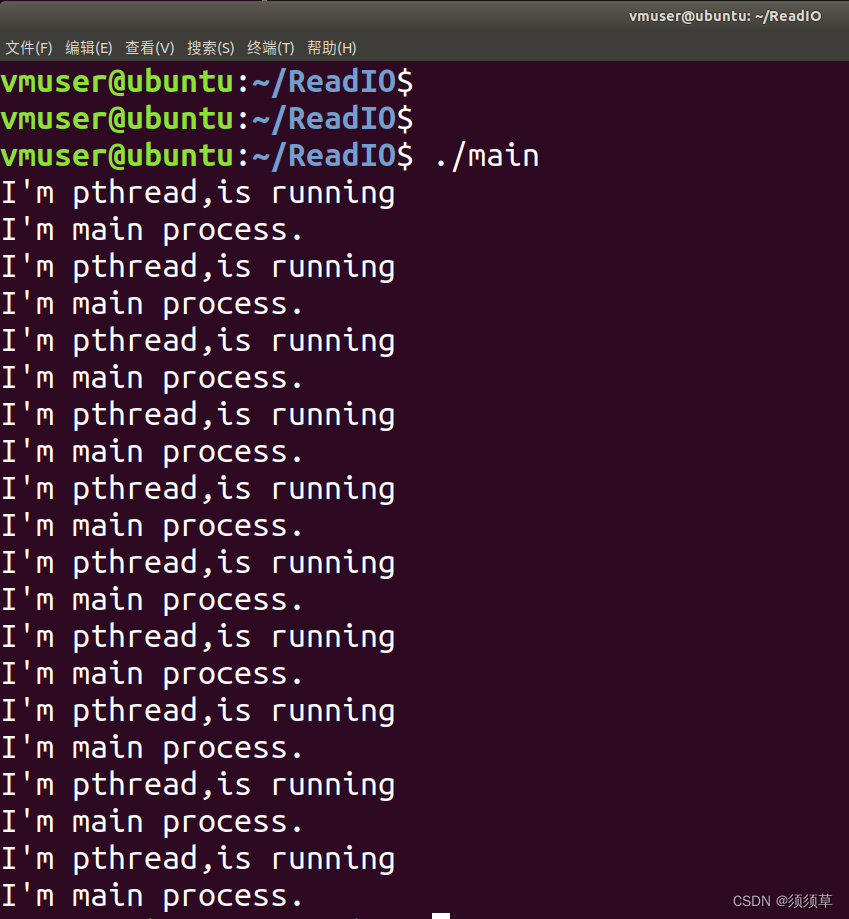
看看CPU的占用率!!
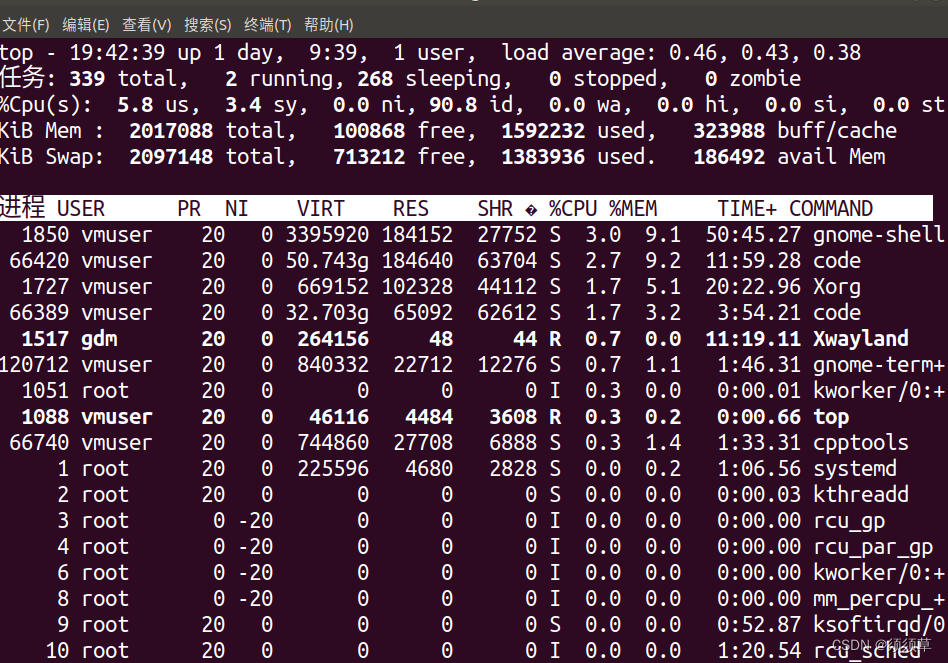
在运行同时刷新了连续几十次,找不到这个进程,原因是CPU占用率太低,都排不上这个列表…
好!非常好!CPU占用率低!
但是这个函数似乎有点延时太长了
三、加重CPU负担
于是我把线程里面的sleep()给去掉后,重新编译运行,代码如下。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <signal.h>
unsigned char I_ucRunning = 0;
static void *Timer_routine(void *arg)
{
while (I_ucRunning != 0)
{
printf("I'm pthread,is running\n");
//sleep(1);
/* code */
}
}
int main(void)
{
int k = 0;
I_ucRunning = 1;
pthread_t t;
int ret= pthread_create(&t, NULL, Timer_routine, NULL);
if(ret){
exit(ret);
}
//
for(k = 0;k < 30;k++)
{
sleep(1);
printf("I'm main process.\n");
}
//
I_ucRunning = 0;
//
pthread_join(t, NULL);
//
exit(0);
}
运行效果是CPU的占用率达到32.7%,非常不好!!
由于我使用虚拟机运行,这种程序对我的电脑是九牛一毛,如果是放到嵌入式系统中,CPU占用率可能到达99.99%,后果是系统很卡,导致其他线程无法合理运行使得。
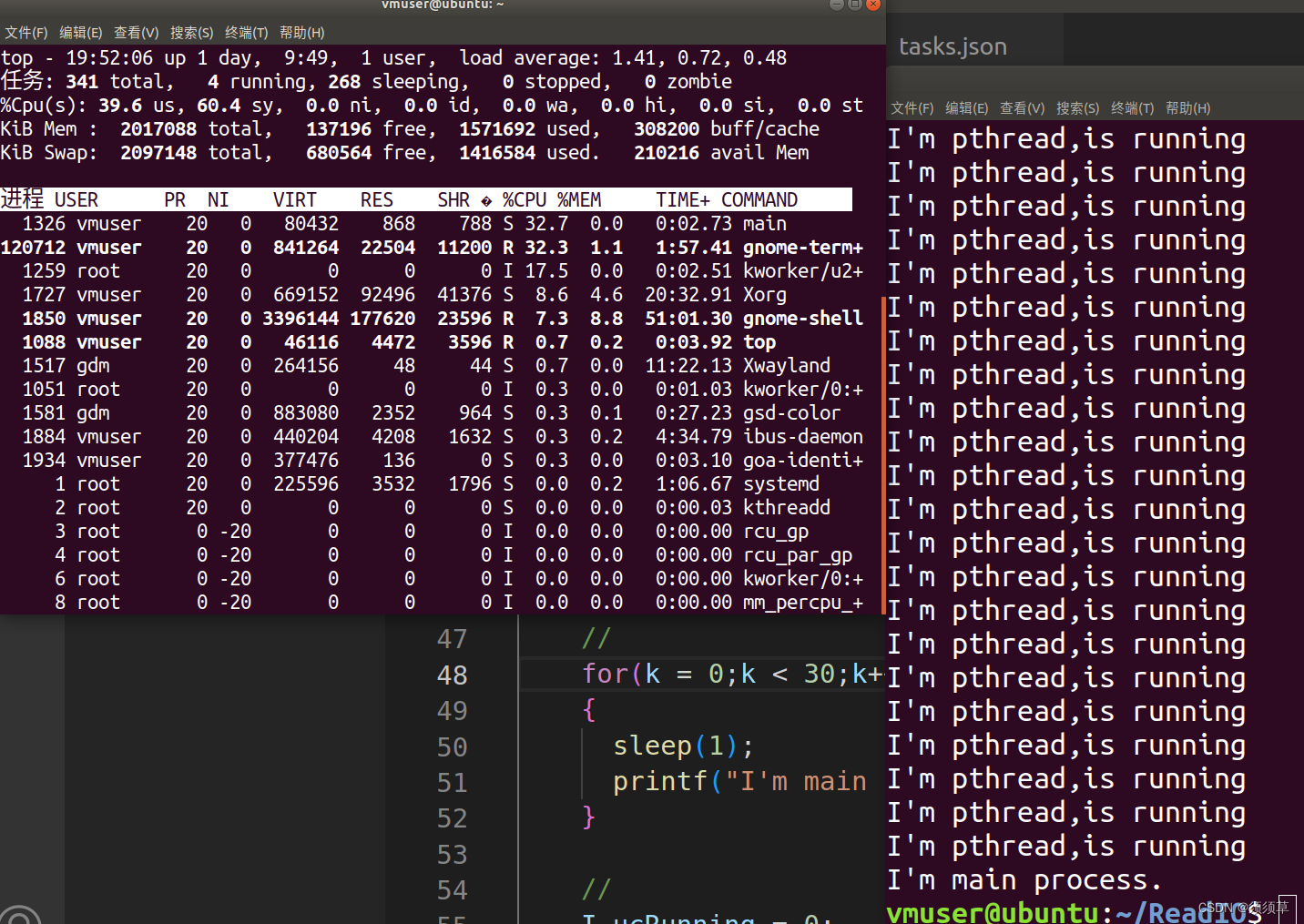
四、总结
合理运用阻塞函数sleep()使得线程阻塞,让出CPU资源给其他进程使用,才是高效运行系统做法,提高了系统安全性和实时性。