目录
- 一、实现框架
- 二、程序实现
- 三、代码讲解
- 1.`self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(1, 1)`
- 2.`model(x_data)`
- 3.`criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='sum'),loss = criterion(y_pred, y_data)`
一、实现框架
1、Prepare dataset
2、Design model using Class (inherit from nn.Module)
3、Construct loss and optimizer (using PyTorch API)
loss是为了计算损失,optimizer是为了优化参数
4、Training cycle (forward,backward,update)
二、程序实现
import torch
# prepare dataset
# x,y是矩阵,3行1列 也就是说总共有3个数据,每个数据只有1个特征
x_data = torch.tensor([[1.0], [2.0], [3.0]])
y_data = torch.tensor([[2.0], [4.0], [6.0]])
# design model using class
"""
our model class should be inherit from nn.Module, which is base class for all neural network modules.
member methods __init__() and forward() have to be implemented
class nn.linear contain two member Tensors: weight and bias
class nn.Linear has implemented the magic method __call__(),which enable the instance of the class can
be called just like a function.Normally the forward() will be called
"""
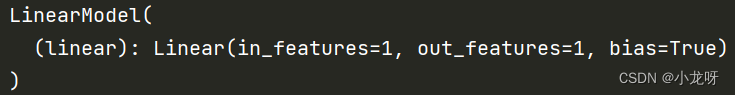
class LinearModel(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LinearModel, self).__init__()
# (1,1)是指输入x和输出y的特征维度,这里数据集中的x和y的特征都是1维的
# 该线性层需要学习的参数是w和b 获取w/b的方式分别是~linear.weight/linear.bias
self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(1, 1)
def forward(self, x):
y_pred = self.linear(x)
return y_pred
model = LinearModel()
print(model)
# construct loss and optimizer
# criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss(size_average = False)
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='sum') # 误差平方和
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
# training cycle forward, backward, update
for epoch in range(100):
y_pred = model(x_data) # forward:predict
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_data) # forward: loss
print(epoch, loss.item())
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度清零
loss.backward() # backward: autograd,自动计算梯度
optimizer.step() # update参数,即更新w和b的值
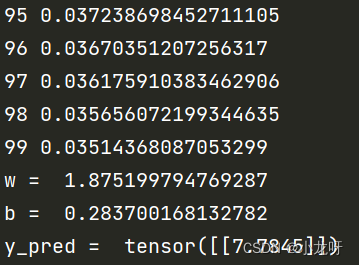
print('w = ', model.linear.weight.item()) #将w以数值打印,只能是一个数的张量可以用.item()
print('b = ', model.linear.bias.item())
x_test = torch.tensor([[4.0]])
y_test = model(x_test)
print('y_pred = ', y_test.data)
模型:
输出(部分截图):
三、代码讲解
1.self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(1, 1)
torch.nn.Linear是一个类,(1,1)分别表示该线性层的输入和输出维度
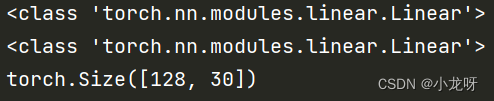
来看下面这个例子(输入size是128x20,经过一个20x30的线性层,输出为128x30):
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
m = nn.Linear(20, 30)
print(type(m))
print(type(nn.Linear(20, 30)))
input = torch.randn(128, 20)
output = m(input)
print(output.size())
更多理解看这里:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Linear.html#torch.nn.Linear
2.model(x_data)
先讲一下torch.nn.Module,Base class for all neural network modules。Your models should also subclass this class.所有神经网络的基类,你的模型应该将其子类化。就是一般我们会继承这个类,主要完成初始化模型,然后前向传播等一些东西。
来看一段重要代码和输出:
import torch
x_data = torch.tensor([1.0])
class LinearModel(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LinearModel, self).__init__()
self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(1, 1, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
n = x
y_pred = self.linear(x)
return y_pred,x
model = LinearModel()
print(type(model))
print(type(LinearModel()))
print(model.forward(x_data))
print(model(x_data))
print(model.__call__(x_data))
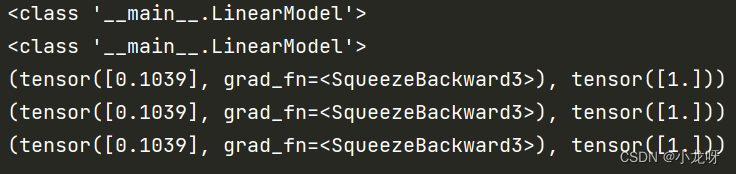
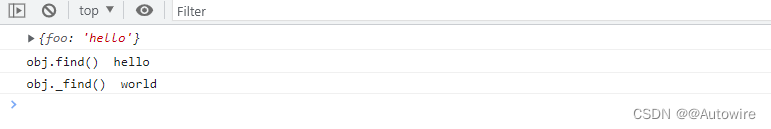
当你定义完LinearModel这个类后,你需要将其实例化为对象(当然对象也是类哈),才能进行调用。这个类需要一个参数,意思是,model = LinearModel(),model(x_data)才可以使用;而不可以直接 LinearModel(x_data)。
另外,model.forward(x_data),model(x_data),model.__call__(x_data)这三个输出一模一样,这和torch.nn.Module的内部封装有关系,具体可以看官方源代码:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/_modules/torch/nn/modules/module.html#Module
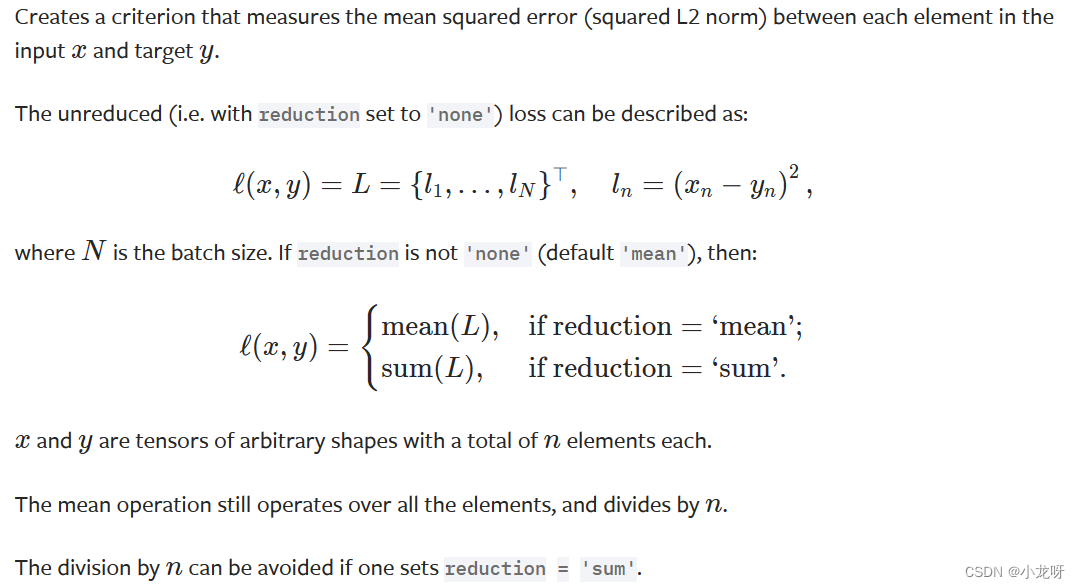
3.criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='sum'),loss = criterion(y_pred, y_data)
这里只需注意一点,就是sum还是mean,sum是预测值与真实值平方和,而mean只不过求了个平均值。