文章目录
- 需求内容:
- 实现:
- 步骤一:导入SpringAOP相关依赖pom.xml
- 步骤二:自定义两个注解
- 步骤三:需要用到的实体类
- **步骤四:切面具体实现**
- 用法
- 1.需要过滤返回值的方法添加注解@FilterByUser
- 2.数据Dto在需要过滤的字段添加@Filter注解,值为数据库中json字段的key
- 3.数据库中添加一条记录
- 4.完成配置的效果
- **实现原理描述**
需求内容:
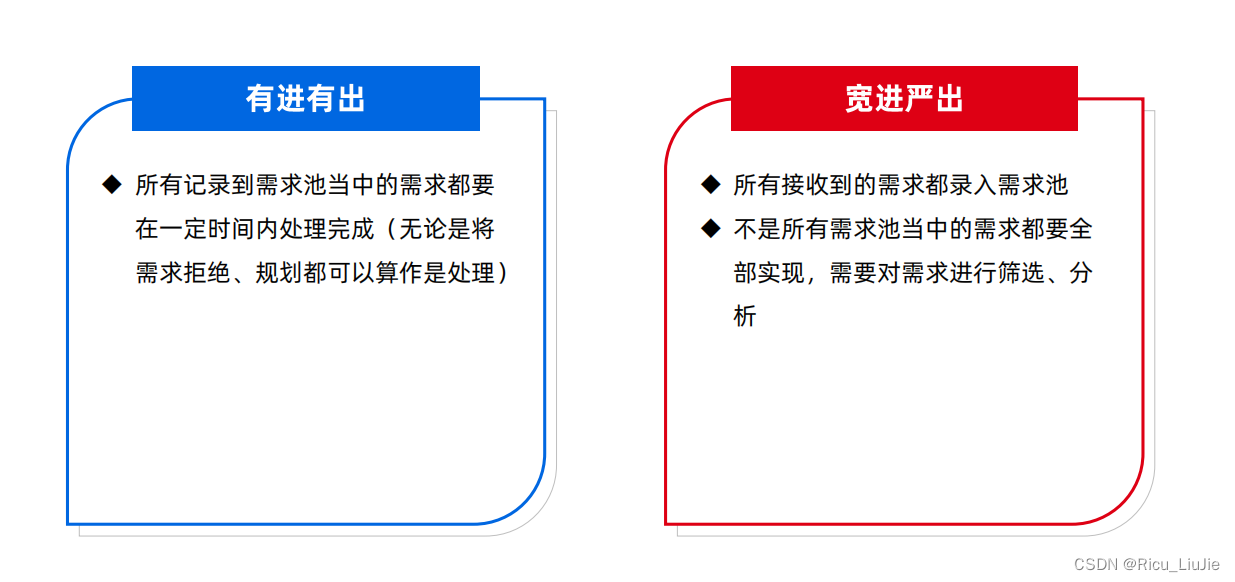
在系统已经完成的情况下,添加以下权限:
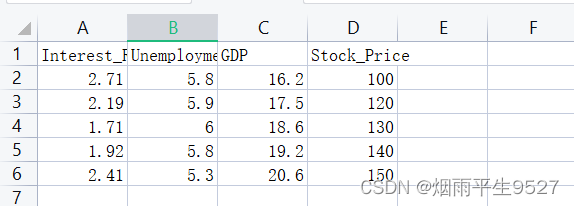
·城市为“上海”和“深圳”的“部门一”用户,只能看到用户表数据中城市为“上海或深圳”且部门为“部门一的子部门”。
所用技术包含,自定义注解,SpringAOP切面,反射以及其他SpringBoot项目常用
实现:
步骤一:导入SpringAOP相关依赖pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
<version>2.6.6</version>
</dependency>
步骤二:自定义两个注解
package cn.fy.anno;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author Fy
* 自定义注解,在实体类中有该注解的字段即可以被过滤
* @Date 2022年12月14日 11:12:59
*/
@Target({ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Filter {
//{"bumen":["部门11","部门12","部门13","部门14"]} 则keyName为 bumen
//此处用“bumen”只是为了证明可以和实体类的dept不同
String value() default "";
}
package cn.fy.anno;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface FilterByUser {
}
步骤三:需要用到的实体类
1.要查询要过滤的数据实体类,需继承2实体类,或(包含2实体类中需要查询的字段,并修改对应切面中获取前端传递用户账号的方法)
package cn.fy.dto;
import cn.fy.anno.Filter;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Data
public class User extends QueryDto implements Serializable {
private String userName;
@Filter("bumen")
//写成拼音只是为了证明可以与实体类字段名不一致
private String dept;
@Filter("chengshi")
private String city;
}
2.接收前端传递参数的查询实体类
package cn.fy.dto;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class QueryDto {
int pageIndex;
int pageSize;
String role;
//登录的用户账号
String userName;
}
3.权限数据库表对应的实体类和对应Mapper
package cn.fy.dto;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @author Fy
* @since 2023-02-10
*/
@Data
@TableName("user_power")
public class UserPower implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@TableId("id")
private Integer id;
@TableField("user_name")
private String userName;
@TableField("create_time")
private String createTime;
@TableField("json")
private String json;
}
package cn.fy.sql;
import cn.fy.dto.UserPower;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
/**
* @author Fy
* @since 2023-02-10
*/
@Mapper
public interface UserPowerMapper extends BaseMapper<UserPower> {
}
步骤四:切面具体实现
package cn.fy.aspect;
import cn.fy.anno.Filter;
import cn.fy.dto.UserPower;
import cn.fy.dto.QueryDto;
import cn.fy.sql.UserPowerMapper;
import cn.fy.sql.UserPowerMapper;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.LambdaQueryWrapper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Component
@Aspect
@Slf4j
public class PowerAspect {
@Resource
private UserPowerMapper userPowerMapper;
//需要限定包的话则自行添加@exectution
@Pointcut("@annotation(cn.fy.anno.FilterByUser)")
public void pointCut() {
}
@Around("pointCut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
Object reDto = null;
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
try {
//执行方法并获得返回值
reDto = joinPoint.proceed(args);
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
log.error("", throwable);
throw new RuntimeException(throwable);
}
QueryDto queryDto = null;
for (Object arg : args) {
if (arg instanceof QueryDto) {
queryDto = (QueryDto) arg;
break;
}
}
if (queryDto == null) {
return reDto;
}
//此部分为MybatisPlus查询数据库方法,可自行替换
LambdaQueryWrapper<UserPower> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(UserPower::getUserName, queryDto.getUserName());
UserPower powerDto = userPowerMapper.selectOne(queryWrapper);
log.info(JSON.toJSONString(powerDto));
log.info("---查询时间戳---" + System.currentTimeMillis());
JSONObject jsonObject = null;
if (powerDto == null) {
return reDto;
}
try {
jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(powerDto.getJson());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("", e);
}
if (jsonObject == null) {
return reDto;
}
try {
if (reDto instanceof List) {
//是集合
List list = (List) reDto;
List successList = new ArrayList();
//循环整个集合
for (Object o : list) {
Field[] fields = o.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
List<Boolean> booleanList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Field field : fields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
Filter annotation = field.getAnnotation(Filter.class);
if (annotation != null) {
String keyName = annotation.value();
Object o1 = jsonObject.get(keyName);
//如果获取到了key的话
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(o1)) {
List list1 = (List) o1;
//如果当前记录在记录中的话
booleanList.add(list1.contains(field.get(o)));
if (list1.contains(field.get(o))) {
log.info("key为" + keyName + ":的值【" + field.get(o) + "】在配置的权限中");
}
}
}
}
if (!booleanList.contains(false)) {
//证明这个数据是对的
successList.add(o);
}
}
return successList;
} else {
return reDto;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("", e);
}
return reDto;
}
}
用法
1.需要过滤返回值的方法添加注解@FilterByUser
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-2o1ptGjs-1676532488414)(C:\Users\song.cai\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\1676531140607.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/baafd617560746d088dfb21df8413c04.png)
2.数据Dto在需要过滤的字段添加@Filter注解,值为数据库中json字段的key
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-EKD75W9x-1676532488415)(C:\Users\song.cai\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\1676531216000.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/81314db6b59c4abfa457adcac43f182b.png)
3.数据库中添加一条记录
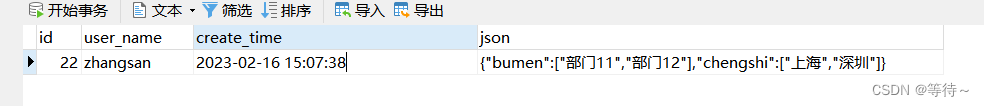
4.完成配置的效果
原输出结果
[User(userName=user163122156, dept=部门11, city=北京),
User(userName=user163122156, dept=部门11, city=上海),
User(userName=user163122156, dept=部门2, city=上海),
User(userName=user163122156, dept=部门11, city=深圳)]
加过滤之后输出结果
[User(userName=user163122156, dept=部门11, city=上海)]
实现原理描述
利用@Aspect注解来对切面进行编写,通过注解形式的切入点表达式,对加了@FilterByUser注解的方法进行过滤。利用@Around注解过滤修改原方法的返回值,在切面中通过反射获取原方法返回实体类中加了@Filter注解的字段,通过去查询数据库对该实体类中该字段的值进行比较过滤,多个@Filter需要全部校验通过才放行该对象,否则直接过滤掉不展示。





![[TPAMI‘21] Heatmap Regression via Randomized Rounding](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b0bb27f8ba1c47d79090725976527be3.png)