93.复原IP地址
看完题后的思路
- 典型分割问题
- 略
- lue
- 略
- 剪枝条件
sub: 1) 不是一位首字母为0 2)大于三位 3)介于0-255之间
4) 当已分割得到3个时,第四个直接从startIndex到末尾就行
代码
ArrayList<String> slist = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> restoreIpAddressesPath = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
restoreIpAddressesBT(s,0);
return slist;
}
public void restoreIpAddressesBT(String s,int startIndex) {
if (startIndex==s.length()){
if (restoreIpAddressesPath.size()==4){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (String s1 : restoreIpAddressesPath) {
sb.append(s1+".");
}
sb.delete(sb.length()-1,sb.length());
slist.add(sb.toString());
}
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i <s.length() ; i++) {
String substring = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1);
// 剪枝
// 如果已经有3个了,直接看剩下的能不能凑成第四个就行
if (restoreIpAddressesPath.size()==3&&valIsValid(s.substring(i+1))==-1){
return; // 本层全不能用
}
// 其余情况
if (valIsValid(substring)==-1){
continue;
}
restoreIpAddressesPath.add(substring);
restoreIpAddressesBT(s,i+1);
restoreIpAddressesPath.remove(restoreIpAddressesPath.size()-1);
}
}
public int valIsValid(String str){
if (str==null){
return -1;
}
if (str.length()>1&&str.charAt(0)=='0'){
return -1;
}
if (str.length()>3){
return -1;
}
int val=0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
val=val*10+(str.charAt(i)-'0');
}
if (val>255){
return -1;
}
return val;
}
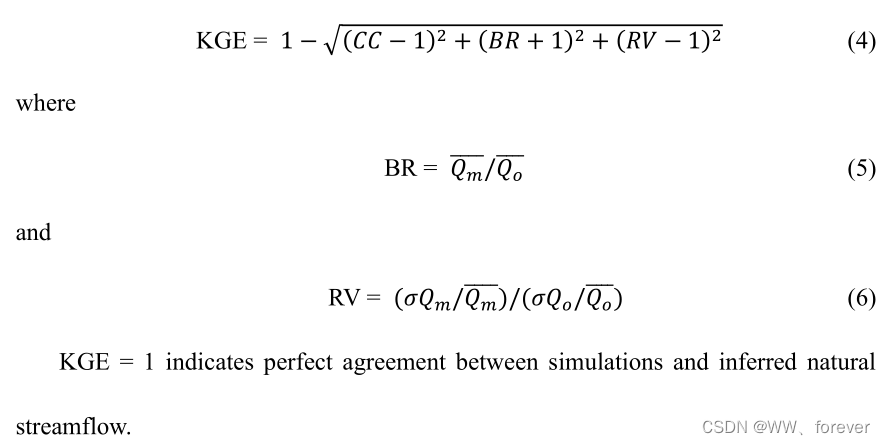
复杂度
收获
- 分割常用的递归出口
(1)startIndex==数组长度
缺点: 如果是分割有段数要求,例如ip,可能分割很多段后才到递归出口,1.1.1.1.1.1.1 再判断,白白浪费性能。
改进:当已经分割三段时,第四段直接判断,这样可以剪掉部分,但是最后还是会一个一个试
public void restoreIpAddressesBT(String s,int startIndex) {
if (startIndex==s.length()){
if (restoreIpAddressesPath.size()==4){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (String s1 : restoreIpAddressesPath) {
sb.append(s1+".");
}
sb.delete(sb.length()-1,sb.length());
slist.add(sb.toString());
}
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i <s.length() ; i++) {
String substring = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1);
// 剪枝
// 如果已经有3个了,直接看剩下的能不能凑成第四个就行
if (restoreIpAddressesPath.size()==3&&valIsValid(s.substring(startIndex))==-1){
return; // 本层全不能用
}
if (valIsValid(substring)==-1){
continue;
}
restoreIpAddressesPath.add(substring);
restoreIpAddressesBT(s,i+1);
restoreIpAddressesPath.remove(restoreIpAddressesPath.size()-1);
}
}
(2)如果有段数要求,直接用段数作为剪枝条件
if (restoreIpAddressesPath.size()==4){
if (startIndex==s.length()){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (String s1 : restoreIpAddressesPath) {
sb.append(s1+".");
}
sb.delete(sb.length()-1,sb.length());
slist.add(sb.toString());
}
return;
}
这样只要到段数,就会判断,不会再 1.1.1.1.1.1.1这样分割
2. 三刷敲一遍
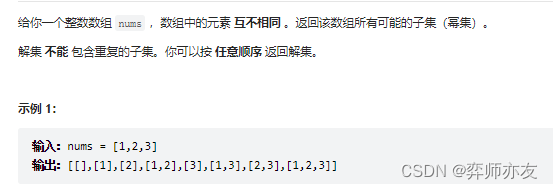
78.子集
看完题后的思路
一.0. 本题本质上是个组合问题,[]的处理可以在递归出口前将path加入,即向上提一层
- void f(【】,startIndex)
- 不用递归终止,用循环终止即可
- 递归
res.add(path);
递归终止
循环引擎
二. 为什么递归到最后,path为[]? 回溯删除的是自己,还是本节点?

代码
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ires = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> ipath = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
subsetsBT(nums,0);
System.out.println(ipath);
return ires;
}
public void subsetsBT(int[] nums,int startIndex) {
// 找所有从根节点的子路径,为处理空置,先加入
ires.add(new ArrayList<>(ipath));
// 递归终止条件 直接使用循环终止
// 循环引擎
for (; startIndex <nums.length ; startIndex++) {
// 剪枝 无
//三件套
ipath.add(nums[startIndex]);
subsetsBT(nums,startIndex+1);
ipath.remove(ipath.size()-1); // 删除的是startIndex
}
}
}
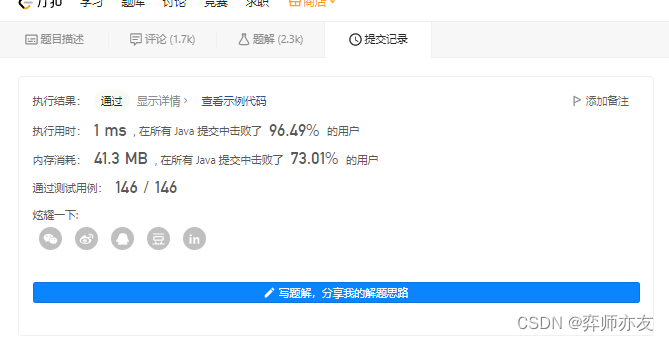
复杂度
收获
- 三刷大脑过一遍
- 组合问题之子集问题,找到所有从根节点出发的子路径,包含【】
90.子集II
看完题后的思路
- 基本子集+横向去重
代码
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ires = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> ipath = new ArrayList<>();
// 90. 子集 II
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
boolean[] using = new boolean[nums.length];
Arrays.sort(nums);
subsetsWithDupBT(nums,using,0);
return ires;
}
public void subsetsWithDupBT(int[] nums,boolean[] using,int startIndex) {
ires.add(new ArrayList<>(ipath));
// 终止 无
// 循环引擎
for (int i = startIndex; i <nums.length ; i++) {
// 剪枝
if (i!=0&&nums[i]==nums[i-1]&&!using[i-1]){
continue;
}
//三件套
using[i]=true;
ipath.add(nums[i]);
subsetsWithDupBT(nums,using,i+1);
ipath.remove(ipath.size()-1); // 删除的是startIndex
using[i]=false;
}
}
}
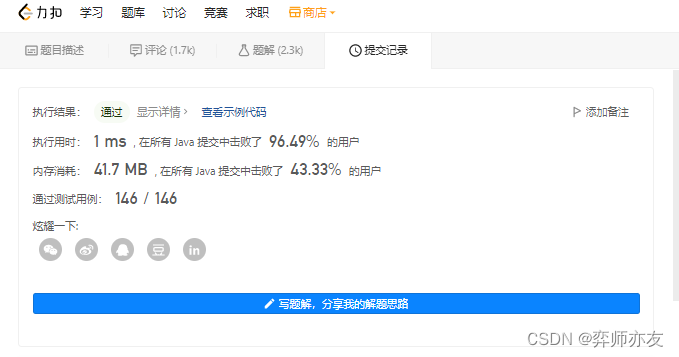
复杂度

收获
三刷过