Verilog-2005支持一些简单的数学函数,其参数的数据类型只能是integer和real型。
Integer型数学函数
$clog2是一个以2为底的对数函数,其结果向上取整,返回值典型的格式:
integer result;
result = $clog2(n);
最典型的应用就是通过参数化的方式来求某个变量的位宽,在另一篇文章已经对用法做了详细的介绍:Verilog设计中如何匹配变量的位宽?($clog2系统函数)
Real型数学函数
其参数数据类型为real型,返回值同样为real型,这意味着下面这些数学函数都无法被综合:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| $ln(x) | N自然对数(以e为底的对数) |
| $log10(x) | 十进制对数(以10为底的对数) |
| exp(x) | e^x ,e=2.718281828... |
| sqrt(x) | 开平方 |
| $pow(x, y) | x^y |
| $floor(x) | 向下取整 |
| $ceil(x) | 向上取整 |
| $hypot(x, y) | sqrt(xx + yy)。对两个数平方和开平方 |
| $sin(x) | sin |
| $cos(x) | cos |
| $tan(x) | tan |
| $asin(x) | arcsin |
| $acos(x) | arccos |
| $atan(x) | arccos |
| $atan2(x, y) | x/y的反正切 |
| $sinh(x) | 双曲正弦 |
| $cosh(x) | 双曲余弦 |
| $tanh(x) | 双曲正切 |
| $asinh(x) | 反双曲正弦 |
| $acosh(x) | 反双曲余弦 |
| $atanh(x) | 反双曲正切 |
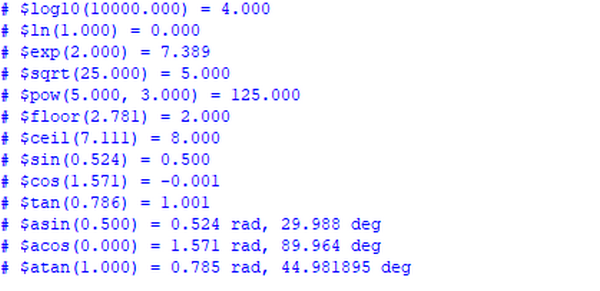
写个简单的testbench到modelsim验证一下:
module tb_math_fuc;
real x, y; //这些函数的参数需要是real类型,返回也是real类型
initial begin //0.3f表示取小数点后3位,下同
x = 10000;$display("$log10(%0.3f) = %0.3f", x, $log10(x)); //以10为底的对数
x = 1;$display("$ln(%0.3f) = %0.3f", x, $ln(x)); //以e为底的对数
x = 2;$display("$exp(%0.3f) = %0.3f", x, $exp(x)); //e^x
x = 25;$display("$sqrt(%0.3f) = %0.3f", x, $sqrt(x)); //开平方
x = 5;y = 3;$display("$pow(%0.3f, %0.3f) = %0.3f", x, y, $pow(x, y)); //x^y
x = 2.7813;$display("$floor(%0.3f) = %0.3f", x, $floor(x)); //向下取整
x = 7.1111;$display("$ceil(%0.3f) = %0.3f", x, $ceil(x)); //向上取整
x = 30 * (22.0/7.0) / 180;$display("$sin(%0.3f) = %0.3f", x, $sin(x)); //sin函数
x = 90 * (22.0/7.0) / 180;$display("$cos(%0.3f) = %0.3f", x, $cos(x)); //cos函数
x = 45 * (22.0/7.0) / 180;$display("$tan(%0.3f) = %0.3f", x, $tan(x)); //tan函数
x = 0.5;$display("$asin(%0.3f) = %0.3f rad, %0.3f deg", x, $asin(x), $asin(x) * 7.0/22.0 * 180);//arcsin函数
x = 0;$display("$acos(%0.3f) = %0.3f rad, %0.3f deg", x, $acos(x), $acos(x) * 7.0/22.0 * 180); //arccos函数
x = 1;$display("$atan(%0.3f) = %0.3f rad, %f deg", x, $atan(x), $atan(x) * 7.0/22.0 * 180); //arctan函数
end
endmodule这是验证结果: