注解
定义: 注解是一种注释机制,它可以注释包、类、方法、变量、参数,在编译器生成类文件时,标注可以被嵌入到字节码中。
注解的分类:
内置注解
Override :重写方法,引用时没有该方法时会编译错误
public class Animals {
public void run(){
System.out.println("动物跑");
}
}public class Cat extends Animals{
@Override
public void run1() {
super.run();
}
}
Deprecated :标记过时方法,会造成编译警告
public class Animals {
@Deprecated
public void run(){
System.out.println("动物跑");
}
}
SuppressWarnings :用于编译器去忽略注解中的声明报告
FunctionalInterface :用于指示被修饰的接口是函数式接口
元注解(修饰注解的注解)
@Retention -标记这个注解存储在哪里
@Documented -标记这些注解是否包含在用户文档中
@Target -标记这些注解时java哪种成员
public enum ElementType {
/** Class, interface (including annotation type), or enum declaration */
//可以应用于类的任何元素
TYPE,
//可以用于字段或属性
/** Field declaration (includes enum constants) */
FIELD,
//可以用于方法级注释
/** Method declaration */
METHOD,
//可以用于方法的参数
/** Formal parameter declaration */
PARAMETER,
//可以应用于构造函数
/** Constructor declaration */
CONSTRUCTOR,
//可以用于局部变量
/** Local variable declaration */
LOCAL_VARIABLE,
/** Annotation type declaration */
ANNOTATION_TYPE,
//可以用于包声明
/** Package declaration */
PACKAGE,
/**
* Type parameter declaration
*
* @since 1.8
*/
TYPE_PARAMETER,
/**
* Use of a type
*
* @since 1.8
*/
TYPE_USE
}@Inherited -标记这个注解时继承于哪个类
@Repeatable -标识某注解可以在同一个声明上使用多次
public enum RetentionPolicy {
/**
* Annotations are to be discarded by the compiler.
*/
SOURCE,//在源文件中有效(源文件保存)
/**
* Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler
* but need not be retained by the VM at run time. This is the default
* behavior.
*/
CLASS,//在class文件中有效(class保存)
/**
* Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler and
* retained by the VM at run time, so they may be read reflectively.
*
* @see java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement
*/
RUNTIME//在运行时有效(运行时保留)
}自定义注解
注解类:
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)//作用在类的属性上
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//运行时生效
public @interface NotNull {
String message() default "";
int length() default 0;
String lengthmessage() default "";
}model类:
public class User {
private int num;
@NotNull(message="姓名不能为空",length=3,lengthmessage="长度不能小于3")
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
}测试代码:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException, Exception {
User user=new User();
Field[] fields=user.getClass().getDeclaredFields();//将类中的字段存储在field数组中
//对数组中的字段进行强循环
for(Field filed:fields){
NotNull notNull=filed.getAnnotation(NotNull.class);//获取注释类型
if(notNull!=null){
Method method = user.getClass().getMethod("get" + getMethodName(filed.getName()));//获取方法对象
Object value = method.invoke(user);//调用类的实例对象
if(value==null){
System.err.println(filed.getName()+notNull.message());//打印输出相应的字段和注释信息
throw new NullPointerException(notNull.message());//抛出异常信息
}
else if(String.valueOf(value).length()< notNull.length()){//判断字符串长度
System.err.println(filed.getName()+notNull.lengthmessage());
}
}
}
}
/**
* 把一个字符串的第一个字母大写
*/
private static String getMethodName(String fildeName) throws Exception {
byte[] items = fildeName.getBytes();
items[0] = (byte) ((char) items[0] - 'a' + 'A');
return new String(items);
}
}
对象克隆
原因:new出来的对象属性都是初始化的值,不能保存当前对象“状态”,clone解决了这个问题
//这种形式的代码复制的是引用,即对象在内存中的地址,car1和car2指向同一个对象
Car car1=new Car();
Car car2=car1;如何实现克隆
克隆分为浅克隆和深克隆,下面就简单的介绍它们之前的区别:
浅克隆(值类型克隆值,引用类型传递地址)
model类:
public class Person implements Cloneable{
int num;
String name;
Address address;
public Person() {
}
public Person(int num, String name) {
this.num = num;
this.name = name;
}
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
protected Person clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Person person = (Person)super.clone();
// person.address = (Address)address.clone(); //深度复制 联同person中关联的对象也一同克隆.
return person;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"num=" + num +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", address=" + address +
'}';
}
}引用类:
public class Address {
String address;
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{" +
"address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
@Override
protected Address clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (Address)super.clone();
}
}测试类:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Address address = new Address();
address.setAddress("汉中");
Person p1 = new Person(100,"jim");
p1.setAddress(address);
Person p2 =p1.clone();
p2.setName("tom");
address.setAddress("西安");//
System.out.println(p1);
}
}
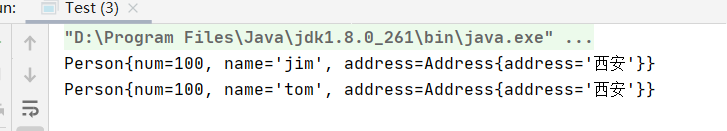
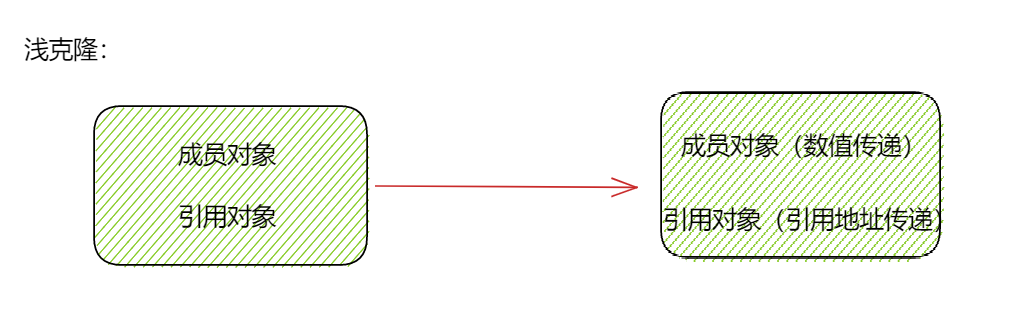

浅克隆中引用对象进行的是引用地址传递,原引用对象和克隆对象指向同一个引用地址
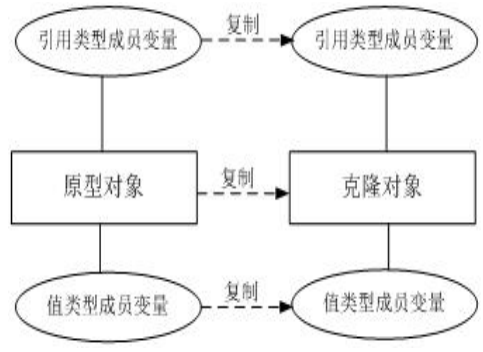
强克隆(值类型克隆值,引用类型克隆一个带有原数据的新的地址)
引用类:
public class Address implements Cloneable{
String address;
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{" +
"address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
@Override
protected Address clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (Address)super.clone();
}
}model类:
public class Person implements Cloneable{
int num;
String name;
Address address;
public Person() {
}
public Person(int num, String name) {
this.num = num;
this.name = name;
}
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
protected Person clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Person person = (Person)super.clone();
person.address = (Address)address.clone(); //深度复制 联同person中关联的对象也一同克隆.
return person;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"num=" + num +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", address=" + address +
'}';
}
}测试:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Address address = new Address();
address.setAddress("汉中");
Person p1 = new Person(100,"jim");
p1.setAddress(address);
Person p2 =p1.clone();
p2.setName("tom");
address.setAddress("西安");
System.out.println(p1);
System.out.println(p2);
}
}
强克隆中的引用类型新创建的地址赋给克隆对象引用类型
我们也可以通过序列化的方式对对象进行克隆,代码如下:
引用类:
public class Address implements Serializable {
String address;
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{" +
"address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
}model类:
public class Person implements Serializable {
int num;
String name;
Address address;
public Person() {
}
public Person(int num, String name) {
this.num = num;
this.name = name;
}
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
/**
* 自定义克隆方法
* @return
*/
public Person myclone() {
Person person = null;
try { // 将该对象序列化成流,因为写在流里的是对象的一个拷贝,而原对象仍然存在于JVM里面。所以利用这个特性可以实现对象的深拷贝
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(baos);
oos.writeObject(this);
// 将流序列化成对象
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(baos.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bais);
person = (Person) ois.readObject();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return person;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"num=" + num +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", address=" + address +
'}';
}
}测试类:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Address address = new Address();
address.setAddress("汉中");
Person p1 = new Person(100,"jim");
p1.setAddress(address);
Person p2 =p1.myclone();
p2.setName("tom");
address.setAddress("西安");
System.out.println(p1);
System.out.println(p2);
}
}