目录
1 Spring对事务的支持
1.1 引入事务场景
1.2 spring对事务的支持
Spring实现事务的两种方式
Spring事务管理API
1.3 事务属性
1.3.1 事务传播行为
1.3.2 事务隔离级别
1.3.3 事务超时
1.3.4 只读事务
1.3.5 异常回滚事务
1.4 事务的全注解式开发
1.5 声明式事务之xml实现方式
2 Spring6整合Junit5
2.1 spring对junit4的依赖
2.2 Spring对JUnit5的支持
3 Spring6集成MyBatis3.5
3.1 实现步骤
3.2 具体实现
4 Spring中的八大模式
4.1 简单工厂模式
4.2 工厂方法模式
4.3 单例模式
4.4 代理模式
4.5 装饰器模式
4.6 观察者模式
4.7 策略模式
4.8 模板方法模式
1 Spring对事务的支持
事务我们之前都很了解了。
1.1 引入事务场景
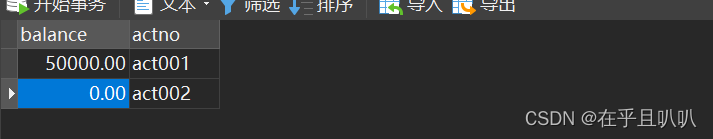
以银行转账为例:act001账户给act002账户转钱,必须同时成功或同时失败(act001减去钱成功并且act002加上相应的钱成功),否则可能会平白无故丢钱
连接数据库的技术采用Spring框架的JdbcTemplate。
第一步:准备数据库
创建数据库表:
添加依赖:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.itzw</groupId>
<artifactId>spring6-010-tx-bank</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<!--仓库-->
<repositories>
<!--spring里程碑版本的仓库-->
<repository>
<id>repository.spring.milestone</id>
<name>Spring Milestone Repository</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<!--依赖-->
<dependencies>
<!--spring context-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.0-M2</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring jdbc-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>6.0.0-M2</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.30</version>
</dependency>
<!--德鲁伊连接池-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.13</version>
</dependency>
<!--@Resource注解-->
<dependency>
<groupId>jakarta.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>第二步:创建包结构
com.itzw.bank.pojo
com.itzw.bank.service
com.powernode.bank.service.impl
com.itzw.bank.dao
com.itzw.bank.dao.impl
第三步:准备pojo类
package com.itzw.bank.pojo;
public class Account {
private String actno;
private double balance;
public Account(String actno, double balance) {
this.actno = actno;
this.balance = balance;
}
public Account(){}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"actno='" + actno + '\'' +
", balance=" + balance +
'}';
}
public String getActno() {
return actno;
}
public void setActno(String actno) {
this.actno = actno;
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
}
第四步:编写持久层
package com.itzw.bank.dao;
import com.itzw.bank.pojo.Account;
public interface AccountDao {
/**
* 根据账号查找信息
* @param actno
* @return
*/
Account selectByActno(String actno);
/**
* 修改信息
* @param account
* @return
*/
int update(Account account);
}
package com.itzw.bank.dao.imlp;
import com.itzw.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.itzw.bank.pojo.Account;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
//JdbcTemplate是spring提供好的类
@Resource
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public Account selectByActno(String actno) {
String sql = "select * from t_act where actno = ?";
Account account = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Account.class), actno);
return account;
}
@Override
public int update(Account account) {
String sql = "update t_act set balance = ? where actno = ?";
int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, account.getBalance(), account.getActno());
return count;
}
}
第五步:编写业务层
package com.itzw.bank.service;
public interface AccountService {
/**
* 转账
* @param fromActno 转出账户
* @param toActno 转入账户
* @param money 转账金额
*/
void transfer(String fromActno,String toActno,double money);
}
package com.itzw.bank.service.impl;
import com.itzw.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.itzw.bank.pojo.Account;
import com.itzw.bank.service.AccountService;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class AccountServiceImlp implements AccountService {
@Resource
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money) {
//判断转出账户余额是否充足
Account fromAccount = accountDao.selectByActno(fromActno);
if (fromAccount.getBalance() < money){
throw new RuntimeException("余额不足,赶紧充钱!");
}
//余额充足
Account toAccount = accountDao.selectByActno(toActno);
//先修改内存中的余额
fromAccount.setBalance(fromAccount.getBalance() - money);
toAccount.setBalance(toAccount.getBalance() + money);
//修改数据库中的余额
int count = accountDao.update(fromAccount);
count += accountDao.update(toAccount);
if (count == 2){
System.out.println("转账成功");
}else {
System.out.println("转账失败");
}
}
}
第六步:编写spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itzw.bank"/>
<bean id="druidDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql//127.0.0.1:3306/spring6"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>第七步:编写表示层(测试程序)
package com.itzw.spring6.test;
import com.itzw.bank.service.AccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-shiwu.xml");
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountServiceImlp", AccountService.class);
accountService.transfer("act001","act002",10000);
}
}
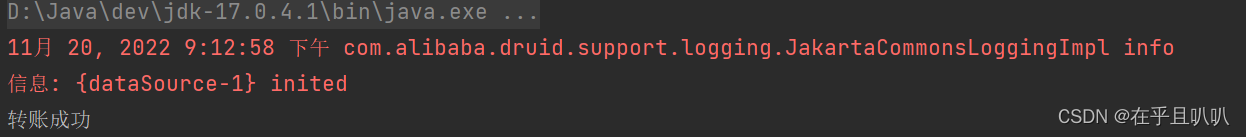

模拟异常:
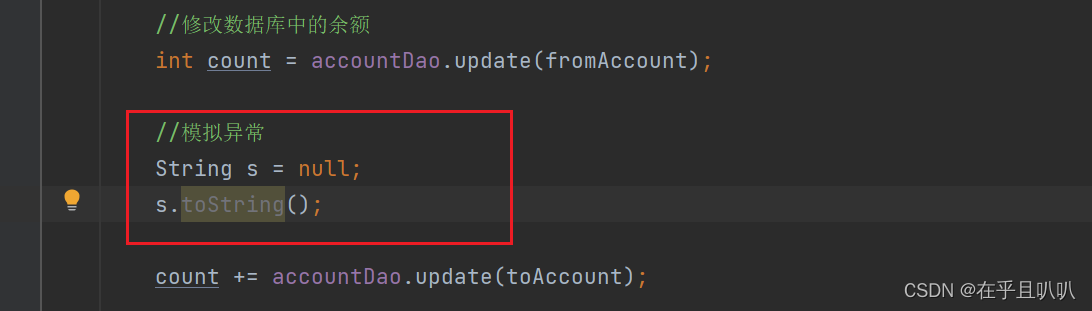
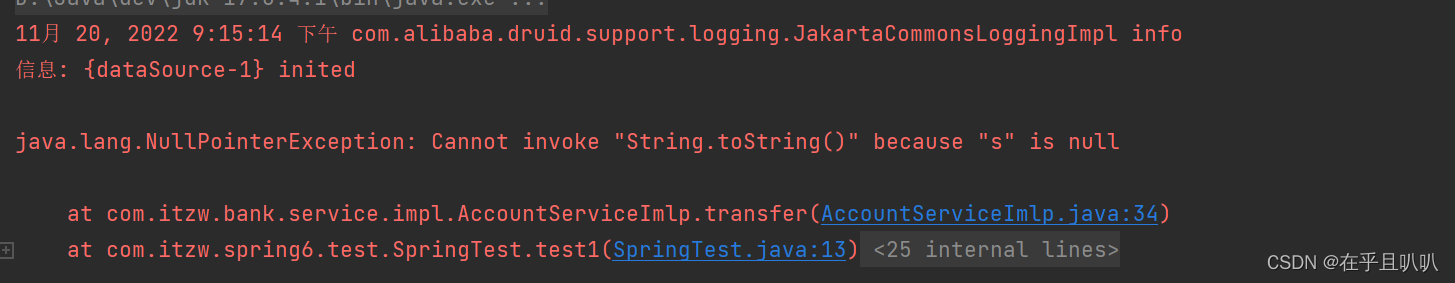
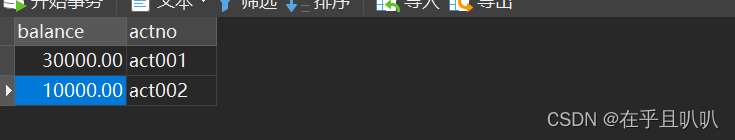
丢了一万
1.2 spring对事务的支持
Spring实现事务的两种方式
- 编程式事务:通过编写代码的方式来实现事务的管理。
- 声明式事务:基于注解方式;基于XML配置方式
Spring事务管理API
Spring对事务的管理底层实现方式是基于AOP实现的。采用AOP的方式进行了封装。所以Spring专门针对事务开发了一套API,API的核心接口是PlatformTransactionManager
这个接口是spring事务管理器的核心接口,在spring6中它有两个实现:
- DataSourceTransactionManager:支持JdbcTemplate、MyBatis、Hibernate等事务管理。
- JtaTransactionManager:支持分布式事务管理。
如果要在Spring6中使用JdbcTemplate,就要使用DataSourceTransactionManager来管理事务。(Spring内置写好了,可以直接用。)
注解实现:
第一步:在spring配置文件中配置事务管理器
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"/>
</bean>第二步:在spring配置文件中引入tx命名空间。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">第三步;在spring配置文件中配置“事务注解驱动器”,开始注解的方式控制事务。
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/> 第四步:在service类上或方法上添加@Transactional注解
在类上添加该注解,该类中所有的方法都有事务。在某个方法上添加该注解,表示只有这个方法使用事务。
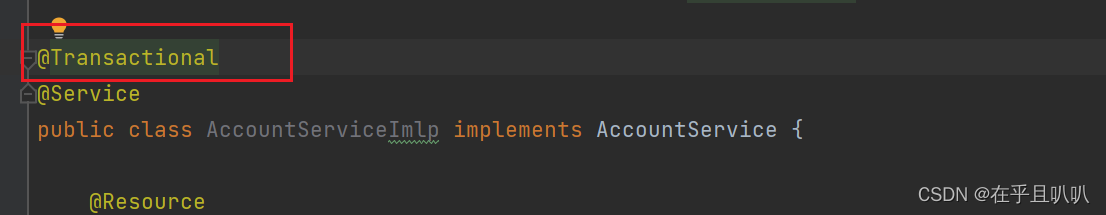
我们直接在类上加上这个注解表示这个类的所有方法都使用事务机制
再次测试,依然出错但是数据库的余额没有改变
1.3 事务属性
事务属性包括哪些
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.transaction.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface Transactional {
@AliasFor("transactionManager")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String transactionManager() default "";
String[] label() default {};
Propagation propagation() default Propagation.REQUIRED;
Isolation isolation() default Isolation.DEFAULT;
int timeout() default -1;
String timeoutString() default "";
boolean readOnly() default false;
Class<? extends Throwable>[] rollbackFor() default {};
String[] rollbackForClassName() default {};
Class<? extends Throwable>[] noRollbackFor() default {};
String[] noRollbackForClassName() default {};
}
事务中的重点属性:
- 事务传播行为
- 事务隔离级别
- 事务超时
- 只读事务
- 设置出现哪些异常回滚事务
- 设置出现哪些异常不回滚事务
1.3.1 事务传播行为
什么是事务的传播行为?
在service类中有a()方法和b()方法,a()方法上有事务,b()方法上也有事务,当a()方法执行过程中调用了b()方法,事务是如何传递的?合并到一个事务里?还是开启一个新的事务?这就是事务传播行为。
事务传播行为在spring框架中被定义为枚举类型:
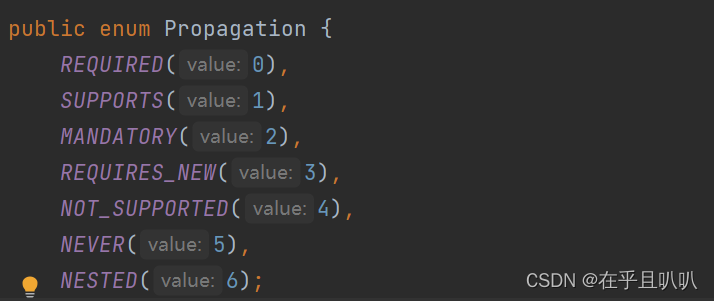
一共有七种传播行为:
- REQUIRED:支持当前事务,如果不存在就新建一个(默认)【没有就新建,有就加入】
- SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行【有就加入,没有就不管了】
- MANDATORY:必须运行在一个事务中,如果当前没有事务正在发生,抛出异常【有就加入,没有就抛异常】
- REQUIRES_NEW:开启一个新的事务,如果一个事务已经存在,则将这个存在的事务挂起【不管有没有,直接开启一个新事务,开启的新事务和之前的事务不存在嵌套关系】
- NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式运行,如果有事务存在,挂起当前事务【不支持事务,存在就挂起】
- NEVER:以非事务方式运行,如果有事务存在,抛出异常【不支持事务,存在就抛异常】
- NESTED:如果当前正有一个事务在进行中,则该方法应当运行在一个嵌套式事务中。被嵌套的事务可以独立于外层事务进行提交或回滚。如果外层事务不存在,行为就像REQUIRED一样。【有事务的话,就在这个事务里再嵌套一个完全独立的事务,嵌套的事务可以独立的提交和回滚。没有事务就和REQUIRED一样。】
编写程序测试一下传播行为:
我们在AccountService接口中再写一个方法为save,用来保存信息。再写一个类实现这个接口重写save方法:
@Resource(name = "accountService2")
private AccountService accountService;
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
@Override
public void save(Account account) {
accountDao.insert(account);
Account account2 = new Account("act004", 1200);
accountService.save(account2);
}package com.itzw.bank.service.impl;
import com.itzw.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.itzw.bank.pojo.Account;
import com.itzw.bank.service.AccountService;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service("accountService2")
public class AccountServiceImpl2 implements AccountService {
@Override
public void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money) {
}
@Resource(name = "accountDaoImpl")
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
@Override
public void save(Account account) {
accountDao.insert(account);
}
}
当然我们还要写一个dao方法用来插入信息:
@Override
public int insert(Account account) {
String sql = "insert into t_act(actno,balance) values (?,?)";
int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, account.getActno(), account.getBalance());
return count;
}在这里我们使用的传播行为是REQUIRED,也就是说当service2中的save方法支持前面的事务也就是支持service1中的save方法的事务。如果前面没有事务就使用service2中的save方法自己的事务。我们测试:
@Test
public void test2(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-shiwu.xml");
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountServiceImlp", AccountService.class);
Account account = new Account("act003", 2000);
accountService.save(account);
}按理说会新增两条记录:
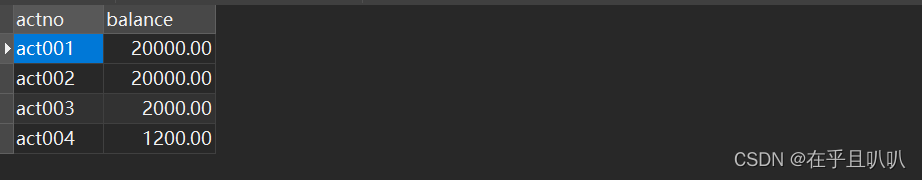
确实如此,但我们搞一个异常再试试:我们先把新增的记录删掉
在service2中搞个异常:
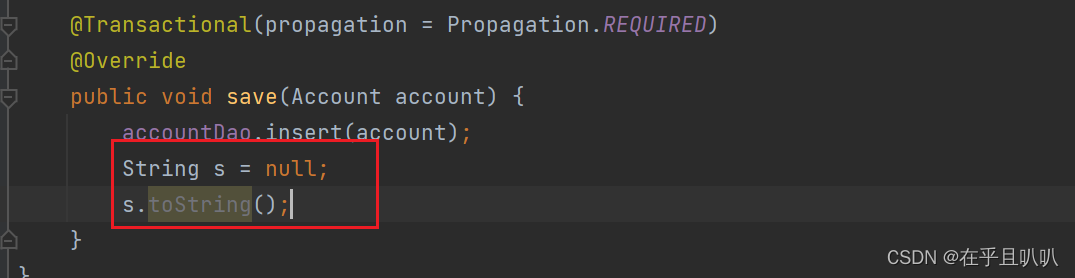
在service1中try-catch这个异常,看看有没有用:
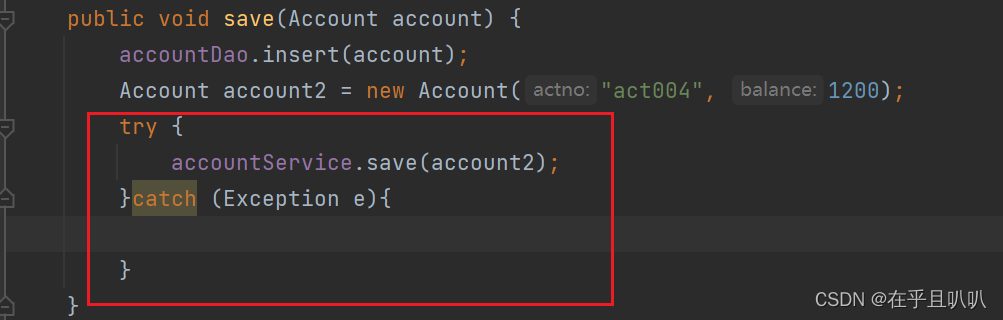
我们再测试:
报错了,而且数据库一条记录也没有新增,由此我们可以看出这两个save方法使用的是同一个事务
我们修改传播形式:将service2中的save修改为
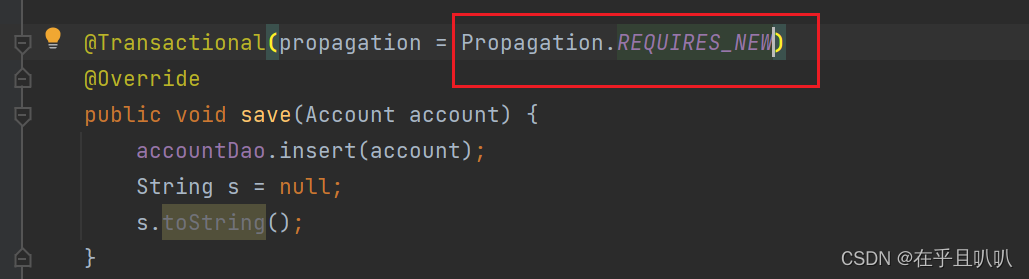
它表示不管前面有没有事务都会开启一个新的事务,也就是说这两个save方法使用的是两个事务,那么service2中的新增异常是不是不会影响到service1中的新增?
我们运行程序发现确实数据库表中只增加了一个数据act001
对了,我们测试前最好加入log4j2日志框架
1.3.2 事务隔离级别
简单理解为两个事务之间有一堵墙
数据库中读取数据存在的三大问题:(三大读问题)
- 脏读:读取到没有提交到数据库的数据,叫做脏读。
- 不可重复读:在同一个事务当中,第一次和第二次读取的数据不一样。
- 幻读:读到的数据是假的。
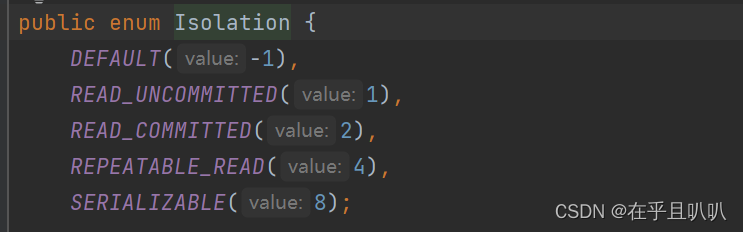
事务隔离级别包括四个级别:
- 读未提交:READ_UNCOMMITTED,这种隔离级别,存在脏读问题,所谓的脏读(dirty read)表示能够读取到其它事务未提交的数据。
- 读提交:READ_COMMITTED,解决了脏读问题,其它事务提交之后才能读到,但存在不可重复读问题。
- 可重复读:REPEATABLE_READ,解决了不可重复读,可以达到可重复读效果,只要当前事务不结束,读取到的数据一直都是一样的。但存在幻读问题。
- 序列化:SERIALIZABLE,解决了幻读问题,事务排队执行。不支持并发。
大家可以通过一个表格来记忆:
| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
| 读未提交 | 有 | 有 | 有 |
| 读提交 | 无 | 有 | 有 |
| 可重复读 | 无 | 无 | 有 |
| 序列化 | 无 | 无 | 无 |
在spring中如何设置隔离级别?
测试事务隔离级别:READ_UNCOMMITTED 和 READ_COMMITTED
怎么测试:一个service负责插入,一个service负责查询。负责插入的service要模拟延迟。
理想的测试结果是:使用读未提交时在数据没有提交到数据库我们就能查到这个数据。而读提交时在数据没有提交到数据库时我们是不能查到这个数据的。
package com.itzw.bank.service.impl;
import com.itzw.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.itzw.bank.pojo.Account;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service("is1")
public class IsolationService1 {
@Resource(name = "accountDaoImpl")
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_UNCOMMITTED)
public void selectByActno(String actno){
Account account = accountDao.selectByActno(actno);
System.out.println(account);
}
}
package com.itzw.bank.service.impl;
import com.itzw.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.itzw.bank.pojo.Account;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service("is2")
public class IsolationService2 {
@Resource(name = "accountDaoImpl")
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void insert(Account account){
accountDao.insert(account);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000*20);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
测试:
@Test
public void test4(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-shiwu.xml");
IsolationService1 is1 = applicationContext.getBean("is1", IsolationService1.class);
is1.selectByActno("act004");
}
@Test
public void test3(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-shiwu.xml");
IsolationService2 is2 = applicationContext.getBean("is2", IsolationService2.class);
Account act = new Account("act004",8490127);
is2.insert(act);
}我们先运行test3插入数据,在数据插入前运行test4,即使没插入结束我们还是能查到数据。
我们修改隔离级别为READ_COMMITTED
修改查询方法的隔离级别:
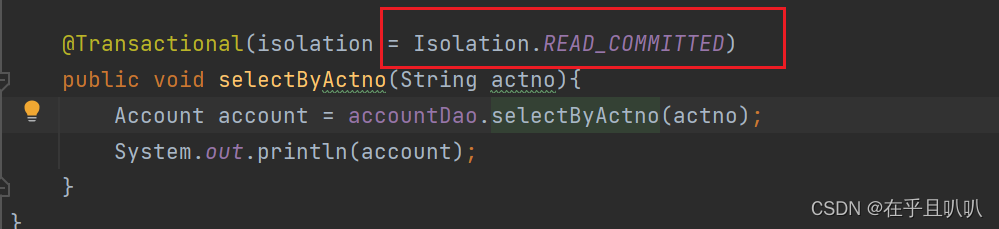
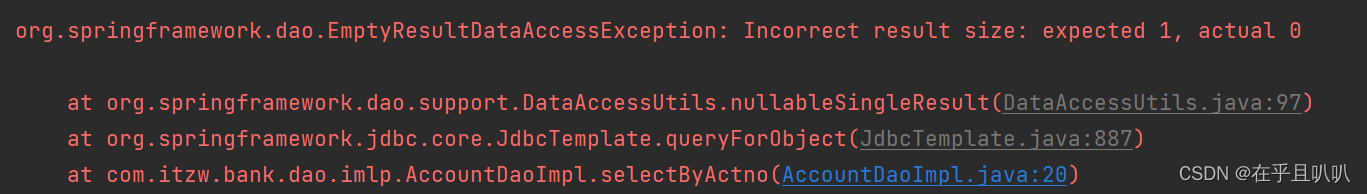
我们再测试,报错没有查到
1.3.3 事务超时
@Transactional(timeout = 10)以上代码表示设置事务的超时时间为10秒。
表示超过10秒如果该事务中所有的DML语句还没有执行完毕的话,最终结果会选择回滚。
默认值-1,表示没有时间限制。
这里有个坑,事务的超时时间指的是哪段时间?
在当前事务当中,最后一条DML语句执行之前的时间。如果最后一条DML语句后面很有很多业务逻辑,这些业务代码执行的时间不被计入超时时间。
比如:
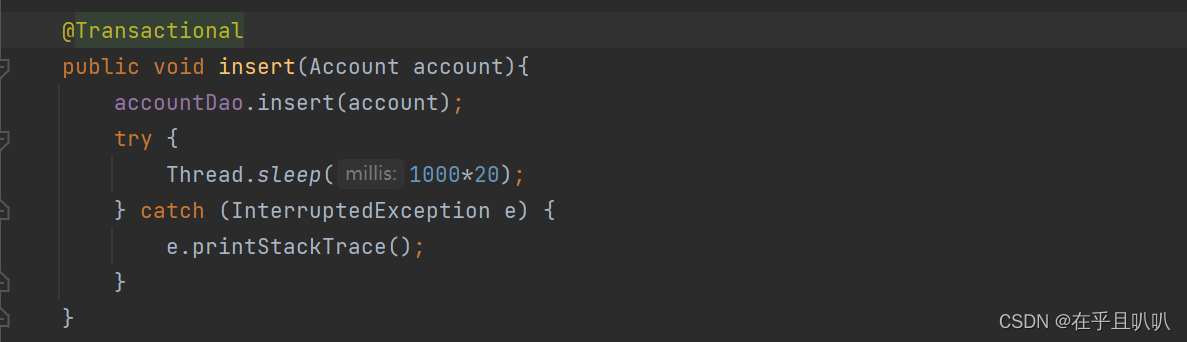
这里最后一条DML语句之后的睡眠20秒不算进超时时间里。放到insert之前才算。
当然,如果想让整个方法的所有代码都计入超时时间的话,可以在方法最后一行添加一行无关紧要的DML语句。
1.3.4 只读事务
@Transactional(readOnly = true)将当前事务设置为只读事务,在该事务执行过程中只允许select语句执行,delete insert update均不可执行。
该特性的作用是:启动spring的优化策略。提高select语句执行效率。
如果该事务中确实没有增删改操作,建议设置为只读事务。
1.3.5 异常回滚事务
设置哪些异常回顾事务:
@Transactional(rollbackFor = RuntimeException.class)表示只有发生RuntimeException异常或该异常的子类异常才回滚
设置哪些异常不回滚事务:
@Transactional(noRollbackFor = NullPointerException.class)表示发生NullPointerException或该异常的子类异常不回滚,其他异常则回滚。
1.4 事务的全注解式开发
编写一个类来代替配置文件,代码如下:
package com.itzw.bank;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration //代理spring.xml文件
@ComponentScan("com.itzw.bank")
@EnableTransactionManagement //开启事务注解
public class Spring6Config {
@Bean("druidDataSource")
public DataSource getDataSource(){
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/spring6");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("123456");
return dataSource;
}
@Bean("jdbcTemplate")
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource){
JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate();
template.setDataSource(dataSource);
return template;
}
@Bean("transactionManager")
public DataSourceTransactionManager getDataSourceTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
dataSourceTransactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return dataSourceTransactionManager;
}
}
注意:拿第一个Bean注解举例:Spring框架看到这个@Bean注解后,会调用这个被标注的方法,这个方法的返回值是一个java对象,这个java对象会自动纳入IoC容器管理。返回的对象就是Spring容器当中的一个Bean了。并且这个bean的名字是dataSource
在第二个Bean的方法的参数中的DataSource,spring在调用这个方法的时候会自动给我们传递过来一个DataSource对象,是根据类型自动转配
测试程序:
@Test
public void testNoXMl(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Spring6Config.class);
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountServiceImlp", AccountService.class);
accountService.transfer("act001","act002",10000);
}1.5 声明式事务之xml实现方式
下次一定写
2 Spring6整合Junit5
2.1 spring对junit4的依赖
我们先引入依赖,需要一个spring对junit的支持相关依赖:
<!--仓库-->
<repositories>
<!--spring里程碑版本的仓库-->
<repository>
<id>repository.spring.milestone</id>
<name>Spring Milestone Repository</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<!--spring context依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.0-M2</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring对junit的支持相关依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>6.0.0-M2</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit4依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
声明bean:
package com.itzw.spring6.bean;
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
public User(){}
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itzw.spring6.bean"/>
</beans>这是我们以前使用的方法:
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
User user = applicationContext.getBean("user", User.class);
System.out.println(user);
}spring对junit4的支持:
package com.itzw.spring6.test;
import com.itzw.spring6.bean.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:spring.xml")
public class SpringJunit4Test {
@Autowired
private User user;
@Test
public void test(){
System.out.println(user);
}
}
Spring提供的方便主要是这几个注解:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:spring.xml")
在单元测试类上使用这两个注解之后,在单元测试类中的属性上可以使用@Autowired。比较方便。
2.2 Spring对JUnit5的支持
引入JUnit5的依赖,Spring对JUnit支持的依赖还是:spring-test:
<!--junit5依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter</artifactId>
<version>5.9.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>package com.itzw.spring6.test;
import com.itzw.spring6.bean.User;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:spring.xml")
public class SpringJUnit5Test {
@Autowired
private User user;
@Test
public void test(){
System.out.println(user);
}
}
在JUnit5当中,可以使用Spring提供的以下两个注解,标注到单元测试类上,这样在类当中就可以使用@Autowired注解了。
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:spring.xml")
3 Spring6集成MyBatis3.5
3.1 实现步骤
第一步:准备数据库表
- 使用t_act表(账户表)
第二步:Idea中创建一个模块,引入依赖
- spring-context
- spring-jdbc
- mysql驱动
- mybatis
- mybatis-spring:mybatis提供的与spring框架集成的依赖
- 德鲁伊连接池
- junit
第三步:基于三层架构实现,所以提前创建好所有的包
- com.itzw.bank.mapper
- com.itzw.bank.service
- com.itzw.bank.service.impl
- com.itzw.bank.pojo
第四步:编写pojo
- Account,属性私有化,提供公开的setter getter和toString。
第五步:编写mapper接口
- AccountMapper接口,定义方法
第六步:编写mapper配置文件
- 在配置文件中配置命名空间,以及每一个方法对应的sql。
第七步:编写service接口和service接口实现类
- AccountService
- AccountServiceImpl
第八步:编写jdbc.properties配置文件
- 数据库连接池相关信息
第九步:编写mybatis-config.xml配置文件
- 该文件可以没有,大部分的配置可以转移到spring配置文件中。
- 如果遇到mybatis相关的系统级配置,还是需要这个文件。
第十步:编写spring.xml配置文件
- 组件扫描
- 引入外部的属性文件
- 数据源
- SqlSessionFactoryBean配置:注入mybatis核心配置文件路径;注入数据源;指定别名包
- Mapper扫描配置器:指定扫描的包
- 事务管理器DataSourceTransactionManager:注入数据源
- 启用事务注解:注入事务管理器
第十一步:编写测试程序,并添加事务,进行测试
3.2 具体实现
第一步:准备数据库
之前我们都是使用Navicat创建数据库,这次我们换一个,如果懒得打开Navicat,我们也可以直接使用idea创建,但是Navicat依然是专业的创建数据库的工具:
第二步:在idea创建模块,引入依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>spring6-012-spring-mybatis</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<!--仓库-->
<repositories>
<!--spring里程碑版本的仓库-->
<repository>
<id>repository.spring.milestone</id>
<name>Spring Milestone Repository</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<!--spring-jdbc-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>6.0.0-M2</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring-context-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.0-M2</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.30</version>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.10</version>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis-spring:mybatis提供的与spring框架集成的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.0.7</version>
</dependency>
<!--德鲁伊连接池-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.13</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
第三步:基于三层架构实现,所以提前创建好所有的包
第四步:编写pojo
package com.itzw.bank.pojo;
public class Account {
private String actno;
private double balance;
public Account() {
}
public Account(String actno, double balance) {
this.actno = actno;
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"actno='" + actno + '\'' +
", balance=" + balance +
'}';
}
public String getActno() {
return actno;
}
public void setActno(String actno) {
this.actno = actno;
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
}
第五步:编写mapper接口
package com.itzw.bank.mapper;
import com.itzw.bank.pojo.Account;
import java.util.List;
public interface AccountMapper {
/**
* 插入信息
* @param act
* @return
*/
int insert(Account act);
/**
* 根据账号删除信息
* @param actno
* @return
*/
int deleteByActno(String actno);
/**
* 修改信息
* @param act
* @return
*/
int update(Account act);
/**
* 根据账号查询信息
* @param actno
* @return
*/
Account selectByActno(String actno);
/**
* 查询所有信息
* @return
*/
List<Account> selectAll();
}
第六步:编写mapper配置文件
一定要注意,按照下图提示创建这个目录。注意是斜杠不是点儿。在resources目录下新建。并且要和Mapper接口包对应上,还有mapper配置文件的名字要和mapper接口一样:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.itzw.bank.mapper.AccountMapper">
<insert id="insert">
insert into t_act values (#{actno},#{balance})
</insert>
<delete id="deleteByActno">
delete from t_act where actno = #{actno}
</delete>
<update id="update">
update t_act set actno = #{actno},balance = #{balance} where actno = #{actno}
</update>
<select id="selectByActno" resultType="account">
select * from t_act where actno = #{actno}
</select>
<select id="selectAll" resultType="account">
select * from t_act
</select>
</mapper>第七步:编写service接口和service接口实现类
注意编写的service实现类纳入IoC容器管理:
package com.itzw.bank.service;
import com.itzw.bank.pojo.Account;
import java.util.List;
public interface AccountService {
/**
* 开户
* @param act
* @return
*/
int save(Account act);
/**
* 销户
* @param actno
* @return
*/
int deleteByActno(String actno);
/**
* 修改信息
* @param act
* @return
*/
int modify(Account act);
/**
* 查询所有账户信息
* @return
*/
List<Account> selectAll();
/**
* 转账
* @param fromActno
* @param toActno
* @param money
* @return
*/
int transfer(String fromActno,String toActno,double money);
}
这里使用了事务处理
package com.itzw.bank.service.impl;
import com.itzw.bank.mapper.AccountMapper;
import com.itzw.bank.pojo.Account;
import com.itzw.bank.service.AccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.List;
@Transactional
@Service("accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountMapper accountMapper;
@Override
public int save(Account act) {
int count = accountMapper.insert(act);
return count;
}
@Override
public int deleteByActno(String actno) {
int count = accountMapper.deleteByActno(actno);
return count;
}
@Override
public int modify(Account act) {
int count = accountMapper.update(act);
return count;
}
@Override
public List<Account> selectAll() {
List<Account> accounts = accountMapper.selectAll();
return accounts;
}
@Override
public int transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money) {
Account fromAct = accountMapper.selectByActno(fromActno);
//余额不足
if (fromAct.getBalance() < money) {
throw new RuntimeException("余额不足");
}
Account toAct = accountMapper.selectByActno(toActno);
//余额充足,修改内存余额
fromAct.setBalance(fromAct.getBalance() - money);
toAct.setBalance(toAct.getBalance() + money);
//修改数据库余额
int count = accountMapper.update(fromAct);
count += accountMapper.update(toAct);
if (count == 2){
System.out.println("转账成功");
}else {
System.out.println("转账失败");
}
return count;
}
}
第八步:编写jdbc.properties配置文件
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring6
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123456第九步:编写MyBatis核心配置文件
放在类的根路径下,只开启日志,其他配置到spring.xml中。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
</settings>
</configuration>第十步:编写spring.xml配置文件
注意:当你在spring.xml文件中直接写标签内容时,IDEA会自动给你添加命名空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!--组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itzw.bank"/>
<!--引入外部的属性文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"/>
<!--数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!--注入数据-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<!--MyBatis核心配置文件-->
<property name="configLocation" value="mybatis-config.xml"/>
<!--起别名-->
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.itzw.bank.pojo"/>
</bean>
<!--mapper扫描器-->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.itzw.bank.mapper"/>
</bean>
<!--事务管理器-->
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--开启事务注解-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager"/>
</beans>第十一步:测试程序
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class);
accountService.transfer("act001","act002",10000);
}测试没问题
4 Spring中的八大模式
这个我们先了解一下,以后有能力了再细看
4.1 简单工厂模式
BeanFactory的getBean()方法,通过唯一标识来获取Bean对象。是典型的简单工厂模式(静态工厂模式);
4.2 工厂方法模式
FactoryBean是典型的工厂方法模式。在配置文件中通过factory-method属性来指定工厂方法,该方法是一个实例方法。
4.3 单例模式
Spring用的是双重判断加锁的单例模式。请看下面代码,我们之前讲解Bean的循环依赖的时候见过:

4.4 代理模式
Spring的AOP就是使用了动态代理实现的。
4.5 装饰器模式
JavaSE中的IO流是非常典型的装饰器模式。
Spring 中配置 DataSource 的时候,这些dataSource可能是各种不同类型的,比如不同的数据库:Oracle、SQL Server、MySQL等,也可能是不同的数据源:比如apache 提供的org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource、spring提供的org.springframework.jndi.JndiObjectFactoryBean等。
这时,能否在尽可能少修改原有类代码下的情况下,做到动态切换不同的数据源?此时就可以用到装饰者模式。
Spring根据每次请求的不同,将dataSource属性设置成不同的数据源,以到达切换数据源的目的。
Spring中类名中带有:Decorator和Wrapper单词的类,都是装饰器模式。
4.6 观察者模式
定义对象间的一对多的关系,当一个对象的状态发生改变时,所有依赖于它的对象都得到通知并自动更新。Spring中观察者模式一般用在listener的实现。
Spring中的事件编程模型就是观察者模式的实现。在Spring中定义了一个ApplicationListener接口,用来监听Application的事件,Application其实就是ApplicationContext,ApplicationContext内置了几个事件,其中比较容易理解的是:ContextRefreshedEvent、ContextStartedEvent、ContextStoppedEvent、ContextClosedEvent
4.7 策略模式
策略模式是行为性模式,调用不同的方法,适应行为的变化 ,强调父类的调用子类的特性 。
getHandler是HandlerMapping接口中的唯一方法,用于根据请求找到匹配的处理器。
比如我们自己写了AccountDao接口,然后这个接口下有不同的实现类:AccountDaoForMySQL,AccountDaoForOracle。对于service来说不需要关心底层具体的实现,只需要面向AccountDao接口调用,底层可以灵活切换实现,这就是策略模式。
4.8 模板方法模式
Spring中的JdbcTemplate类就是一个模板类。它就是一个模板方法设计模式的体现。在模板类的模板方法execute中编写核心算法,具体的实现步骤在子类中完成。