一 问题描述
黑盒子代表一个原始数据库,存储一个整数数组和一个特殊的 i 变量。最初的时刻,黑盒子是空的,i=0,黑盒子处理一系列命令(事务)。有两种类型的事务。
① ADD(x),将元素 x 放入黑盒子中。
② GET,将 i 增加1,并给出包含在黑盒子中的所有整数中第 i 小的值。第 i 小的值是黑盒子中按非降序排序后第 i个位置的数字。
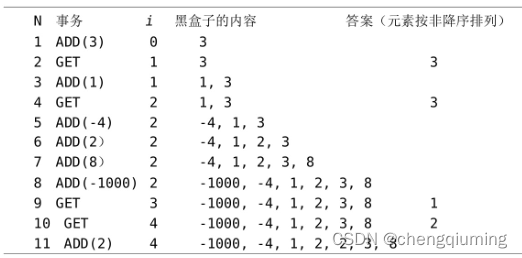
示例如下:
写一个有效的算法来处理给定的事务序列。ADD 和 GET事务的最大数量均为 30000,用两个整数数组来描述事务的顺序:
① A(1), A(2),…,A(M ),包含黑盒子中的一系列元素,A 值是绝对值不超过 2 000 000 000 的整数,M≤30000,对上面的示例,序列A=(3, 1,-4, 2,8,-1000, 2);
② u(1), u(2), …,u (N),表示在第 1 个、第 2 个,以此类推,直到第 N 个 GET事务时包含在黑盒子中的元素个数。对上面的示例,u=(1, 2, 6, 6)。假设自然数序列 u(1), u(2), …, u(N ) 按非降序排序,则对 u 序列的第 p 个元素执行 GET 事务,实际上是找 A(1), A(2), …, A(u(p)) 序列中第 p 小的数。
二 输入和输出
1 输入
输入包含(按给定顺序)M , N , A(1), A(2), …, A(M), u (1), u (2), …, u (N )。
2 输出
按照给定的事务顺序输出答案序列,每行一个数字。
三 输入和输出样例
1 输入样例
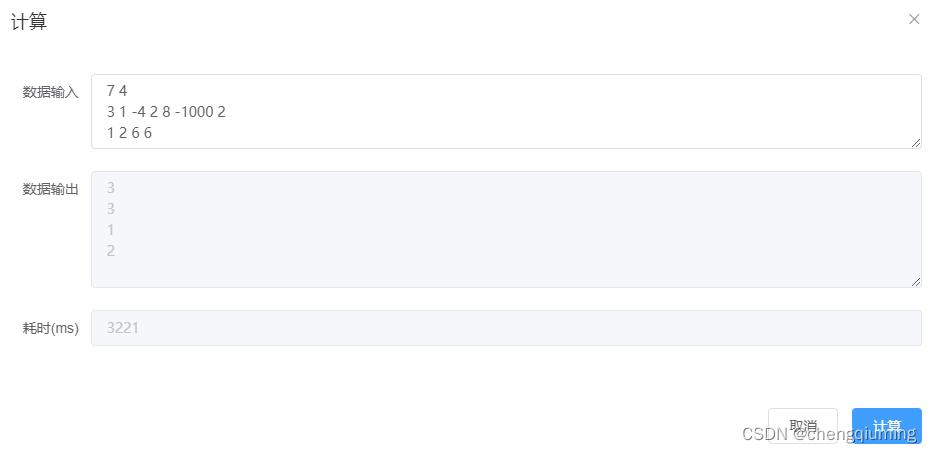
7 4
3 1 -4 2 8 -1000 2
1 2 6 6
2 输出样例
3
3
1
2
四 分析和设计
可以创建平衡二叉树,查找第 k 小,采用 Treap 解决。
本问题要控制黑盒子中的元素数量,然后查询第 k 小。u =(1, 2, 6, 6),在黑盒子中有 1 个数时查询第 1 小;在黑盒子中有 2 个数时查询第 2小;在黑盒子中有 6 个数时查询第 3 小;在黑盒子中有 6 个数时查询第 4 小。
五 代码
package com.platform.modules.alg.alglib.poj1442;
import java.util.Random;
public class Poj1442A {
public String output = "";
private int maxn = 30010;
int num[] = new int[maxn];
int num1[] = new int[maxn];
int n, cnt, root; //结点数,结点存储下标累计,树根
private node tr[] = new node[maxn];
public Poj1442A() {
for (int i = 0; i < tr.length; i++) {
tr[i] = new node();
}
}
public String cal(String input) {
int n, a, b, m;
String[] line = input.split("\n");
String[] nums = line[0].split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(nums[0]);
m = Integer.parseInt(nums[1]);
String[] elements = line[1].split(" ");
String[] element1s = line[2].split(" ");
root = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
num[i] = Integer.parseInt(elements[i - 1]);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
num1[i] = Integer.parseInt(element1s[i - 1]);
}
int t = 1, k = 1;
while (t <= m) {
while (k <= num1[t]) {
root = Insert(root, this.num[k]);
k++;
}
int ans = Findkth(root, t++);
output += ans + "\n";
}
return output;
}
// 生成新结点
int New(int val) {
tr[++cnt].val = val;
tr[cnt].pri = Math.abs(new Random().nextInt()) % 100;
tr[cnt].num = tr[cnt].size = 1;
tr[cnt].rc = tr[cnt].lc = 0;
return cnt;
}
// 更新子树大小
void Update(int p) {
tr[p].size = tr[tr[p].lc].size + tr[tr[p].rc].size + tr[p].num;
}
// 右旋
int zig(int p) {
int q = tr[p].lc;
tr[p].lc = tr[q].rc;
tr[q].rc = p;
tr[q].size = tr[p].size;
Update(p);
// 现在 q 为根
p = q;
return p;
}
// 左旋
int zag(int p) {
int q = tr[p].rc;
tr[p].rc = tr[q].lc;
tr[q].lc = p;
tr[q].size = tr[p].size;
Update(p);
// 现在 q 为根
p = q;
return p;
}
// 在 p 的子树插入值 val
int Insert(int p, int val) {
if (p == 0) {
p = New(val);
return p;
}
tr[p].size++;
if (val == tr[p].val) {
tr[p].num++;
return p;
}
if (val < tr[p].val) {
tr[p].lc = Insert(tr[p].lc, val);
if (tr[p].pri < tr[tr[p].lc].pri)
p = zig(p);
} else {
tr[p].rc = Insert(tr[p].rc, val);
if (tr[p].pri < tr[tr[p].rc].pri)
p = zag(p);
}
return p;
}
// 求第 k 小的数
int Findkth(int p, int k) {
if (p == 0) return 0;
int t = tr[tr[p].lc].size;
if (k < t + 1) return Findkth(tr[p].lc, k);
else if (k > t + tr[p].num) return Findkth(tr[p].rc, k - (t + tr[p].num));
else return tr[p].val;
}
}
class node {
int lc, rc; // 左右孩子
int val, pri; // 值,优先级
int num, size; // 重复个数,根的子树的大小
}六 测试