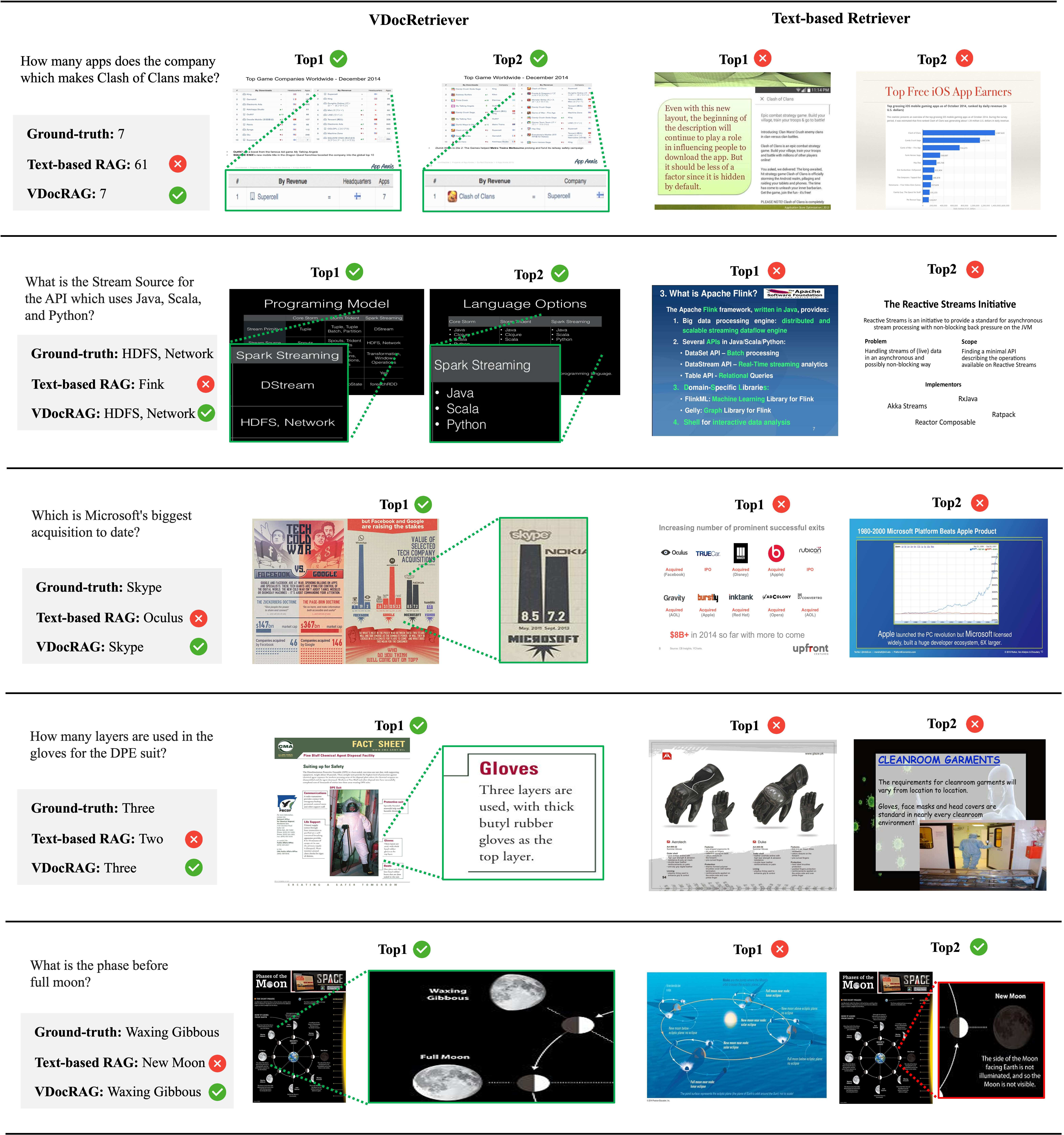
C++17 新特性简解
一、核心语言特性
1. 结构化绑定(Structured Bindings)
用途:解构复合类型(如元组、结构体)为独立变量
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <tuple>
int main() {
// 解构 std::pair
std::pair<int, double> p{42, 3.14};
auto [x, y] = p;
std::cout << "Pair: " << x << ", " << y << "\n";
// 解构结构体
struct Point { int a; int b; };
Point pt{10, 20};
auto& [a, b] = pt; // 引用绑定
a = 100;
std::cout << "Point: " << pt.a << ", " << pt.b << "\n";
return 0;
}
2. if/switch 初始化语句
用途:在条件语句中声明临时变量,限制作用域
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int getValue() { return 42; }
int main() {
std::vector<int> vec{1, 2, 3};
// if 初始化
if (auto it = std::find(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 2); it != vec.end()) {
std::cout << "Found: " << *it << "\n";
}
// switch 初始化
switch (int key = getValue(); key) {
case 42: std::cout << "Answer\n"; break;
default: break;
}
return 0;
}
3. 内联变量(Inline Variables)
用途:允许头文件中直接定义全局变量
示例:
// header.h
inline int globalCount = 0; // 多文件包含安全
struct MyClass {
inline static int instanceCount = 0; // 类内初始化静态成员
};
// main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "header.h"
int main() {
MyClass::instanceCount++;
std::cout << "Global: " << globalCount << ", Instance: " << MyClass::instanceCount << "\n";
return 0;
}
4. 折叠表达式(Fold Expressions)
用途:简化可变参数模板展开
示例:
#include <iostream>
template<typename... Args>
auto sum(Args... args) {
return (args + ...); // 折叠求和
}
int main() {
std::cout << "Sum: " << sum(1, 2, 3, 4) << "\n"; // 输出 10
return 0;
}
5. 类模板参数推导(CTAD)
用途:自动推导模板参数类型
示例:
#include <vector>
#include <tuple>
int main() {
std::pair p{1, "hello"}; // 推导为 pair<int, const char*>
std::vector v{1, 2, 3}; // 推导为 vector<int>
std::tuple t{4, 3.14, "π"}; // 推导为 tuple<int, double, const char*>
return 0;
}
6. constexpr 扩展
用途:支持更多编译期计算
示例:
#include <iostream>
constexpr int factorial(int n) {
if (n <= 1) return 1;
return n * factorial(n - 1);
}
int main() {
constexpr int val = factorial(5);
static_assert(val == 120); // 编译期验证
std::cout << "5! = " << val << "\n";
return 0;
}
二、标准库增强
1. 文件系统库(Filesystem)
头文件:<filesystem>
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <filesystem>
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
int main() {
fs::path p = fs::current_path() / "test.txt";
if (fs::exists(p)) {
std::cout << "文件大小: " << fs::file_size(p) << "字节\n";
}
return 0;
}
2. 新容器类型
| 类型 | 用途 | 示例代码 |
|---|---|---|
std::optional<T> | 表示可能不存在的值 | [见下方] |
std::variant<T...> | 类型安全的联合体 | [见下方] |
std::any | 存储任意类型 | [见下方] |
std::string_view | 非拥有字符串视图 | [见下方] |
完整示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <optional>
#include <variant>
#include <any>
#include <string_view>
int main() {
// optional
std::optional<int> opt = 42;
if (opt) std::cout << "Optional: " << *opt << "\n";
// variant
std::variant<int, std::string> v = "hello";
std::cout << "Variant: " << std::get<std::string>(v) << "\n";
// any
std::any a = 3.14;
if (a.type() == typeid(double)) {
std::cout << "Any: " << std::any_cast<double>(a) << "\n";
}
// string_view
std::string_view sv = "Hello World";
std::cout << "View: " << sv.substr(0, 5) << "\n";
return 0;
}
3. 并行算法
头文件:<execution>
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <execution>
int main() {
std::vector<int> data{5, 3, 1, 4, 2};
// 并行排序
std::sort(std::execution::par, data.begin(), data.end());
// 并行遍历
std::for_each(std::execution::par, data.begin(), data.end(), [](int x) {
std::cout << x << " ";
});
return 0;
}
三、其他改进
1. 嵌套命名空间简化
namespace A::B::C { // 等价于 namespace A { namespace B { namespace C {
class MyClass {};
}}
int main() {
A::B::C::MyClass obj;
return 0;
}
2. 强制复制省略
struct NonCopyable {
NonCopyable() = default;
NonCopyable(const NonCopyable&) = delete;
};
NonCopyable create() {
return NonCopyable{}; // C++17 必须省略拷贝
}
int main() {
NonCopyable obj = create();
return 0;
}
3. 新增属性
[[nodiscard]] int critical() { return 42; }
int main() {
critical(); // 警告:返回值未使用
return 0;
}
四、完整可编译代码示例
#include <iostream>
#include <tuple>
#include <vector>
#include <filesystem>
#include <optional>
#include <algorithm>
#include <execution>
// 结构化绑定
void demo_structured_binding() {
auto [x, y] = std::make_tuple(42, 3.14);
std::cout << "Tuple: " << x << ", " << y << "\n";
}
// 文件系统
void demo_filesystem() {
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
fs::path p = fs::current_path();
std::cout << "当前路径: " << p << "\n";
}
// 并行算法
void demo_parallel() {
std::vector<int> data{5, 3, 1, 4, 2};
std::sort(std::execution::par, data.begin(), data.end());
for (int n : data) std::cout << n << " ";
}
int main() {
demo_structured_binding();
demo_filesystem();
demo_parallel();
return 0;
}
五、编译与运行
- 编译命令:
g++ -std=c++17 -o cpp17_demo cpp17_demo.cpp -lstdc++fs