STC32G12K128单片机GPIO模式SPI操作NorFlash并实现FatFS文件系统
- NorFlash简介
- NorFlash操作
- 驱动代码
- 文件系统
- 测试代码
NorFlash简介
NOR Flash是一种类型的非易失性存储器,它允许在不移除电源的情况下保留数据。NOR Flash的名字来源于其内部结构中使用的NOR逻辑门。与另一种常见的闪存类型NAND Flash相比,NOR Flash提供了更快速的读取速度和随机访问能力,这使得它非常适合用于存储需要频繁、快速访问的代码或数据。
NOR Flash的特点包括:
- 快速读取:NOR Flash的读取速度非常快,适合执行存储于其中的程序代码。
- 随机访问:可以像SRAM一样进行随机访问,这使得它非常适合存储和运行代码。
- 写入和擦除速度较慢:尽管读取速度快,但NOR Flash的写入和擦除操作相对缓慢。
- 可靠性高:NOR Flash提供了比NAND Flash更高的可靠性和更低的位错误率。
- 成本较高:相对于每比特的价格来说,NOR Flash比NAND Flash要贵,尤其是在大容量存储方面。
应用场景
- NOR Flash通常用于那些需要快速启动和执行代码的应用中,例如嵌入式系统、消费电子产品以及汽车电子等。此外,由于其高可靠性和快速的读取速度,它也常被用来存储关键的固件或引导加载程序。
- 尽管NAND Flash在大规模数据存储上更为常用(如USB驱动器、SSD等),但在需要高效能执行代码的小型设备中,NOR Flash仍然是一个优选。随着技术的发展,NOR Flash也在不断进化以满足新的市场需求。
NorFlash操作
本文以Puya P25Q64SH 8MB Norflash为例




指令表


驱动代码
drv_spi_norflash.h
#ifndef __DRV_SPI_NORFLASH_H__
#define __DRV_SPI_NORFLASH_H__
#include "app_config.h"
#include "Type_def.h"
#if TCFG_DRV_SPI_NORFLASH_SUPPORT
#define NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE 256 // 256Byte
#define NORFLASH_SECTOR_SIZE 4096 // 4KB
#define NROFLASH_HALF_BLOCK_SIZE 32768 // 32KB
#define NORFLASH_BLOCK_SIZE 65536 // 64KB
#define NORFLASH_FATFS_SECTOR_SIZE (NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE * 2) // EatFs 文件系统读写扇区大小 支持页擦除的Norflash设置为2页
/* 指令表 */
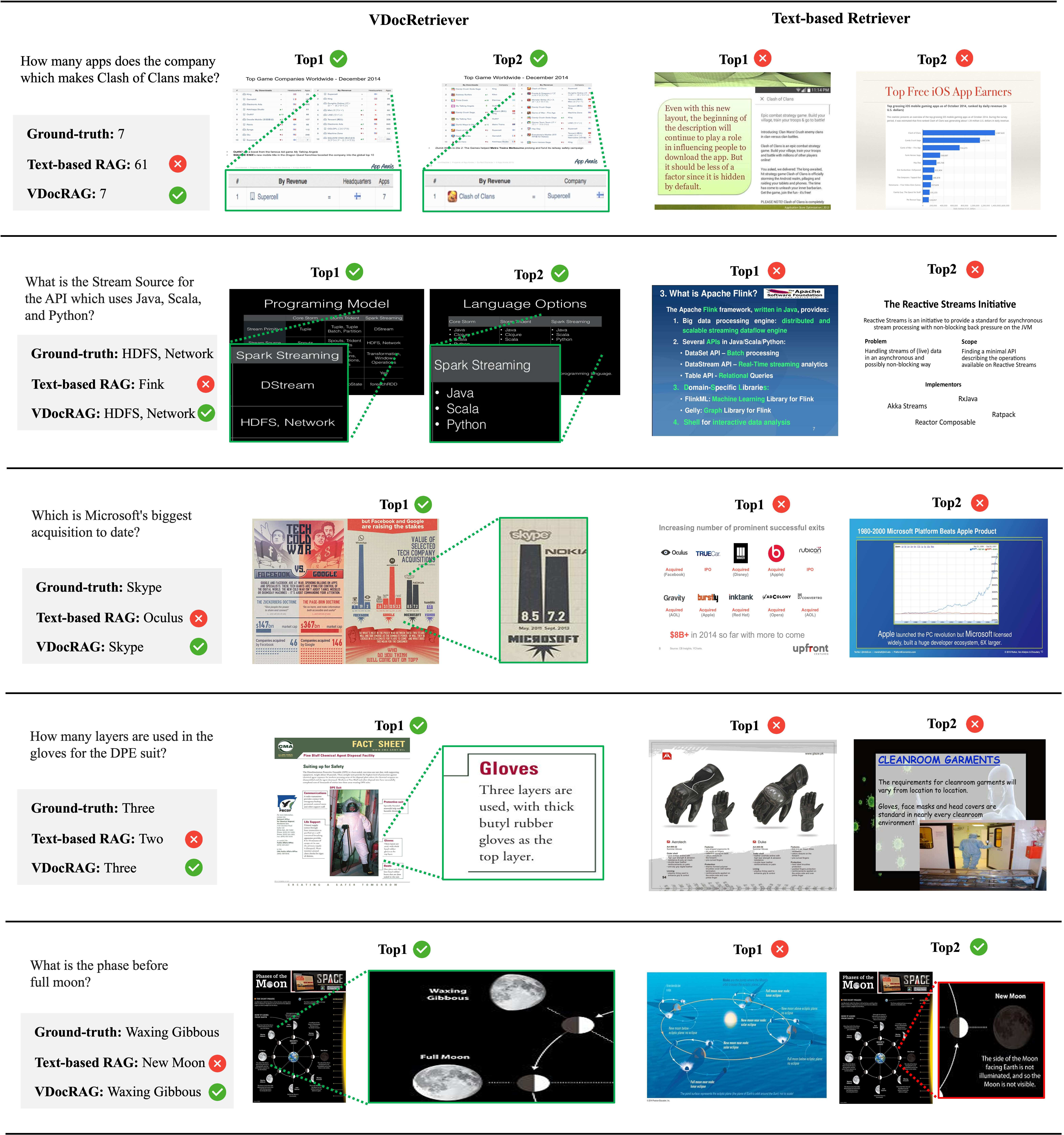
#define NOR_WriteEnable 0x06 /* 写使能 */
#define NOR_WriteDisable 0x04 /* 写禁止 */
#define NOR_VolatileSRWriteEnable 0x50
#define NOR_ReleasePowerDown 0xAB
#define NOR_ManufactDeviceID 0x90
#define NOR_JEDEC_ID 0x9F
#define NOR_ReadUniqueID 0x5A
#define NOR_ReadData 0x03
#define NOR_FastRead 0x0B
#define NOR_PageProgram 0x02
#define NOR_PageErase 0x81 /* 擦除1个页 256字节 ,部分Norflash不支持页擦除! */
#define NOR_SectorErase_4KB 0x20 /* 擦除1个扇区=4KB */
#define NOR_BlockErase_32KB 0x52 /* 擦除半个块=32KB */
#define NOR_BlockErase_64KB 0xD8 /* 擦除1个块=64KB */
#define NOR_ChipErase 0x60 /* or 0xC7 */
#define NOR_ReadStatusREG1 0x05
#define NOR_WriteStatusREG1 0x01
#define NOR_ReadStatusREG2 0x35
#define NOR_WriteStatusREG2 0x31
#define NOR_ReadStatusREG3 0x15
#define NOR_WriteStatusREG3 0x11
#define NOR_ReadSFDPREG 0x5A
#define NOR_EraseSecurityREG 0x44
#define NOR_ProgramSecurityREG 0x42
#define NOR_ReadSecurityREG 0x48
#define NOR_EraseProgramSuspend 0x75
#define NOR_EraseProgramResume 0x7A
#define NOR_Powerdown 0xB9
#define NOR_EnableReset 0x66
#define NOR_ResetDevice 0x99
#define NOR_FastReadDualOutput 0x3B
#define NOR_FastReadDual_IO 0xBB
#define NOR_QuadInputPageProgram 0x32
#define NOR_FastReadQuadOutput 0x6B
#define NOR_FastReadQuad_IO 0xEB
#define NOR_WordReadQuad_IO 0xE7
#define NOR_SetBurstWithWrap 0x77
#define NOR_DummyByte 0xFF
enum {
NORFLASH_ERASE_PAGE=0, /* 擦除页 256Byte */
NORFLASH_ERASE_SECTOR, /* 擦除扇区 4KB */
NORFLASH_ERASE_HALF_BLOCK, /* 擦除半块 32KB*/
NORFLASH_ERASE_BLOCK, /* 擦除整块 64KB*/
NORFLASH_ERASE_ALLCHIP, /* 擦除全部空间 */
};
// #pragma pack(1)
// #pragma pack()
// #pragma pack(push,1)
// #pragma pack(pop)
#pragma pack(1)
struct norflash_reg_t{
union {
struct {
uint8_t BUSY:1; // S0
uint8_t WEL: 1; // S1
uint8_t PB0: 1; // S2
uint8_t PB1: 1; // S3
uint8_t BP2: 1; // S4
uint8_t _TB: 1; // S5
uint8_t _SEC: 1; // S6
uint8_t SRP0: 1; // S7
}R;
uint8_t _data;
}REG1;
union {
struct {
uint8_t SRP1: 1; // S8
uint8_t _QE: 1; // S9
uint8_t LB0: 1; // S10
uint8_t LB1: 1; // S11
uint8_t LB2: 1; // S12
uint8_t LB3: 1; // S13
uint8_t CMP: 1; // S14
uint8_t SUS: 1; // S15
}R;
uint8_t _data;
}REG2;
union {
struct {
uint8_t Reserved2: 5;
// uint8_t DRV2: 1; // S21
uint8_t DRVS: 2; // S21 S22
uint8_t Reserved1: 1; // S23
}R;
uint8_t _data;
}REG3;
};
#pragma pack()
struct jedec_id_t {
uint8_t manufacturer_id; /* 制造商ID */
uint8_t memory_type; /* 存储类型 */
uint8_t capacity; /* 存储容量 */
};
struct norflash_dev_t {
uint16_t device_id;
uint32_t page_size;
uint32_t sector_size;
uint32_t sector_count;
uint32_t block_size;
struct jedec_id_t jedec_id;
struct norflash_reg_t reg;
};
struct norflash_dev_t* NorFlash_Handler(void);
void NorFlash_Read_JEDEC_ID(void);
uint16_t NorFlash_ReadID(void);
void NorFlash_ReadStatus(void);
void NorFlash_Sleep(void);
void NorFlash_Wakeup(void);
uint8_t NorFlash_Erase(uint8_t eraser, uint32_t address);
uint8_t NorFlash_ReadBuffer(uint8_t *buffer, uint32_t address, uint32_t len);
uint8_t NorFlash_WritePage(uint8_t *buffer, uint32_t address, uint32_t len);
uint8_t NorFlash_WriteBuffer(uint8_t *buffer, uint32_t address, uint32_t len);
uint8_t NorFlash_Init(void);
uint8_t NorFlash_GPIO_Config(void);
void NorFlash_Test(void);
#endif
#endif
drv_spi_norflash.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "config.h"
#include "STC32G_Timer.h"
#include "STC32G_GPIO.h"
#include "STC32G_NVIC.h"
#include "STC32G_Exti.h"
#include "STC32G_Delay.h"
#include "app_config.h"
#include "drv_spi_norflash.h"
#include "debug.h"
#if TCFG_DRV_SPI_NORFLASH_SUPPORT
#define NOR_CS P77 // CS 片选
#define NOR_DI P76 // DI 数据输入
#define NOR_CLK P75 // CLK 时钟
#define NOR_DO P74 // DO 数据输出
#define NOR_WP P73 // WP 写保护 不使用可接至VCC
#define NOR_HOLD P74 // HOLD 引脚保持 不使用可接至VCC
static struct norflash_dev_t xdata norflash_dev;
#define __this norflash_dev
/**
* @brief 获取NorFlash设备句柄
* @param 无
* @return struct norflash_dev_t类型指针
*/
struct norflash_dev_t* NorFlash_Handler(void)
{
return (struct norflash_dev_t*)&norflash_dev;
}
/**
* @brief NorFlash读字节
* @param 无
* @return 读取字节数据
*/
static uint8_t NorFlash_Read(void)
{
// CLK下升沿DO输出数据
uint8_t i,dat=0;
NOR_DO = 1;
for (i=0; i<8; i++)
{
NOR_CLK=1;
dat<<=1;
dat |= NOR_DO;
NOR_CLK=0;
}
return dat;
}
/**
* @brief NorFlash写字节
* @param dat:写入字节数据
* @return 无
*/
static void NorFlash_Write(uint8_t dat)
{
// CLK上升沿DI读入数据
uint8_t i;
for (i=0; i<8; i++)
{
NOR_CLK=0;
NOR_DI = (dat&0x80);
NOR_CLK=1;
dat <<=1;
}
NOR_CLK= 0;
NOR_DI = 0;
}
/**
* @brief NorFlash读写字节(写入1字节数据,同时读取1字节数据)
* @param dat:写入字节数据
* @return 读取字节数据
*/
static uint8_t NorFlash_ReadWrite(uint8_t dat)
{
// CLK上升沿DI读入数据
// CLK下升沿DO输出数据(CLK=0数据变化,CLK=1数据锁存 读取数据)
uint8_t i,read=0;
NOR_DO = 1;
for (i=0; i<8; i++)
{
NOR_CLK = 0;
NOR_DI = (dat&0x80);
dat <<= 1;
NOR_CLK=1;
read<<=1;
read |= NOR_DO;
}
NOR_CLK=0;
NOR_DI = 0;
return read;
}
/**
* @brief NorFlash等待准备好信号(BUSY标志位)
* @param 无
* @return 0:准备好,1:忙状态
*/
static uint8_t NorFlash_WaitReady(void)
{
uint8_t tryes;
uint8_t value=0;
tryes = 200;
do {
NOR_CS = 0;
NorFlash_Write(NOR_ReadStatusREG1);
__this.reg.REG1._data = NorFlash_Read();
NOR_CS = 1;
delay_ms(5);
}while(__this.reg.REG1.R.BUSY&&tryes--);
if (__this.reg.REG1.R.BUSY) {
return 1; // 出错
} else {
return 0; // 正常
}
}
void NorFlash_SendAddress(uint32_t address)
{
if (0) { // 4Byte Address Enable
NorFlash_Write((uint8_t)((address>>24)&0xFF));
}
NorFlash_Write((uint8_t)((address>>16)&0xFF));
NorFlash_Write((uint8_t)((address>>8)&0xFF));
NorFlash_Write((uint8_t)(address&0xFF));
}
/**
* @brief NorFlash读取状态寄存器
* @param 无
* @return 无
*/
void NorFlash_ReadStatus(void)
{
NOR_CS = 0;
NorFlash_Write(NOR_ReadStatusREG1);
__this.reg.REG1._data = NorFlash_Read();
// __this.SREG1 = NorFlash_Read();
NOR_CS = 1;
NOR_CS = 0;
NorFlash_Write(NOR_ReadStatusREG2);
__this.reg.REG2._data = NorFlash_Read();
// __this.SREG2 = NorFlash_Read();
NOR_CS = 1;
NOR_CS = 0;
NorFlash_Write(NOR_ReadStatusREG3);
__this.reg.REG3._data = NorFlash_Read();
// __this.SREG3 = NorFlash_Read();
NOR_CS = 1;
log_d("REG1:%02X, BUSY:%d, WEL:%d, SRP0:%d\n", __this.reg.REG1._data, __this.reg.REG1.R.BUSY, __this.reg.REG1.R.WEL, __this.reg.REG1.R.SRP0);
log_d("REG2:%02X\n", __this.reg.REG2._data);
log_d("REG3:%02X, DRVS:%d\n", __this.reg.REG3._data, __this.reg.REG3.R.DRVS);
}
/**
* @brief NorFlash休眠
* @param 无
* @return 无
*/
void NorFlash_Sleep(void)
{
NOR_CS = 0;
NorFlash_Write(NOR_Powerdown);
NOR_CS = 1;
}
/**
* @brief NorFlash唤醒
* @param 无
* @return 无
*/
void NorFlash_Wakeup(void)
{
NOR_CS = 0;
NorFlash_Write(NOR_ReleasePowerDown);
NOR_CS = 1;
}
/**
* @brief NorFlash读取JEDEC ID
* @param 无
* @return 无
*/
void NorFlash_Read_JEDEC_ID(void)
{
NOR_CS = 0;
NorFlash_Write(NOR_JEDEC_ID);
__this.jedec_id.manufacturer_id = NorFlash_Read(); // Manufacturer ID
__this.jedec_id.memory_type = NorFlash_Read(); // Memory Type
__this.jedec_id.capacity = NorFlash_Read(); // Capacity
NOR_CS = 1;
}
/**
* @brief NorFlash读取设备ID
* @param 无
* @return 2字节设备ID
*/
uint16_t NorFlash_ReadID(void)
{
uint16_t device_id=0xFFFF;
#if 0
NOR_CS = 0;
NorFlash_Write(NOR_ManufactDeviceID);
// 写入address:0x000000
NorFlash_Write(0x00);
NorFlash_Write(0x00);
NorFlash_Write(0x00);
// 读取Device ID 2Byte
device_id = NorFlash_Read();
// log_d("ID:%X",device_id);
device_id <<= 8;
device_id |= NorFlash_Read();
NOR_CS = 1;
#else
NOR_CS = 0;
NorFlash_ReadWrite(NOR_ManufactDeviceID);
// 写入address:0x000000
NorFlash_SendAddress(0x000000);
// 读取Device ID 2Byte
device_id = NorFlash_ReadWrite(NOR_DummyByte);
device_id <<= 8;
device_id |= NorFlash_ReadWrite(NOR_DummyByte);
NOR_CS = 1;
#endif
return device_id;
}
uint8_t NorFlash_Erase(uint8_t eraser, uint32_t address)
{
uint32_t i;
u8 eraser_cmd;
// 执行擦除命令前先检查忙状态
if (NorFlash_WaitReady()) {
log_d("Erase Wait 1 Error\n");
return 1;
}
switch(eraser)
{
case NORFLASH_ERASE_PAGE:
log_i("NORFLASH_ERASE_PAGE\n");
address = address / 256 * 256; // 页对齐,1页=256字节
eraser_cmd = NOR_PageErase;
break;
case NORFLASH_ERASE_SECTOR:
log_i("NORFLASH_ERASE_SECTOR\n");
address = address / 4096 * 4096; // 扇区对齐,1扇区=4096字节
eraser_cmd = NOR_SectorErase_4KB;
break;
case NORFLASH_ERASE_HALF_BLOCK:
log_i("NORFLASH_ERASE_HALF_BLOCK\n");
address = address / 32768 * 32768; // 半块对齐,半个块=32768字节=32KB
eraser_cmd = NOR_BlockErase_32KB;
break;
case NORFLASH_ERASE_BLOCK:
log_i("NORFLASH_ERASE_BLOCK\n");
address = address / 65535 * 65535; // 块对齐,1个块=65535字节=64KB
eraser_cmd = NOR_BlockErase_64KB;
break;
case NORFLASH_ERASE_ALLCHIP:
log_i("NORFLASH_ERASE_ALLCHIP\n");
eraser_cmd = NOR_ChipErase;
break;
default:
log_e("Erase CMD Error\n");
return 1;
}
// 发送写使能命令
NOR_CS = 0;
NorFlash_Write(NOR_WriteEnable);
NOR_CS = 1;
// 发送擦除命令
NOR_CS = 0;
NorFlash_Write(eraser_cmd);
if (NOR_ChipErase != eraser_cmd) {
// 不是擦除全片命令,写入地址
NorFlash_SendAddress(address);
}
NOR_CS = 1;
if (NorFlash_WaitReady()) {
log_d("Erase Wait 2 Error\n");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
uint8_t NorFlash_ReadBuffer(uint8_t *buffer, uint32_t address, uint32_t len)
{
uint32_t i;
NOR_CS = 0;
NorFlash_Write(NOR_ReadData);
NorFlash_SendAddress(address);
for(i=0; i<len; i++)
{
buffer[i] = NorFlash_Read();
}
NOR_CS = 1;
return 0;
}
uint8_t NorFlash_WritePage(uint8_t *buffer, uint32_t address, uint32_t len)
{
uint32_t i;
NOR_CS = 0;
NorFlash_Write(NOR_WriteEnable);
NOR_CS = 1;
NOR_CS = 0;
NorFlash_Write(NOR_PageProgram);
NorFlash_SendAddress(address);
for(i=0; i<len; i++)
{
NorFlash_Write(buffer[i]);
}
NOR_CS = 1;
if (NorFlash_WaitReady()) {
log_d("Write Wait Error\n");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
uint8_t NorFlash_WriteBuffer(uint8_t *buffer, uint32_t address, uint32_t len)
{
uint8_t num_of_page = 0, num_of_single = 0, addr = 0, count = 0, temp = 0;
addr = address % NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE;
count = NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE - addr;
num_of_page = len / NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE;
num_of_single = len % NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE;
/* address is NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE aligned */
if(0 == addr){
/* len < NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE */
if(0 == num_of_page)
NorFlash_WritePage(buffer,address,len);
/* len > NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE */
else{
while(num_of_page--){
NorFlash_WritePage(buffer,address,NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE);
address += NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE;
buffer += NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE;
}
NorFlash_WritePage(buffer,address,num_of_single);
}
}else{
/* address is not NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE aligned */
if(0 == num_of_page){
/* (len + address) > NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE */
if(num_of_single > count){
temp = num_of_single - count;
NorFlash_WritePage(buffer,address,count);
address += count;
buffer += count;
NorFlash_WritePage(buffer,address,temp);
}else
NorFlash_WritePage(buffer,address,len);
}else{
/* len > NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE */
len -= count;
num_of_page = len / NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE;
num_of_single = len % NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE;
NorFlash_WritePage(buffer,address, count);
address += count;
buffer += count;
while(num_of_page--){
NorFlash_WritePage(buffer,address,NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE);
address += NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE;
buffer += NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE;
}
if(0 != num_of_single)
NorFlash_WritePage(buffer,address,num_of_single);
}
}
return 0;
}
uint8_t NorFlash_Init(void)
{
log_d("NorFlash_Init\n");
NOR_WP = 1;
NOR_HOLD = 1;
NOR_CS = 1;
NOR_CLK = 0;
NOR_DI = 0;
NOR_DO = 0;
NorFlash_Read_JEDEC_ID();
log_d("manufacturer_id:0x%X\n", __this.jedec_id.manufacturer_id);
log_d("memory_type:0x%X\n", __this.jedec_id.memory_type);
log_d("capacity:0x%X\n", __this.jedec_id.capacity);
__this.device_id = NorFlash_ReadID();
log_d("DeviceID:0x%04X\n", __this.device_id);
#if 0
__this.page_size = 256;
__this.sector_size = 16*256; // 4KB
__this.sector_count = 16777216/4096;// 扇区个数=总容量/扇区大小
__this.block_size = 16*16*256; // 64KB
#endif
}
uint8_t NorFlash_GPIO_Config(void)
{
// P7_SPEED_LOW(GPIO_Pin_7|GPIO_Pin_6|GPIO_Pin_5|GPIO_Pin_4|GPIO_Pin_3|GPIO_Pin_2);
P7_SPEED_HIGH(GPIO_Pin_7|GPIO_Pin_6|GPIO_Pin_5|GPIO_Pin_4|GPIO_Pin_3|GPIO_Pin_2);
P7_PULL_UP_ENABLE(GPIO_Pin_7|GPIO_Pin_6|GPIO_Pin_5|GPIO_Pin_4|GPIO_Pin_3|GPIO_Pin_2);
P7_DRIVE_MEDIUM(GPIO_Pin_7|GPIO_Pin_6|GPIO_Pin_5|GPIO_Pin_4|GPIO_Pin_3|GPIO_Pin_2);
// P7_DRIVE_HIGH(GPIO_Pin_7|GPIO_Pin_6|GPIO_Pin_5|GPIO_Pin_4|GPIO_Pin_3|GPIO_Pin_2);
P7_MODE_OUT_PP(GPIO_Pin_7|GPIO_Pin_6|GPIO_Pin_5|GPIO_Pin_3|GPIO_Pin_2);
// 配置DI为高阻输入模式
P7_MODE_IO_PU(GPIO_Pin_4);
// P7_MODE_IN_HIZ(GPIO_Pin_4);
P7_DIGIT_IN_ENABLE(GPIO_Pin_4);
// P7_PULL_UP_ENABLE(GPIO_Pin_4);
// P7_PULL_UP_DISABLE(GPIO_Pin_4);
}
#if 0
#define D_NORFLASH_TEST_ADDR 0x000000 //(0x400000)
void NorFlash_Test(void)
{
int i=0;
uint8_t buffer[256*4];
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
NorFlash_Erase(NORFLASH_ERASE_SECTOR, D_NORFLASH_TEST_ADDR);
log_d("Erase Sector\n");
for(i=0; i<512; i++)
{
if (i<256)
buffer[i] = i;
else
buffer[i] = 0x3A;
}
NorFlash_WritePage(buffer, D_NORFLASH_TEST_ADDR, 512);
log_d("Norflash Write\n");
NorFlash_ReadBuffer(buffer, D_NORFLASH_TEST_ADDR, 512);
log_d("NorFlash Read:\n");
for(i=0; i<512; i++)
{
log_d("%02x,", buffer[i]);
}
log_d("\n");
}
#endif
#endif
文件系统
FatFs/diskio.c
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Low level disk I/O module SKELETON for FatFs (C)ChaN, 2019 */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* If a working storage control module is available, it should be */
/* attached to the FatFs via a glue function rather than modifying it. */
/* This is an example of glue functions to attach various exsisting */
/* storage control modules to the FatFs module with a defined API. */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "ff.h" /* Obtains integer types */
#include "diskio.h" /* Declarations of disk functions */
#include "app_config.h"
#if TCFG_LIB_FATFS_SUPPORT
#if TCFG_DRV_SD_CARD_SPI_SUPPORT
#include "drv_sd.h"
#endif
#if TCFG_DRV_SPI_NORFLASH_SUPPORT
#include "drv_spi_norflash.h"
#endif
#include "debug.h"
/* Definitions of physical drive number for each drive */
#define DEV_RAM 0 /* Example: Map Ramdisk to physical drive 0 */
#define DEV_MMC 1 /* Example: Map MMC/SD card to physical drive 1 */
#define DEV_USB 2 /* Example: Map USB MSD to physical drive 2 */
#define DEV_NOR 3 /* NorFlash */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Get Drive Status */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
DSTATUS disk_status (
BYTE pdrv /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
)
{
DSTATUS stat = STA_NOINIT;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case DEV_RAM :
// result = RAM_disk_status();
// translate the reslut code here
log_d("disk_status DEV_RAM\n");
return stat;
case DEV_MMC :
// result = MMC_disk_status();
// translate the reslut code here
stat = 0;
log_d("disk_status DEV_MMC\n");
return stat;
case DEV_USB :
// result = USB_disk_status();
// translate the reslut code here
log_d("disk_status DEV_USB\n");
return stat;
case DEV_NOR:
#if TCFG_DRV_SPI_NORFLASH_SUPPORT
log_d("disk_status DEV_NOR\n");
stat = 0;
#endif
return stat;
}
return STA_NOINIT;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Inidialize a Drive */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
DSTATUS disk_initialize (
BYTE pdrv /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
)
{
DSTATUS stat;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case DEV_RAM :
// result = RAM_disk_initialize();
// translate the reslut code here
log_d("disk_initialize DEV_RAM\n");
return stat;
case DEV_MMC :
// result = MMC_disk_initialize();
// translate the reslut code here
#if TCFG_DRV_SD_CARD_SPI_SUPPORT
if(SD_Init() == 0) {
stat = 0;
} else {
stat = RES_ERROR;
}
#endif
log_d("disk_initialize DEV_MMC\n");
return stat;
case DEV_USB :
// result = USB_disk_initialize();
// translate the reslut code here
log_d("disk_initialize DEV_USB\n");
return stat;
case DEV_NOR:
#if TCFG_DRV_SPI_NORFLASH_SUPPORT
log_d("disk_initialize DEV_NOR\n");
NorFlash_Init();
stat = 0;
#endif
return stat;
}
return STA_NOINIT;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Read Sector(s) */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
DRESULT disk_read (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
BYTE *buff, /* Data buffer to store read data */
LBA_t sector, /* Start sector in LBA */
UINT count /* Number of sectors to read */
)
{
DRESULT res;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case DEV_RAM :
// translate the arguments here
// result = RAM_disk_read(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
log_d("disk_read DEV_RAM\n");
return res;
case DEV_MMC :
// translate the arguments here
// result = MMC_disk_read(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
#if TCFG_DRV_SD_CARD_SPI_SUPPORT
if (count == 1) {
if (SD_ReadSingelBlock(buff, sector) == 0) {
res = RES_OK;
} else {
res = RES_ERROR;
}
} else {
if (SD_ReadMultipleBlock(buff, sector, count) == 0) {
res = RES_OK;
} else {
res = RES_ERROR;
}
}
#endif
log_d("disk_read DEV_MMC\n");
return res;
case DEV_USB :
// translate the arguments here
// result = USB_disk_read(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
log_d("disk_read DEV_USB\n");
return res;
case DEV_NOR:
#if TCFG_DRV_SPI_NORFLASH_SUPPORT
log_d("disk_read DEV_NOR\n");
NorFlash_ReadBuffer(buff, sector*NORFLASH_FATFS_SECTOR_SIZE, count*NORFLASH_FATFS_SECTOR_SIZE);
res = RES_OK;
#endif
return res;
}
return RES_PARERR;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Write Sector(s) */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#if FF_FS_READONLY == 0
DRESULT disk_write (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
const BYTE *buff, /* Data to be written */
LBA_t sector, /* Start sector in LBA */
UINT count /* Number of sectors to write */
)
{
DRESULT res;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case DEV_RAM :
// translate the arguments here
// result = RAM_disk_write(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
log_d("disk_write DEV_RAM\n");
return res;
case DEV_MMC :
// translate the arguments here
// result = MMC_disk_write(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
#if TCFG_DRV_SD_CARD_SPI_SUPPORT
if (count == 1) {
if (SD_WriteSingleBlock(buff, sector) == 0) {
res = RES_OK;
} else {
res = RES_ERROR;
}
} else {
if (SD_WriteMultipleBlock(buff, sector, count) == 0) {
res = RES_OK;
} else {
res = RES_ERROR;
}
}
#endif
log_d("disk_write DEV_MMC\n");
return res;
case DEV_USB :
// translate the arguments here
// result = USB_disk_write(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
log_d("disk_write DEV_USB\n");
return res;
case DEV_NOR:
{
#if TCFG_DRV_SPI_NORFLASH_SUPPORT
uint8_t i;
BYTE *buf = buff;
log_d("disk_write DEV_NOR\n");
for (i=0; i<count; i++)
{
// 写之前必须先擦除写入扇区:擦除512字节 = 2页
NorFlash_Erase(NORFLASH_ERASE_PAGE, sector * NORFLASH_FATFS_SECTOR_SIZE); // 擦除页
NorFlash_Erase(NORFLASH_ERASE_PAGE, sector * NORFLASH_FATFS_SECTOR_SIZE + NORFLASH_PAGE_SIZE); // 擦除页
NorFlash_WriteBuffer(buf, sector * NORFLASH_FATFS_SECTOR_SIZE, NORFLASH_FATFS_SECTOR_SIZE);
sector += 1;
}
res = RES_OK;
#endif
return res;
}
}
return RES_PARERR;
}
#endif
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Miscellaneous Functions */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
DRESULT disk_ioctl (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
BYTE cmd, /* Control code */
void *buff /* Buffer to send/receive control data */
)
{
DRESULT res = RES_OK;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case DEV_RAM :
// Process of the command for the RAM drive
log_d("disk_ioctl DEV_RAM cmd:0x%02x\n", cmd);
return res;
case DEV_MMC :
#if TCFG_DRV_SD_CARD_SPI_SUPPORT
// Process of the command for the MMC/SD card
log_d("disk_ioctl DEV_MMC cmd:%d\n", cmd);
if (CTRL_SYNC == cmd) {
log_d("CTRL_SYNC\n");
} else if (GET_SECTOR_COUNT == cmd) {
log_d("GET_SECTOR_COUNT\n");
// *(DWORD *)buff = 1536;
} else if (GET_SECTOR_SIZE == cmd) {
log_d("GET_SECTOR_SIZE\n");
*(WORD *)buff = 512;
} else if (GET_BLOCK_SIZE == cmd) {
log_d("GET_BLOCK_SIZE\n");
*(WORD *)buff = 1 ; //每次擦除一个扇区
} else if (CTRL_TRIM == cmd) {
log_d("CTRL_TRIM\n");
}
#endif
return res;
case DEV_USB :
// Process of the command the USB drive
log_d("disk_ioctl DEV_USB cmd:%d\n", cmd);
return res;
case DEV_NOR:
#if TCFG_DRV_SPI_NORFLASH_SUPPORT
log_d("disk_ioctl DEV_NOR cmd:%d\n", cmd);
if (CTRL_SYNC == cmd) {
log_d("CTRL_SYNC\n");
res = RES_OK;
} else if (GET_SECTOR_SIZE == cmd) {
log_d("GET_SECTOR_SIZE\n");
// 这个是文件系统每次操作的扇区大小,不一定非要和Norflash的扇区大小一致,但最小值一般为512字节。
// 一般单片机RAM资源有限文件系统不能是以实际扇区或块大小来操作
// 这里定义文件系统扇区大小为2个页,需要Norflash支持页擦除指令
*(DWORD *)buff = NORFLASH_FATFS_SECTOR_SIZE; // NorFlash 最小读写扇区大小
res = RES_OK;
} else if (GET_SECTOR_COUNT == cmd) {
log_d("GET_SECTOR_COUNT\n");
*(DWORD *)buff = 8192; //NorFlash扇区个数 = 总容量/文件系统扇区大小 4MB=(4194304/512)=8192个扇区;
res = RES_OK;
} else if (GET_BLOCK_SIZE == cmd) {
log_d("GET_BLOCK_SIZE\n");
*(DWORD *)buff = 1; //每次擦除的扇区个数,1
res = RES_OK;
} else if (CTRL_TRIM == cmd) {
log_d("CTRL_TRIM\n");
res = RES_OK;
}
#endif
return res;
}
return RES_PARERR;
}
/**
* @brief 获取日期
*/
DWORD get_fattime (void)
{
/*
Return Value
Currnet local time shall be returned as bit-fields packed into a DWORD value. The bit fields are as follows:
bit31:25
Year origin from the 1980 (0..127, e.g. 37 for 2017)
bit24:21
Month (1..12)
bit20:16
Day of the month (1..31)
bit15:11
Hour (0..23)
bit10:5
Minute (0..59)
bit4:0
Second / 2 (0..29, e.g. 25 for 50)
*/
return ((DWORD)(2010 - 1980) << 25) | ((DWORD)1 << 16) | ((DWORD)0 << 11) | ((DWORD)0 << 5) | ((DWORD)0 >> 1);
}
#if 0
DWORD get_fattime (void)
{
time_t t;
struct tm *stm;
t = time(0);
stm = localtime(&t);
return (DWORD)(stm->tm_year - 80) << 25 |
(DWORD)(stm->tm_mon + 1) << 21 |
(DWORD)stm->tm_mday << 16 |
(DWORD)stm->tm_hour << 11 |
(DWORD)stm->tm_min << 5 |
(DWORD)stm->tm_sec >> 1;
}
#endif
#endif //TCFG_LIB_FATFS_SUPPORT
FatFs/ffconf.h
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ Configurations of FatFs Module
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FFCONF_DEF 5380 /* Revision ID */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ Function Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_FS_READONLY 0
/* This option switches read-only configuration. (0:Read/Write or 1:Read-only)
/ Read-only configuration removes writing API functions, f_write(), f_sync(),
/ f_unlink(), f_mkdir(), f_chmod(), f_rename(), f_truncate(), f_getfree()
/ and optional writing functions as well. */
#define FF_FS_MINIMIZE 0
/* This option defines minimization level to remove some basic API functions.
/
/ 0: Basic functions are fully enabled.
/ 1: f_stat(), f_getfree(), f_unlink(), f_mkdir(), f_truncate() and f_rename()
/ are removed.
/ 2: f_opendir(), f_readdir() and f_closedir() are removed in addition to 1.
/ 3: f_lseek() function is removed in addition to 2. */
#define FF_USE_FIND 1
/* This option switches filtered directory read functions, f_findfirst() and
/ f_findnext(). (0:Disable, 1:Enable 2:Enable with matching altname[] too) */
#define FF_USE_MKFS 1
/* This option switches f_mkfs(). (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_FASTSEEK 1
/* This option switches fast seek feature. (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_EXPAND 0
/* This option switches f_expand(). (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_CHMOD 1
/* This option switches attribute control API functions, f_chmod() and f_utime().
/ (0:Disable or 1:Enable) Also FF_FS_READONLY needs to be 0 to enable this option. */
#define FF_USE_LABEL 1
/* This option switches volume label API functions, f_getlabel() and f_setlabel().
/ (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_FORWARD 0
/* This option switches f_forward(). (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_STRFUNC 0
#define FF_PRINT_LLI 0
#define FF_PRINT_FLOAT 0
#define FF_STRF_ENCODE 3
/* FF_USE_STRFUNC switches the string API functions, f_gets(), f_putc(), f_puts()
/ and f_printf().
/
/ 0: Disable. FF_PRINT_LLI, FF_PRINT_FLOAT and FF_STRF_ENCODE have no effect.
/ 1: Enable without LF - CRLF conversion.
/ 2: Enable with LF - CRLF conversion.
/
/ FF_PRINT_LLI = 1 makes f_printf() support long long argument and FF_PRINT_FLOAT = 1/2
/ makes f_printf() support floating point argument. These features want C99 or later.
/ When FF_LFN_UNICODE >= 1 with LFN enabled, string API functions convert the character
/ encoding in it. FF_STRF_ENCODE selects assumption of character encoding ON THE FILE
/ to be read/written via those functions.
/
/ 0: ANSI/OEM in current CP
/ 1: Unicode in UTF-16LE
/ 2: Unicode in UTF-16BE
/ 3: Unicode in UTF-8
*/
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ Locale and Namespace Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_CODE_PAGE 936 //932
/* This option specifies the OEM code page to be used on the target system.
/ Incorrect code page setting can cause a file open failure.
/
/ 437 - U.S.
/ 720 - Arabic
/ 737 - Greek
/ 771 - KBL
/ 775 - Baltic
/ 850 - Latin 1
/ 852 - Latin 2
/ 855 - Cyrillic
/ 857 - Turkish
/ 860 - Portuguese
/ 861 - Icelandic
/ 862 - Hebrew
/ 863 - Canadian French
/ 864 - Arabic
/ 865 - Nordic
/ 866 - Russian
/ 869 - Greek 2
/ 932 - Japanese (DBCS)
/ 936 - Simplified Chinese (DBCS)
/ 949 - Korean (DBCS)
/ 950 - Traditional Chinese (DBCS)
/ 0 - Include all code pages above and configured by f_setcp()
*/
#define FF_USE_LFN 0
#define FF_MAX_LFN 255
/* The FF_USE_LFN switches the support for LFN (long file name).
/
/ 0: Disable LFN. FF_MAX_LFN has no effect.
/ 1: Enable LFN with static working buffer on the BSS. Always NOT thread-safe.
/ 2: Enable LFN with dynamic working buffer on the STACK.
/ 3: Enable LFN with dynamic working buffer on the HEAP.
/
/ To enable the LFN, ffunicode.c needs to be added to the project. The LFN feature
/ requiers certain internal working buffer occupies (FF_MAX_LFN + 1) * 2 bytes and
/ additional (FF_MAX_LFN + 44) / 15 * 32 bytes when exFAT is enabled.
/ The FF_MAX_LFN defines size of the working buffer in UTF-16 code unit and it can
/ be in range of 12 to 255. It is recommended to be set 255 to fully support the LFN
/ specification.
/ When use stack for the working buffer, take care on stack overflow. When use heap
/ memory for the working buffer, memory management functions, ff_memalloc() and
/ ff_memfree() exemplified in ffsystem.c, need to be added to the project. */
#define FF_LFN_UNICODE 0
/* This option switches the character encoding on the API when LFN is enabled.
/
/ 0: ANSI/OEM in current CP (TCHAR = char)
/ 1: Unicode in UTF-16 (TCHAR = WCHAR)
/ 2: Unicode in UTF-8 (TCHAR = char)
/ 3: Unicode in UTF-32 (TCHAR = DWORD)
/
/ Also behavior of string I/O functions will be affected by this option.
/ When LFN is not enabled, this option has no effect. */
#define FF_LFN_BUF 255
#define FF_SFN_BUF 12
/* This set of options defines size of file name members in the FILINFO structure
/ which is used to read out directory items. These values should be suffcient for
/ the file names to read. The maximum possible length of the read file name depends
/ on character encoding. When LFN is not enabled, these options have no effect. */
#define FF_FS_RPATH 0
/* This option configures support for relative path.
/
/ 0: Disable relative path and remove related API functions.
/ 1: Enable relative path. f_chdir() and f_chdrive() are available.
/ 2: f_getcwd() is available in addition to 1.
*/
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ Drive/Volume Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_VOLUMES 4 //1
/* Number of volumes (logical drives) to be used. (1-10) */
#define FF_STR_VOLUME_ID 0
#define FF_VOLUME_STRS "RAM","NAND","CF","SD","SD2","USB","USB2","USB3"
/* FF_STR_VOLUME_ID switches support for volume ID in arbitrary strings.
/ When FF_STR_VOLUME_ID is set to 1 or 2, arbitrary strings can be used as drive
/ number in the path name. FF_VOLUME_STRS defines the volume ID strings for each
/ logical drive. Number of items must not be less than FF_VOLUMES. Valid
/ characters for the volume ID strings are A-Z, a-z and 0-9, however, they are
/ compared in case-insensitive. If FF_STR_VOLUME_ID >= 1 and FF_VOLUME_STRS is
/ not defined, a user defined volume string table is needed as:
/
/ const char* VolumeStr[FF_VOLUMES] = {"ram","flash","sd","usb",...
*/
#define FF_MULTI_PARTITION 0
/* This option switches support for multiple volumes on the physical drive.
/ By default (0), each logical drive number is bound to the same physical drive
/ number and only an FAT volume found on the physical drive will be mounted.
/ When this feature is enabled (1), each logical drive number can be bound to
/ arbitrary physical drive and partition listed in the VolToPart[]. Also f_fdisk()
/ will be available. */
#define FF_MIN_SS 512
#define FF_MAX_SS 512
/* This set of options configures the range of sector size to be supported. (512,
/ 1024, 2048 or 4096) Always set both 512 for most systems, generic memory card and
/ harddisk, but a larger value may be required for on-board flash memory and some
/ type of optical media. When FF_MAX_SS is larger than FF_MIN_SS, FatFs is
/ configured for variable sector size mode and disk_ioctl() needs to implement
/ GET_SECTOR_SIZE command. */
#define FF_LBA64 0
/* This option switches support for 64-bit LBA. (0:Disable or 1:Enable)
/ To enable the 64-bit LBA, also exFAT needs to be enabled. (FF_FS_EXFAT == 1) */
#define FF_MIN_GPT 0x10000000
/* Minimum number of sectors to switch GPT as partitioning format in f_mkfs() and
/ f_fdisk(). 2^32 sectors maximum. This option has no effect when FF_LBA64 == 0. */
#define FF_USE_TRIM 0
/* This option switches support for ATA-TRIM. (0:Disable or 1:Enable)
/ To enable this feature, also CTRL_TRIM command should be implemented to
/ the disk_ioctl(). */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ System Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_FS_TINY 0
/* This option switches tiny buffer configuration. (0:Normal or 1:Tiny)
/ At the tiny configuration, size of file object (FIL) is shrinked FF_MAX_SS bytes.
/ Instead of private sector buffer eliminated from the file object, common sector
/ buffer in the filesystem object (FATFS) is used for the file data transfer. */
#define FF_FS_EXFAT 0
/* This option switches support for exFAT filesystem. (0:Disable or 1:Enable)
/ To enable exFAT, also LFN needs to be enabled. (FF_USE_LFN >= 1)
/ Note that enabling exFAT discards ANSI C (C89) compatibility. */
#define FF_FS_NORTC 0
#define FF_NORTC_MON 11
#define FF_NORTC_MDAY 1
#define FF_NORTC_YEAR 2024
/* The option FF_FS_NORTC switches timestamp feature. If the system does not have
/ an RTC or valid timestamp is not needed, set FF_FS_NORTC = 1 to disable the
/ timestamp feature. Every object modified by FatFs will have a fixed timestamp
/ defined by FF_NORTC_MON, FF_NORTC_MDAY and FF_NORTC_YEAR in local time.
/ To enable timestamp function (FF_FS_NORTC = 0), get_fattime() need to be added
/ to the project to read current time form real-time clock. FF_NORTC_MON,
/ FF_NORTC_MDAY and FF_NORTC_YEAR have no effect.
/ These options have no effect in read-only configuration (FF_FS_READONLY = 1). */
#define FF_FS_NOFSINFO 0
/* If you need to know correct free space on the FAT32 volume, set bit 0 of this
/ option, and f_getfree() at the first time after volume mount will force
/ a full FAT scan. Bit 1 controls the use of last allocated cluster number.
/
/ bit0=0: Use free cluster count in the FSINFO if available.
/ bit0=1: Do not trust free cluster count in the FSINFO.
/ bit1=0: Use last allocated cluster number in the FSINFO if available.
/ bit1=1: Do not trust last allocated cluster number in the FSINFO.
*/
#define FF_FS_LOCK 0
/* The option FF_FS_LOCK switches file lock function to control duplicated file open
/ and illegal operation to open objects. This option must be 0 when FF_FS_READONLY
/ is 1.
/
/ 0: Disable file lock function. To avoid volume corruption, application program
/ should avoid illegal open, remove and rename to the open objects.
/ >0: Enable file lock function. The value defines how many files/sub-directories
/ can be opened simultaneously under file lock control. Note that the file
/ lock control is independent of re-entrancy. */
#define FF_FS_REENTRANT 0
#define FF_FS_TIMEOUT 1000
/* The option FF_FS_REENTRANT switches the re-entrancy (thread safe) of the FatFs
/ module itself. Note that regardless of this option, file access to different
/ volume is always re-entrant and volume control functions, f_mount(), f_mkfs()
/ and f_fdisk(), are always not re-entrant. Only file/directory access to
/ the same volume is under control of this featuer.
/
/ 0: Disable re-entrancy. FF_FS_TIMEOUT have no effect.
/ 1: Enable re-entrancy. Also user provided synchronization handlers,
/ ff_mutex_create(), ff_mutex_delete(), ff_mutex_take() and ff_mutex_give(),
/ must be added to the project. Samples are available in ffsystem.c.
/
/ The FF_FS_TIMEOUT defines timeout period in unit of O/S time tick.
*/
/*--- End of configuration options ---*/
测试代码
#if 1 // Norflash 文件系统测试
static FATFS nor_fatfs; // 必须是全局变量
static BYTE nor_work[FF_MAX_SS]; // 必须是全局变量
FRESULT res;
FIL nor_fp;
// 挂在文件系统
res = f_mount(&nor_fatfs, "3:", 1); // 挂载SD卡,0=DEV_RAM, 1=DEV_MMC, 2=DEV_USB, 3=DEV_NOR
log_d("norflash f_mount res:%d\n", res);
if (res == FR_NO_FILESYSTEM) {
// 无文件系统,尝试创建文件系统
res = f_mkfs("3:", 0, nor_work, sizeof(nor_work));
if (FR_OK == res) {
/* 格式化后,先取消挂载 */
f_mount(NULL, "3:", 1); // 取消文件系统
res = f_mount(&nor_fatfs, "3:", 1); // 挂载文件系统
log_d("norflash f_mount 222 res:%d\n", res);
}
}
if (FR_OK == res) {
// 挂载成功
}
// 写文件
#define D_TEST_STR "The realm of fast artificial neural networks (ANNs) stands as a pinnacle of modern computational intelligence. These networks mimic the human brain’s ability to learn from vast amounts of data, making them invaluable in processing complex patterns quickly. The core of their speed lies in their unique architecture, which allows for parallel processing, akin to how neurons in the human brain operate simultaneously. At the heart of these networks are activation functions, which determine the output of neural computations. These functions are crucial as they introduce non-linearity into the system, enabling the network to learn and make sense of complicated data inputs. By effectively handling these computations, fast ANNs can perform tasks ranging from image recognition to language processing at remarkable speeds."
res = f_open(&nor_fp , "3:abcd.txt" , FA_CREATE_ALWAYS|FA_OPEN_ALWAYS|FA_READ |FA_WRITE );
printf("write f_open res = %d\r\n",res);
if (FR_OK == res) {
unsigned int wb;
if (f_write(&nor_fp, D_TEST_STR, strlen(D_TEST_STR), &wb) == FR_OK) {
log_d("write ok:%d\n", wb);
} else {
log_d("write err\n");
}
}
f_sync(&nor_fp);
f_close(&nor_fp);
// 读文件
unsigned int rb;
unsigned char buf[1024]={0};
res = f_open(&nor_fp , "3:abcd.txt" , FA_OPEN_ALWAYS|FA_READ |FA_WRITE );
printf("rd res f_open = %d\r\n",res);
if (f_read(&nor_fp, (char*)buf, sizeof(buf), &rb) == FR_OK) {
log_d("read buf %d:%s\n", rb, buf);
} else {
log_d("read buf err\n");
}
f_close(&nor_fp);
#endif