目录
JDBC
使用JDBC连接到MySQL
使用 Statement
使用 PreparedStatement
Statement 和 PreparedStatement 区别
在 java 中如何连接到 MySQL 数据库,执行 SQL 查询,并处理查询结果?
JDBC
java 程序连接到 mysql,首先需要下载 JDBC 驱动程序。JDBC是一个允许 Java 程序连接到数据库并与之交互的库。
JDBC 驱动程序通常是一个 JAR 文件:MySQL :: Download Connector/J
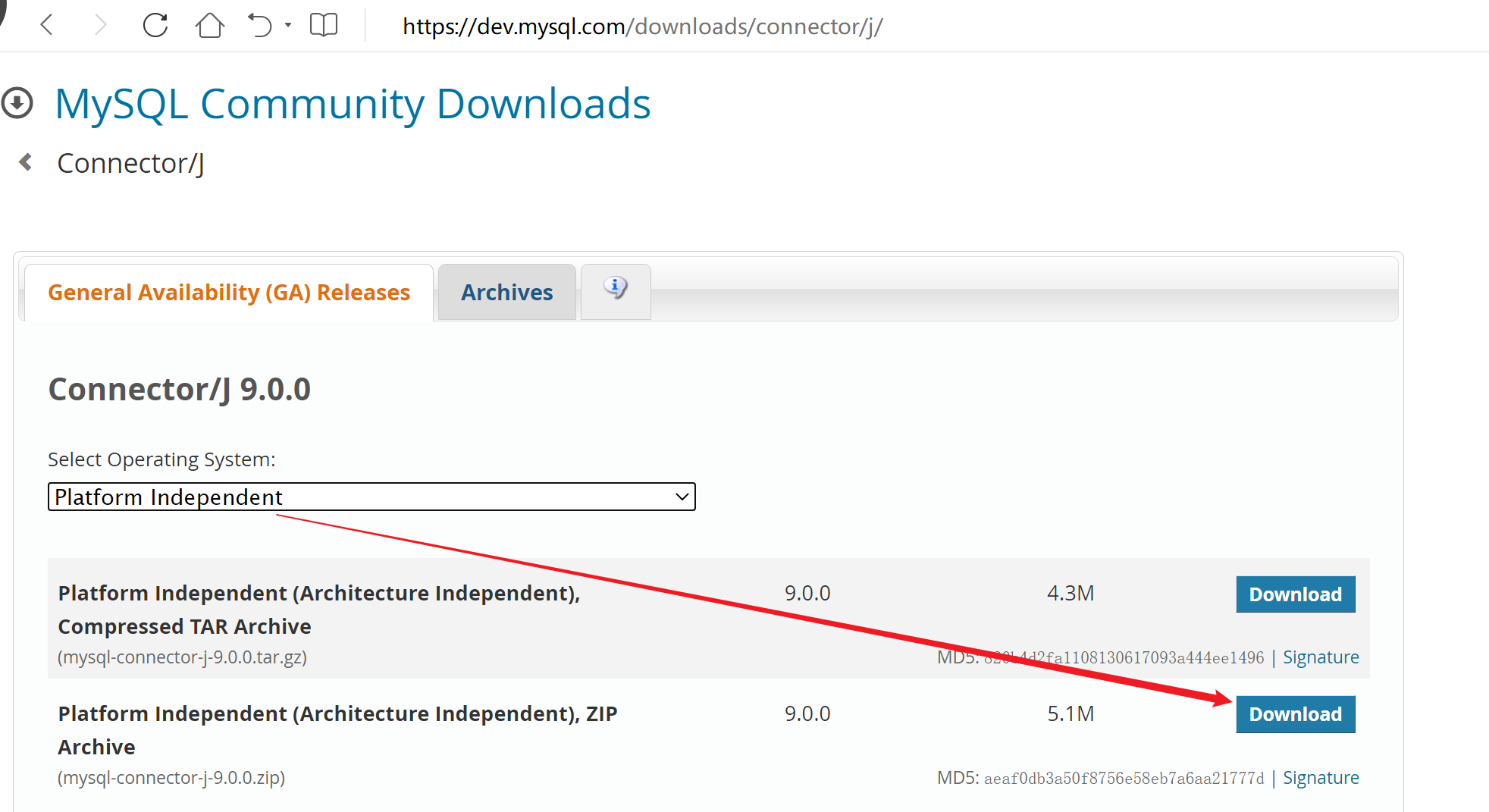
下载后将该 jar 文件放在项目任意文件夹中,在 idea 中选中该 JAR 文件右键,选择添加到库即可。这样,当Java程序尝试加载JDBC驱动程序时,JVM(Java虚拟机)能够在类路径中找到并加载它。
使用JDBC连接到MySQL
在使用 Java 的 JDBC 连接到 MySQL 数据库时,有两种主要的方法来执行 SQL 语句:Statement 和 PreparedStatement。这两种方法各有优缺点,适用于不同的场景。
使用 Statement
在 Java 的数据库编程中,Statement 对象是一个非常重要的接口。
- 定义:
Statement是用于执行静态 SQL 语句并返回它所生成结果的接口。 - 特点:
-
- 每次执行 SQL 语句时,数据库都需要重新解析和编译 SQL 语句,这会影响性能。
- 容易受到 SQL 注入攻击,因为 SQL 语句和参数是动态拼接的。
- 适用于执行一次性的、不带参数的 SQL 语句。
如下以拼接的方式执行sql语句,易受到sql注入的攻击
package demo;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class MySQLConnectionExample {
// 数据库连接信息
private static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/security";
private static final String USER = "root";
private static final String PASS = "root";
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 打开连接
System.out.println("Connecting to database...");
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS); //连接到数据库,如果连接成功,connection 变量将引用一个有效的数据库连接。
// 如果连接成功,打印一条消息
if (connection != null) {
System.out.println("Successfully connected to the database!");
// 通过调用 connection.createStatement() 方法创建一个 Statement 对象,用于执行 SQL 查询。
statement = connection.createStatement();
//以拼接的方式执行sql语句,易受到sql注入的攻击
String n = "2";
// 执行 SQL 查询
String sql = "SELECT * FROM security.users WHERE id=" + n + " LIMIT 0,1";
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
// 处理查询结果
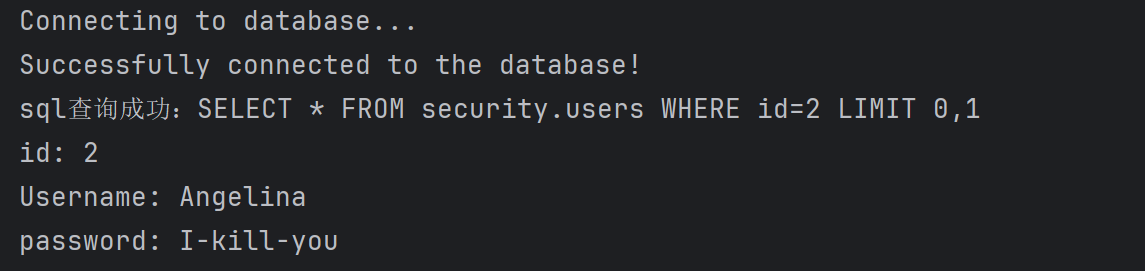
while (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println("sql查询成功:" + sql);
String id = resultSet.getString("id");
String username = resultSet.getString("username");
String password = resultSet.getString("password");
// 打印结果或进行其他处理
System.out.println("id: " + id);
System.out.println("Username: " + username);
System.out.println("password: " + password);
// 可以根据需要添加更多列的处理
}
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// 处理 JDBC 错误
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭 ResultSet
try {
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
// 关闭 Statement
try {
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
// 关闭 Connection
try {
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
使用 PreparedStatement
- 定义:
PreparedStatement是Statement的子接口,用于执行带参数的预编译 SQL 语句。 - 特点:
-
- 预编译 SQL 语句,提高性能。编译后的 SQL 语句可以多次执行而不需要重新解析。
- 防止 SQL 注入攻击,因为参数是通过占位符(通常是问号
?)进行绑定的,数据和查询逻辑是分开的。 - 适用于需要多次执行相同 SQL 语句但使用不同参数的情况。
执行后 sql 语句显示如下,貌似能被注入
SELECT * FROM security.users WHERE id='1' and 1=2 --+' LIMIT 1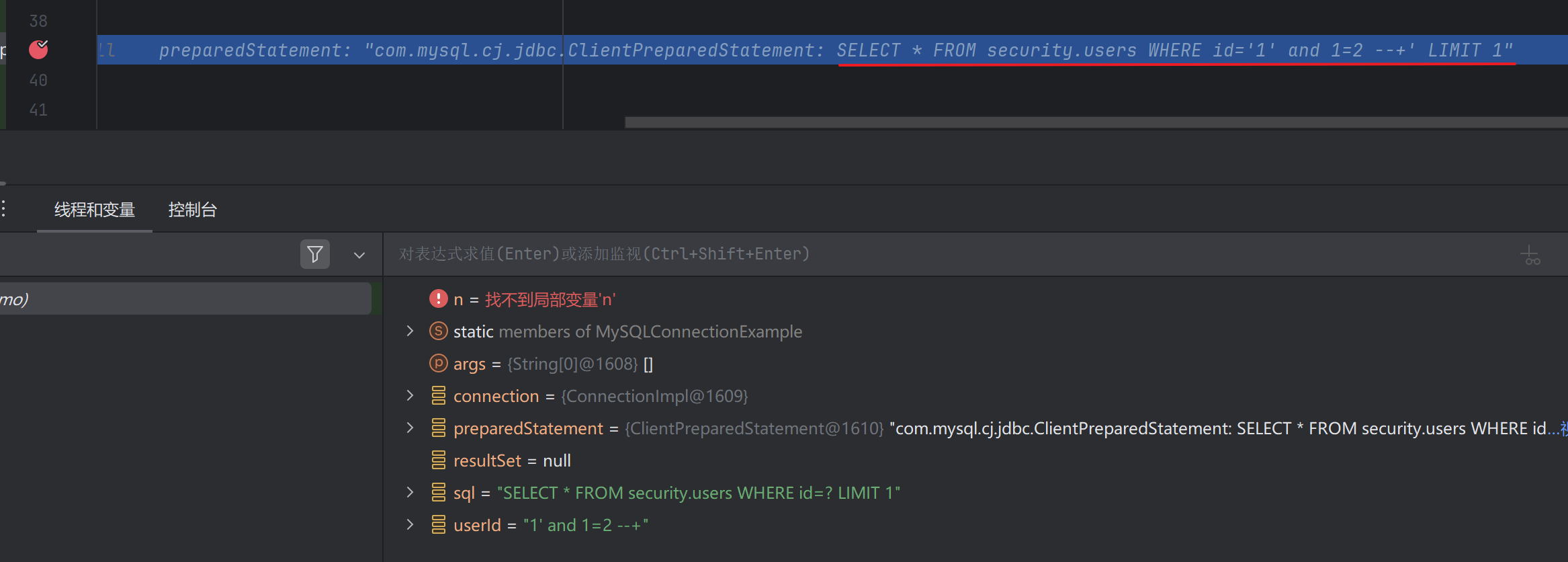
但其实 PreparedStatement 会将参数值作为单独的参数传递给数据库,而不是直接拼接到 SQL 语句中。所以 1' and 1=2 --+ 只是作为一个参数值赋值给 id。实际执行的是如下 sql 语句
SELECT * FROM security.users WHERE id='1\' and 1=2 --+' LIMIT 1
而这条语句实际执行效果等于如下语句。因为 mysql 会尝试将 1\' and 1=2 --+ 转换为整数 1,具体可以看MySQL 的隐式类型转换,从而防止了 sql 注入。
SELECT * FROM security.users WHERE id='1' LIMIT 1
package demo;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class MySQLConnectionExample {
// 数据库连接信息
private static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/security";
private static final String USER = "root";
private static final String PASS = "root";
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 打开连接
System.out.println("Connecting to database...");
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS);
// 如果连接成功,打印一条消息
if (connection != null) {
System.out.println("Successfully connected to the database!");
// 准备 SQL 语句,使用占位符 ?
String sql = "SELECT * FROM security.users WHERE id=? LIMIT 1";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 设置占位符的值, 其中 1 是占位符的位置(从 1 开始计数),userId 是要设置的值。
String userId = "1' and 1=2 --+"; // 假设要查询的用户 ID 为 1
preparedStatement.setString(1, userId);
// 执行 SQL 查询
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
// 处理查询结果
while (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println("SQL 查询成功");
String id = resultSet.getString("id");
String username = resultSet.getString("username");
String password = resultSet.getString("password");
// 打印结果或进行其他处理
System.out.println("id: " + id);
System.out.println("Username: " + username);
System.out.println("password: " + password);
// 可以根据需要添加更多列的处理
}
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// 处理 JDBC 错误
e.printStackTrace();
} finally
{
// 关闭 ResultSet
try {
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
// 关闭 PreparedStatement
try {
if (preparedStatement != null) {
preparedStatement.close();
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
// 关闭 Connection
try {
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}Statement 和 PreparedStatement 区别
- 性能:
PreparedStatement通常比Statement性能更高,因为它允许数据库预编译 SQL 语句。 - 安全性:
PreparedStatement能够防止 SQL 注入攻击,而Statement则容易受到这种攻击。 - 适用场景:
Statement适用于执行一次性的、不带参数的 SQL 语句;而PreparedStatement则适用于需要多次执行相同 SQL 语句但使用不同参数的情况。

![OSError: [Errno 22] Invalid argument:无效的参数完美解决方法](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f597d142ee39408fa77ec010472cde5e.png)